Genus Streptococci
Microscopical appearance
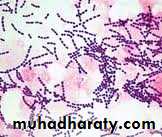
Gram +ve spherical or oval cocci.arranged in chains of various lengths
Non- motile
Non-spore forming
Some of them possess a capsule.
Cultural characteristics
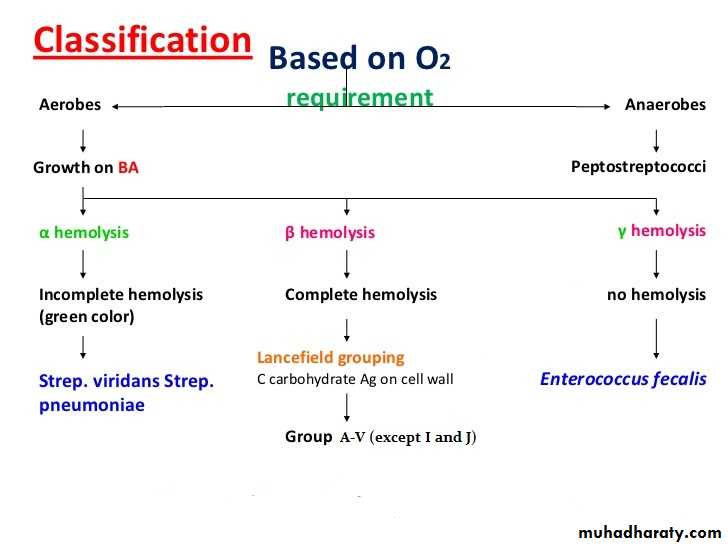
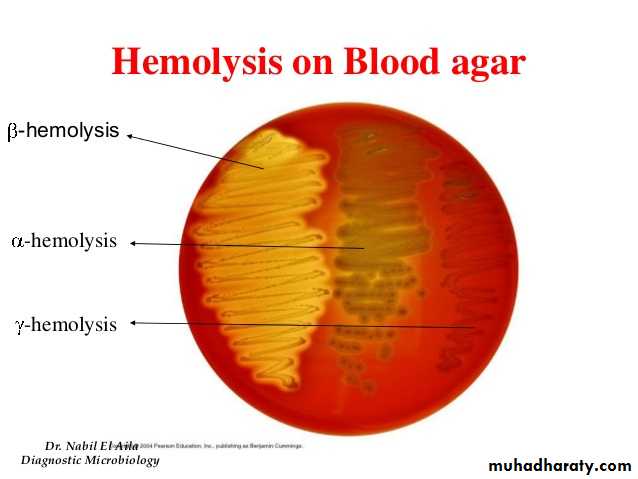
Small semitransparent, low convex .Fastidious in their growth, require enriched medium such as Blood agar.
Aerobic or facultatively anaerobic, some are obligatory anaerobic.
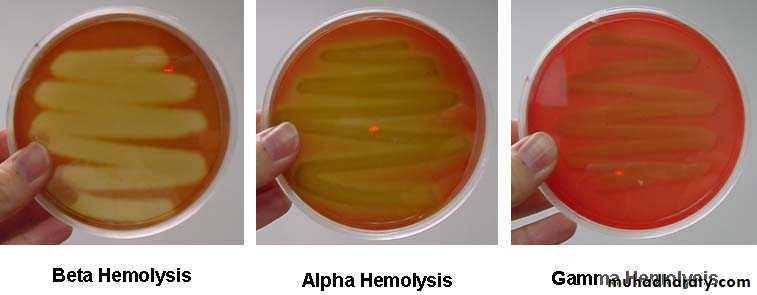
Can be divided into three groups according to their effect on red blood cell in the agar.
Biochemical tests
Catalase test : NegativeHippurate Hydrolysis Test
CAMP Test
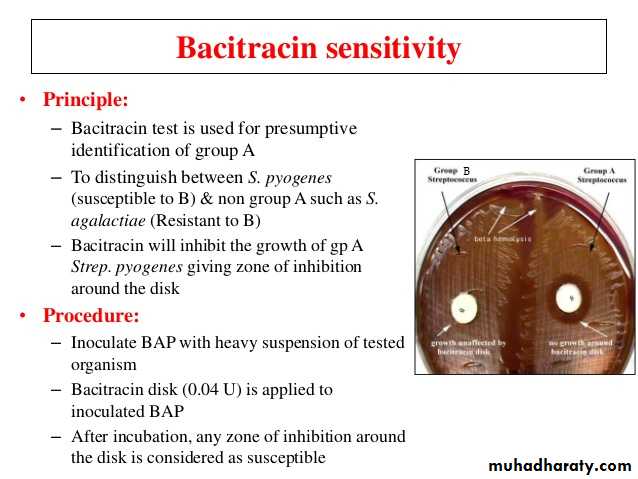
Sensitivity to Bacitracin
Hippurate Hydrolysis Test
Principle
Hippurate benzoic acid + glycine
Procedure :
Incubate a large loop of a β streptococci culture in to 0.4 ml of the sodium hippurate medium and incubate for 2 hours at 37 OC.Add 0.2 ml of the ninhydrin reagent.
Incubate for 30 min at 37 OC.
Result:
The presence of a deep purple color after the adition of ninhydrin reagent within 10 minutes indicate the presence of glycine.S. agalagtia ( + )
S. pyogenes ( - )
Hippuricase
Ninhydrin
deep blue or purple color
CAMP Test "Christie–Atkins–Munch-Petersen"
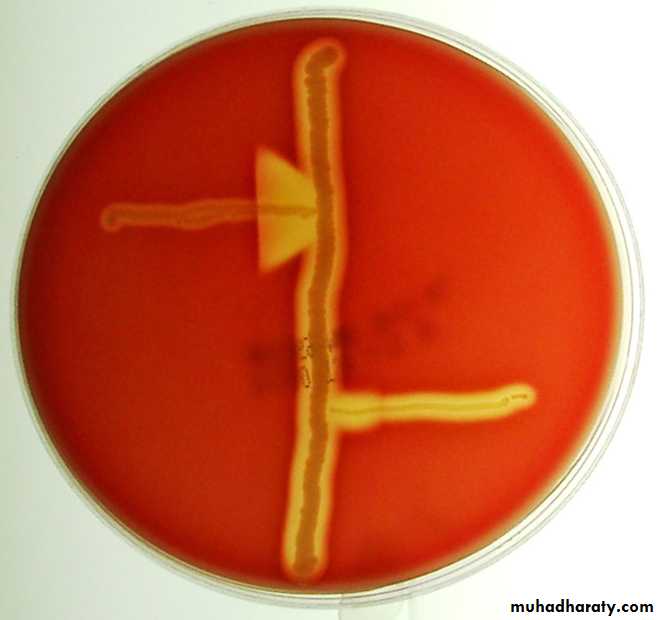
Procedure:1-single streak of Staph. aureus and streptoccocus are made perpendicular to each other.
2- (3-5) mm distance was left between two streaks.
3- after incubation , a positive result appear as an arrowhead shaped zone of complete hemolysis.
S.agalactia is CAMP test positive While non group B streptococci are negative.
Principle:
Group B streptococci produce extracellular protein (CAMP factor).
CAMP act synergistically with the Beta – lysin of Staph. aureus and enhances the lysis of RBC.
CAMP test :
Beta-hemolytic Staphylococcus aureusS.agalactiae
Beta hemolytic Streptococci not S. pyogenes
S. agalagtia
S. pyogenesB
• A
Lancefield grouping
• Mucoid ,slightly larger• Pin point
• Colonies
Resistance
Sensitive• Bacitracin sensitivity test
• Positive
• negative
Hippurate Hydrolysis Test
• Positive
• negative
CAMP
Streptococcus pneumonia
Microscopical appearance
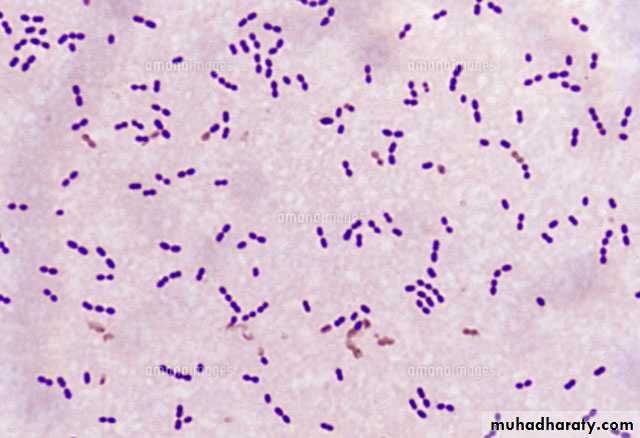
Gram +ve lancet-shape cocci, arranged in pairs or short chains
capsulated
Cultural characteristics
Facultatively anaerobic, grow well in 5-10% CO2Fastidious cause alpha-hemolysis on blood agar.
Small colonies,flat,mucoid, 1 mm in diameter.
Biochemical tests
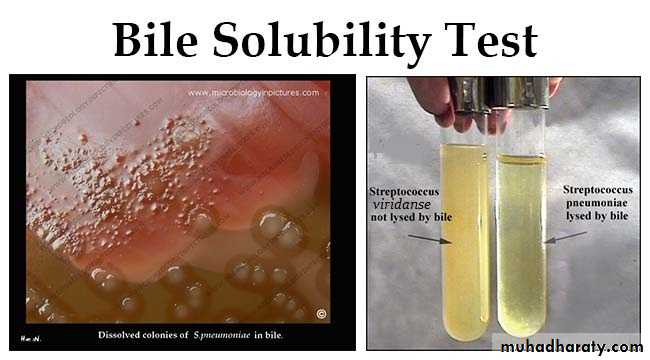
Catalase test : NegativeBile solubility
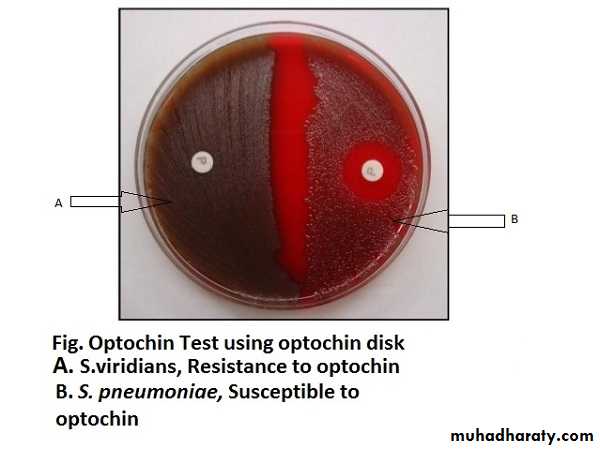
Optochin sensitivity test
Principle
• S. pneumoniae possesses an autolytic enzyme which lyses the cell’s own wall during division. The addition of bile salts (sodium deoxycholate) activates the autolytic enzyme and the organisms rapidly autolyse. Other α haemolytic streptococci do not possess such an active system and therefore do not dissolve in bile.
• The bile solubility can be detected by one of two methods:
• 1- Broth test.
• Procedure
• (0.5ml) of 10% bile solution is added to the test tube( 5ml of the broth culture of the organism to be tested ).
• Incubate at 37 OC for 15 min.
• Record the result.
• Bile solubility
• 2- Agar blate test.
• Procedure
• a loopful or small drop 2% bile solution is placed over selected colonies .
• Incubate at 37 OC for 30 min.
• Record the result.
Disappearance of the colonies treated with 2% bile solution
The suspension of S . Pneumoniae will be clear while that of S.viridanse remains turbidOptochin sensitivity test
How to differentiate between S. pneumoniae and S. viridanse
S. viridanse
S. pneumoniae
Cocci in Chins
• lancet –shape diplococcimorphology
ResistanceSensitive
• Optochin sensitivity test
• Insoluble
• Soluble• Bile solubility
Enterococcus
Enterococci are gram-positive cocci which often occur in pairs (diplococci) and in short chains.
Non motile
Non-spore forming
The colonies on blood agar are gray/smooth colonies that are gamma-hemolytic.
Growth in 6.5% NaCl.
Hydrolze esculin in 40% bile
Bile esculin test :
Principle:esculin dextrose + esculetin
Ferric ionsdark brown or black complex
Positive result
Negative resultBile esculin agar
10% bile salts , esculin , Ferric Ammonium Citrate