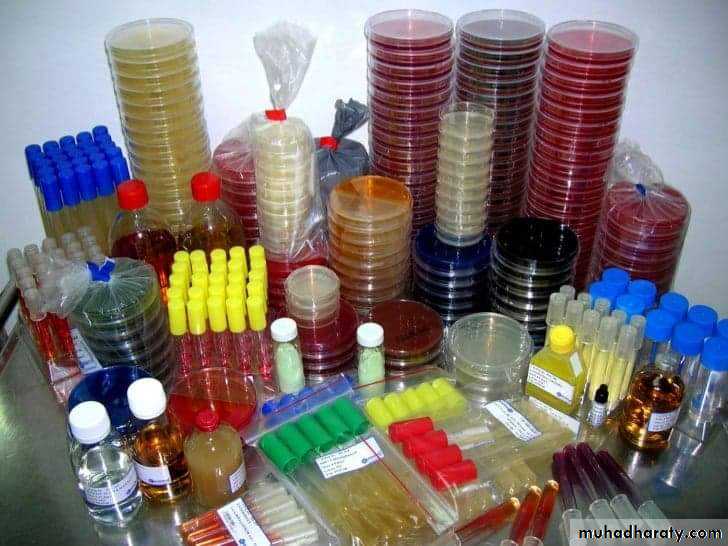
Culture media & Sterilization
Culture media
Culture media
Are used for recognition and identification of microorganisms.Are contained in test tubes, plates ( Petri Dishes ), flasks, screw capped bottles.
Containers must be cleaned.
Media and containers are sterilized by heat.
Medium poured into sterile containers.
Common ingredients of culture media
Peptone.
Meat extract.
NaCl.
Agar (conc. 1.5 - 2%).
pH (7.2 - 7.4).
Therefore, pH of media should be adjusted ( using 10% NaOH or HCL ).
Types of culture media
Culture media can be divided according to :A. Physical state ( Consistency ) of media into :
Liquid ( fluid ) media : e.g. nutrient broth, peptone water, brain heart infusion broth for primary cultivation.
Solid media : e.g. nutrient agar, MacConkey's agar, blood agar, chocolate agar for cultivation of bacteria.
Semisolid media : for cultivation of spirochetes and motility (agar, 0.4 - 0.8%).
B. Use of media :
1. Simple or basal media : e.g., nutrient broth & agar, peptone water, are used for cultivation of the common m.o..2. Special – Purpose media : e.g., enriched, selective, differential, transport, sensitivity media.
Enriched media :
Are simple media enriched with appropriate substances, e.g., ( blood, 5 - 10 % ), ( glucose, 1 - 2% ), ( serum and ascitic fluid 10% ), are used for cultivation of fastidious m.o. like Streptococci.Selective media :
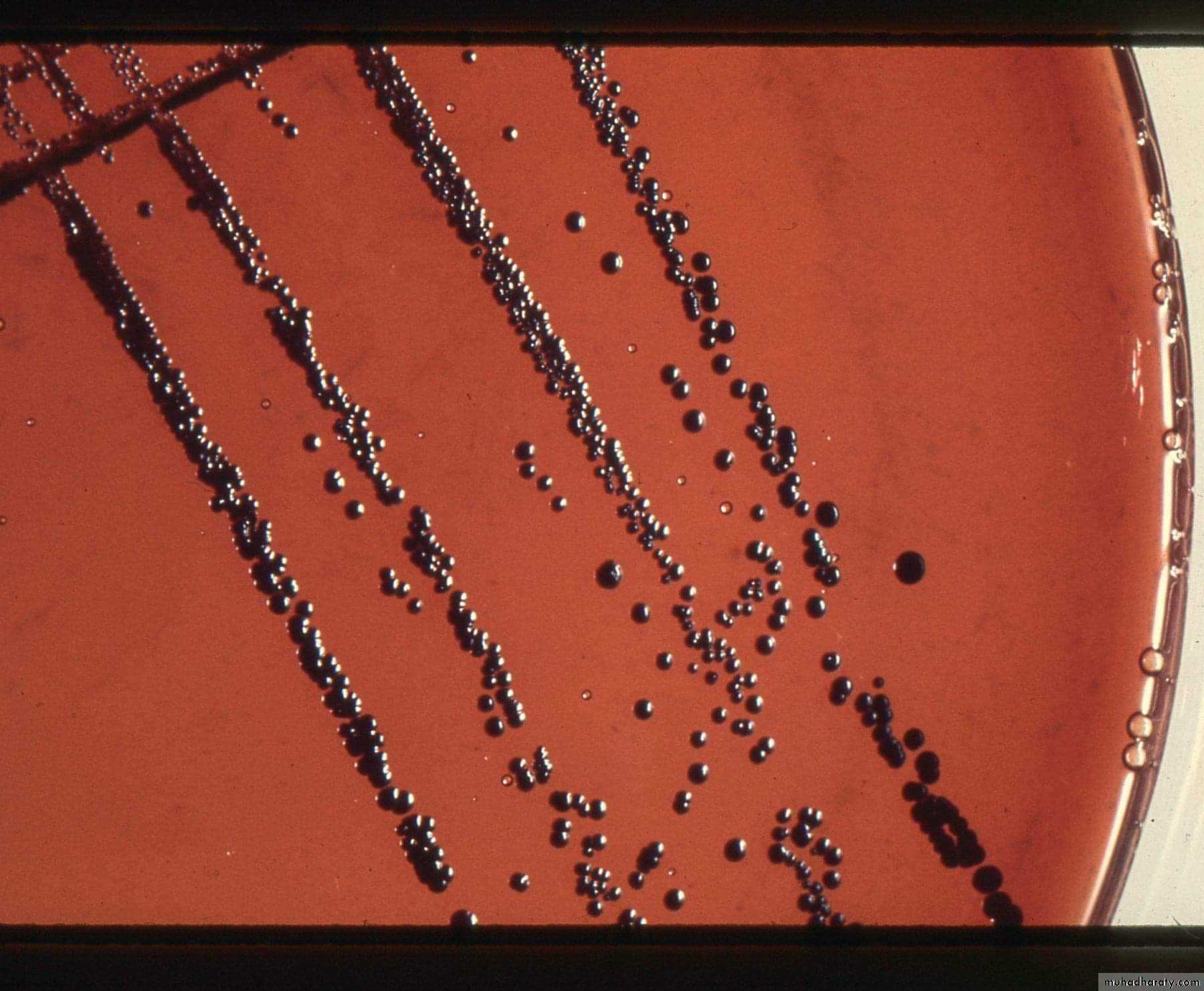
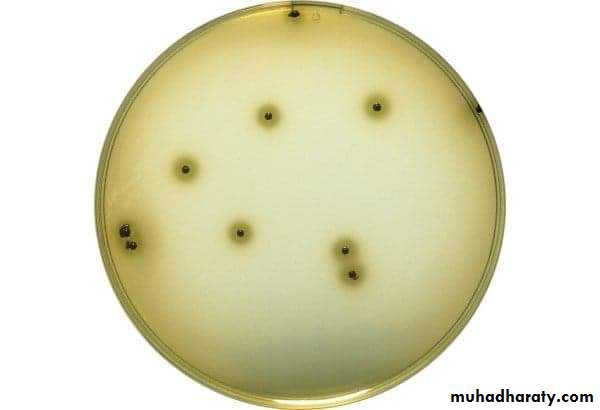
Are media containing inhibitory substance, e.g., ( bile salts, antibiotics, dyes ) which favour the growth of the concerned m.o. and inhibit the growth of others, e.g., MacConkey's agar, Potassium tellurite agar, Bismuth sulphite agar etc…..Corynebacterium diphtheria Salmonella typhi produces black colonies by a metallic sheen
Differential media :
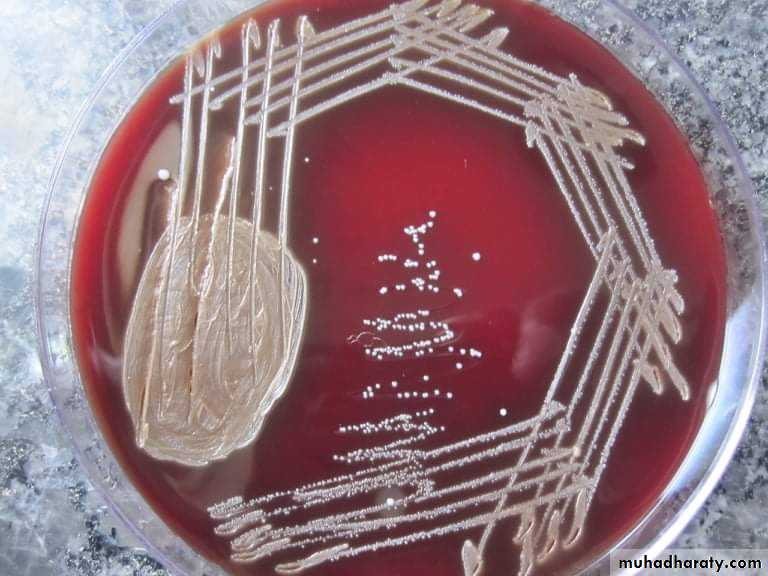
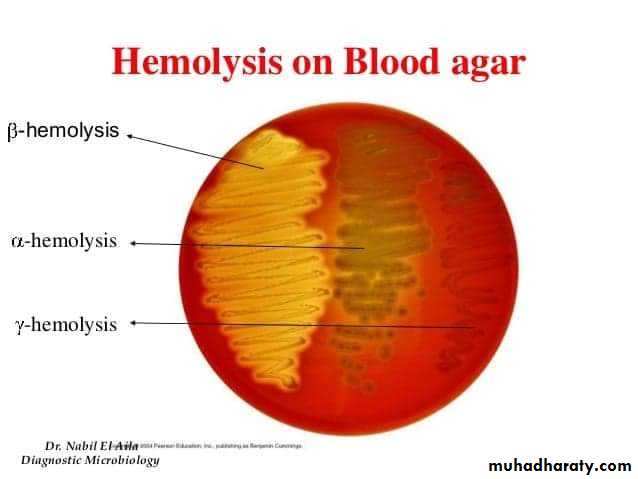
Are media used for growth of certain species produce characteristic growth or certain effects can be easily recognized in the medium, e.g., haemolytic and non-haemolytic species on blood agar.Sterilization
Is the destruction & removal of all living m.o. in or on an object. In bacteriology, surgery and medicine sterilization of instruments, drugs and other supplies is important for the prevention of infection.Types of sterilization
1. Physical methods :A. Heat :
1. Dry heat :
Red heat, e.g.,
heating of platinum loop,
points of forceps, etc……
2. Flaming :
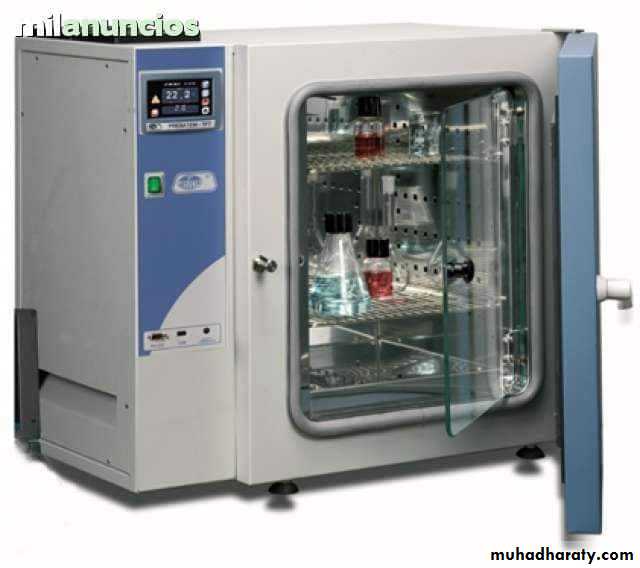
Used for needles, mouth of culture tubes, etc…..3. Hot air oven :
Is the best method for sterilizing dry glassware's, forceps, scalpels, powders, fat, greases, etc….., temperature of 160°C for 1 hour is employed.
4. Infra – red radiation :
The source employed is an electrically heat element.** A temperature of 180°C can be attained.
Moist heat
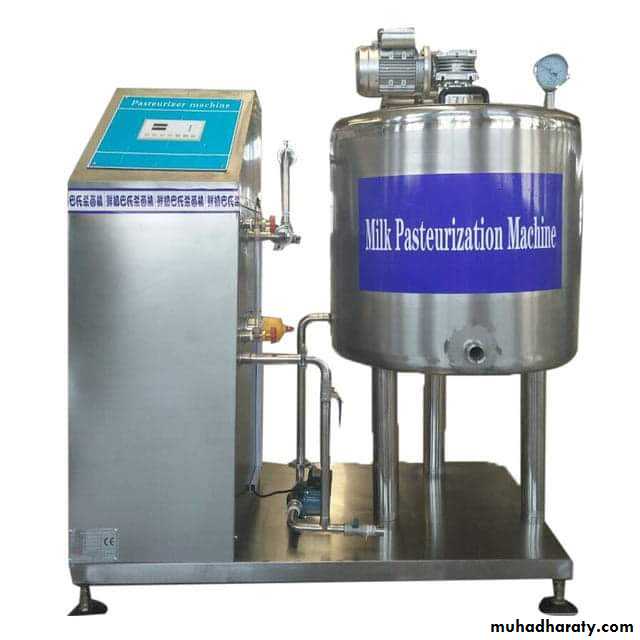
1. At a temperature below 100°C :Example pasteurization of milk, the temperature 63 – 66°C for 30 min or 71°C for 15 sec. this will kill all non – spore forming pathogens such as Myco. Tuberculosis and various Salmonellae.
2. At temperature of 100°C :
A. Boiling at 100°C for 5 – 10 min :This is sufficient to kill all non– sporing and many sporing m.o..B. Steaming at 100°C : e.g.Tyndallization which involves steaming for 30 min. on each 3 successive days . After heating, the medium is incubated to allow spores to germinate and vegetative organisms to grow will be killed by the second steaming, the 3rd heating is a safety precaution.
3. At a temperature above 100°C :
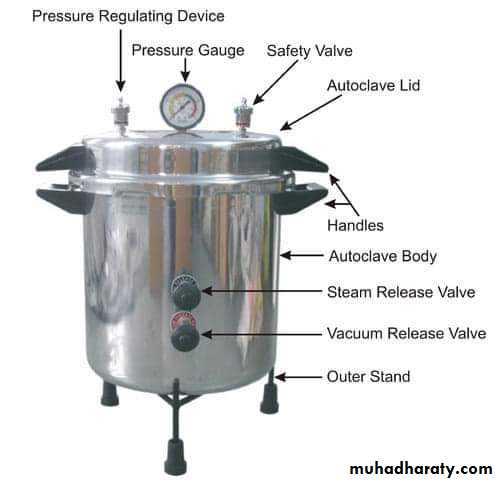
Steam under increased pressure,( autoclaving ).This is the usual method of sterilizing bacteriological media, surgical instruments, towels, dressing, gloves, etc….
The minimum values required for sterilization in an efficient autoclave are : 151 b / inch 2 121 °C 15 min.
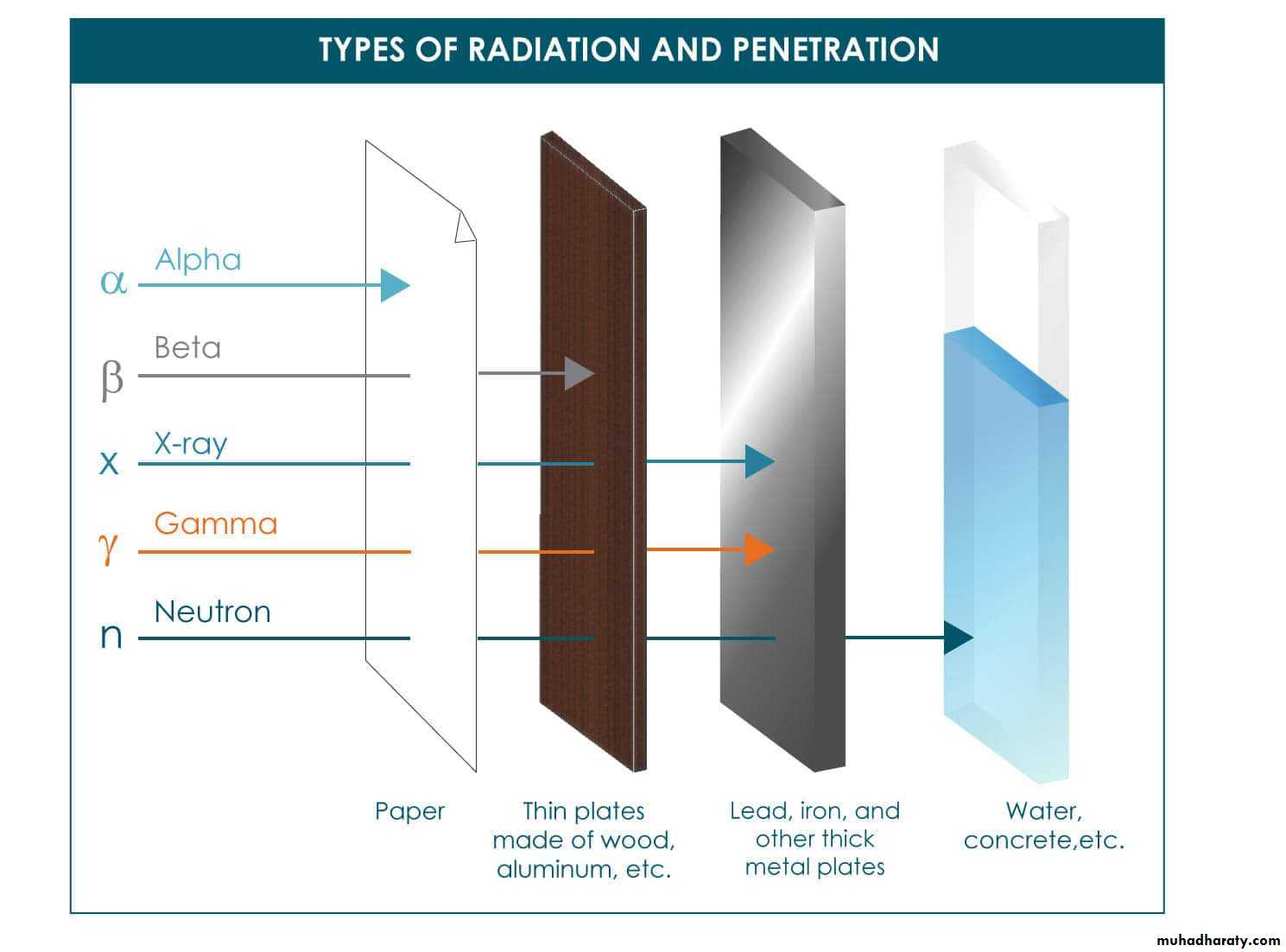
B. RADIATION
1) Direct sun light :Kills vegetative organisms rapidly, but spores are much more resistant.
2) Ultra violet light :
Is commonly used to sterilize the air in the hospital operating rooms.
3) Ionizing radiation : Includes high speed electrons, X – rays.
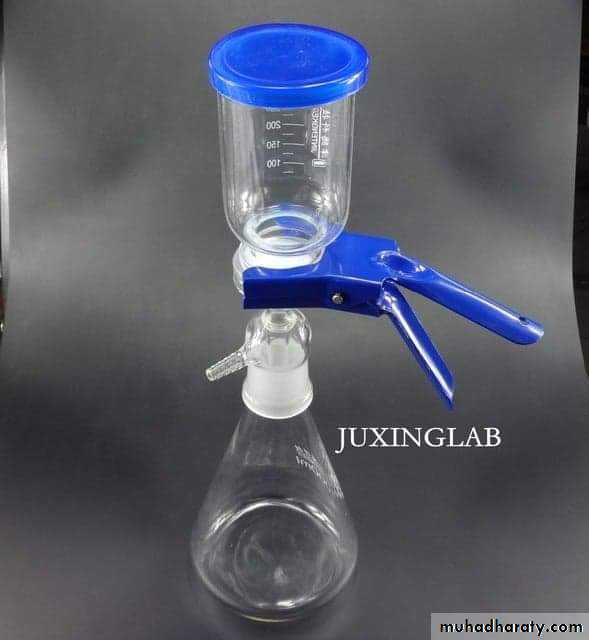
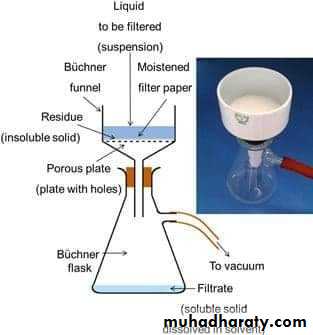
C. FILTRATION
To render fluids, including bacterial cultures, free from bacteria by passing them through special filters, e.g., Seitz filter. This method is used in sterilizing liquids that would be damaged by heat such as : serum, antibiotics solutions, sugars, toxins, etc…..Chemical methods
Chemical sterilizing agents are widely used and a few of them have little effect on spores.Disinfectants :
Are potent but toxic preparations. Disinfection means the destruction or removal of pathogenic m.o. to render the objects non - infective.
Antiseptics :
Are substances non - toxic for superficial application to living tissues which either kill m.o. or prevent their growth.
E.g. of both : acids and alkaline organic metallic compounds ( merthiolate ), halogens, alcohol, phenol, organic dyes, detergents & soaps.
Testing the efficiency of sterilization
1. Chemical indicators :Brown‘ s Sterilization control tubes contain red solution change to green solution after Sterilization.
2. Adhesive tape :
Bowie – Dick autoclave tape test.