DR . Hussein AL Dabbagh Lec : 6
CORRECTIVE PHASE OF PERIODONTAL THERAPY
(Surgical phase)( phase 2)
Introduction
Once the factors responsible for the periodontal disease have been controlled or eliminated, the goal of treatment becomes the correction of residual damage, thereby creating an environment that can more easily be maintained in a state of health. These corrections are accomplished by various surgical techniques .The objectives of periodontal surgical intervention are:
Surgical elimination of periodontal pocket.Access creation for proper scaling and root planning.
Establishing gingival morphology that facilitate the self performed plaque
control measures.
May aim at the regeneration of periodontal attachment loss due to P .D.
General indication of periodontal surgery.
. Areas with irregular bony contours, deep craters.Impaired access for scaling and root planning due to presence of certain impeding factors as a wide tooth surface, root fissures, root furrows & furcation involvement. These factors may make even a shallow pocket demanding a surgical access gaining.
Impaired access for self performed plaque control measures such as gingival hyperplasia or crater that complicates such procedures.
Correction of gross gingival abnormalities (for esthetic reason).
Shifting of gingival margin apically to a plaque retaining restoration.
To facilitate a proper restorative therapy.
CONTRAINDICATIONS OF PERIODONTAL SURGERY
1. Uncooperative patient
2. Patients with systemic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, malignancy, liver diseases, blood disorders, uncontrolled-diabetes, consultation with the patient’s physician is essential.
3. Where thorough subgingival scaling and good home care will remove or control the lesion.
4. Where patient motivation is inadequate.
5. In the presence of infection.
6. Where the prognosis is so poor that tooth loss is inevitable.
Periodontal surgery includes:
Curettage, gingivoplasty, gingivectomy, flaps, osseous surgery & mucogingivalsurgery.
A – Curettage:
It was extensively used in past to remove the lining of periodontal pockets but it is very difficult to be mastered & no longer be used nowadays.B – Gingivoplasty & gingivectomy.
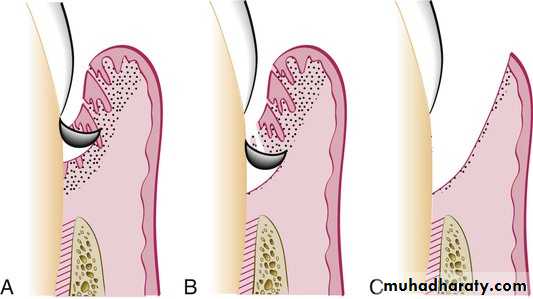
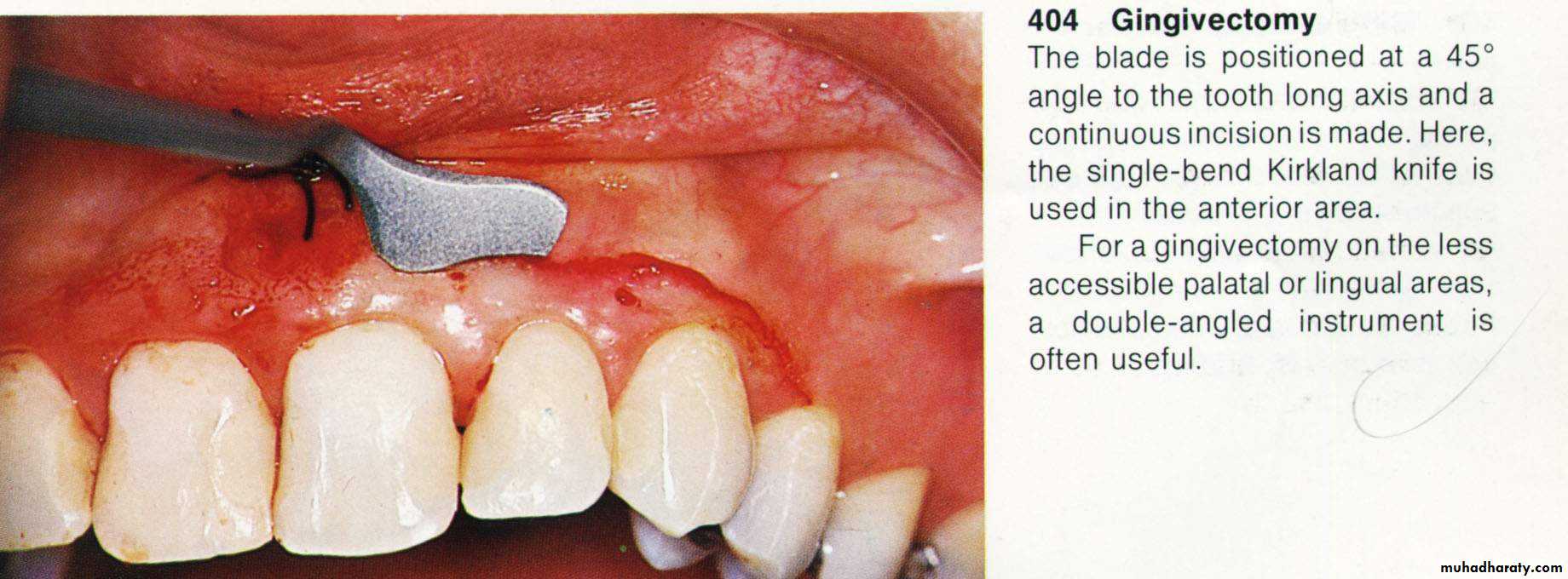
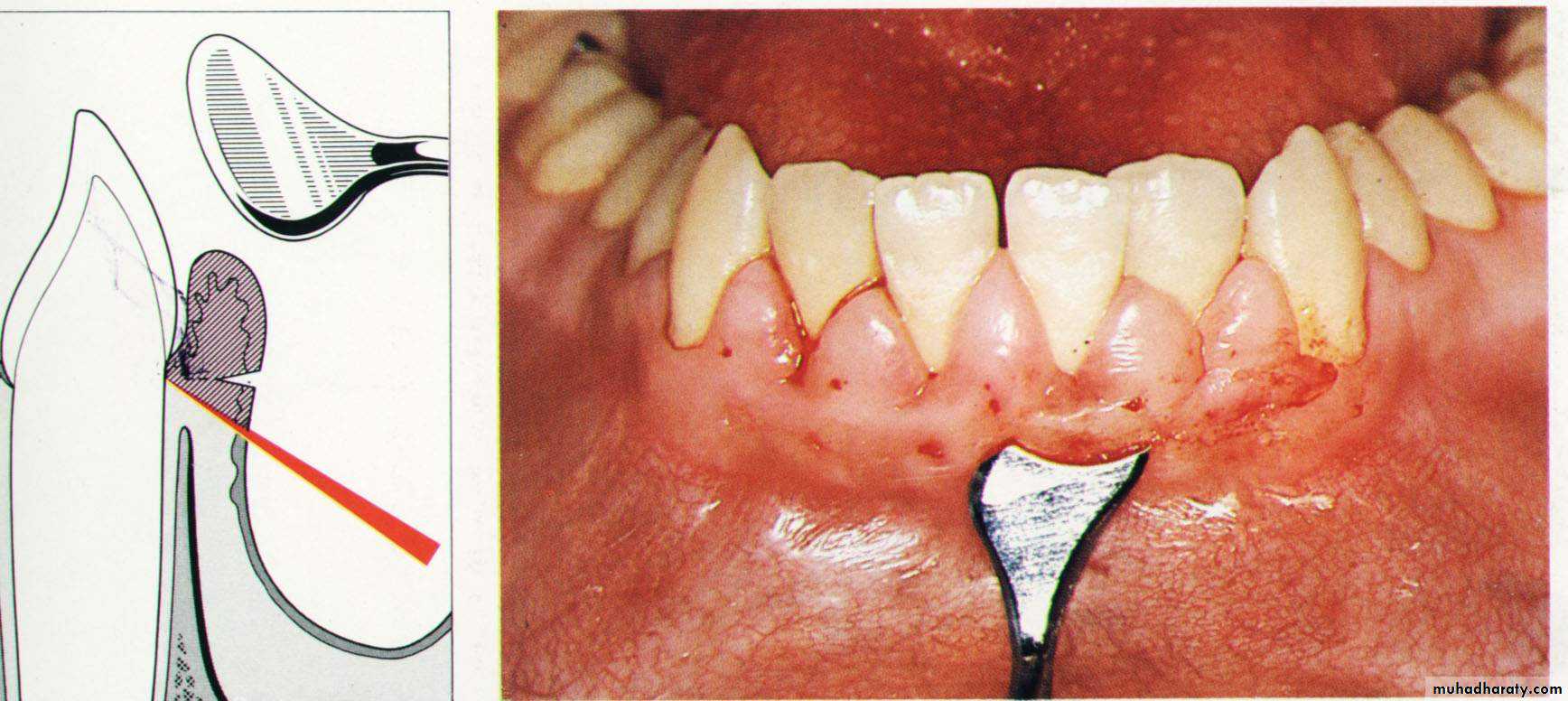
The minor alterations in gingival morphology usually termed gingivoplasty while the procedures that compromised a major amount of gingival tissues termed as gingivectomy.Goldman gingivectomy procedure:
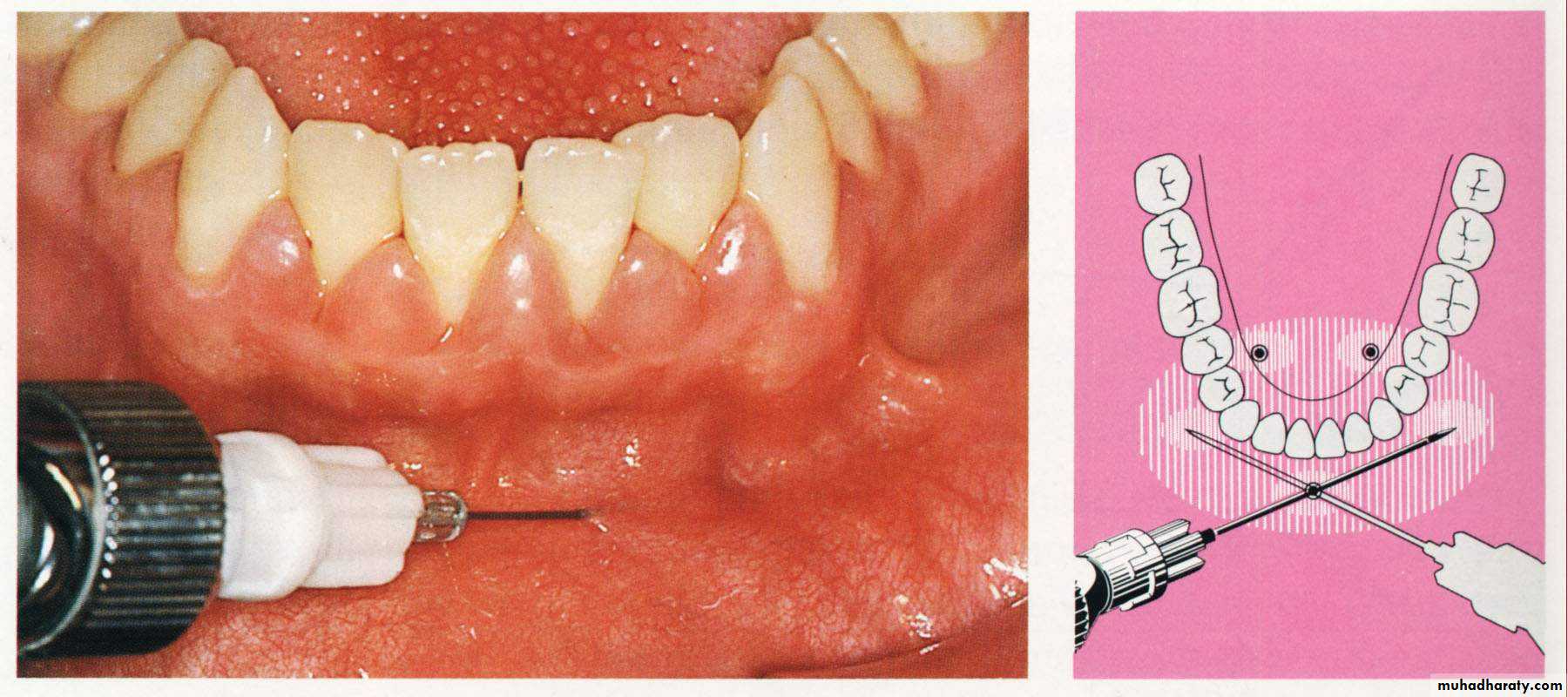
1. Giving of local anesthesia.
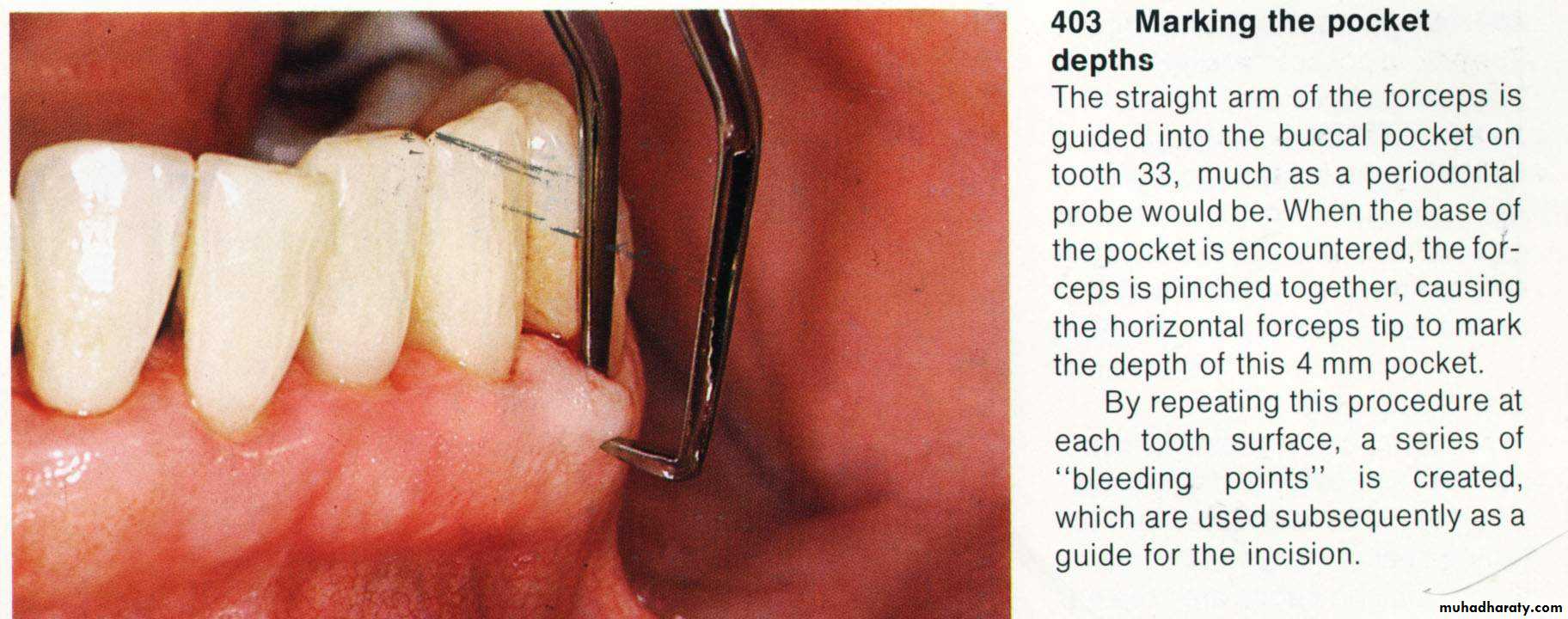
2. Determination of the bleeding points by using the pocket depth marker.
Primary beveled incision, which carried out according to the bleeding points.
4. Secondary incision to separate the interproximal soft tissues form the
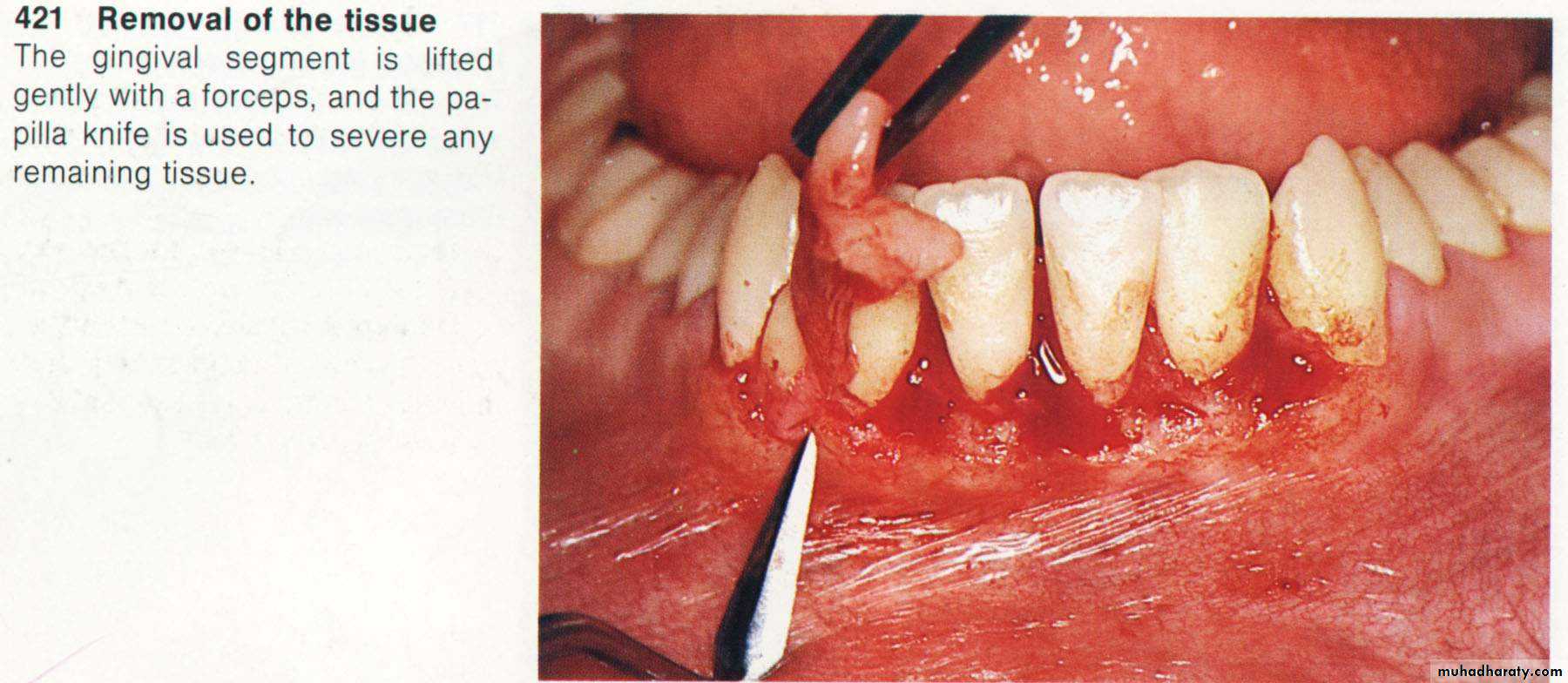
interdental periodonteum.5. Careful removal of the incised tissues by a curette or a scalar.
6. The bleeding can be controlled by a gauze pack inter proximally.
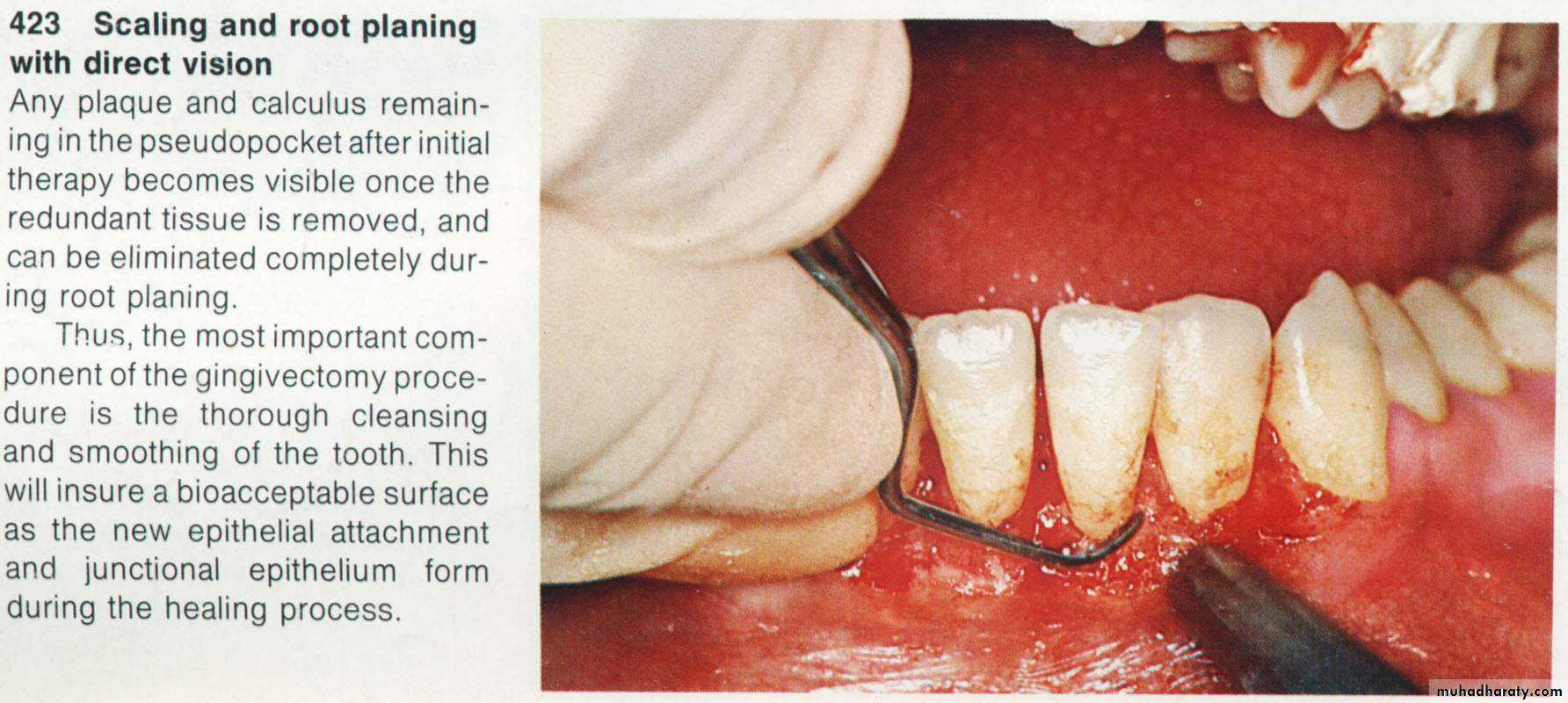
& performing of a careful scaling for the exposed root surface.7. Adjustment of the gingival contour & checking of the dentogingival area.
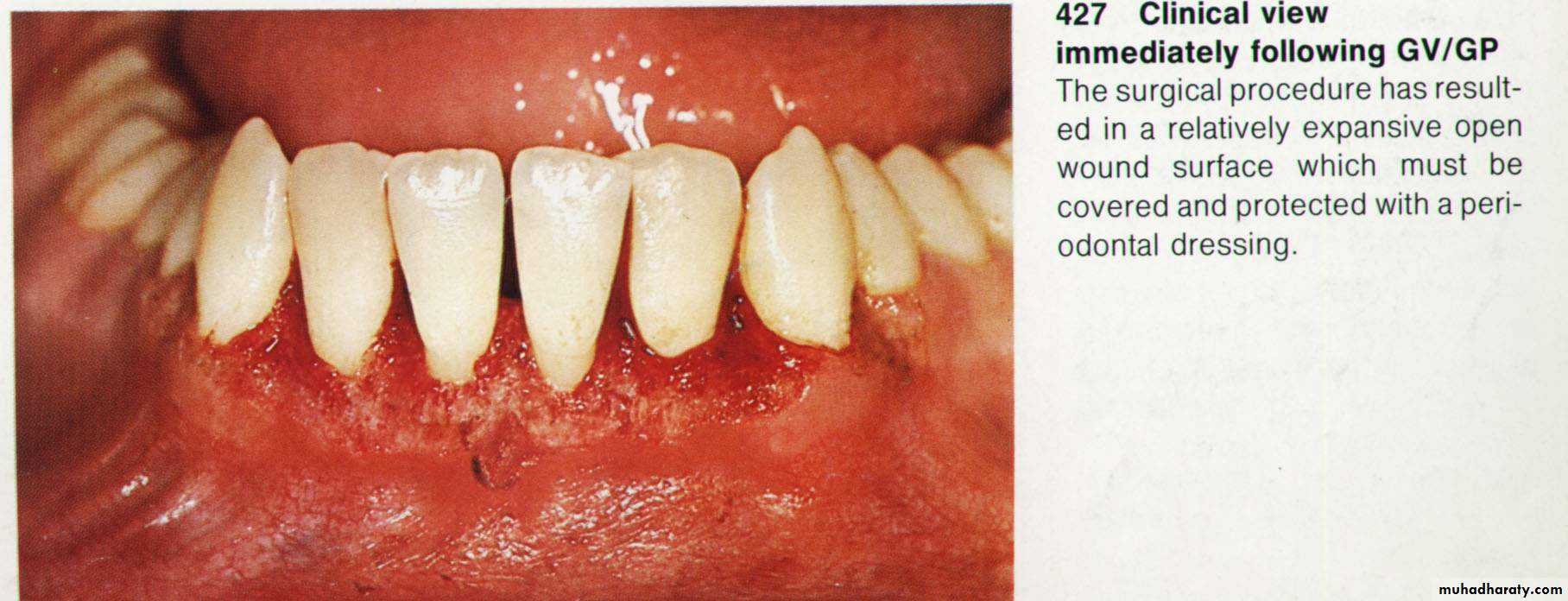
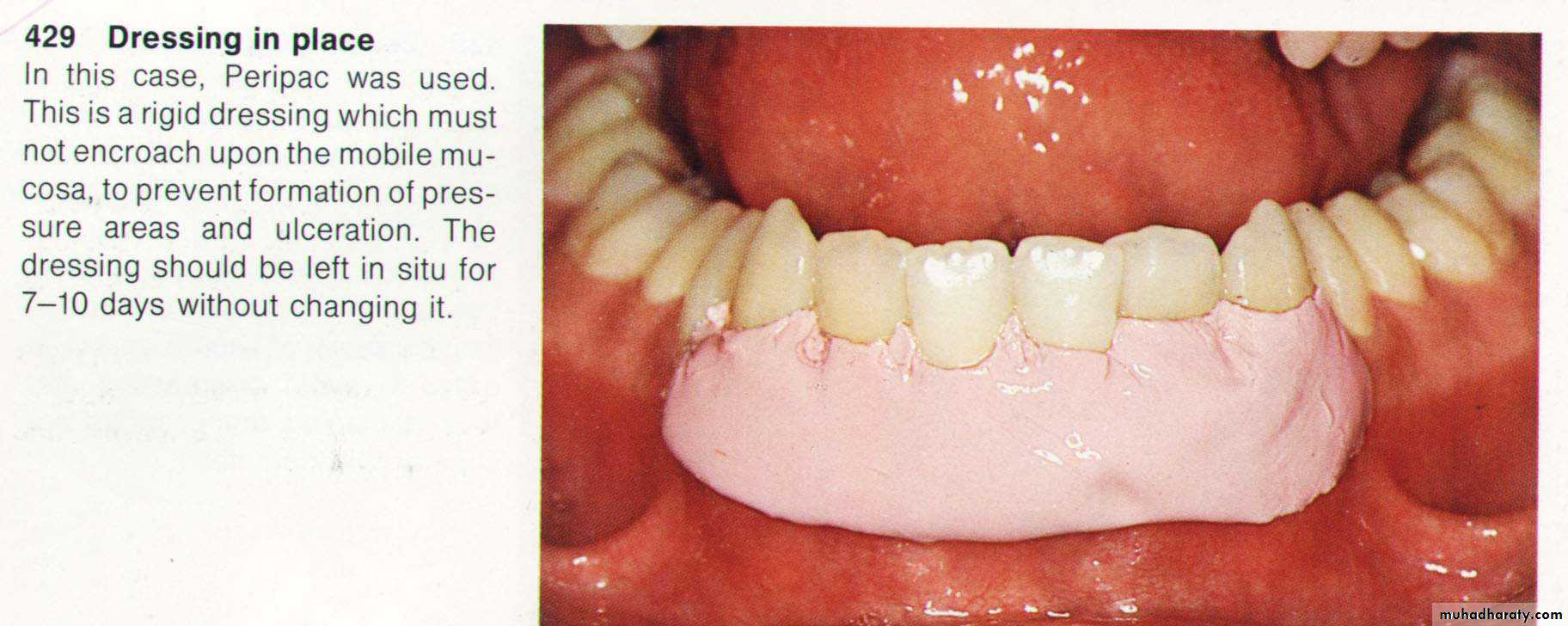
8. Dressing of the wound for (7 – 10 days).
9. Dressing removal & polishing.
C - Flaps in periodontal surgery:
They are usually conducted for their following advantages:The keratinized gingiva is preserved.
Provides better access to the underlying bone.
Furcation areas can be exposed.
The gingival margin can be adjusted as the flap can be replaced or
repositioned.
Provides more patient comfort postoperatively.
Indications of flaps:
As an alternative to gingivectomy when periodontal surgery is indicated.In treatment of infra bony pockets.
When the base of the pocket extend apical to the muco gingival junction.
When the gingivectomy will lead to an unacceptable aesthetic results.
Definitions:
Full thickness flap: flap includes, epithelia, connective tissue, periosteum reflected from underneath bone (muco periosteal flap)
Contraindications: •Area where treatment for osseous defect with mucogingival problem is not required. •Thin periodontal tissue with probable osseous dehiscence and osseous fenestration.
•Area where alveolar bone is thin.
Partial thickness flap: flap includes, epithelia and connective tissue reflected form bone and periosteum (split flap).
Reversed bevel incision: opposite to the gingivectomy incision.
Replaced flap: a flap which is sutured again to the same position as that before the operation (un repositioned flap).
•The major blood supply to a flap is at its base and travels in an apical to coroal direction.
•Recommended flap length (height)‐to‐base ratio should be no greater than 2:1
Reposition flap: a flap which is sutured in other position than that before the operation. They could be coronaly, apically or laterally repositioned.
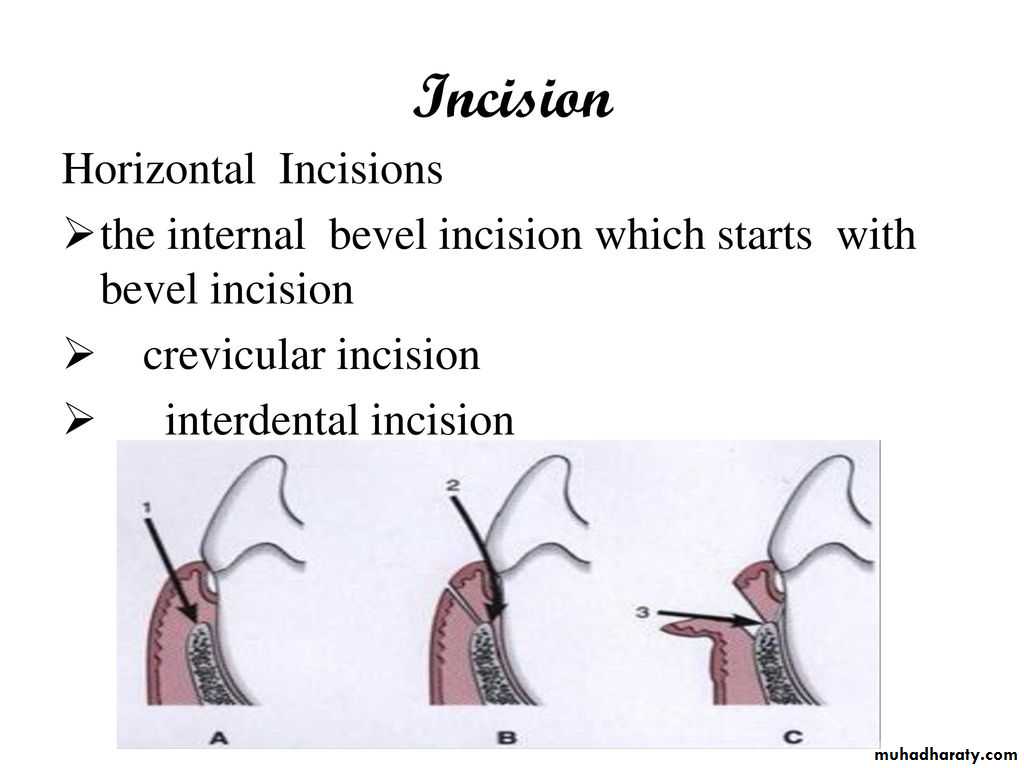
HORIZONTAL INCISIONS •Horizontal incisions are directed along the margin of the gingiva in a mesial or a distal direction.
•three types of horizontal incisions have been recommended:
The internal bevel incision, which starts at a distance from the gingival margin and is aimed at the bone crest, and
The crevicular incision, which starts at the bottom of the pocket and is directed to the bone margin.
In addition, the interdental incisionis performed after the flap is elevated.
INTERNAL BEVEL INCISION
1st incision 1º incision Reverse bevel incision11 or 15 surgical scalpel used
Starts at a distance from the gingival margin aiming at the bone crest.
CREVICULAR INCISION
Also known as second incision, Made from the base of the pocket to the crest of the bone ,This incision, together with the initial reverse bevel incision, forms a V-shaped wedge ending at or near the crest of bone.
VERTICAL INCISIONS
Can be used on one or both ends of the horizontal incisionMust extend beyond the mucogingival line, reaching the alveolar mucosa, to allow for the release of the flap to be displaced
Vertical incisions in the lingual and palatal areas are avoided
Replaced flap(un repositioned flap , Nondisplaced flaps)
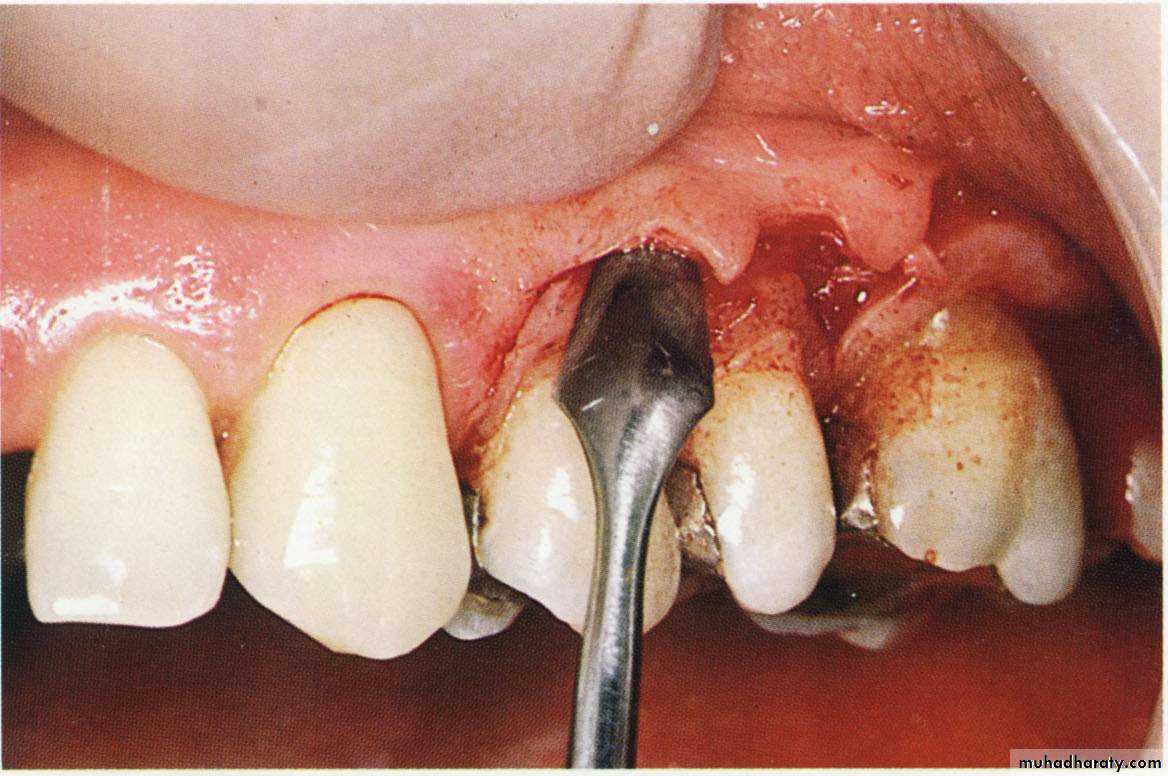
Currently, it is the most commonlyperformed type of periodontal surgery.•It differs from the modified Widman flap in that the soft tissue pocket wall is removd with the initial incision; thus it may be considered an internal bevel gingivect, Initial incision through marginal gingiva to the crest of the alveolar. Knife should be parallel to the long axis of the tooth. The distance between the surface of the tooth and the incision depends on the depth of the pocket .Be sure in removing all the Sulcular epithelium from the margin of the incision, vertical incision can be done if needed.
The flap is then reflected, and all the tissue around and between the teeth should be removed. Thorough root planning and cleaning of the infra-bony pocket can be performed.
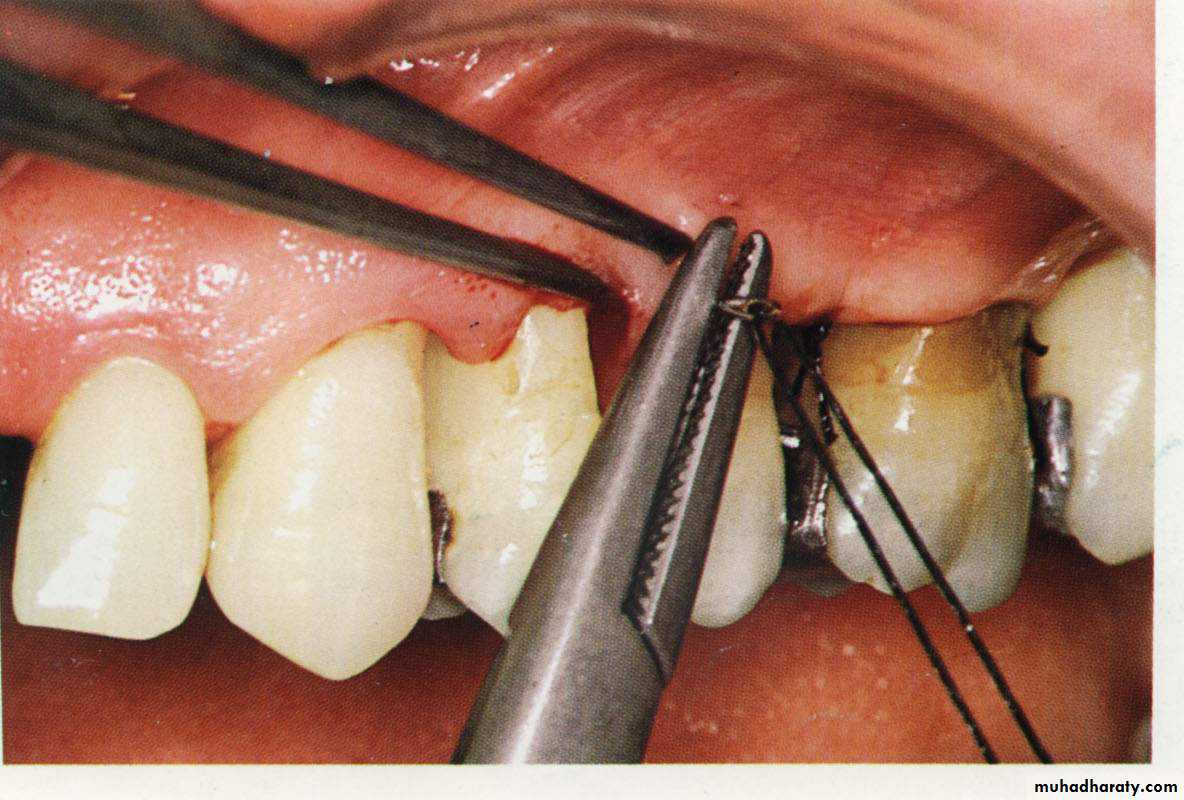
The flap margins are now sutured again and the area can then covered with periodontal pack.
Apically repositioned flap
It can be used for both pocket eradication as well as widening the zone of attached gingiva. •It can be a full thickness (mucoperiosteal) or a split thickness (mucosal) flap. The initial incision is performed as before, but preserves most of the attached gingiva, by locating the incision as near to tooth surface as possible. Vertical incision must be extended to the muco buccal junction. After thorough root planning the flap is then undermined and push apical to the level of the alveolar bone. On the palatal side, the flap can not be pushed apically, but the margin is undermined before suturing. The flap is sutured in a way that its margin is now located apical to its original position.ADVANTAGES:
•Eliminates periodontal pocket.
•Preserves attached gingiva and increases its width. •Establishes gingival morphology facilitating good hygiene. •Ensures healthy root surface necessary for the biologic width on alveolar margin and lengthened clinical crown.