Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
1
Imaging Technique
1 - Plain film :
a — Supine (AP ) view .
b - Erect ( .AP ) view .
2 - Contrast examinations:
a - Barium sulphate used to opacified the bowel & shows the mucosa .
b — Water-soluble contrast like gastrografin used when perforation or leakage
from anastomosis are suspected .
3 — Ultrasound :
a – Conventional transabdominal ultrasound
b — Endoscopic ultrasound used in the assessment esophageal, gastric, rectal,
pancreatic tumors
4 - Computed tomography ( C.T) :
a — It shows the whole wall of the organ & the surrounding structure .
b — Evaluation of the lumen by using gastro graphin or air ( CT pneumocolon&
virtual coloscopy )
c - Diagnosis & staging of G.I.T tumors .
d — Evaluation of acute abdomen like acute appendicitis , intestinal obstruction &
bowel perforation .
5 - M.R.l :
a — Used in the assessment of liver metastases .
b— Assessment of local spread of rectal tumor before surgery .
c — Assessment of perianal fistula & abscess .
6 - Nuclear medicine : PET / C.T used to shows metastases in patients with GIT
tumors
Esophagus
* Started at the upper esophageal sphincter at the level of C6 & finishes at the lower
esophageal sphincter at the level of D11, it is about (25) cm in length.

Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
2
* Consist of inner circular & outer longitudinal muscles coat which predominately
striated muscle in the upper third & predominantly smooth muscle in the lower two
thirds.
* The esophageal mucosa is stratified squamous epithelium & changes to columnar
epithelium at the gastro-esophageal junction .
* The aortic arch & left main bronchus indent the left anterolateral wall of the
esophagus.
* Lymphatic drainage of the upper esophagus into cervical nodes, mid esophagus into
pre-aortic nodes & the lower esophagus drain to the coeliac & gastric nodes.
Plain film
Chest x Ray can shows the following:
1 - Dilated esophagus with air fluid level through heart shadow as in case of achalasia.
2. - Opaque foreign body.
3 — Check the position of nasogastric tube.
Ba swallow
Is the standard contrast examination, normal esophagus has smooth outline when filled
with Ba, when empty seen as 3-4 longitudinal parallel lines .
Indications of Ba swallow:
1- swallowing disorders (functional abnormalities).
2- Determining the length of esophageal structure (structural abnormality).
3- Assessment of gastroesophageal reflux.
4— postoperative assessment of esophageal anastomosis, anti reflux & obesity
reduction surgery.
Normal esophagus Ba swallow:
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
3
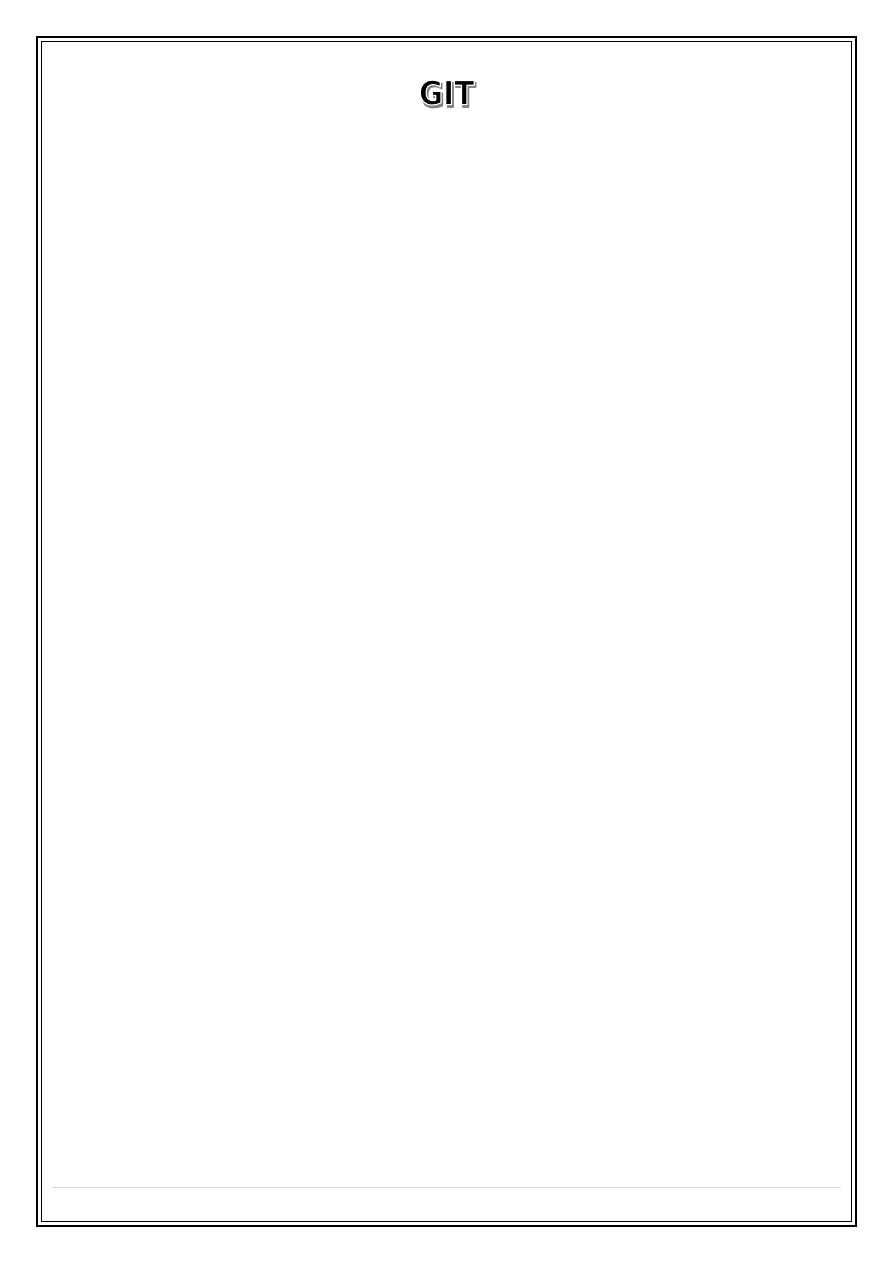
Normal endoscopic ultrasound
A - mucosa B- muscularis mucosa C – submucosa D- muscularis propria E-adventitia
Esophageal abnormalities
1 - Esophageal carcinoma 60 % are squamous cell carcinoma, the main risk Factor
are cigarette smoking & alcohol consumption.
Adenocarcinoma form 40 % of esophageal malignancy arising in the lower esophagus
due to columnar epithelial metaplasia as a result of longstanding reflux esophagitis
(Barrett's' esophagus)
Most patient with esophageal carcinoma presented with dysphagia with tumor already
spread to regionalL.N, 5 years survival less than 10 % .
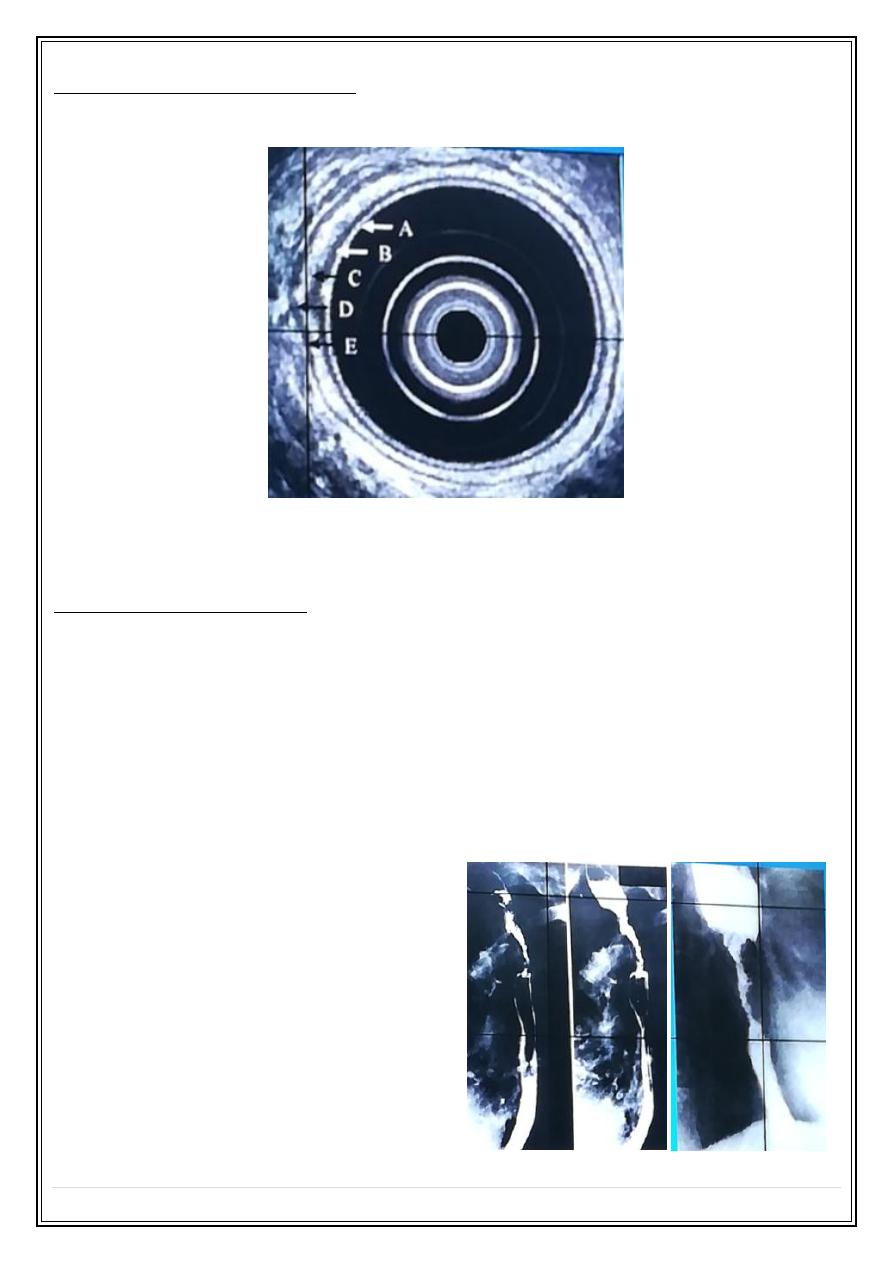
Ba swallow shows constant irregular stricture with dilatation of the upper end
(shouldering) .
Endoscopic ultrasound shows the tumor as
hypoechoic mass , it also can shows
adjacent LN enlargement.
C.T shows the tumor as esophageal wall
thickening & shows local spread to the
mediastinal LN, far spread to the liver &
lung.
Esophageal carcinoma Ba swallow:
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
4
CT appearance of esophageal carcinoma:
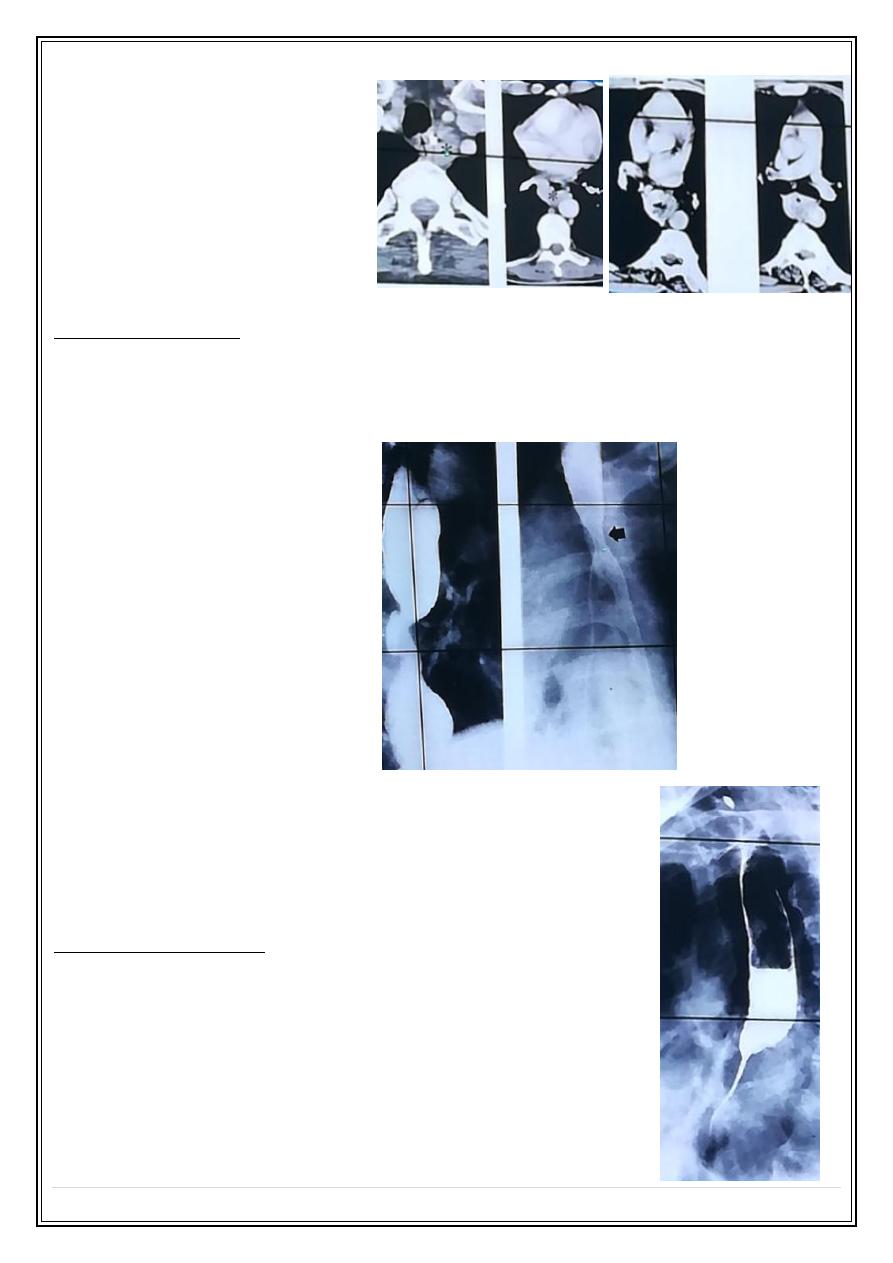
2- Peptic stricture: found at the lower part of esophagus usually associated with
hiatus hernia & gastro-esophageal reflux.
The peptic stricture is short with smooth outlines & tapering ends, about 10% of patients
with reflux esophagitis have Barret's esophagus 15% of them develop adenocarcinoma
Peptic stricture:
3- Corrosive stricture result from incidental or suicidal
swallowing of strong acids or alkaline, the stricture is long &
started at the level of aortic arch which usually smooth with
tapered ends as seen in Ba swallow.
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
5
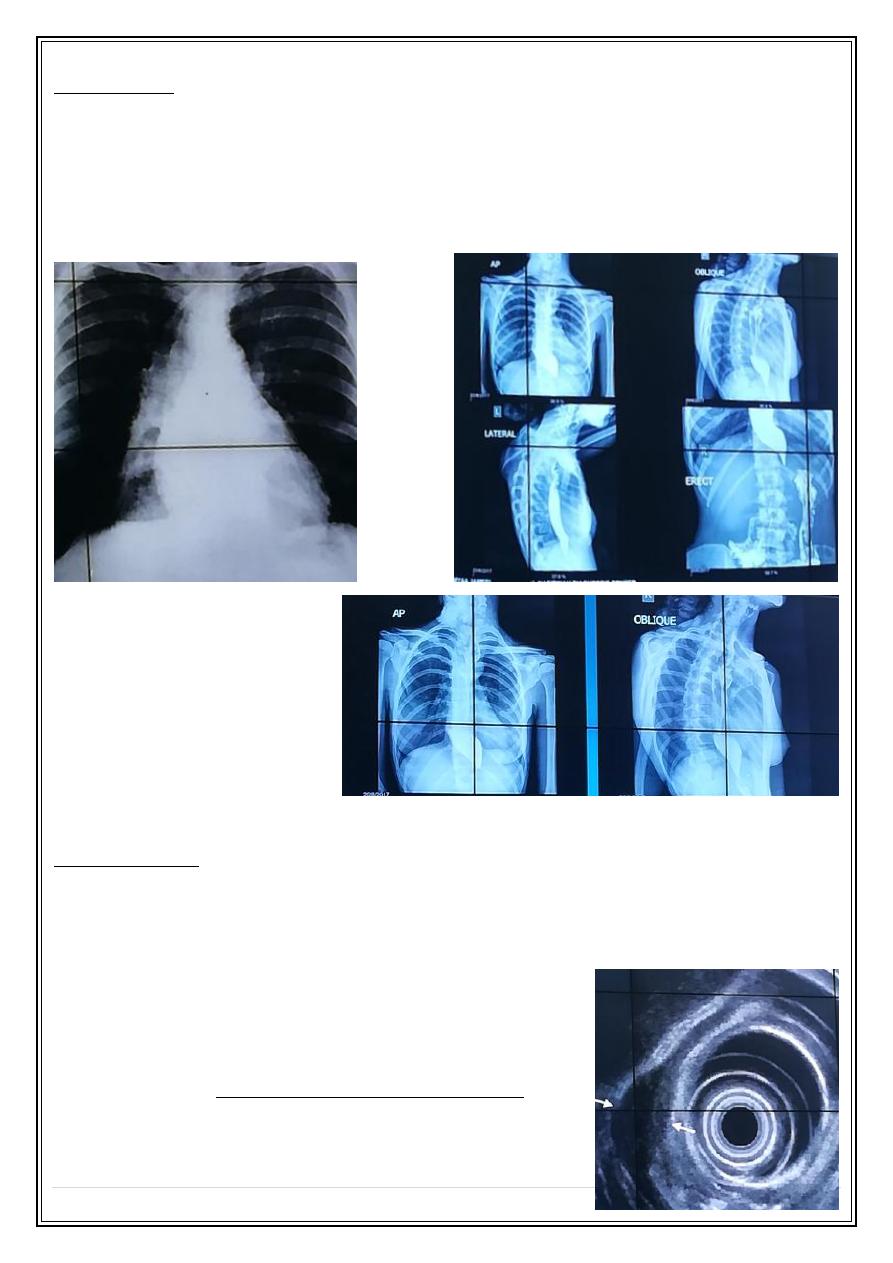
4- Achalasia is a motor disorder of the esophagus caused degeneration of Auerbachs
plexus in the lower esophagus resulted into failure of relaxation of the cardioesophageal
sphincter, it cause dysphagia for both solid and liquids.
Ba swallow show gastro-esophageal junction as smooth tapering stricture give rat tail or
bird beak appearance with intact mucosa.
Widening mediastinum due to dilated esophagus:
Achalasia Ba Swallow:
5- Leiomyoma: well-encapsulated smooth muscle submucosal tumor commonly found
In the low two thirds of the esophagus. it is usually large all the time of diagnosis.
Ba swallow seen as Intramural mass forming obtuse angle with the normal esophagus
wall. unlike gastric Leiomyoma it rarely ulcerated & have no malignant potential.
Endoscopic ultrasound leiomyoma:

Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
6
6- Anomalous right subclavian artery arise as last major
branch from the aortic arch pass behind the upper esophagus
cause smooth indentation.
7- Esophageal web is thin shelf like projection arise from the
anterior wall of upper esophagus, it may be isolated or as part of
Plummer -Vinson syndrome.
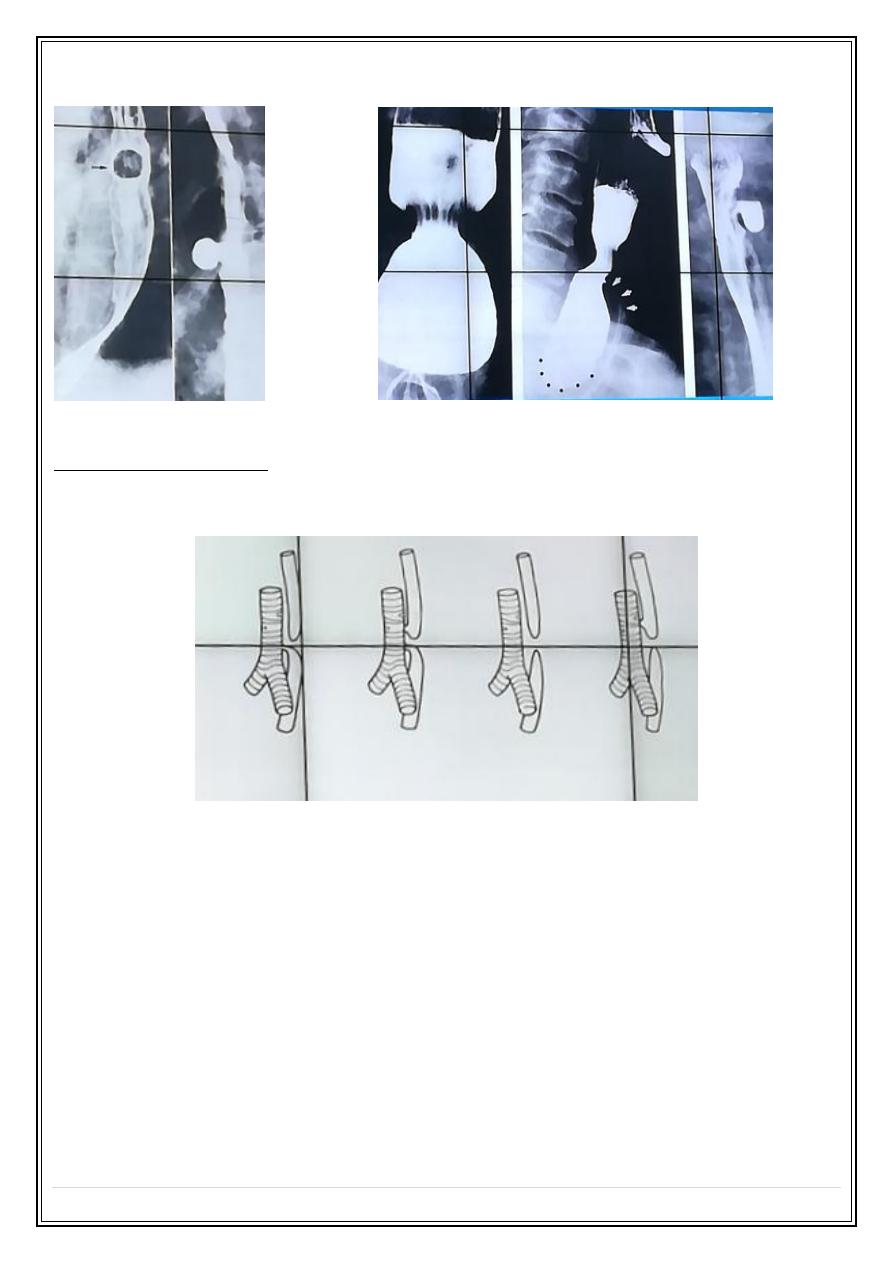
8— Esophageal diverticulum are of the following types
a- pulsion diverticulum develops due to motility abnormality when intramural pressure
increased, they are wide necked and at the level of carina.
b- Traction diverticulum occurs in the mid esophagus resulted from fibrosis of healing
tuberculous L.N.
c- Pharyngeal pouch (Zenkers diverticulum) arise through congenital weakness in the
inferior constrictor muscle of the pharynx and lie behind the esophagus cause
displacement and compression of the esophagus.
Fifth Stage
Diagnostic Imaging
Dr. Abdul-Kareem – Lecture 1
P a g e
7
Pulsion diverticulum:
Posterior pharyngeal diverticulum:
9- Esophageal atresia in which the esophagus ends as blind pouch in the
mediastinum, the most frequently type is blind sac like upper part with fistula between
the lower segment and the trachiobronchial tree .
Thank you,,,
