Lecture two
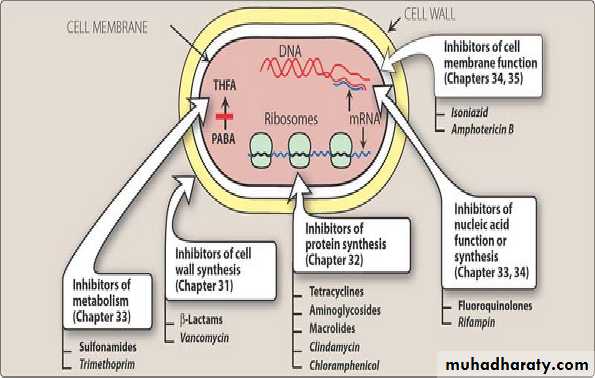
Antibiotic classifyThe antimicrobial drug classified according to the mechanism of action:
1. Inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis.
(Bactericidal)
2. Inhibition of protein synthesis.‘Cidal’ or ‘Static’
3. Inhibition of organism production by
interfering with nucleic acid synthesis : Inhibits bacterial synthesis of RNA & DNA
4-inhibition of metabolism
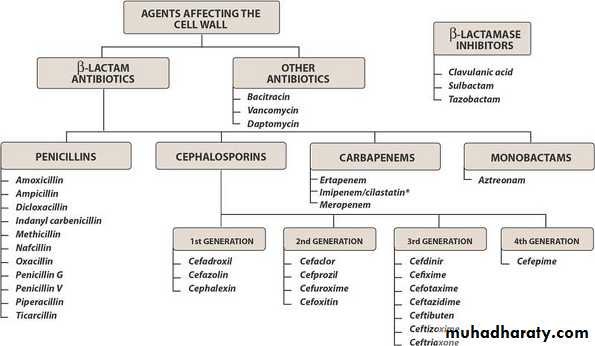
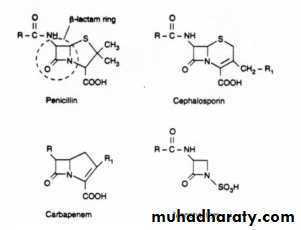
β-lactams( penicillins, cephalosporins ). Vancomycin
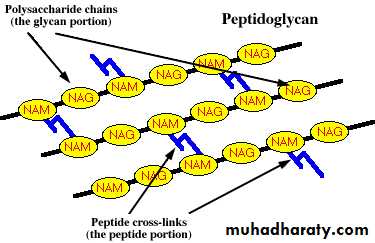
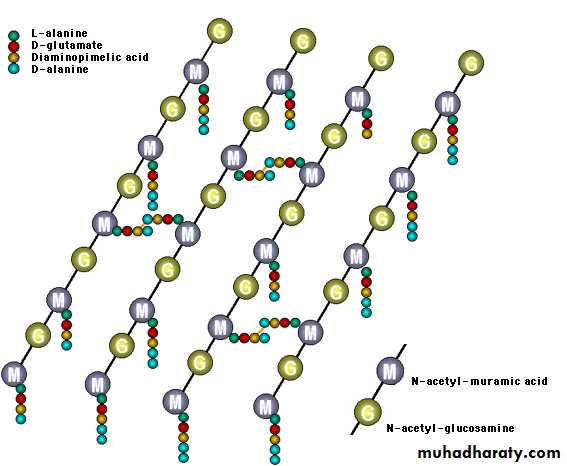
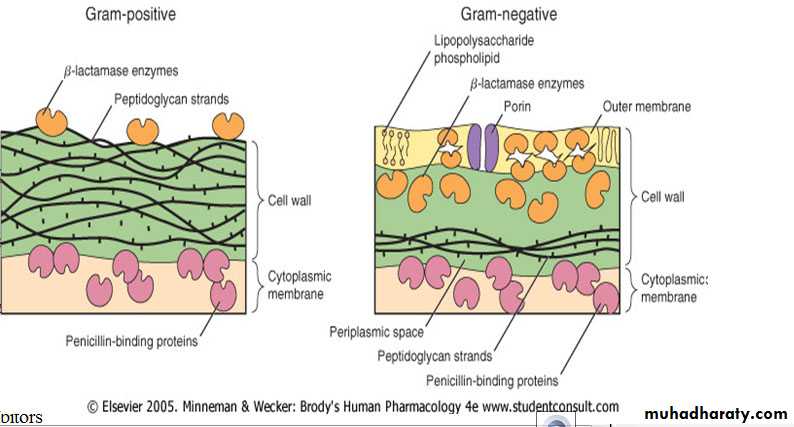
1- Inhibitors of bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis.Antibiotic selectively interfere with the synthesis of bacterial cell wall (a structure that mammalian cell do not possess ) the cell wall is a polymer called peptidoglycan that consist of glycan unit joint to each other by peptide cross –links and the designation of peptidoglycan cell wall to be maximally effective .
These agents require actively proliferating M.O , they have little or no effect on bacteria that are not growing and dividing .
.
Penicillin
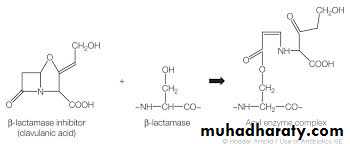
Beta Lactamase inhibitor (Claulanic acid and Sulbactam)Suicide Inhibitors
Monobactam
Carbapenem
Cephalosporins
Beta Lactamase
Penicillins
T
β
Beta Lactam ring is broken by –
Penicillinase (Beta Lactamase), and by gastric acid.Resultant Product is Penicilloic acid with
No anti-bacterial activity but
Acts as antigenic determinant (Major determinant)
Antibacterial mechanism of β-lactams
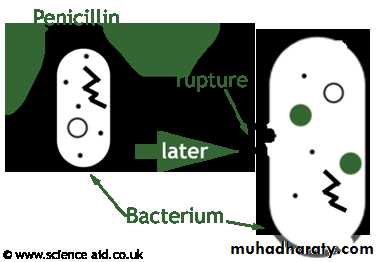
Inactivation of cell wall enzymes (PBP-s)Cessation of cell wall sythesis
during active cell growth and divison
Cell lysis = bactericidal effect
antagonised by bacteriostatic agents
PenicillinsMechanism of action
It interfere with last step of cell synthesis by inactivation of some penicillin binding protein which a bacterial enzymes involved in
bacterial cell wall synthesis.
or penicillin Inhibit transpeptidase (enzyme responsible for cross –linkage between peptidoglycan chain ).
All resulting in exposure of the osmotically less stable membrane and cell lysis occur so it Bactericidal and only effective against rapidly growing organism that synthesis peptidoglycan cell wall .
Betalactam Antibiotics
.
Penicillins are more effective against Gram+ bacteria. This is because Gram + bacteria have penicillin binding proteins (PBP)on their walls.
Kinetics:
- absorption vary with the preparation depending on their acid stability and protein binding- absorption of most oral penicillins
(except amoxicillin) impaired by food and drugs should be given 1-2 hours before or after meal.
- Excreted primarily by the kidneys (90% tubular secretion, 10% glomerular filtration) small amount through bile and feces, sputum and milk; renal excretion inhibited by probenecid.
• Penicillin class
• Drug• Antimicrobial spectrum
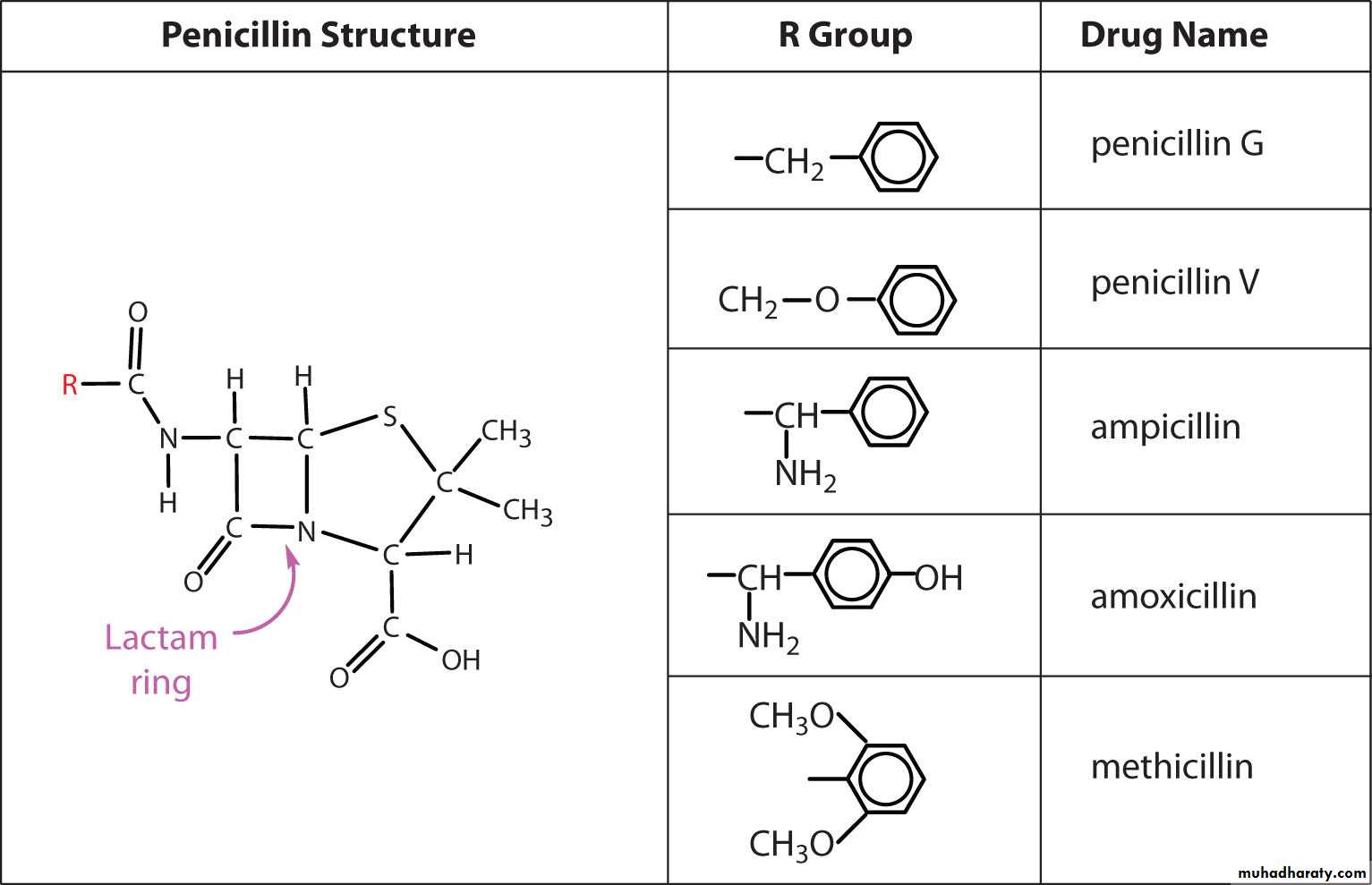
• Natural Penicillins
• Penicillin G
• Penicillin V
• gram+ cocci and bacilli,some
• gram– cocci (Neisseria)
• Penicillinase resistant
• Nafcillin
• Cloxacillin
• Dicloxacillin
• Oxacillin
• Staphylococcus aureus
• Broad-spectrum
• (Aminopenicillins)
• Ampicillins
• Amoxicillin
• Bacampicillin
• Extended spectrumSame as
• Pen G plus some gram(–) organisms
• Extended spectrum
• Ticarcillin
• Piperacillin
• Carbenicillin
• Mezlocillin
• Same as broad spectrum
• Plus additional gram(–)coverage, including Pseudomonas
• Penicillin/β - Lactamase inhibitor combination
• amoxicillin clavulanate (Augmentin) ampicillin/sulbactam (Unasyn) piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn)
• ticarcillin/clavulanate (Timentin)
• Extended spectrumSame as
• Pen G plus some gram(–) organisms and Staphylococcus aureus
Types of Penicillins according to the spectrum
1- Penicillin G:
its prototype of Penicillin
available as sodium , potassium , procaine or benzathin salts
The potassium salts given IV produce the most rapid and highest blood level whereas benzathin salts IM produce much less level
The potassium and procaine salts given IM produce intermedite blood level .
procaine and , benzathin is suspension given I M only, benzathin penicillin use once monthly in patient with history of rhumatic heart disease, syphilis
2- Penicillin V: spectrum similar to penicillin G , it given orally and it produce higher blood level .
Its used in the treatment and prevention of dental infection , usual dose is 500 mg twice daily for 5-7 days usually in form of salt with potassium because its more soluble.
3- penicillinase resistant penicillins
( Methicillin , Nafcillin , Oxacillin , cloxacillin , DicloxacillinThese drugs should be used only against penicillinase producing Staphylococci ,
Developed to overcome the penicillinase enzyme of S. aureus that inactivates natural penicillins
4.Antipseudomonal penicillins: Carbenicillin,ticarcillin and piperacillin are called antipseudomonal penicillins because of their activity against P. aeruginosa
Piperacillin is the most potent of these antibiotics. They are effective against many gram-negative bacilli.
uses of antipseudomonal penicillins
Serious infection caused by pseudomonas or proteus likeBurns,urinary tract infection,septicaemia.
Extent spectrum pencillin
5- Aminopenicillins (Broad Spectrum) Developed to increase activity against gram-negative aerobes.
Ampicillins and amoxicillin Has wide spectrum than PG and effect against pseudomonas aerrginosa and some strain of proteus and it given parentally .
Amoxicillin is preferable than Ampicillin because it:
a. produce higher blood level
b. better absorption
c. require less frequency dosing (Tid)
d. it absorbed not affected by food
e. its drug of choice for prophylaxis of RH disease prior to dental procedure .
6- (Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid)-------- Augmentin
Developed to enhance activity against -lactamase producing organisms.β-lactamase inhibitors
those are certain molecules that can inactivate β-lactamases enzyme in bacteria
.A. Clavulanic Acid –
-potent inhibitor of beta-lactamases
-combined with Amoxicillin called (Augmentin)
The combination widens the antimicrobial spectrum
B. Sulbactam and Ampicillin ( Unasyn)
a.Dental infection
Periodental abscess,periapical abscess,pericoronitis,oralcellulitis.
B.Medical use
pharyngitis,tonsillitis,pneumonia,gonorrhea, syphilis,diphtheria,
and meningitis
c. Prophylactic, benzathin penicillin use once monthly in patient with history of rheumatics heart disease
Uses of penicillin
Uses of ampicillin
1.dental infections2.respiratory tract infections(bronchitis,sinusitis)
Dose:
Oral:250-500mg four times dialy.
Inj.500mg-1g(vial)
Indication of coamoxiclav
1.skin and soft tissue infection2.UTI
3.RTI
4.Dental infection caused by B-lactamase bac.
5.Gonorrrhea
Therapeutic use of penicillin groups in dentistry
1.Infection of dental origin(penicillin V,ampicillin,amoxicillin).
2.sever infection in(malabsorption,vomiting)
use penicillin G.
3.prophylactic (bacterial endocarditis)
4.periodontal infection caused by
gm+ve and gm-ve , aerobic and anaerobic need combination of
(amoxicillin+metronidazole)
5.- pericarditis , osteomytitis
6. -Oral infections are caused by β-lactamase producing microoorganism
should be treated by Penicillinase – resistant penicillin
Adverse reaction
allergy to one P increase the risk of reaction if another P is given and allergy Can occur at any ageallergy can be mild ,moderate , severe (lead to death)
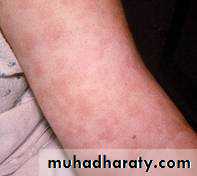
1- Allergy reaction :this is represent a danger with therapy and include all type of hypersensitivity type, which include :
A- anaphylactic reaction : urtecaria , bronchospasm, angiodema ,capillary dilatation ( shock),sudden hypotension and death .
B- delayed serum sickness : fever , skin rashes , lymphadenopathy , splenomegaly ( take 6 days to develop )
Adverse reaction
2- Diarrhea: disturbance of normal balance of intestine M.O (ampicillin)3- Nephritis : cause acute interstitial nephritis(methicillin)
4- Neurotoxicity: it irritant to neuronal tissue cause seizure if injected intrathecally.
5- Cation toxicity : P. administered as sodium or potassium salt , toxicity may caused by large quantity of sodium or potassium
6- P. change the composition of microflora which can be reestablished shortly after therapy is stopped , sometime super infection results
Risk increase
• in elderly patient
• Patient allergic to other antibiotics (multiple allergy syndrome)
• Atopic disease (asthma , allergic rhinitis)
Drug interactions
Antagonized by bacteriostatic antibioticsNSAIDs and probenecid may increase the half life of pencillin by decreasing their renal excretion.
Contraindications:
Patient allergic to penicillinPatient taking anticoagulant
Treatment of Allergic Reactions
Mild: Diphenhydramine 25-50 mg IV/IM/POSevere: Epinephrine 0.03-0.05 mg