
1
CONTRACEPTION
Pearl index ( PI )
It is used to determine the pregnancy rate
- Among 100 women ( HWY )
- Using a contraceptive method for 12 months .
* Perfect use rate represents the theoretical efficiency .
* Typical use rate represents the actual users' experience
(1) Physiological
Advantage have no medical contraindications
Disadvantage not a very reliable contraceptive method
(1) Safe period
the Best is Combination ( sypmto-thermal)
* Calendar method Ovulation occurs 14 d< the 1
st
day of the next cycle
. I.C. is avoided 2 days < & 2 days > the calculated day
. Ovum lives 24 hrs / sperms live 48 hours
* Basal baby temperature I.C. is only allowed after ovulation has occurred
by 3 d , i.e. after 3 d or rise of BBT
* Cervical mucus method I.C. is allowed only after 3 days from
disappearance of wetness
- Estrogen profuse ox mucous ………… sensation of wetness
- After ovulation , CL progesterone ………. Dryness of secretion
(2) Lactational amenorrhea method
Idea : Prolactin inhibition of ovulation
Increasing efficiency from 10 to 90 % by
• Amenorrhea is still present ( esp in 1
st
6 months )
• Regular breast feeding
• No supplement food is given to the baby .
Advantage available from 1
st
day , not costy , healthy to infant
Disadvantage breakthrough bleeding may occur so not reliable .
(3) Coitus interruptus & interfemoris
* Idea withdrawal of penis before ejaculation or IC bed things
* Disadvantage pregnancy may occur ( 20 / HWY ) in spite of ejaculation
outside the vagina or some sperms may be present in
secretion before ejaculation
2
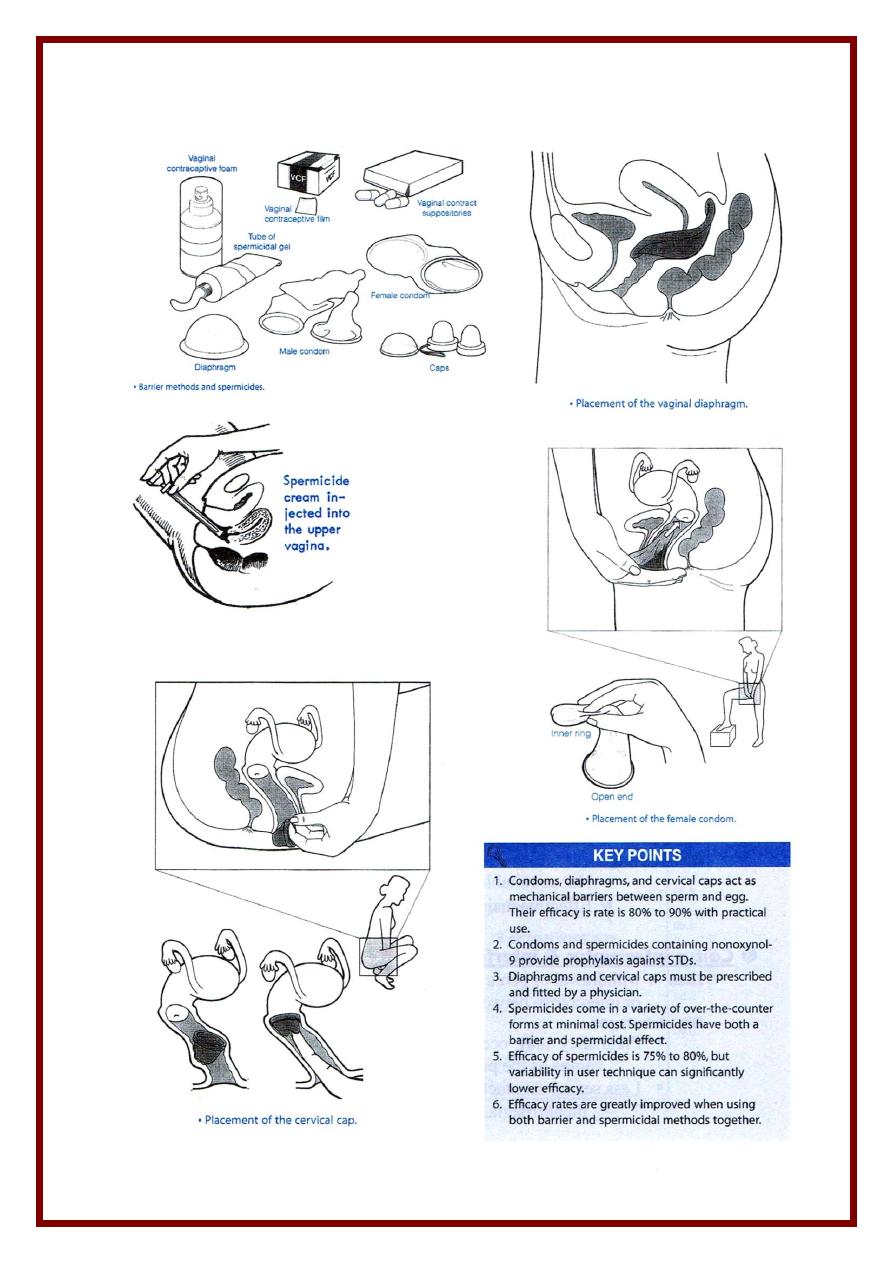
(2) Mechanical
1) Condom
* Male sheath *( French Letter ) 15 x 3.5 x 0.02 – 0.07
* Non contraceptive benefits
- Protect against STD , PID , CIN
- Treatment of immunological infertility
- Collection of semen for semen analysis ( spermicide free )
2) Female condom ( Femidom )
* A polyethylene rubber sheath which lines the vagina ( 17 x 8 cm )
* Has 2 ends a closed end and an open one
3) Vaginal diaphragam ( Dutch cap )
50 – 95 mm
* Inserted in vagina < IC & removed after 8 hrs ( till all sperms die )
* Disadvantages
- Difficult to apply needs well training in the clinic
- May lead to cystitis if large size , not suitable in prolapse
4) Cervical cap
* Applied directly to cervix ( 22 – 25 – 28 – 31 mm )
* Used if there is propalse ( diaphragm can't be applied )
5) Vaginal sponge ( Today )
* Synthetic polyurethane sponge containing nonoxynol-9
* Very easy to insert & remove ( up to 24 hours )
* Disadv. Toxic shock syndrome if left long ( staph aureus )
Disadvantages
- Failure rate 3 – 14 / HWY ( improved by adding spermicidals )
- May lead to allergic reaction ( latex )
- Interrupt natural act ( sensation + erectile difficulties )
(3) Chemical
* Method
- Spermicidals Nonoxynol-9 & Octoxynol-9
- Action destroy sperm memb + O2 uptake
* Supplied as
foam / jell / cream / effervescent tablets / suppositories
* Use
- Inserted 15 min before intercourse } high failure rate
- Intercourse must occur within 2 hours } =
- Delay postcoital douching for 6 hours } 30 / HWY
3
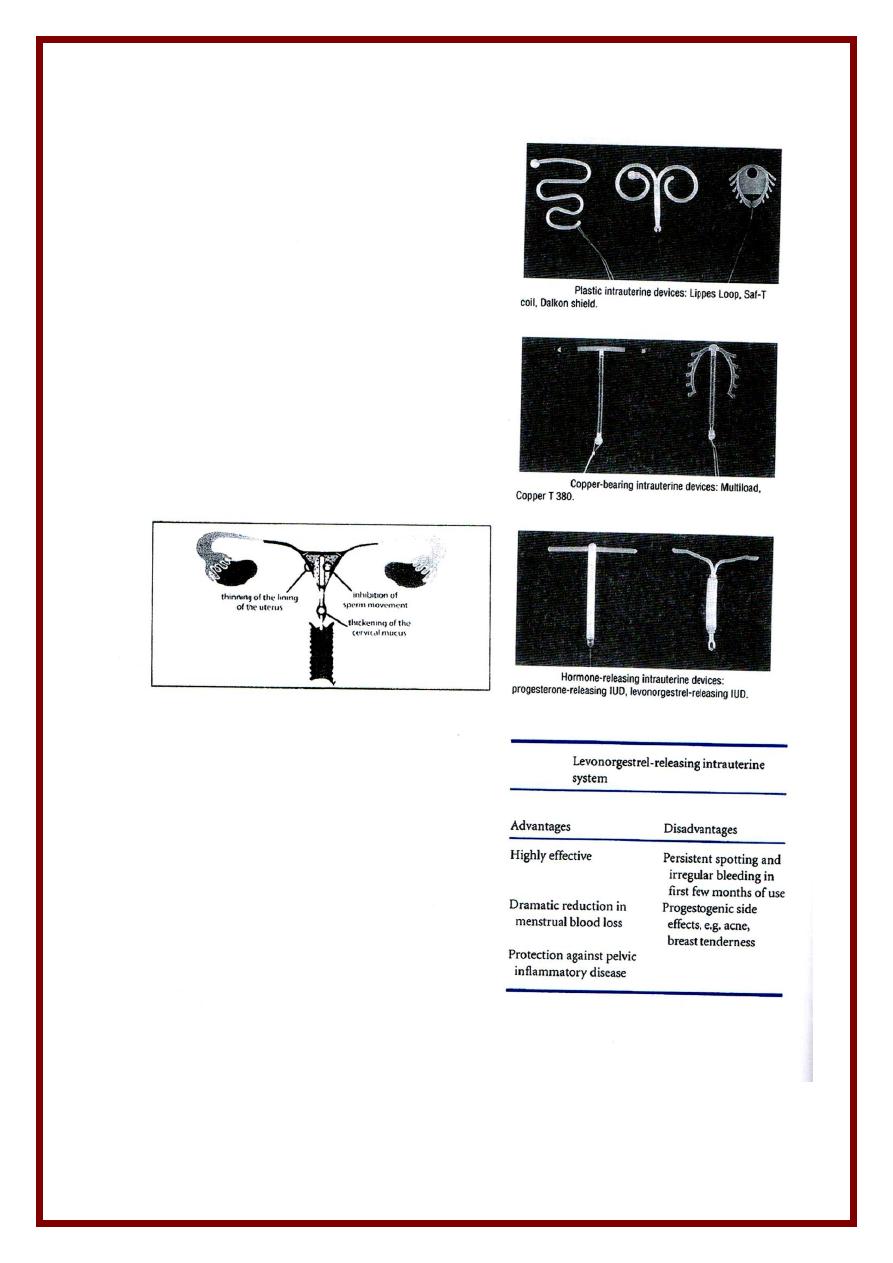
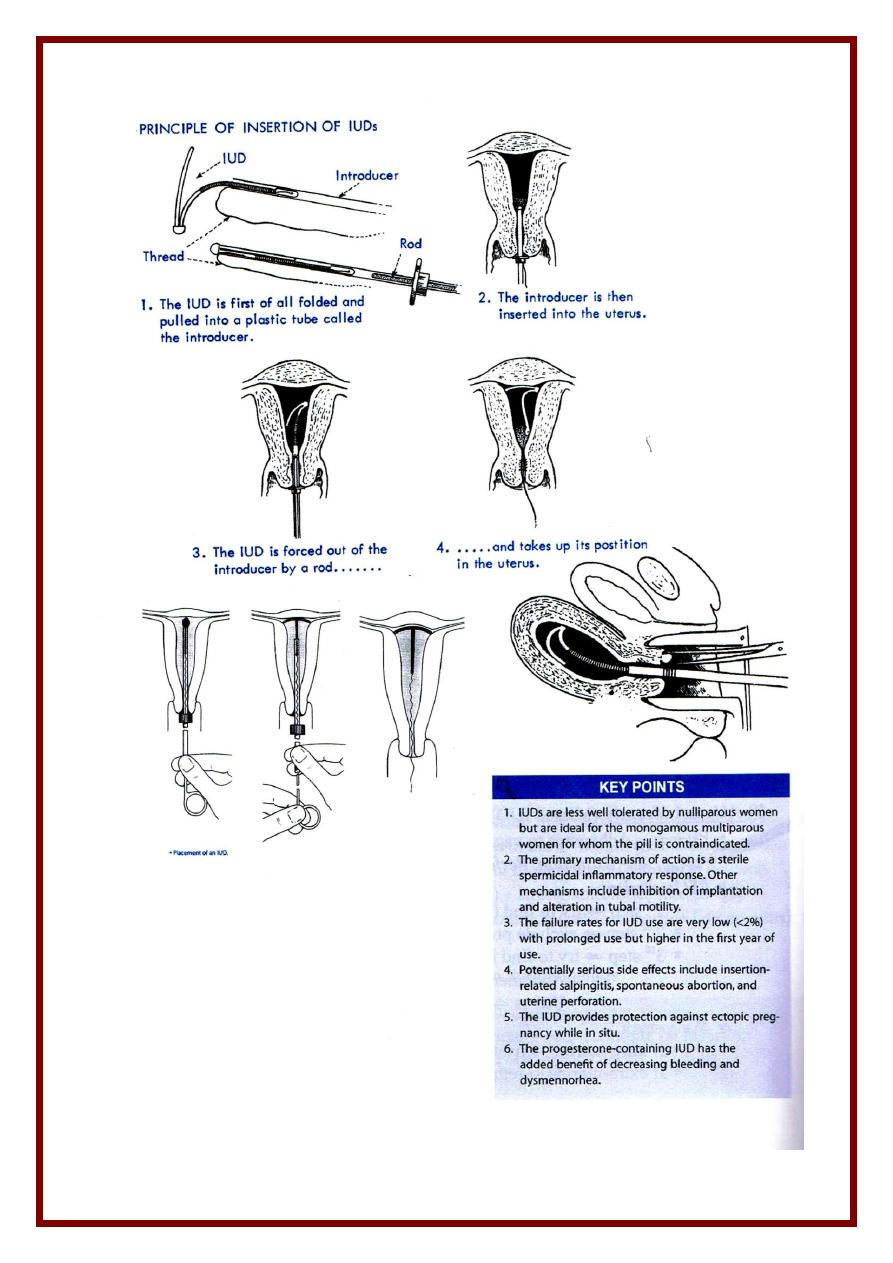
(4) Intrauterine Device
Types
Type
Duration
1) Inert
Lippes loop ( double S shaped )
Indefinite
2) Medicated
Mostly used now :-
- Less pain & bleeding
- Better pregn.
Protection
With copper
- Cu 7 , Cu T 380
A ,
Cu T 380 Ag (+silver)
- Nova T , Multiload Cu 250 , Multioad Cu 375
With progestins
* Progestasert
* Mirena , Levonova ( levonorgesterel )
5 – 10 years
1 yr
5 yrs
Mode of action
1- Aseptic endometritis histological & Histochemical changes in endometrium
2- Uterine & tubal irritability ( due to PG from endometrium )
3. Copper
- Inhibit sperm ( affects motility & capacitation )
- Inhibit endometrium metabolism
- Inhibit carbonic anhydrase enzyme necessary for removal of CO2
4. Progesterone
- Atrophic endometrium
- Thick , scanty , viscid cervical mucous ( prevents sperm ascent )
- Prevents sperm capacitation .
Advantages
• One decision method & cheap
• Left for long periods & reversible on removal .
• No Systemic effects & no interference with intercourse or lactation .
• Reliable ( failure 1 – 2 / HWY ) …. ( 0.2 in Levonava )
• Non-contraceptive benefits of hormone releasing IUCD :
- Treatment of dysfunctional uterine bleeding
- Protection from PID .
contraindications
( mainly local )
IUCD
* Distorted anatomy fibroids , CMF of uterus
* Bleeding severe anemia , bleeding tendency
Threads
* Pelvic infection ( PID ) or previous ectopic
* Immunosuperession , steroids , DM , RHD ( fear of IEC )
Cu ++
* Wilson disease
Undiagnosed
* Amenorrhea suspect pregnancy
* Bleeding suspect malignancy
4
Complications
1) Bleeding
* Post- insertion spotting reassure
* Menorrhagia ( IUCD menstrual flow by 25 – 50 % )
- Due to mechanical irritation of endometrium PG & fibrionolytics
- Treatment exclude pathology 1
st
anti-PG & anti-fibrinolytics .
2) Pain
* Post-insertion exclude perforation then ressure
* Dysmenorrhea spasmodic : accepted … otherwise exclude pathology
3) PJD
* Etiology septic technique during insertion ( threads acts pathology )
* Treatment remove IUD ( 1
st
step ) strong antibiotics ( acc. To C & S )
4) Expulsion
* 50% in 1
st
3 months ; esp during menses
* pdf
- If inserted immediately postpartum
- Too large / too small / Bad technique on insertion
- Local abnormality of uterus / cervix .
5) Perforation
* Pdf same as for expulsion
* At insertion ( 24 hrs ) or later on ( due to gradual perforation )
* Suspected in severe persistent pain & vaginal bleeding during insertion .
6) Pregnancy
* Intrauterine pregnancy i.e. failure ( 1 – 2 / HWY )
- Etiology misplacement , perforation , expulsion
- Presents as amenorrhea confirm by pregnancy test + U/S
- Management :
- If threads accessible remove 25 % risk abortion .
- If not accessible continue pregnancy 50% risk of abortion
* Extrauterine rare ( look ectopic for etiology )
7) Missed threads
* Etiology expulsion , Perforation , Pregnancy
* IUD localization .
- 1
st
step try to find threads it in place by speculum
- 2
nd
step exclude pregnancy ( U/S + pregnancy test )
- 3
rd
step try to find it else where by : X-ray + sound / Hysteroscopy
* Management
- If intrauterine hysteroscopic removal or D & C
- If extrauterine remove by Laparoscopy , laparotomy
5
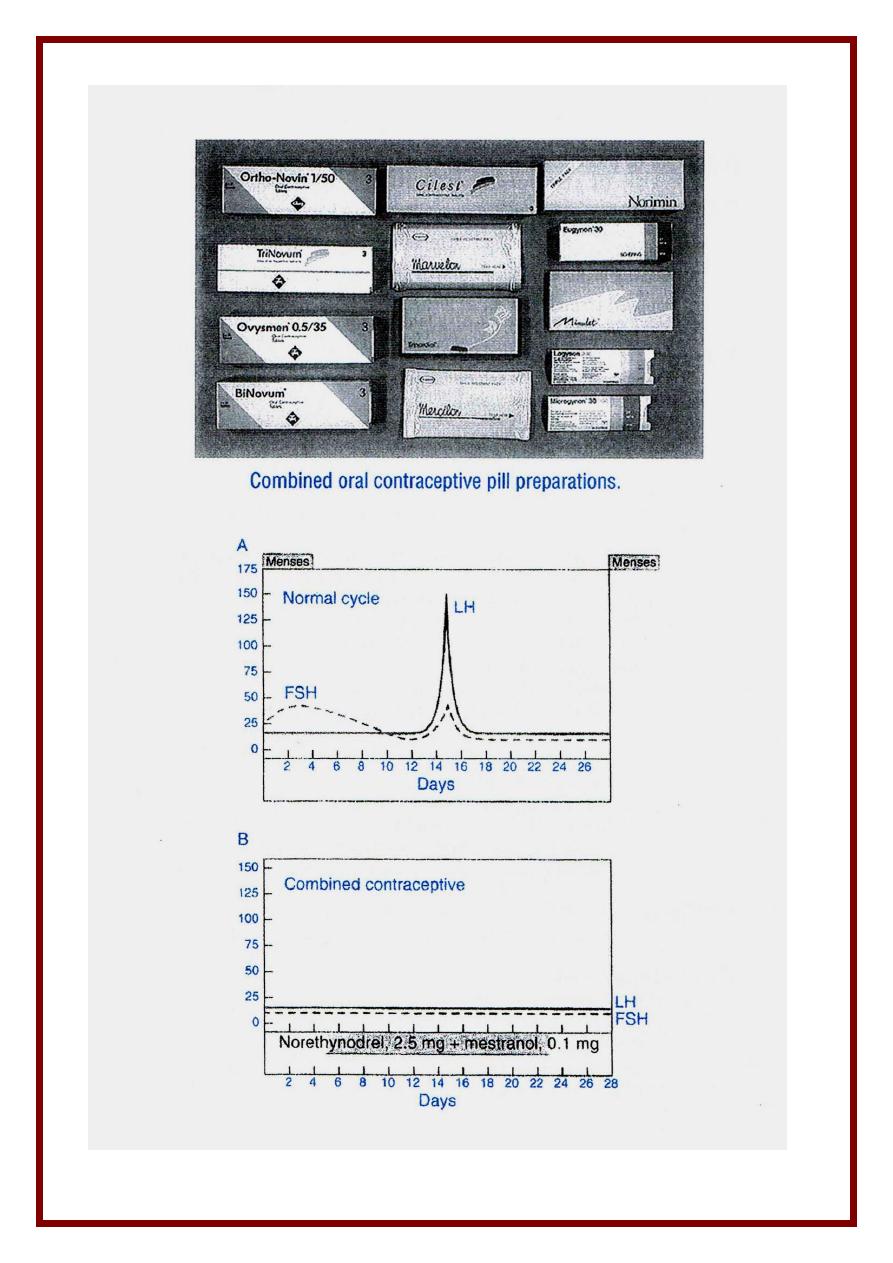
(5) Hormonal
1. COC pills
Here E + P are used throughout the cycle
E. used Ethinyl estradiol or
P. used
1
st
generation
* ESTRANE Norethindrone , Noresthisterone , Norgestrel
* PREGANE Medroxy progesterone acetate
2
nd
generation : Levonorgestrel
3
rd
generation : ( new progestins ) : potency + androgenic effects …
* DESOGESTREL ( Marvelon )
* GESTODENE ( Gynera )
* NORGESTIMATE ( Cilest )
* YASMINE ( DROSPIRENONE )
Types
1) Monophasic all pill contain same concentration of E + P
According to E content may be :
- High dose : 50 Mg EE e.g. ovral
- Low dose : 35/30/20 Mg EE ( less side effects ) e.g. microvlar , norminest …
2) Biphasic all pills taken last 14 days in the cycle have double P concentration
e.g. binovum
3) Triphasic 3 types of pills but all contain E + P in different concentration
trying to mimic nature to side effects e.g. trinovum ……
Made of action
1) Inhibition of ovulation
2) Unfavorable endometrium Pseudo-atrophic state ( P effect )
3) Thick scanty cervical mucous ( interfere with sperm ascent ) ( P effect )
4) Decrease tubal motility ( P effect )
5) Inhibition of sperm capacitation ( P effect )
Missing pills
- If one pill is forgotten take one as soon as possible then the next pill is
taken at usual time .
- If 2 pills are missed 2 pills are taken as soon as she remembers then take
2 pills at the usual time . Extraprecaution is taken for
the rest of the cycle as a backup e.g. condom .
6
Advantages
* Contraception : Failure rate = 0.1 / HYW ( most effective method )
Cheap , east to use , not related to intercourse
* Non contraceptive benefits
- control of dysfunctional uterine bleeding
- Dysmenorrhea & Premenstrual tension decreased
+ Endometriosis , fibroids , endometrial carcinoma
+ Functional ovarian cyst , ovarian carcinoma
- Decreased PID ( thick cervical mucus interfere with bacterial ascent )
side effects & Complications
1) CNS
( P effect )
* Headache & Migraine
* Mood changes depression & irritability
2) CVS
* E effect liability to thrombosis ( effect on clotting factors )
* P effect . Astherosclerosis ( effect on lipid profile )
. HTN ( salt & H
2
O retention & rennin , angiotensin )
3) Breast
* Breast engorgement & mastalgia
* Decreased milk production
* Cancer breast ( with prolonged use > 10 yrs ) but with very little risk
4) GIT
( E effect )
* Nausea & Vomiting esp on 1
st
few weeks
* Tendency to cholestasis , gall stones
* May affect liver enzymes
5) Metabolism
* CHO metabolism insulin antagonism ( E + P effect )
* Weight gain ( salt & water retention or anabolic effect of P )
6) Menstrual
* Amenorrhea
- Exclude pregnancy B-HCG + U/S start pill after 7 days
- If persistent for 2 – 3 months postpill amenorrhea
* Spotting
- If occasional reassure or use pill with more estrogen
- Also may take 2 pills for rest of the cycle
* Breakthrough bleeding
- Stop pills 5 days then restart ( + backup contraception for 2 wks )
- Or use pills with more estrogen
7
Contraindications
1) CNS
- Migraine ……… Epilepsy
- Optic neuritis & glaucoma
2) Cardiovascular
- Patients with history or tendency to thrombosis ….. absolute
- Hypertensive / Cardiac patients
- Smokers / Obese > 35 years
3) Lactation + Known / suspected breast cancer
….. absolute
4) Liver
. Markedly impaired liver function , history of cholestasis
during preg., adenoma …………………….. absolute
. Chronic liver disease , tumors .
5) Diabetes mellitus & thyrotoxicosis
6) Local conditions
* Undiagnosed amenorrhea ? Pregnancy no evidence of teratogenicity
* Bleeding of undiagnosed origin
* Malignant disease of the breast .
POP ( Minipills )
* Noresthisterone Micronor ( 350 Mg )
* Levonorgestrel Microlut ( 30MG )
* Lynestrenol Exluton
Use
: one tablet is taken daily from the 1
st
day of the cycle continuously at the
same time . If forgotten or DELAYEd continue backup 14 days .
Cerazette
Could be delayed yp to 10 – 12 hrs .
Mode of action
* Cx mucous ( thick ) …. Endometrium ( atrophy ) … sperms ( inhibition )
* To less extent alter tubal motility & suppression of ovulation ( 50 % )
Indications :
1. Lactating
2. As there is no estrogen side effects : - CVS ….. Liver
- Old ….. smoker
3. As there is min . Prog. Effect - Diabetics E hypertensive
- Obese
Disadvantages & side effects
* Higher failure rate than combined pills = 1 – 2 / HWY
* Liability to ectopic pregnancy ( due to effect on tubes )
* Menstrual side effects e.g. spotting or irregular cycles
use another type with more progestin but don't use estrogen

8
3. Injectables
Types
* Depot Medroxy-progesterone acetate Depo-Provera 150 mg IM/ 3m
* Noresthisterone oenanthate Noristerat or Norigest 200 mg IM/ 2 m
* Recently . Cyclofem ( DMA 25 mg + estradiol cypionate 5 Mg ) } monthly
. Mesygyna ( DMPA 50 mg + estradiol valerate 5 mh ) } injection
Mode of action
……. The same as COC ( > 99% efficacy )
Advantages
- Lactating
- As there is no estrog ( CDS / liver …. Old / smoker )
- Non-contraceptive benefits : ………. The same as COC
Disadvantage & side effects
* Can't reverse contraception once injection started ( may take up to 9 m )
* Risk of osteporosis if used in younger age ( reversible )
* As there is Prog. effect
- Weight gain in some patients
- Few metabolic effects mild anti-insulin action , Decreased HDL-C
* Menstrual irregularities ( common ) amen , oligomen , irregular bleeding
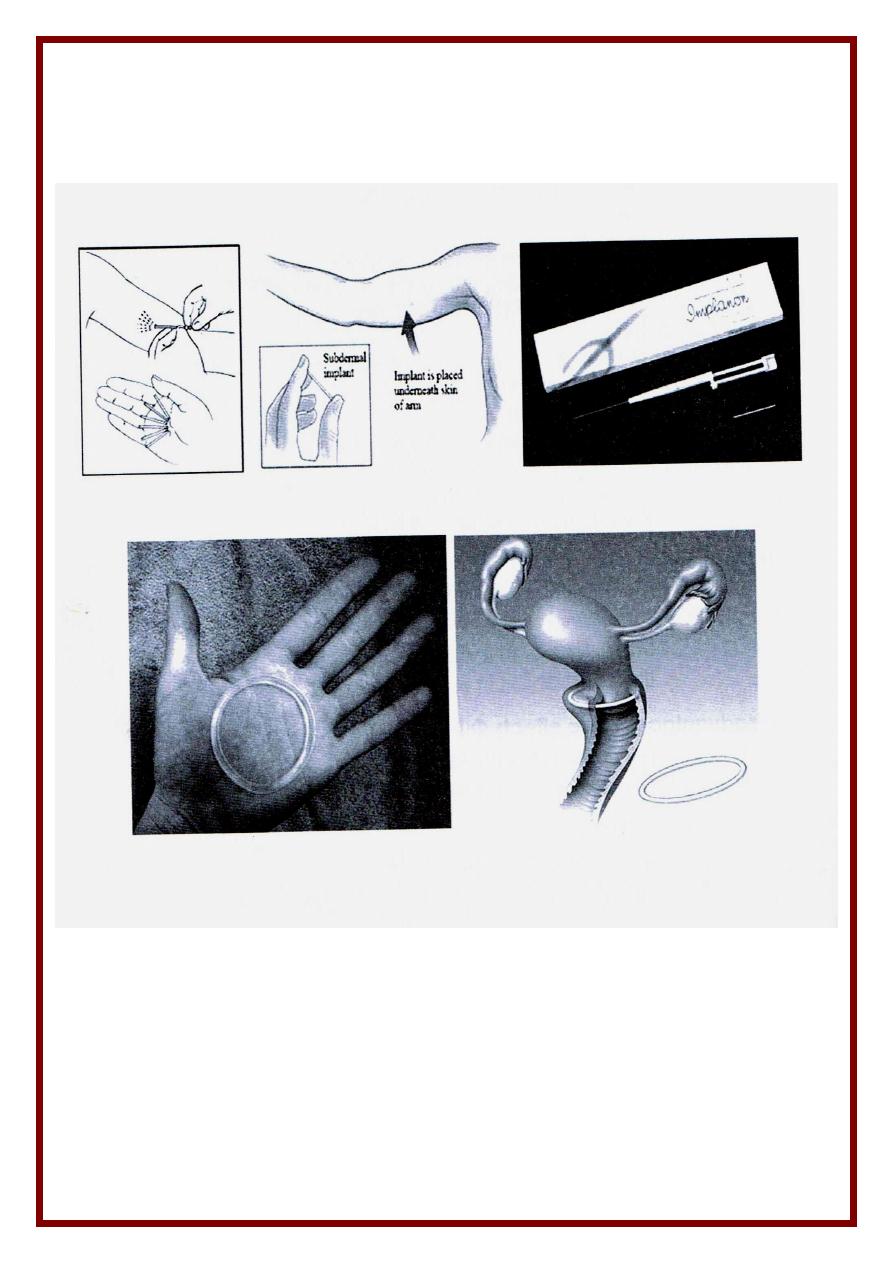
4. Subdermal Implants
Method ( Norplant )
- Six cylinders containing Levonorgestrel ( 36 mg / cylinder )
- Inserted SC on inner aspect of medial side of arm in a fan shaped manner
- Slow release of progestin lasts for 5 years .
Implanon is a single cylinder ( 3 years )
Adv
as injectables but Action is rapidly reversible after removal
Disadv
. . Menstrual irregularities or amenorrhea ( the cause of removal )
. Difficult insertion & removal .
5. Vaginal rings
* Combined vaginal ring
( EE + Levonorgestrel ) inserted 3 wks removed 1 wk
* Progesterone-only vaginal ring
(Levonorgestrel) used monthly or every 3 month
6. Skin patches : Evra
7. P. releasing IUCD
9
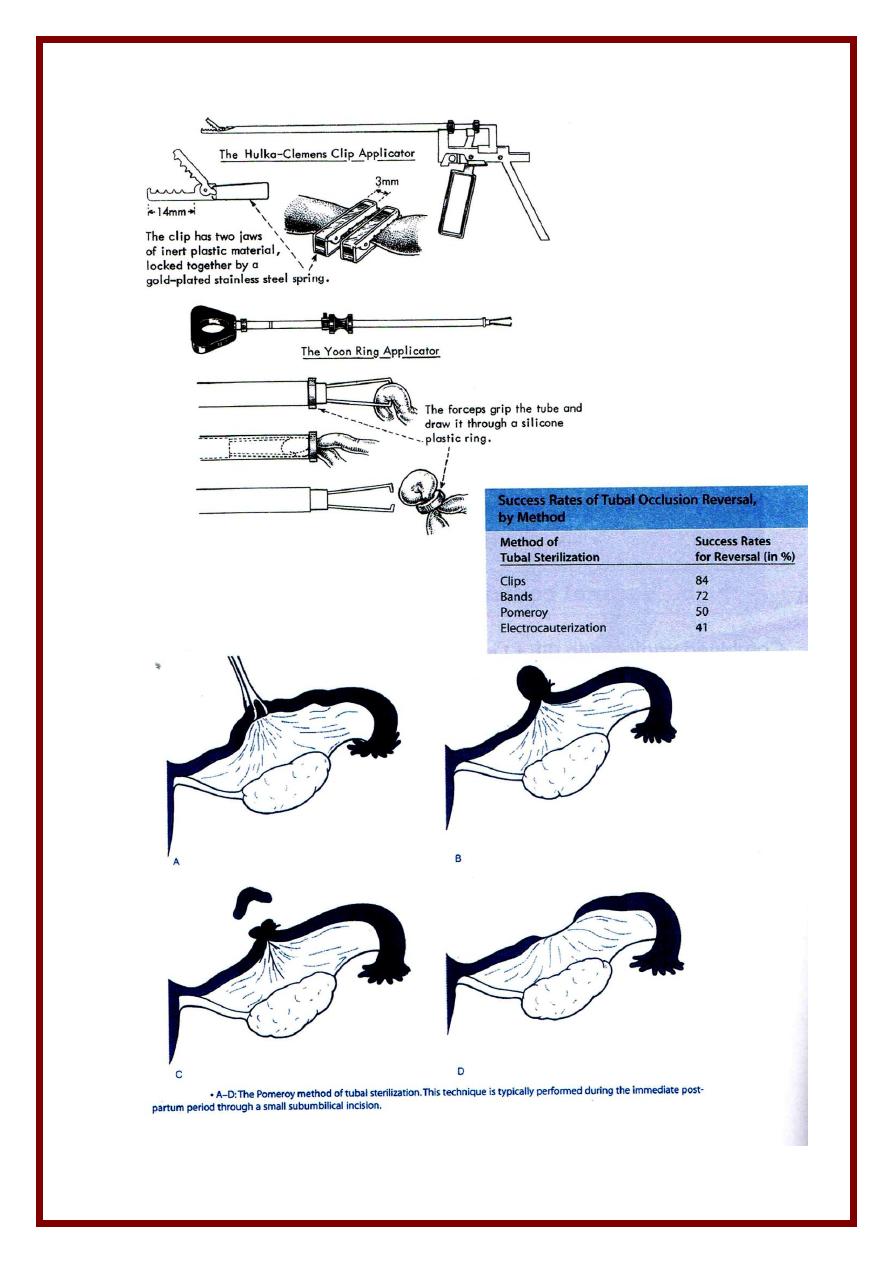
(7) Surgical ( Sterilization )
1) Male
* Bilateral vasectomy ( done under local anesthesia )
* Efficiency confimed by 2 –ve semen analysis after 70 days
2) Female
* Laparoscopy electrocogulation of tube or application of a Falope ring or clip
* Minilapratomy recestion ligation of a part of the tube ( Pomeroy method )
* Postpartum
- At C. section ( common )
- After VD ( 2 – 3 days later via a small sub-umbilical incision )
Indications
permanent contraception in
- Old couple completed their family
- Patients with contraindication for pregnancy .
- Patient completed her family with failed all other methods
Complications
* Pregnancy ( Failure ) 0.1 – 0.4 HWY
* Post-ligation syndrome menorrhagia & congestive dymenorrhea d.t.
interference with venous return hysterectomy
Postpartum contraception
* Breast-feeding
* Barrier method
* IUCD immediate ( high expulsion rate or after 6 wks )
* Progestogen-only contraceptive methods
* Postpartum sterilization with CS or later on ( laparoscopic )
Postcoital ( emergency ) contraction
Hormones
Given immediately or within 72 hours ( the morning after-pill )
Large doses N & V antiemetic must be added
* Estrogen e.g. EE 2mg or Premarin 20 mg daily ……….. for 5 days
* POP e.g. Postinor ( 750 ) Mg levonorgestrel ) : 1 tab …….. repear after 12 hrs
* High dose COC e.g. Ovral : 2 tables ……… repeat after 12 hrs
* Ani-gonadotrophin e.g. Danazol 600 mg ………. Repeat after 12 hrs
* Anti-progesterone e.g. Mifepristone ( Ru-486 ) mg …….. 12 tap once
Mechanical
* IUCD is inserted immediately even up to one week . FR = 1 %
* Menstrual aspiration suction of the uterine contents by Karman cannula
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
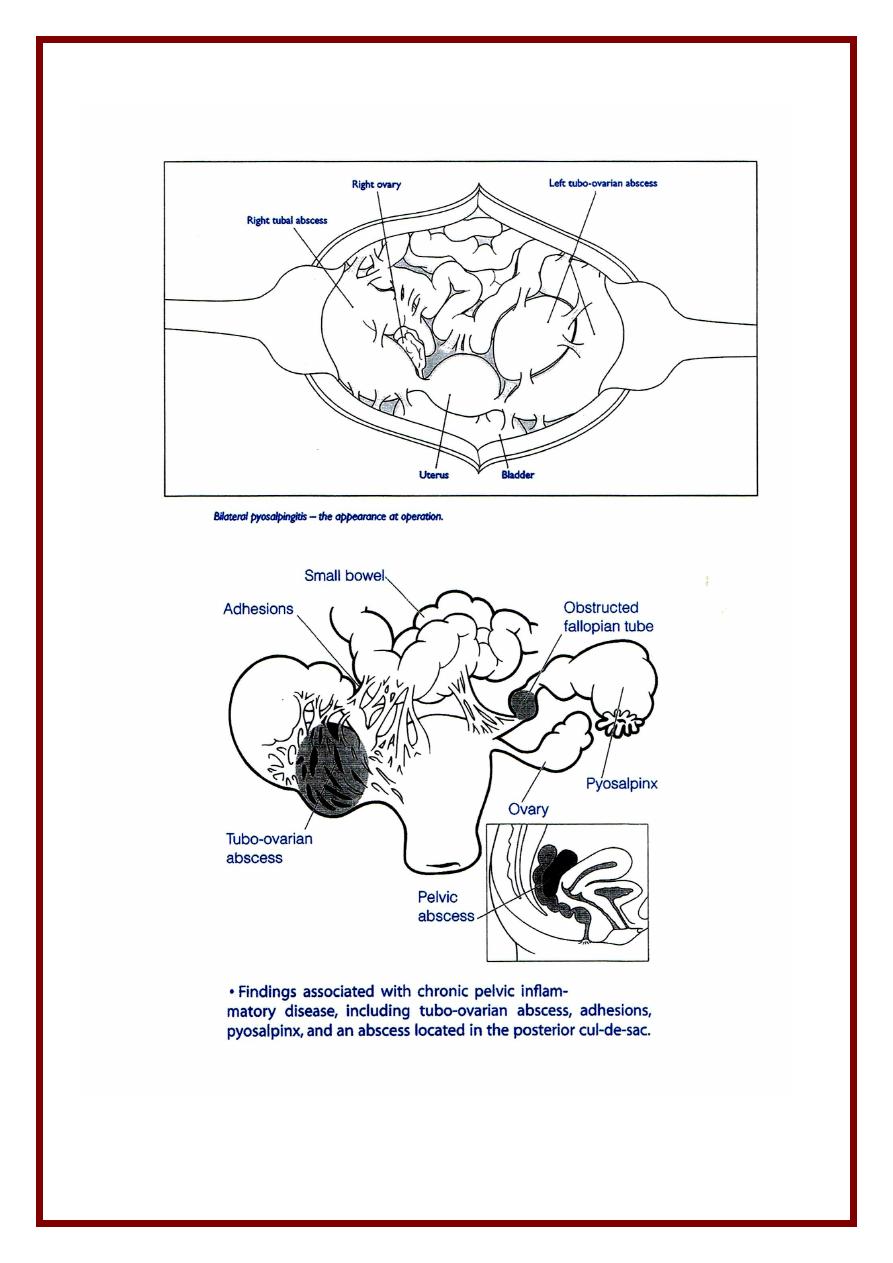
23
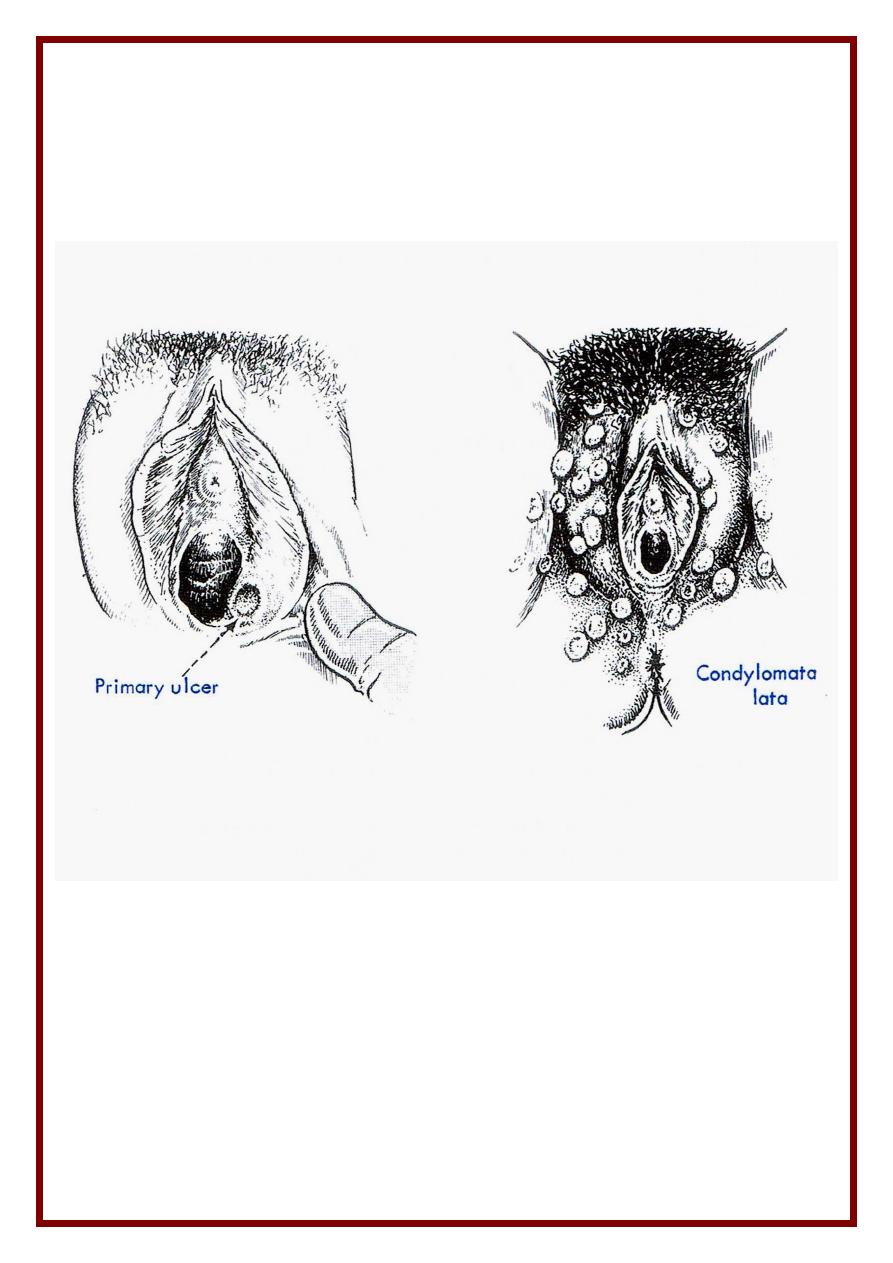
24
