Cardiovascular diseases
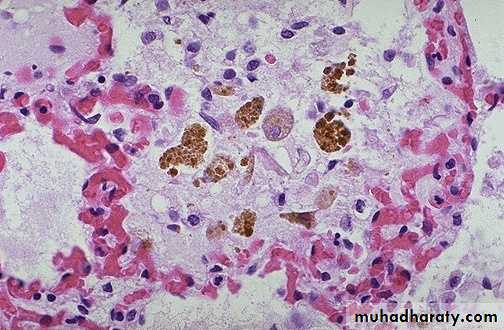
طب الاسنانLeft sided heart failure, Pulmonary congestion with dilated capillaries and leakage of blood into alveolar spaces leads to an increase in hemosiderin-laden macrophages ( heart failure cells)
heart failure cell
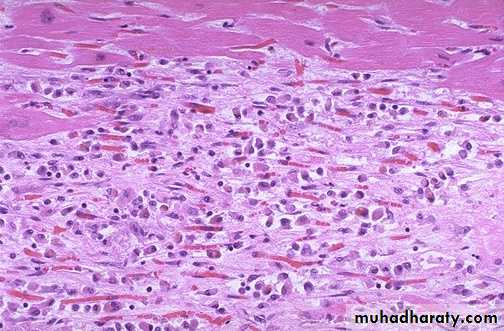
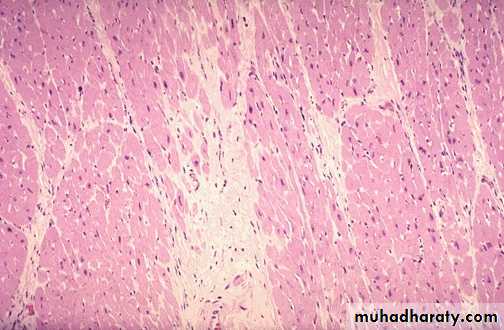
Acute M.I (1-2) days: necrosis of myocardial cells with a dark red contraction band necrosis extending along it, in addition to neutrophils infiltrationIntermediate M.I with 1-2 weeks age: there are remaining normal myocardial fibers at the top. Below these fibers are many macrophages along with numerous capillaries and little collagenization (granulation tissue)
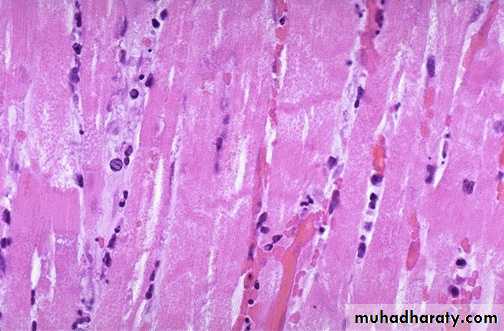
There is pale white collagen within the interstitium between myocardial fibers. This represents an area of remote (old) infarction
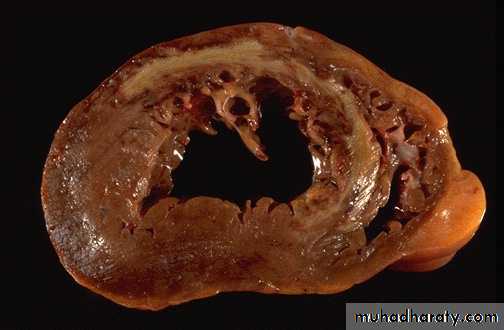
A cross section through the heart demonstrates the left ventricle on the left with a large myocardial infarction. The center is tan with surrounding hyperemia. The infarction is "transmural" in that it extends through the full thickness of the wall.
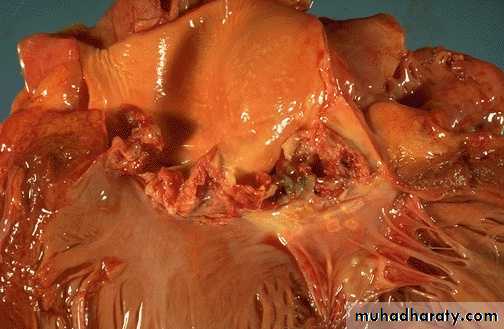
Acute infective endocarditis: Irregular reddish tan destructive vegetations overlie valve cusps that are being destroyed. Portions of the vegetation can break off and become septic emboli.
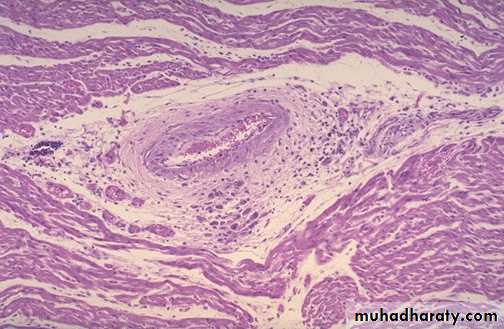
Aschoff nodules of acute rheumatic carditis: acute rheumatic carditis is marked by a granulomatous inflammation "Aschoff nodules" seen in myocardium around vessel.
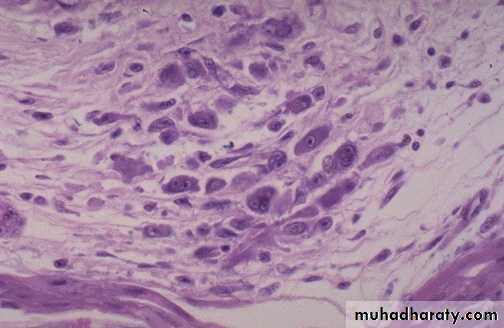
Aschoff nodules at high magnification : The most characteristic component is the antiskow’s cell & Aschoff giant cell. They are large cells with two or more nuclei that have prominent nucleoli, with scattered inflammatory cells
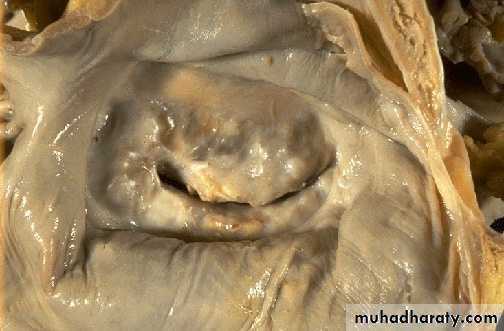
Chronic rheumatic mitral stenosis (fish-mouth shape) due to fibrosis & scarring.Diagnosis: remote complication of rheumatic heart disease
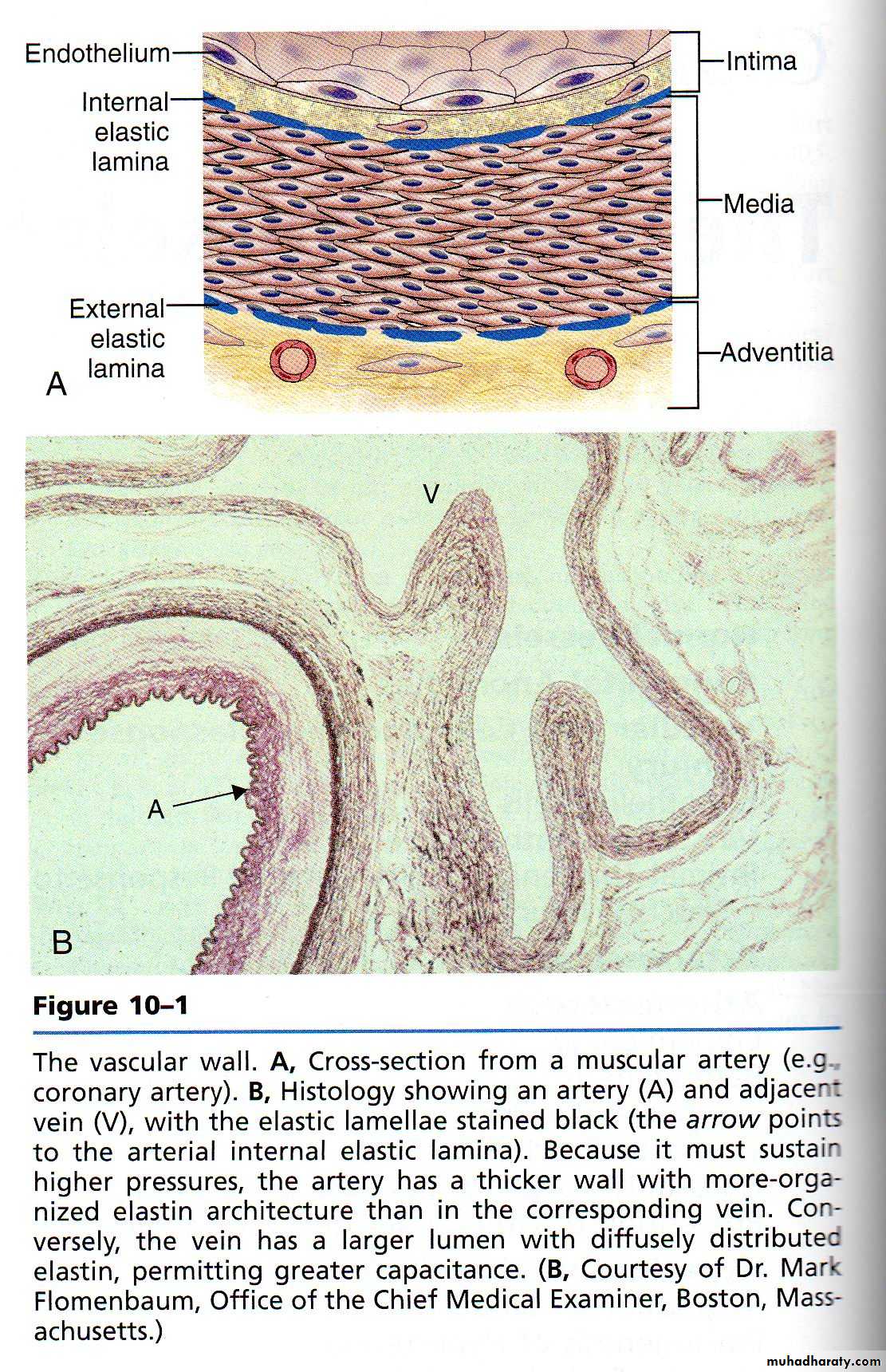
A wall of normal blood vessel
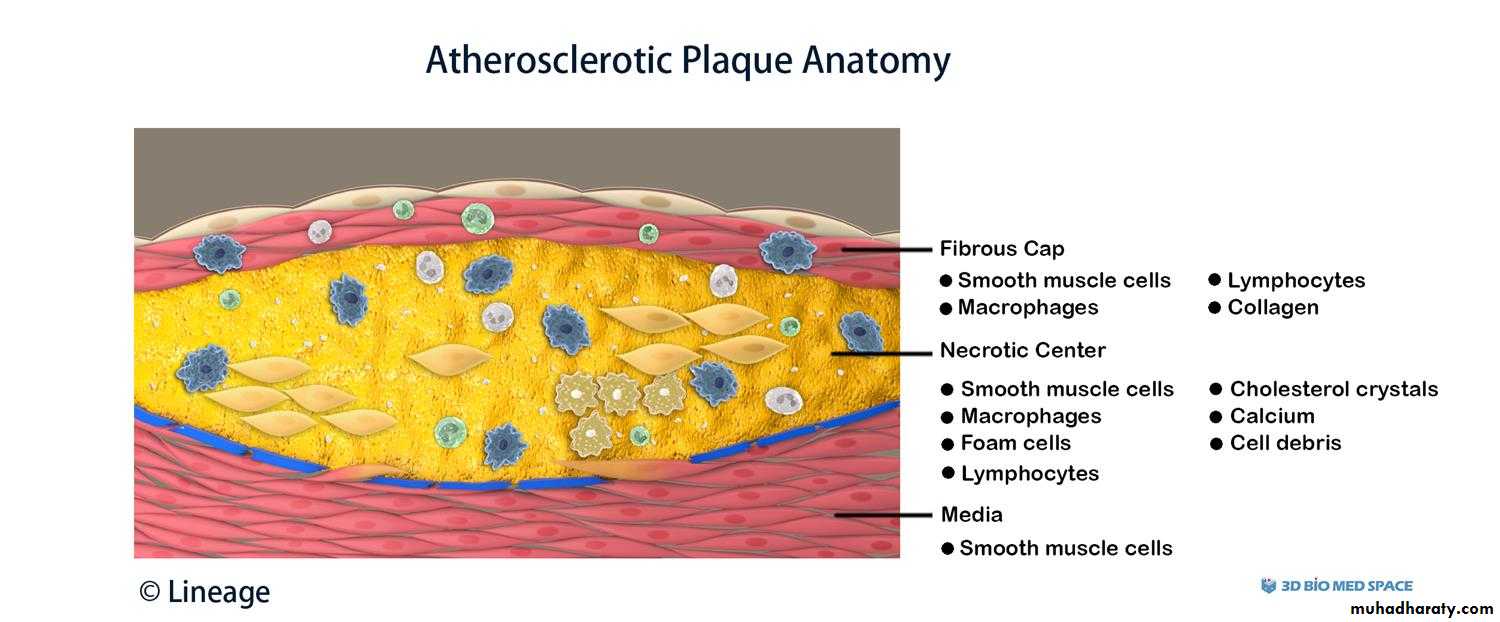
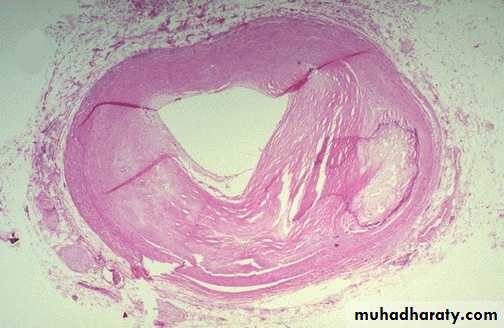
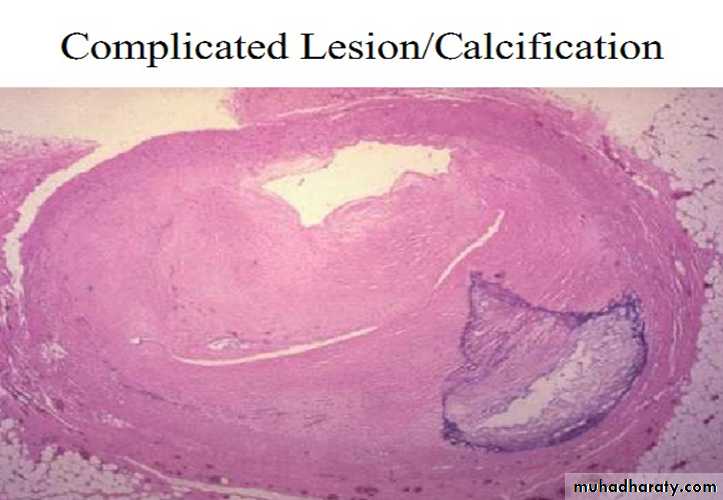
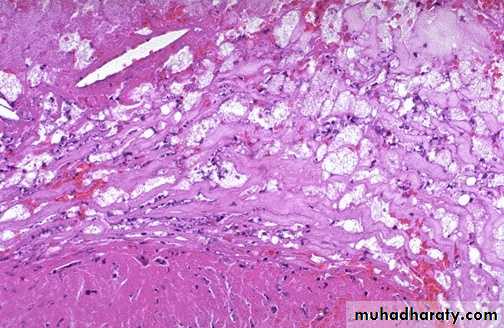
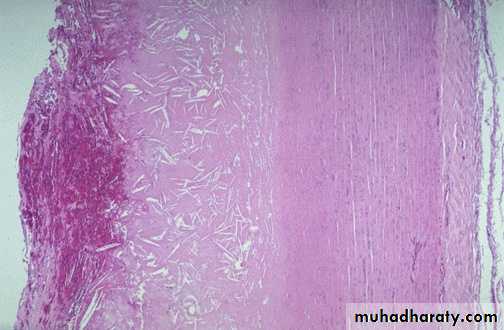
The coronary artery shown here has narrowing of the lumen due to build up of atherosclerotic plaque. Severe narrowing can lead to angina, ischemia, and infarction. At the right : Atheroma is complicated by calcification (arrow)
Atheroma at high magnification : numerous foam cells & cholesterol clefts extracellular lipid material with few inflammatory cells.
Atheroma with numerous cholesterol clefts. Note the ulceration & hemorrhage at the surfaceDiagnosis: complicated atheroma
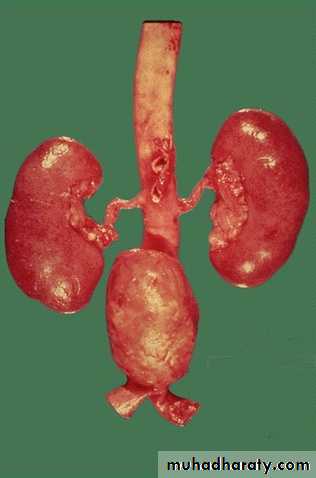
Atherosclerotic aneurysm
large fusiform"bulge" appears just above the aortic bifurcation of the common iliac arteries.Such aneurysms are prone to rupture when they reach about 6 to 7 cm in size.
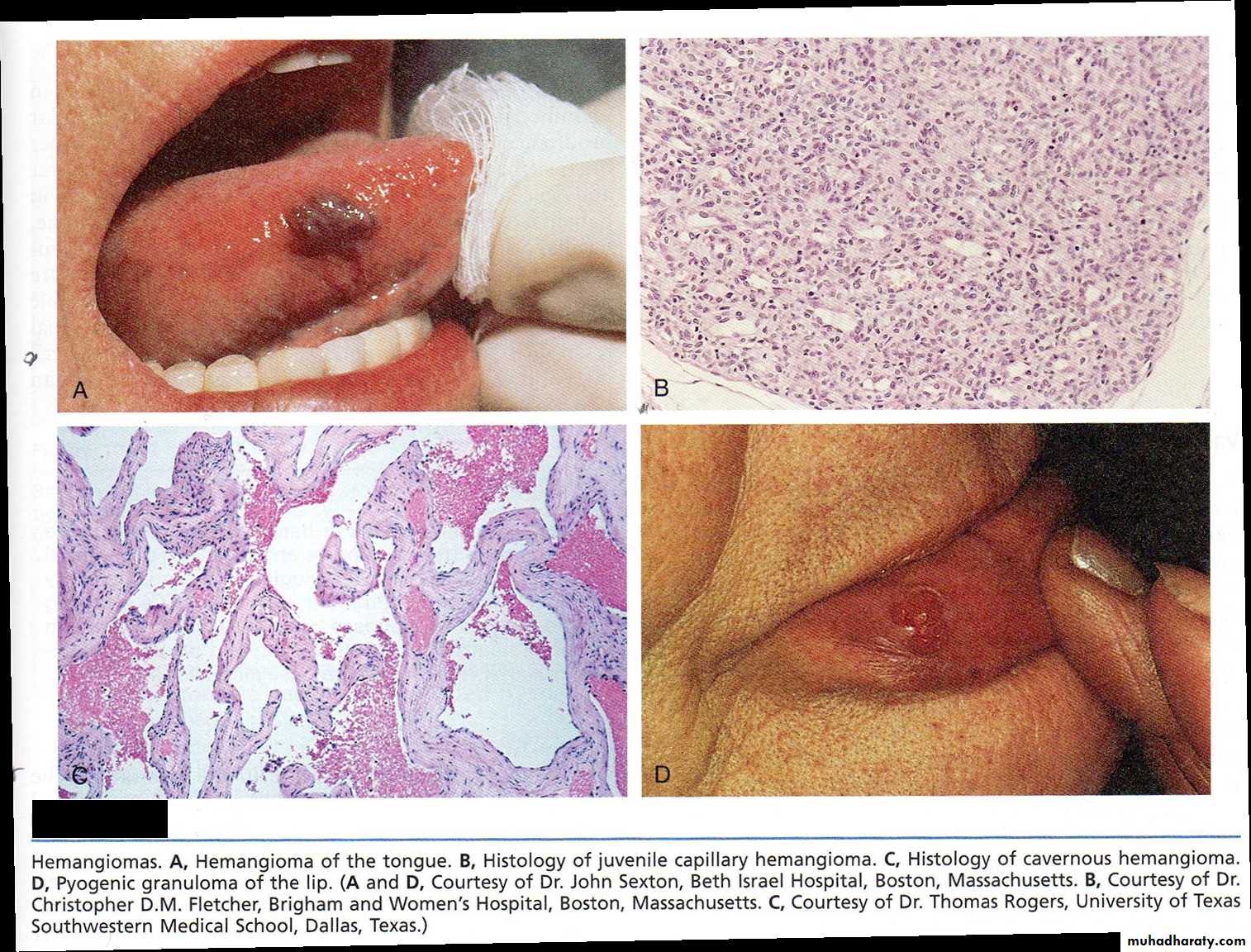
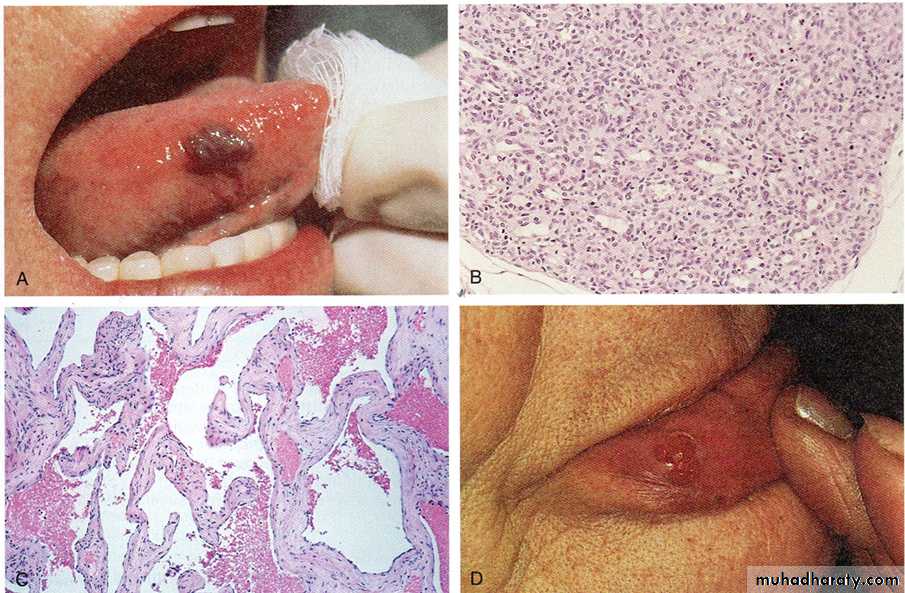
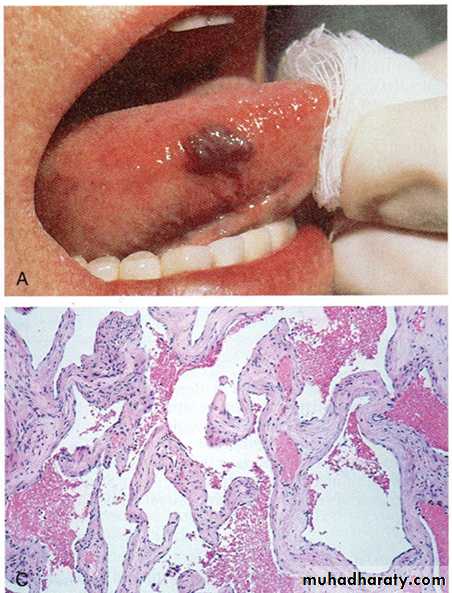
B- histology of capillary hemangioma
A- a mass well circumscribe, dark red in color on the right side of the tongue
Diagnosis: Hemangioma of the tongueC-histology of cavernous
hemangioma.
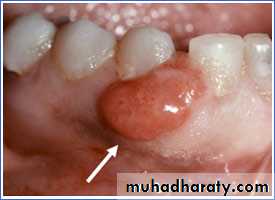
Pyogenic granuloma is a small bright red, glistening bump that typically appears on the face, arms, or hands. It typically has a thin, white border. They may bleed profusely, ulcerate or become crusty, but most are shiny, red, bead-like bump