Lecture Three
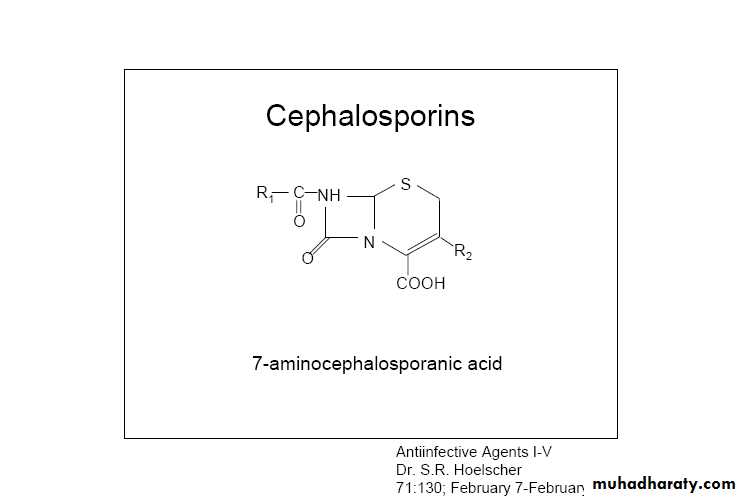
Cephalosporin
• Chemical structure.• Mechanism of action .
• Toxicity.
They are more stable than penicillin to many bacterial β- Lactamase, so they have broader spectrum of activity.
β
Cephalosporin
Mechanism of action:Inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
Bactericidal
types of Cephalosporin
Classified according to bacterial susceptibility and resistance to β- Lactamase into :
Cephalosporins
First generation
cephalexin (Keflex)
Cefadroxil
cefazolin
Second generation
cefaclor (Ceclor)cefoxitin (Mefoxin)
cefotetan
cefuroxime
Third generation
-cefdinir
cefixime (Suprax)
ceftriaxone (Rocephin)
cefotaxime(claforan)
Fourth generation
cefepime (Maxipime)First generation
BactericidalGood activity against gm+ve bacteria
Modest activity against gm-ve bacteria
Most mouth anaerobes are sensetive
cephalexin (Keflex)
Cefadroxil
cephalothin
Cefazolin( IV)
First generation
.Cephalexin(oral)500mg every 6hoursCefadroxil(oral) 500mg-1gm twise dialy.
, Cefazolin(parentral)0.5-2gm every 8 hoursused as a single prophylaxis dose prior to surgery because of its 1.8-hour.
additional intraoperative cefazolin doses may be required if the surgical procedures, including orthopedic surgery because of its ability to penetrate bone..
USES OF first generation
TonsillitisPhyringitis
Urinary tract infection
skin infection (Cellulites).
soft tissue abscess
Cephalosporins
Second generation
-e.g cefaclor(oral),cefuroxime and cefoxitin(im.iv)
-have grater activity against gm-ve microorganism : H.Influenza,meningococci
Bactericidal (gram(+) & and more active against gram (-) with some anaerobic.
Uses in Sinusitis, otitis, Lower Respiratory Tract Infection, mixed anaerobic infections such as peritonitis
Cephalosporins
Third generationCefixime
Cefdinir
Ceftriaxone
Cefotaxime
Ceftazidime
Cefoperazone
Increase activity against gram (-)
more activity against beta-lactamase-producing microbial strains and some inhibit psedumonas.
Third generation
Cefixime 400 mg(orally once daily)or 200mg twise dialy(suprax)Cefdinir 300 mg cap twice daily
Ceftriaxone ,1gm once daily(IM,IV)longer t1/2(8hour)
Cefotaxime 1gm once dialy(IM,IV)
Ceftazidim(pseu.aer) injection every 8-12 hours
Cefoperazone(pseu.aeru+S.typhi and B.fragilis)
Third genaration
Third genaration used in serious infections including
Pneumonia
Immunocompramised patient for sepsis
UTI infection
ENTand skin infection
Third generation
Respiratory tract infection(chronic bronchitis)septicaemias.
Gonorrhoea
Typhoid
ceftriaxone or cefotaxime are effective in the treatment of neonatal and childhood meningitis caused by H. influenzae(high CSF level).
Cephalosporin
Fourth generationCefepime useful for treatment of serious infection in hospitalized infection.
have extended activity
Administered parentally .
Affected against streptococci , staphylococci,
gram (-)E.Coli, p.aeruginsa.
Cross CSF
Pharmacokinetics
Administration: Many of the cephalosporins must be administered IV or IM of their poor oral.
.
Ceftriaxone and Cefoperazone is excreted through the bile into the feces and, therefore, is frequently employed in patients with renal insufficiency.
Therapeutic uses of cephalosporin
1- Tonsillitis , Phyrngitis, Urinary tract infection , skin infection (Cellulites).2- soft tissue abscess.
3- Endocarditis prophylaxis.
4-Surgical prophylaxis (Cefazolin)
5 - in dentistry : Good activity against many orofacial pathogens
Adverse effects
• 1. Hypersensitivity reactions- most common• Anaphylaxis, bronchspasm, urticaria
• Maculopapular rash- more common
• 2. Nephrotoxicity ; esp. cephradine
• 3. Thrombophlebitis ( i.v admin. )
• 4. Superinfections
• 5. Diarrhea- oral cephalosporins, cefoperazone, ceftriaxone .
• 6. cefamandole, & cefoperazone may cause:
• a) bleeding disorders
• b) Flushing, tachycardia, vomiting with alcohol intake (Disulfiram)
Other β-lactam Antibiotics
1. Carbapenems eg (imipenem) meropenem,:
Broad spectrum, it is effect against Penicillinase producing
gram-positive and gram-negative, anaerobes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, (Bactericidal )
it administer I.V, penetration of CSF therefore used to treat Meningitis when inflamed .
UTI Lower respiratory tract infection
Abdominal and gynecological infection.
Skin, soft tissue, bone, joints infections
Other β-lactam Antibiotics
MonobactamAztreonam (Azactam)
Mechanism of action
Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis
Bactericidal : against Enterobacteria and also against gram –ve rods but lack activity against gram +ve and anaerobic MO .
it administer I.V or IM, it may cause skin rash , some time abnormal liver function test ,
, it use as alternative to P and C in patient allergic to them .
Hypersensitivity testing
Other β-lactam Antibiotics
1. Carbapenems eg (imipenem) meropenem,:Broad spectrum, it is effect against Penicillinase producing
gram-positive and gram-negative, anaerobes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, (Bactericidal )
it administer I.V, penetration of CSF therefore used to treat Meningitis when inflamed .
UTI Lower respiratory tract infection
Abdominal and gynecological infection.
Skin, soft tissue, bone, joints infections
Other β-lactam Antibiotics
MonobactamAztreonam (Azactam)
Mechanism of action
Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis
Bactericidal : against Enterobacteria and also against gram –ve rods but lack activity against gram +ve and anaerobic MO .
it administer I.V or IM, it may cause skin rash , some time abnormal liver function test ,
, it use as alternative to P and C in patient allergic to them .