1
L5 Orthopedic D. Wahby Ghalib
Bone Tumors
Classification
Benign
Malignant : primary
secondary
Benign bone tumors
Bone : osteoid osteoma & osteoblastoma
Cartilage : enchondroma, chondroblastoma &
osteochondroma
Blood vessels : haemangioma
Others : giant cell tumour
Benign tumor - like lesions
Bone cysts : simple & aneurysmal
Fibrous cortical defect
Primary malignant bone tumors
Bone : osteosarcoma
Cartilage : chondrosarcoma
Bone marrow : Ewing sarcoma & myeloma
Connective tissue : fibrosarcoma
Others : chordoma & adamantinoma
Secondary malignant bone tumors
Prostate
Breast
Lung
Colon
Kidney
Thyroid
Staging of malignant tumors (Enneking)
I : low grade
II : high grade
III : sarcoma with metastasis
A : intra- compartmental
B : extra-copartmental
2
Surgery for malignant tumors
Wide excision : safe margins
This includes : amputation
limb – salvage surgery
Chemotherapy
Preoperative : (neoadjuvant) 8-12 w
After tumour resection : check tumour necrosis
Postoperative : 6-12 m
Radiotherapy
Residual tumor
Inaccessible tumor
Painful metastasis
Benign bone tumors
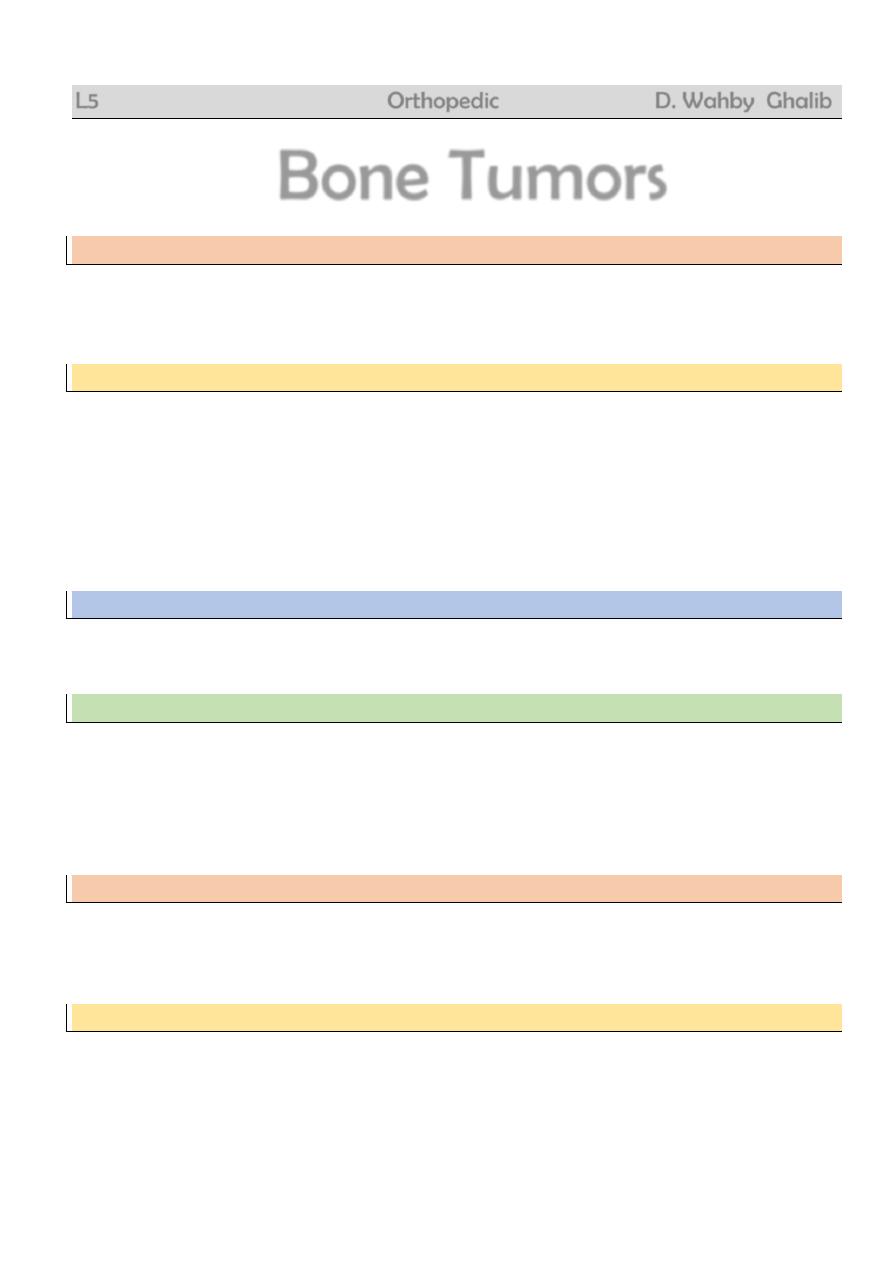
Fibrous cortical defect
= non-ossifying fibroma
Very common
Child
Accidentally on XR
Pain or pathologic fracture
No malignant potential
Rx : curettage + bone graft
3
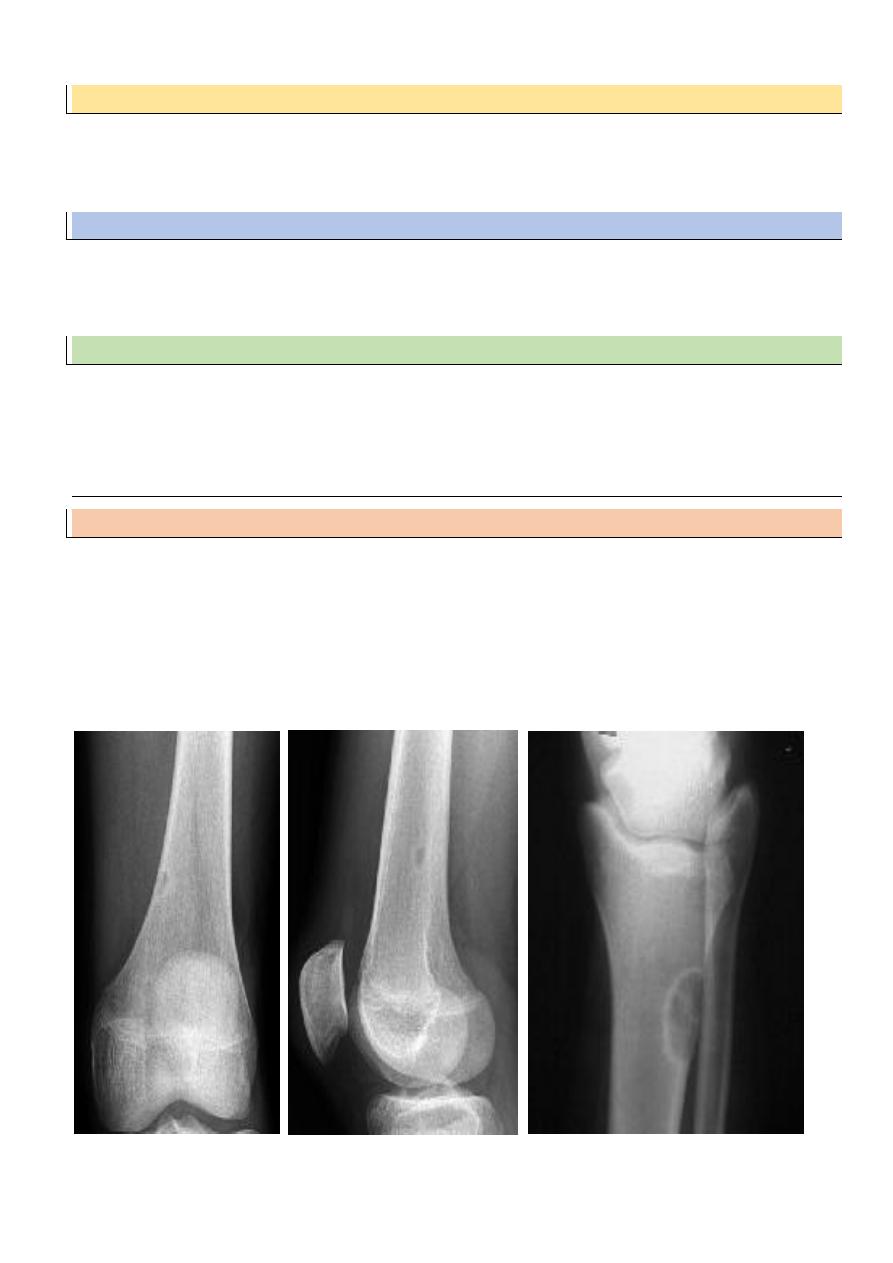
Osteoid osteoma
Patient < 30 yr
Pain > at night relieved by aspirin
In spine
painful scoliosis
No malignant potential
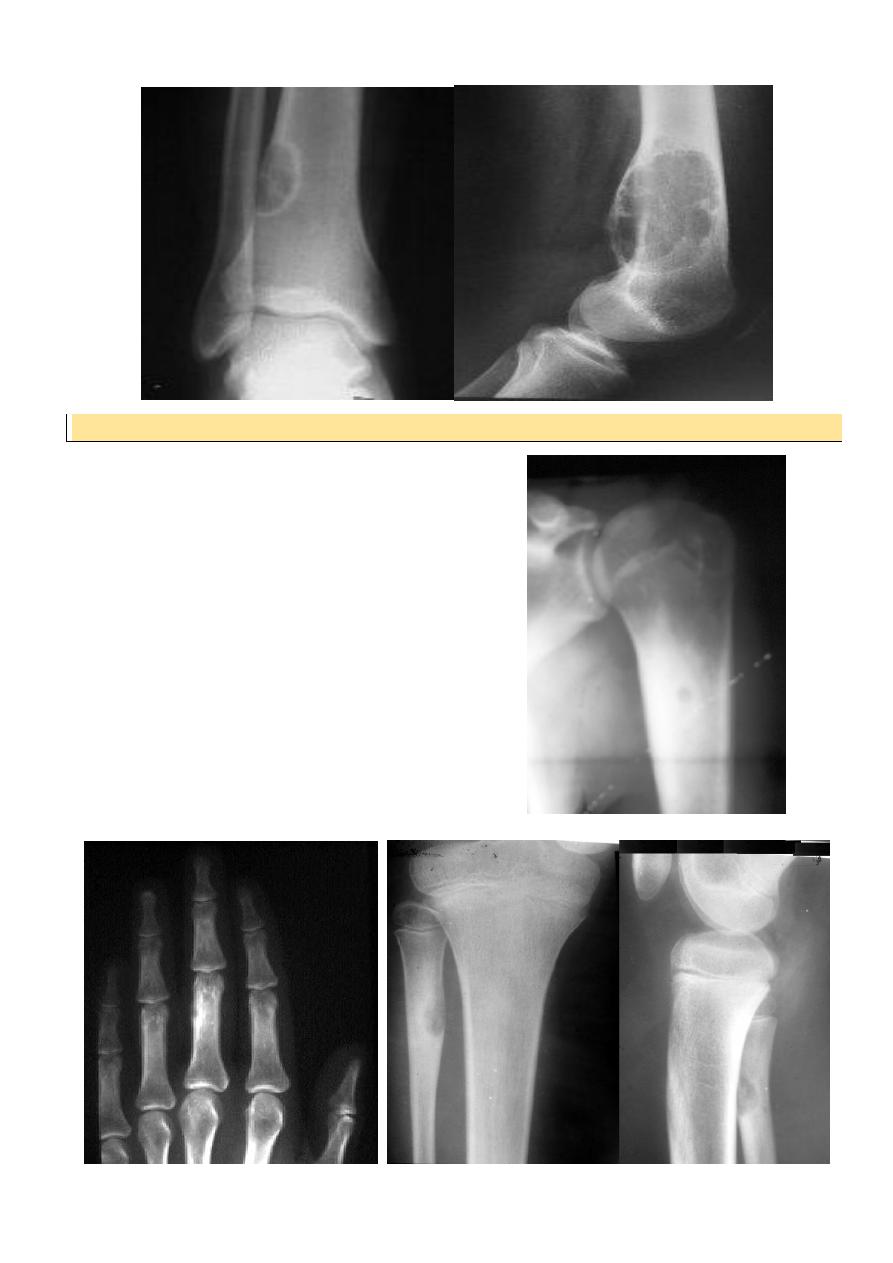
XR : radioluscent nidus surrounded by
o sclerosis
Any bone except the skull
Rx : removal of nidus
4
Osteoblastoma
= O.O. but nidus > 1.5 cm
Compact (ivory) osteoma
Rare
Young adult
Painless lump on outer or inner table of skull
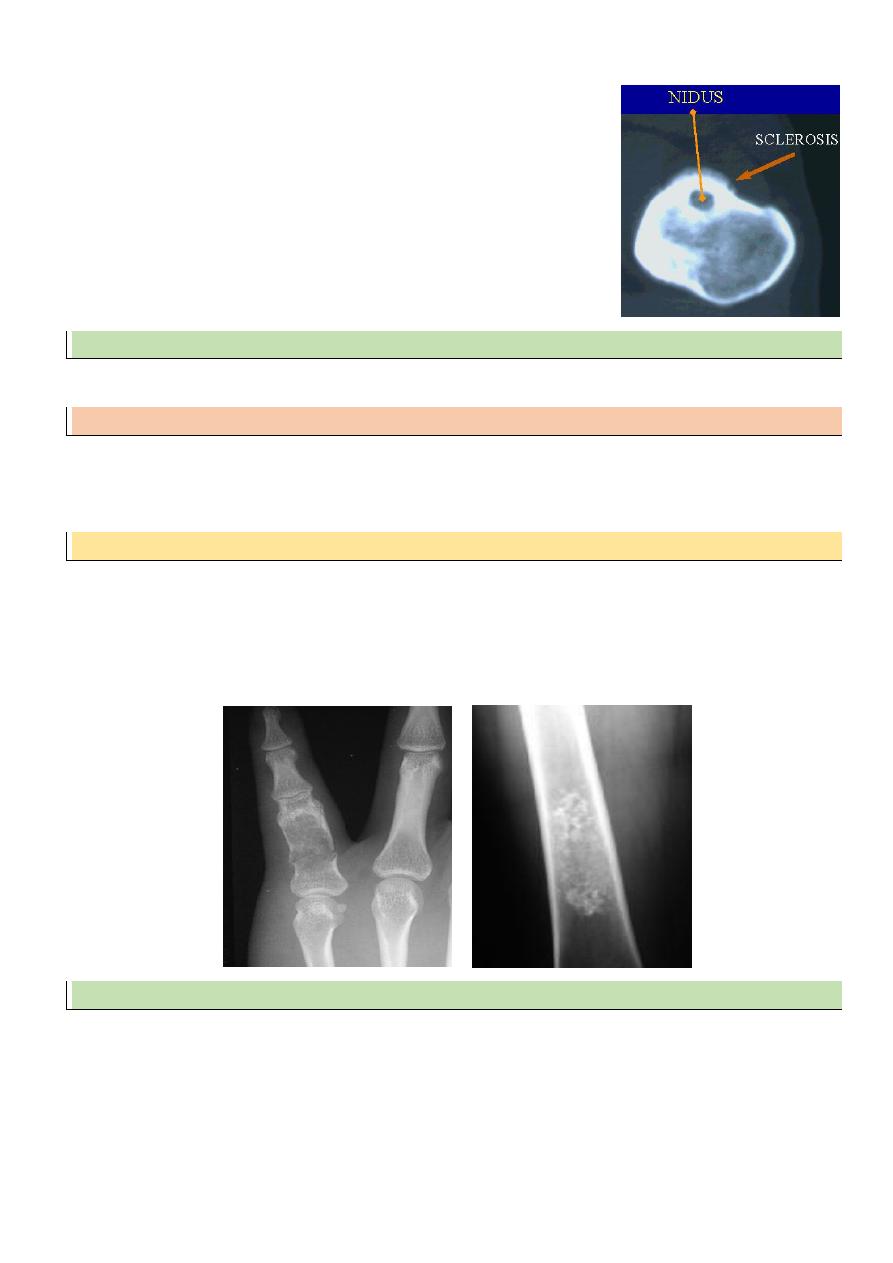
Enchondroma
More in tubular bones of hand
Accidentally or pain / pathologic #
XR : lytic lesion + flecks of calcification
Malignant risk : 2%
Rx : curettage + bone graft
Osteochondroma
= exostosis
Commonest benign bone tumour
It is bone outgrowth covered by cartilage
Hereditary multiple exostosis : AD
Malignant risk : 1% solitary
6% multiple
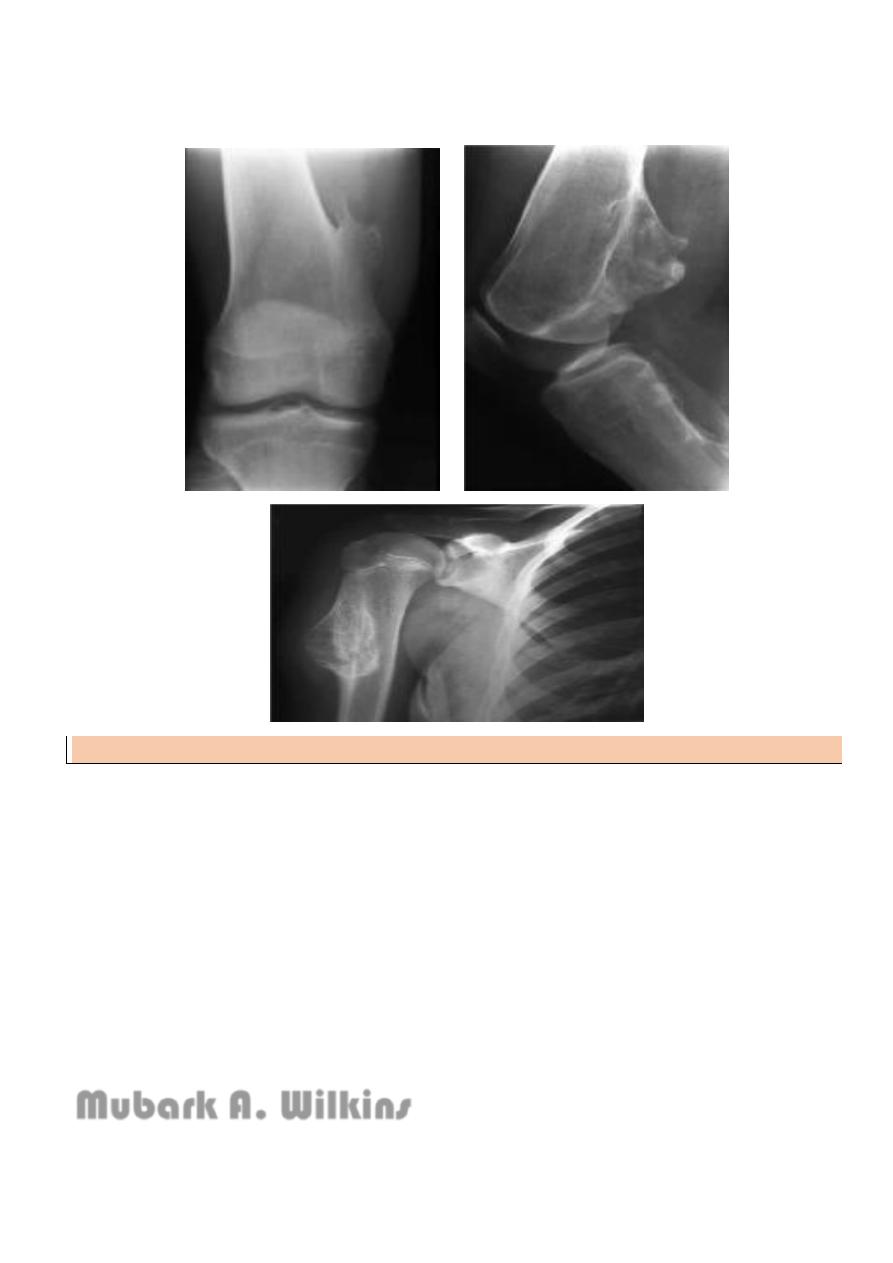
5
If continues to grow > 18 yr suspect malignancy
Rx : excision
Objectives:
Stressing the importance of the bone tumors as being a significant source of mortality
and morbidity.
Training the students to acquire the basic skills of XR interpretation in case of bone
tumors.
Emphasizing the general outlines of treatment including the medical and surgical lines.
Emphasizing the significance of classifying the bone tumors and the tumor-like
conditions.
Stressing the importance of the tumor-like conditions and the sequellae of misdiagnosis.
Mubark A. Wilkins
