• Lect. 4Dr.jawnaa
Other agents effect on cell wall glycopeptide
1- Vancomycin:Mechanism: inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall phospholipids as well as peptidoglycan thus weakening the cell wall and damaging the underlying cell membrane.
It effective primarily against gram-positive organisms It has been lifesaving in the treatment of MRSA and MRSE as well as Enterococcal infections.
uses
• severe infections with resistant gram + organisms• Vancomycin + Gentamycin shows synergy against mixed infections
• Used 1.V in individual with prosthetic heart valve
• Inflammation allowed penetration into meanings
• Patient who have allergy to the B.lactam.in enterococcal endocarditis.
• so the use of the oral formulation is limited to the treatment of severe antibiotic associated C. difficile colitis.
Adverse effect
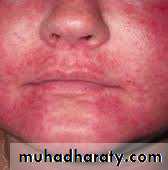
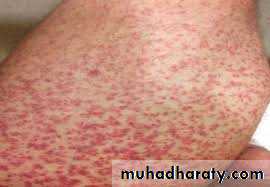
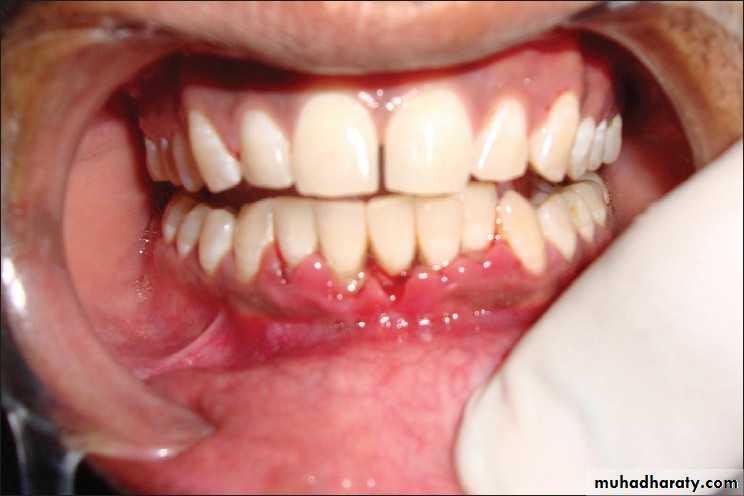
1- fever , chills, phlebitis at infusion site , flushing (red man
syndrome ) and shock due to histamine release
2- Ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity are common when vancomycin
and aminoglycoside administer together .
Red man syndrome
Protein synthesis inhibitor
(Doxycycline and Minocycline)
Tetracyclines
Mechanism of Action
Tetracyclines are broad-spectrumbacteriostatic antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis.
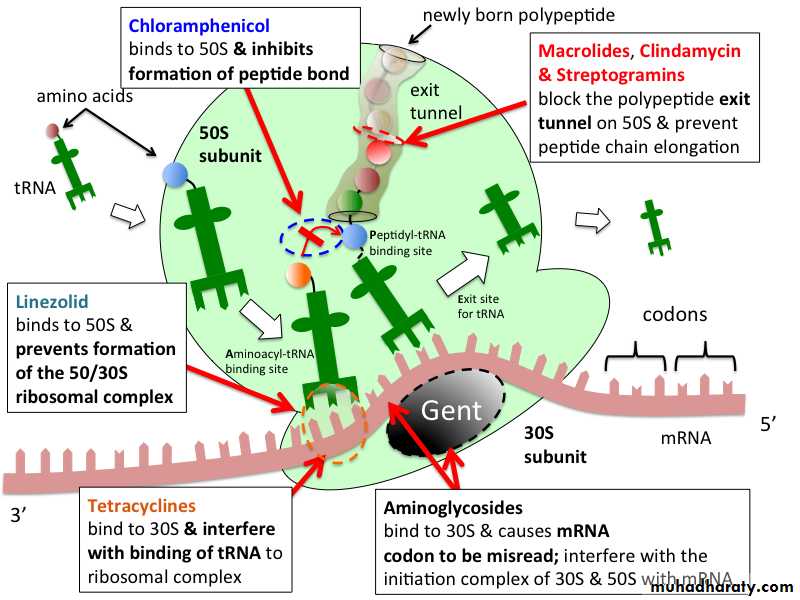
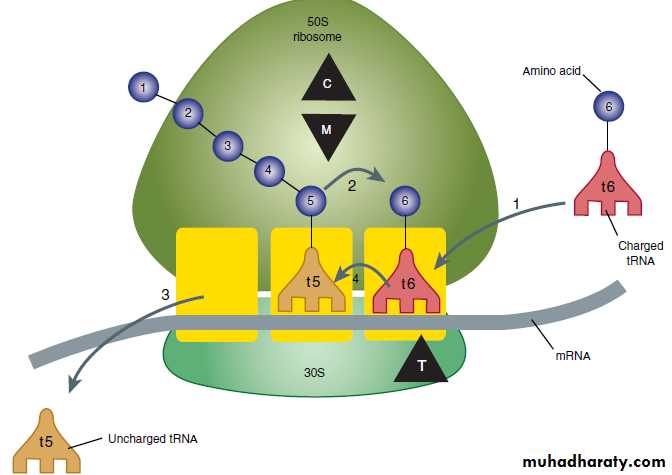
TET inhibit protein synthesis by binding specifically to the 30S ribosome. This appears to prevent access of AA-tRNA to the acceptor site on the mRNA-ribosome complex; preventing the addition of AA to the growing peptide chain.
Antibacterial spectrum
• gram (-) bacteria,
• less understood for gram (+) bacteria
Uses
1. used in Treatment of Cholera , Chlamydia infection , Mycoplasma pneumonia, brucellosis ,rickettsial infections, typhi.• 2. Systemic tetracyclines used in the management of chronic periodontitis
• 3.Tetracyclines are effective in the management of localized aggressive periodontitis and its associated organism, A. actinomycetemcomitans.
• Tetracyclines may also be used subgingivally.
localized aggressive periodontitis
Pharmacokinetics
. Absorption of TET is impaired by food in the stomach,milk products, aluminum OH , Na+ bicarbonate, Ca++
& Mg++, and Fe++ preparations
They bind to tissue undergoing calcification ( teeth and bone) .
It enter CSF but level insufficient for therapeutic and it appear in tears and saliva
It cross placental barrier and concentrated in fetal bones and dentine
all the TET are excreted in the urine and the feces. EXCEPT doxycycline , The drug is excreted by bile and feces. Thus one of the safest of the TET for the treatment of extrarenal infections.
TET also excreted in breast milk
Doxycycline and minocycline are almost totally absorbed on oral administration.
Currently, doxycycline is the preferred tetracycline for parenteral administrationMinocycline enters the brain in the absence of inflammation and also appears in tears and saliva
Adverse Effects of tetracyclines
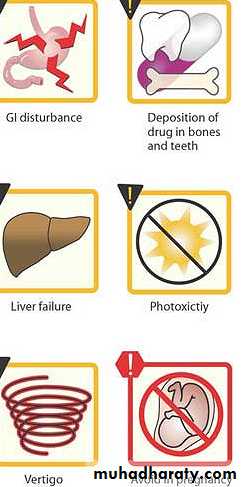
HasWide safety margin, but many side effects:1.Gastrointestinal TET produce GI irritation to a varying degree in some but not all individuals. Nausea, vomiting, burning, diarrhea (common)
Diarrhea must be promptly distinguished from that which results from pseudomembranous colitis - caused by overgrowth of clostridium difficile ( can be life-threatening)
TET like other antimicrobial agents administered orally may lead to development super infections, usually due to strains of bacteria or yeast resistant to these agents.
2. Renal toxicity: TET may aggregate uremia in patients with renal disease by Inhibition protein synthesis –
3. hepatic toxicity :In Pregnant women are particularly sensitive to TET -induced hepatic damage When received high dose of TET
4. Effects on TEETH Children receiving long-or short term therapy with TET may develop brown discoloration of the teeth. The drug deposits in the teeth and bones probably due to its chelating property and the formation of a TET -calcium orthophosphate complex. This discoloration is permanent. Avoid giving to pregnant women and children under the age of 8 years .
Other effects
5. Hypersensitivity : -Rash, hives with itching,6. Photoxicity : darkening of skin & sunburn when patient exposed to sunlight
Contra indication
.
1. TET should not be used in pregnant women and children under 8 years .
2. Tetracycline during 1st trimester of pregnancy can cause birth defects
3. Should not be given to patient with severe liver and renal disease.
Resistance
Resistance to the TET for gram-ve and gram+ve bacteria is mediated by inducible plasmid [the bacteria become resistant only after exposure to the drug].This plasmid mediates the production of a number of proteins that appear to affect transport of the drug into the cell, thereby preventing binding to the ribosome.
Chloramphenicol
Active against wide range of gram+ and anaerobic gram –ve organismDrug either bactericidal or bacteriostatic depend on organism .
It administer orally or IV
Mechanism of action :
binding to 50S ribosomal subunit
• Because of potential toxicity, bacterial resistance, and the availability of many other effective alternatives, chloramphenicol is rarely used.
• It may be considered for treatment of serious rickettsial infections such as typhus and Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
• It is an alternative to a -lactam antibiotic for treatment of meningococcal meningitis occurring in patients who have major hypersensitivity reactions to penicillin or bacterial meningitis caused by penicillin-resistant strains of pneumococci..
• Chloramphenicol is used topically in the treatment of eye infections because of its broad spectrum and its penetration of ocular tissues and the aqueous humor.
Clinical Uses
Adverse effects
The clinical use of chloramphenicol is limited to life-threatening infections because of the serious adverse effects associated with it administration.1.gastrointestinal upsets
2.Superinfection
3.: Aplastic anemia is independent of dose and may occur after therapy has ceased.]
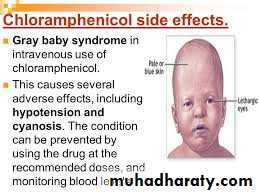
4.Gray baby syndrome