
Management of
labour

Learning objectives:
1-
to distinguish between normal and
abnormal labour
2-
to learn the clinical approach and
dealing with a woman with labour, from
the time of diagnosis to the end of the 3rd
stage of labour

When a pregnant woman started
labour or when she has
spontaneous rupture of membranes
at term she should be admitted and
full assessment of her condition is
accomplished.

FULL HISTORY ON ADMISSION
contractions
vaginal discharge or bleeding
LMP, GA , ANC
past obstetrical history, mode of
deliveries, any history of delivering big
baby? C/S
recent activity of the fetus

PROCEED FOR EXAMINATION
General examination
abdominal examination:
previous scars
Leopold's maneuvers
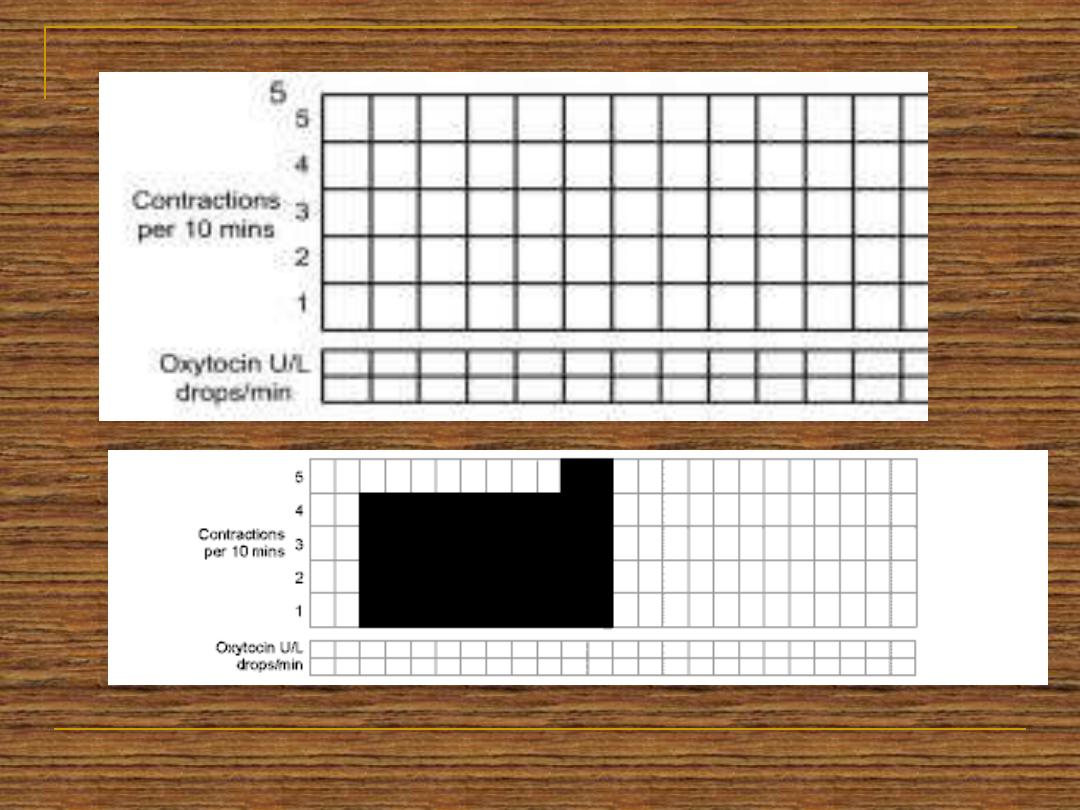
Palpate the abdomen for assessment of the
uterine contractions for at least ten minutes
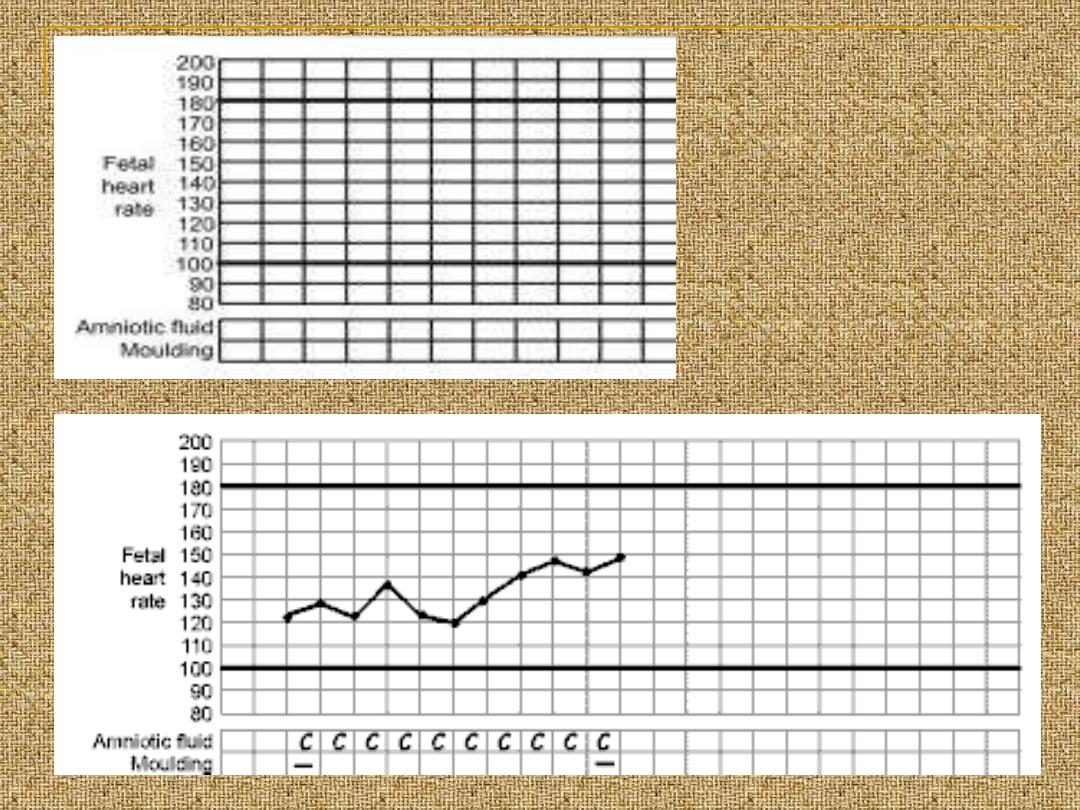
FHR: pinard stethoscope
or sonicaid
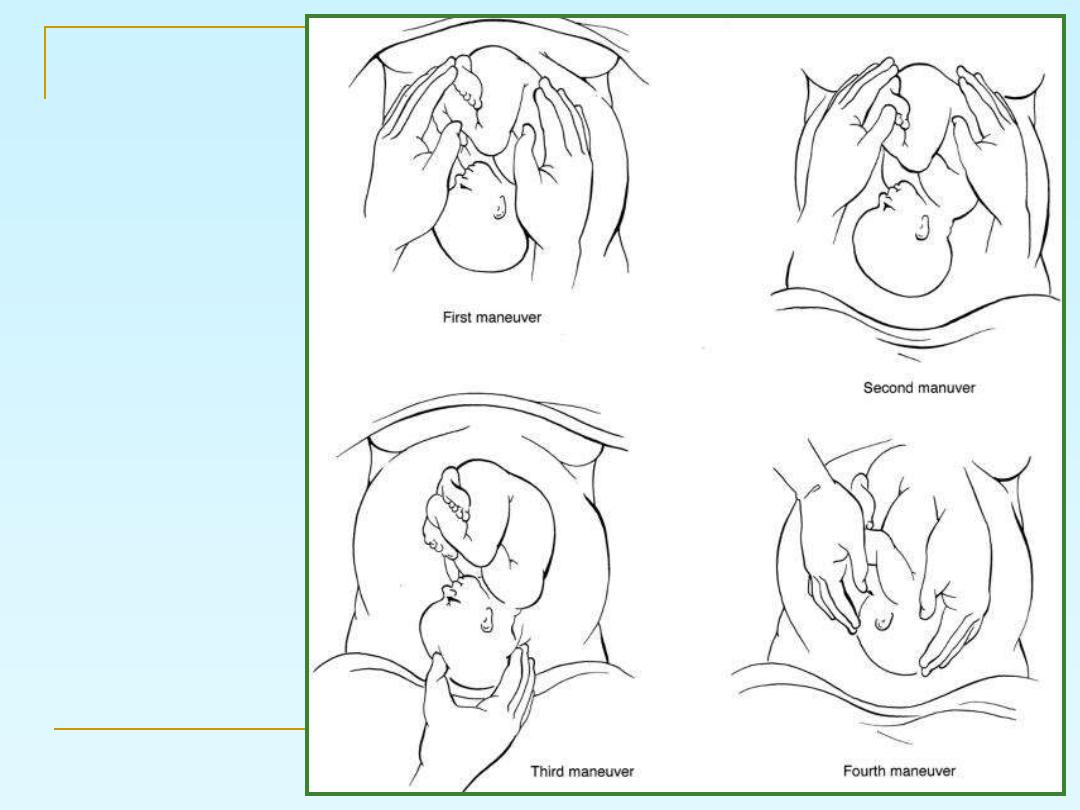
Leopold's
maneuvers

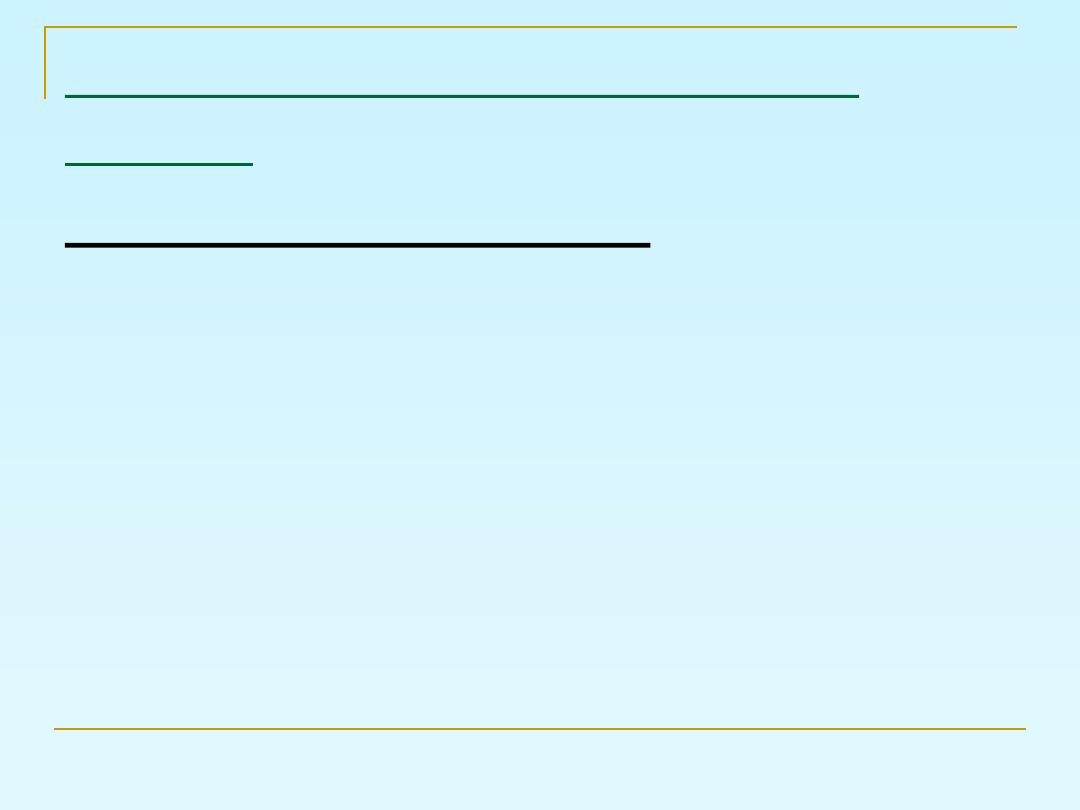
Vaginal examination
Bishop’s score:
It include:
1- dilatation
2- effacement
3- station
4- position of the cervix
5- consistency

ST
1
MANAGEMENT OF THE
STAGE
Woman in the latent phase:
encouraged mobilization,
analgesia,
light foods and drinks
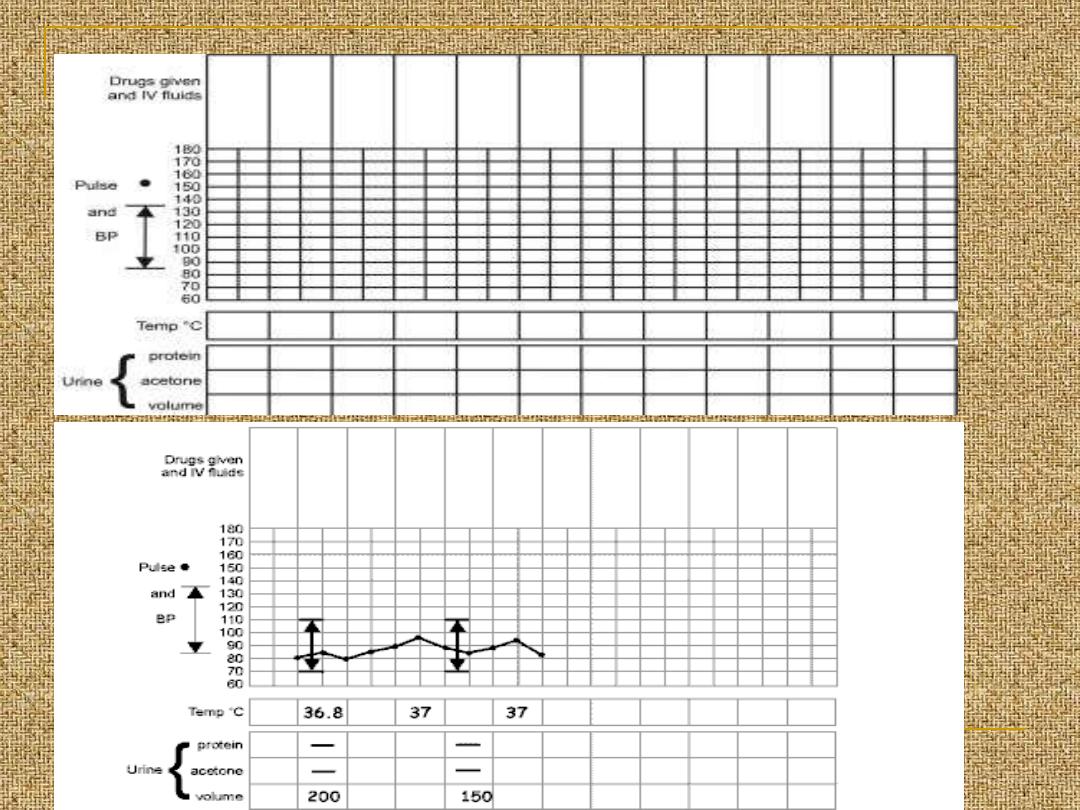
urine testing (for protein and glucose),
CBC.
blood sampling to be available for cross-
match
Intravenous access is recommended

Maternal blood pressure (BP) and pulse
should be recorded every hour during the
first stage of labor and every 10 minutes
during the second stage of labor.
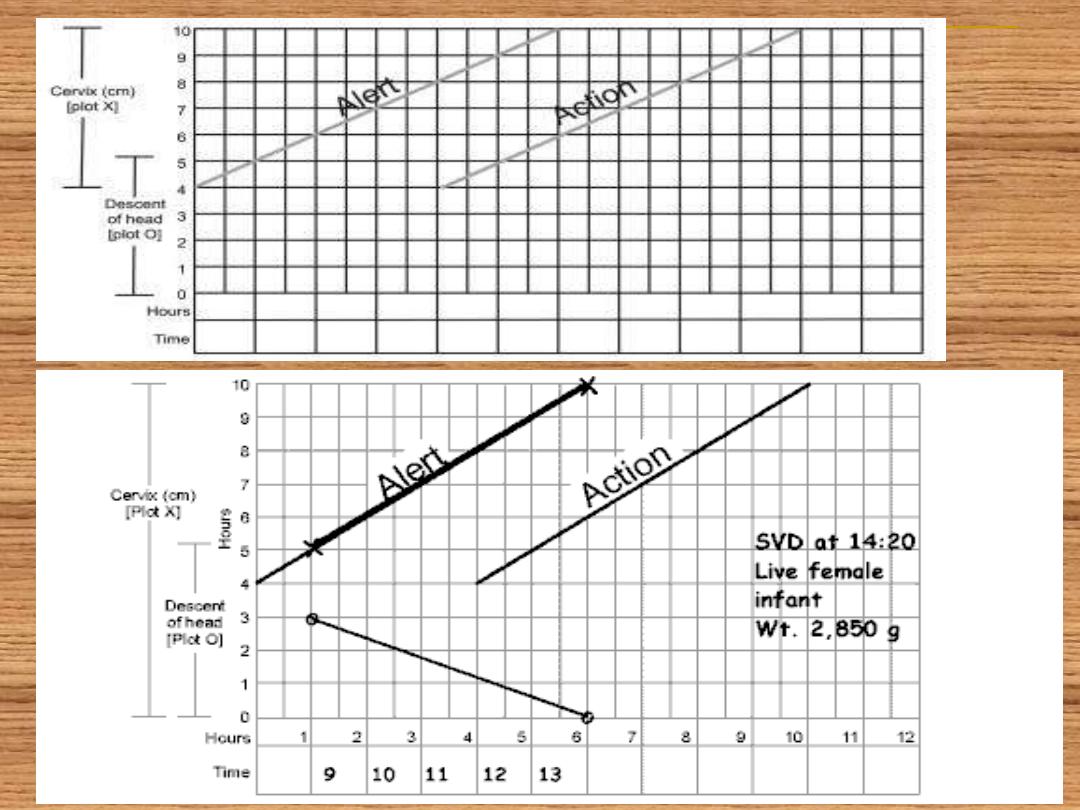
Vaginal examination in early labour is
infrequently performed (4 hourly is the
standard) and the frequency may be
increased accordingly to assess dilatation
and descent of the presenting part.
If the membranes are intact it is not
necessary to do ARM if the labor is
progressing well.
ST STAGE
1
MANAGEMENT OF THE

Adequate monitoring of both the maternal and
fetal conditions
giving her antacid, adequate analgesia and may
be urinary catheter if labor is prolonged and
abnormal.
evacuate the rectum ( may be done by enema) in
the 1st stage.
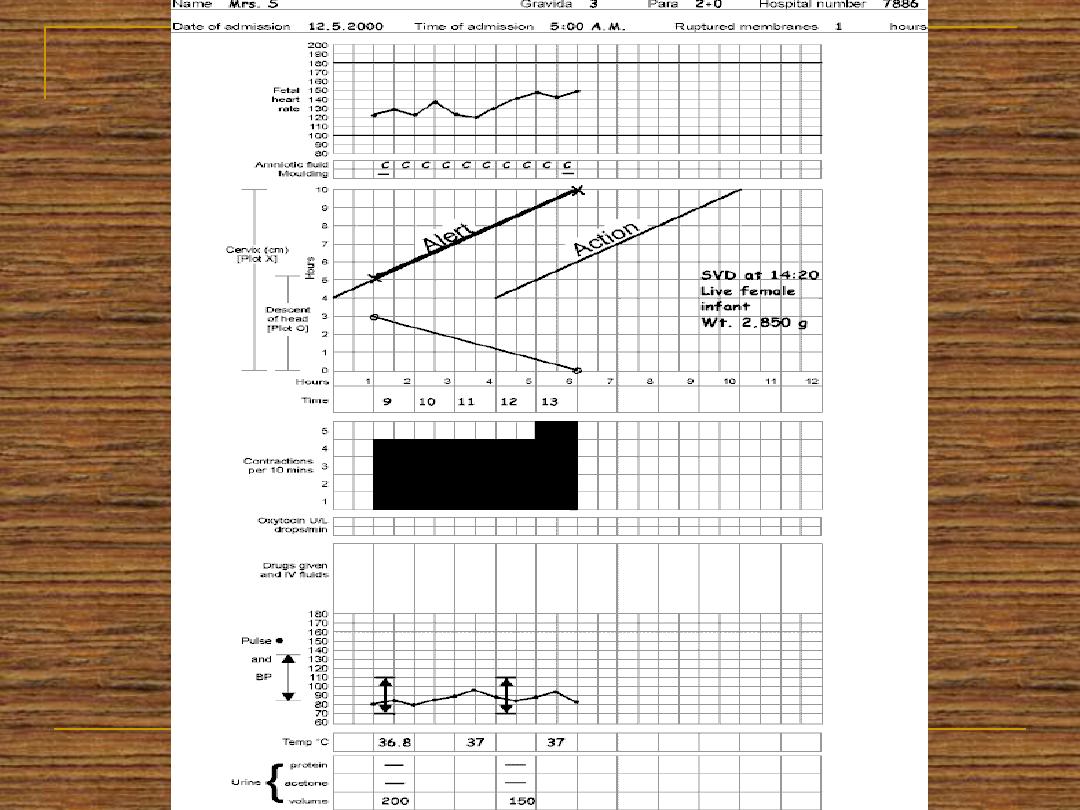
All of the data obtained since the admission to
the labour world should be recorded in a
graphical manner which is called partogram
ST STAGE
1
MANAGEMENT OF THE
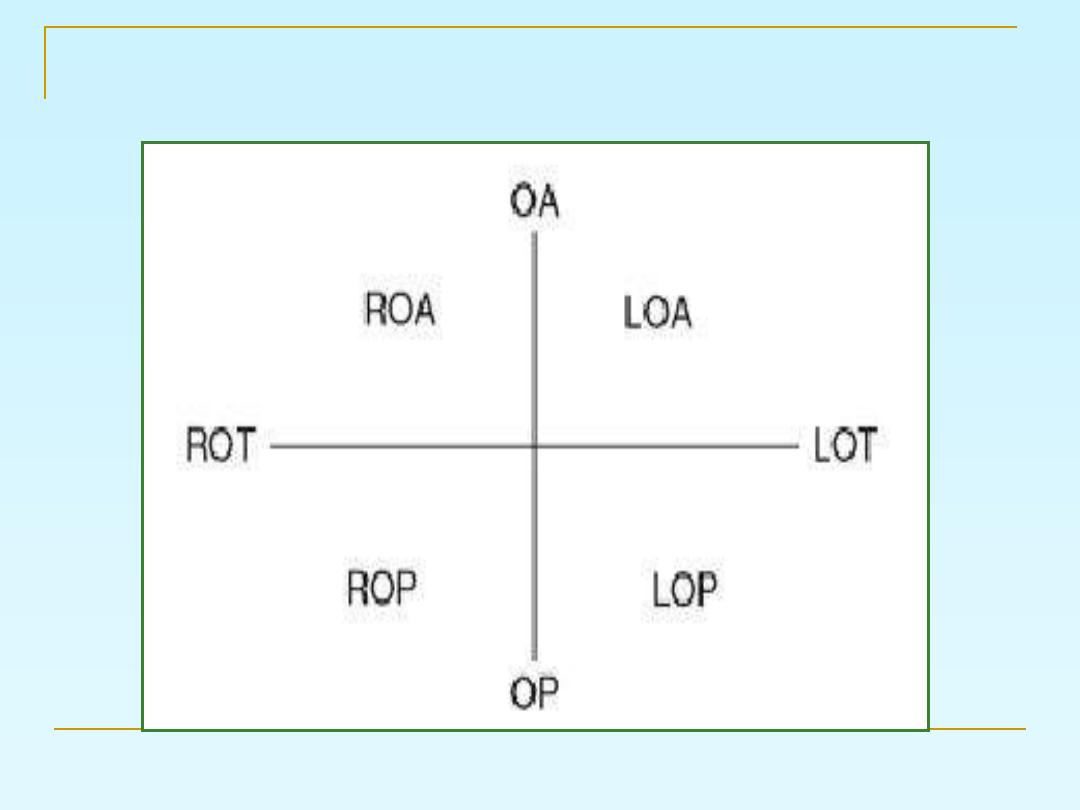
the position of the presenting part
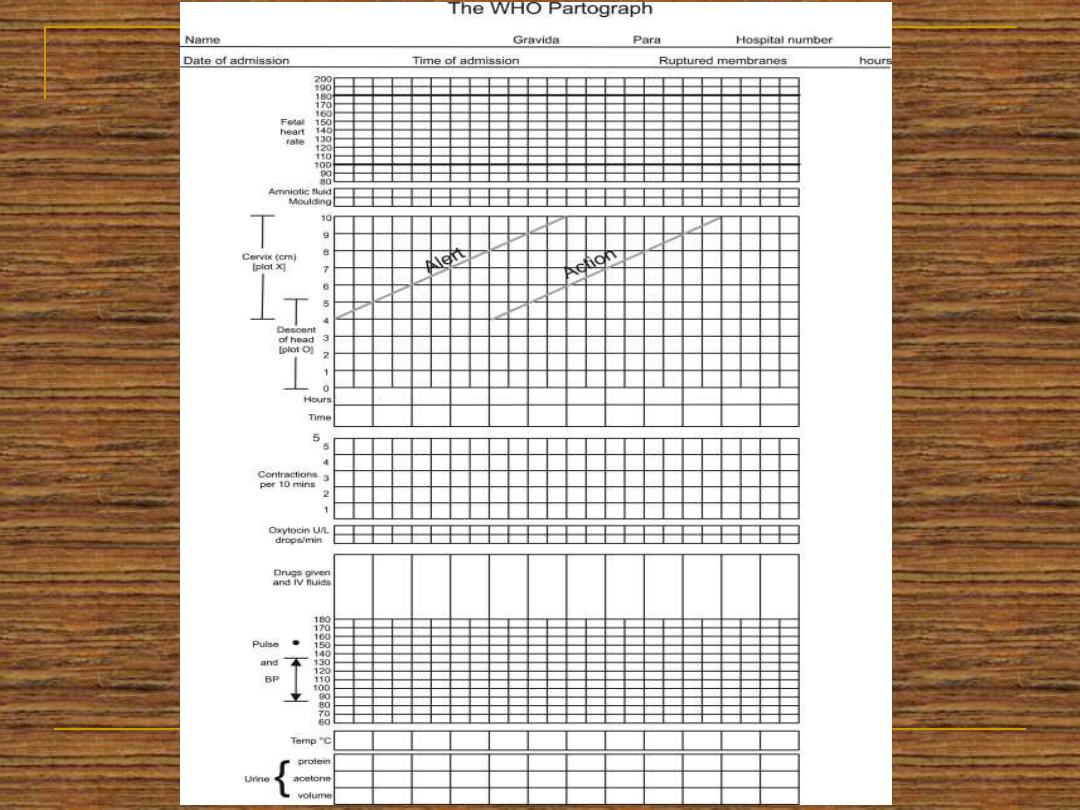

MANAGEMENT OF THE SECOND
STAGE
When the mother reach the active 2
nd
stage
and has urge to push she adopts a lithotomy
position, or left lateral position, or semi
sitting position.
the pushing should be organized with the
contractions to be effective.

When you notice the crowning (the
head passed the pelvic floor and
delivery is imminent).
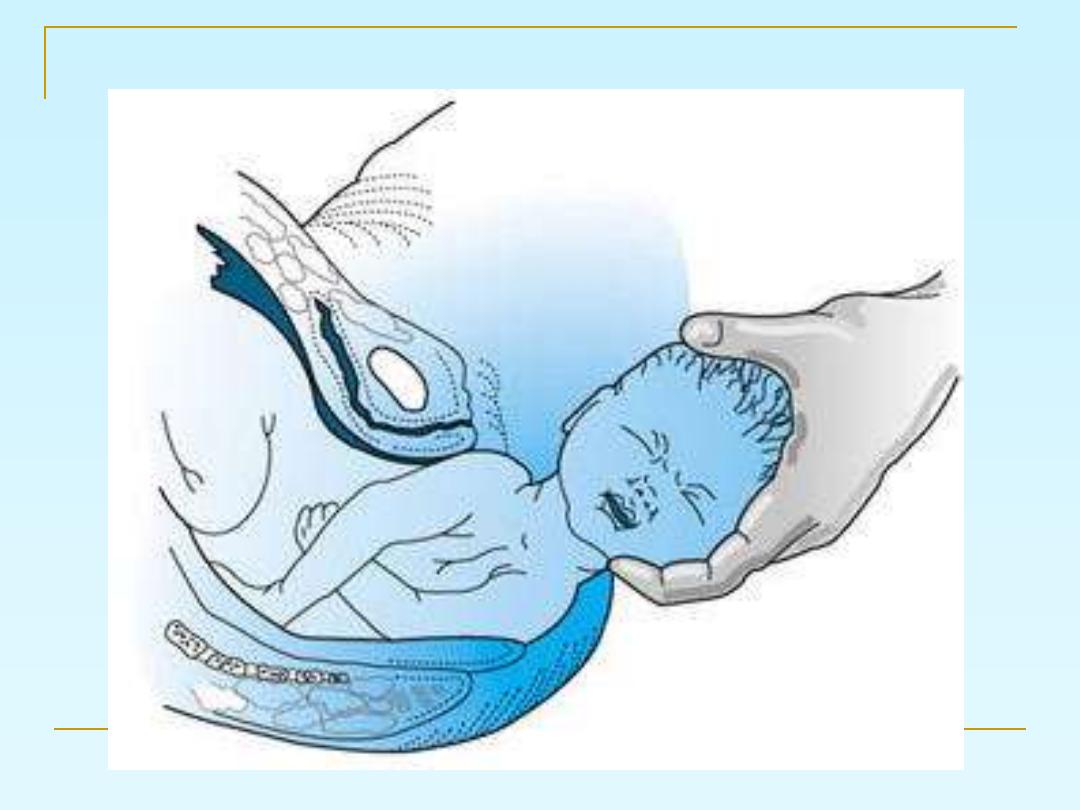
Use the modified Ritgen's manoeuvre:
for the delivery of the head.
The goals of assisted spontaneous
vaginal delivery are reduction of
maternal trauma, prevention of fetal
injury, and initial support of the
newborn

Episiotomy
Episiotomy is an incision into the
perineal body to enlarge the vulval
outlet and facilitate delivery:
1- Midline episiotomy
2-Mediolateral episiotomy

After the head delivery
Then the delivery of the shoulders then the
delivery of the rest of the body
Delay cord clamping
MANAGEMENT OF THE SECOND
STAGE
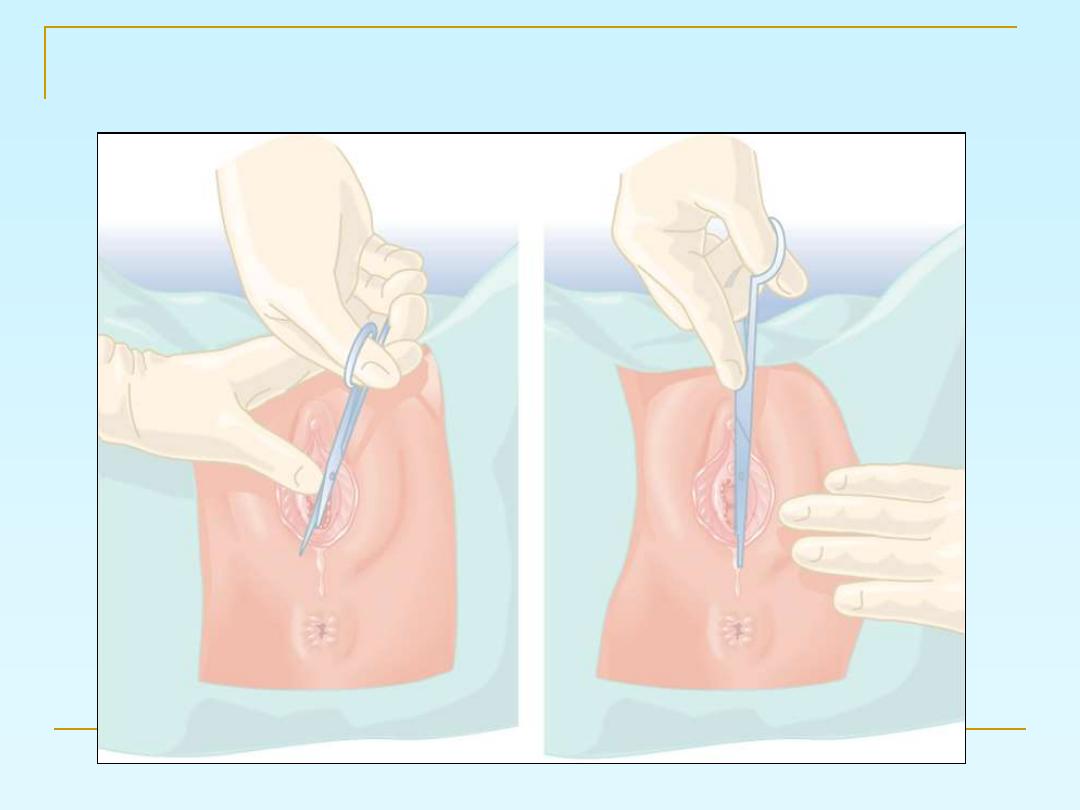
EPISIOTOMY
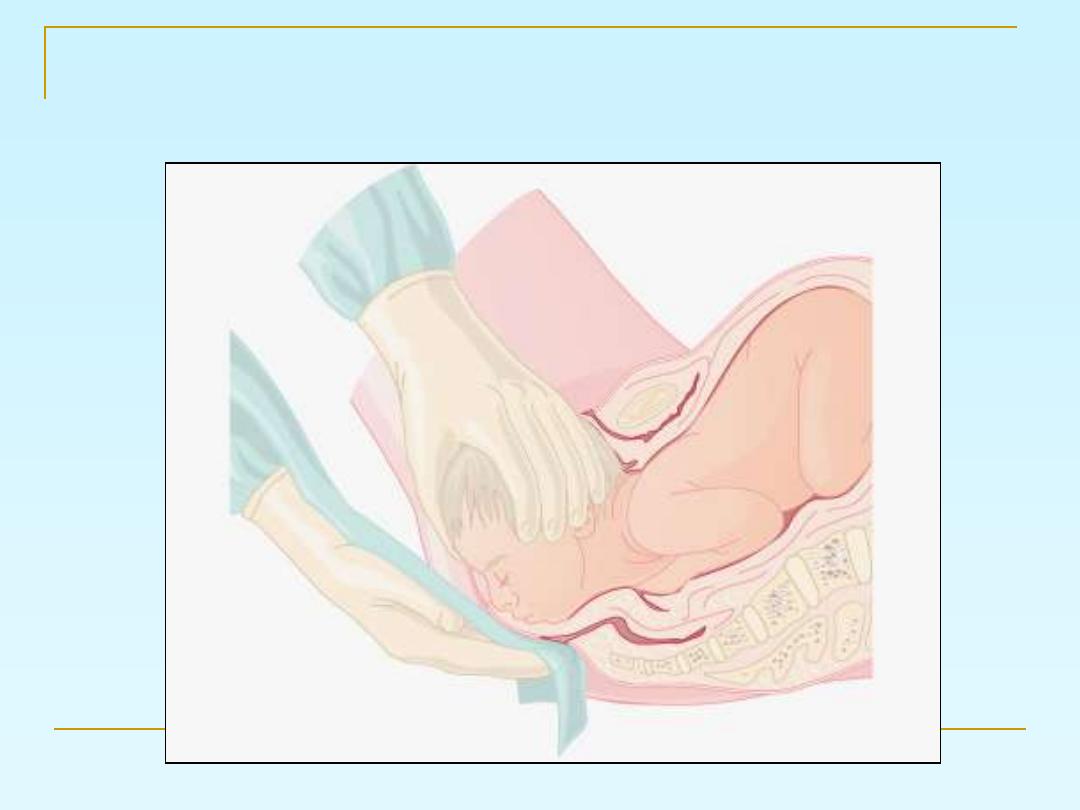
Ritgens maneuver for delivery of head
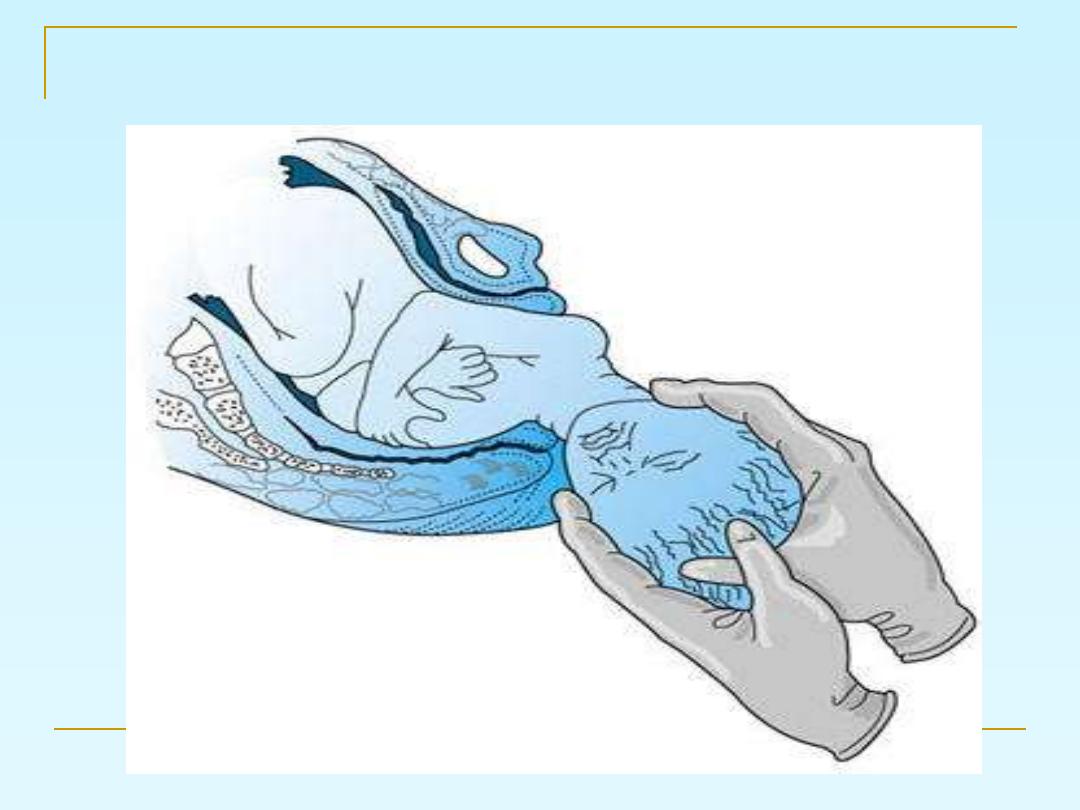
???

MANAGEMENT OF THE THIRD
STAGE
Placental separation occurs as a result of
reduction of the volume of the uterine
cavity by the contractions and retraction
A cleavage plane developed within the
decidua basalis and the placenta lies free
in the lower uterine cavity.

rd stage
3
active management of the
1.
Give10 units oxytocin or syntometrin
with the delivery of the anterior shoulder
to induce uterine contractions
immediately after the delivery of the
baby.
2.
1-2 minutes after baby's delivery;
clamping of the cord

3.
Controlled cord traction to deliver the
placenta and membranes. never pull the
cord when the uterus is not contracted
risk of uterine inversion

Active management of the 3
rd
stage
shortens the 3
rd
stage and reduce
the risk of postpartum
haemorrhage
Aim of active management
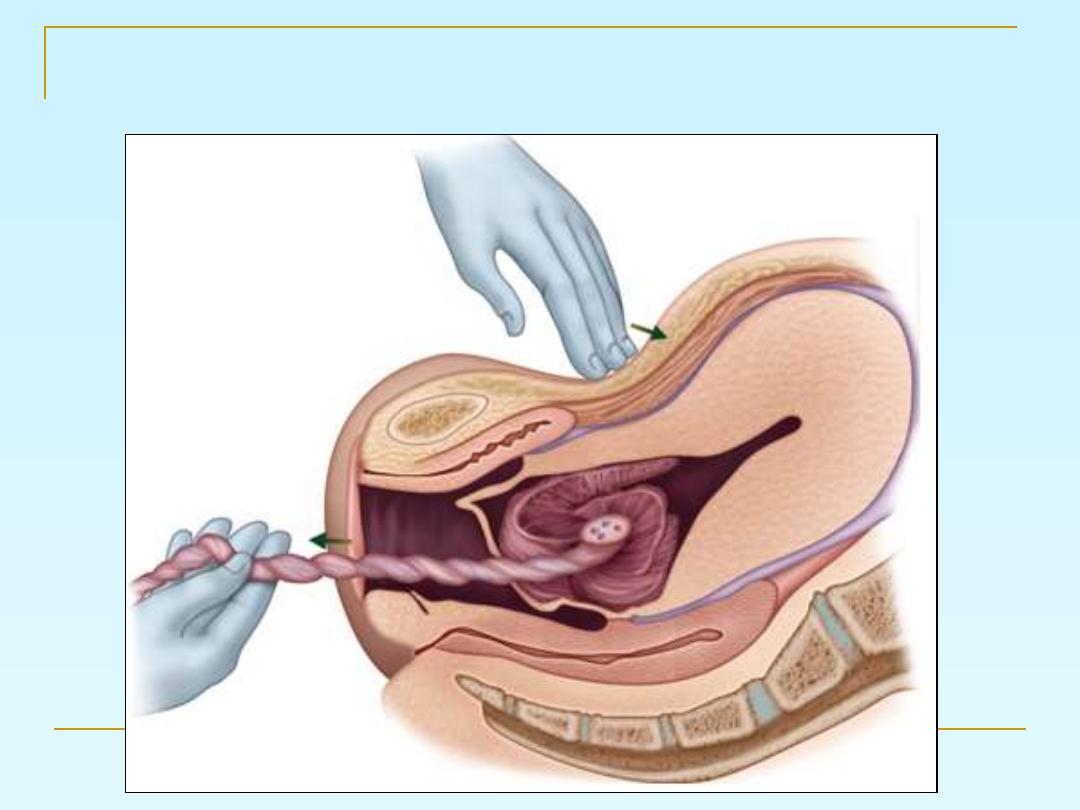
Controlled cord traction

After placental delivery it should be
inspected for any lost cotyledons or
succenturiate lobe.
Finally the vulva must be inspected
for any tears or lacerations in order
to repair them.
