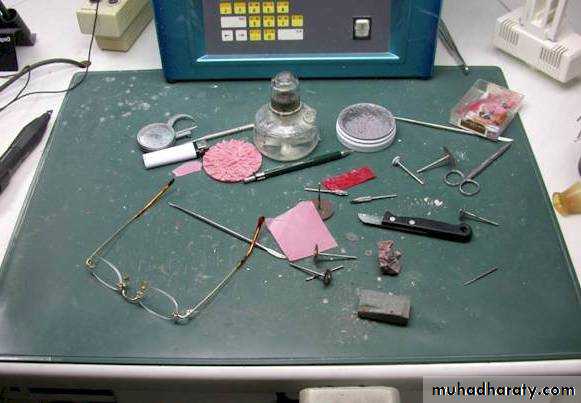
Laboratory Procedures
Duplicating a master or stone castRefractory or Investment cast
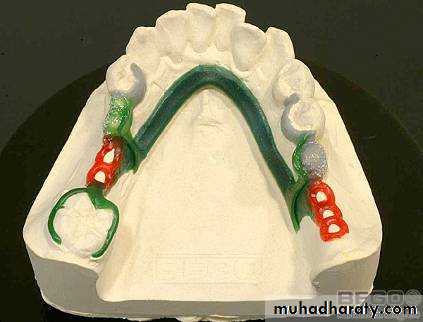
Waxing the removable partial denture framework
Spruing
Investing the sprued pattern
Burnout
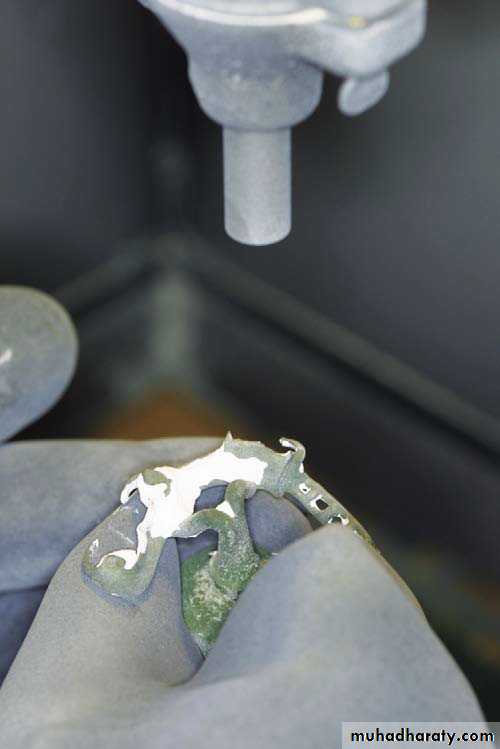
Casting
Removing the casting from the investment
Finishing and polishing of Framework
duplication of the master cast
Duplicating a stone castDuplication consist of making an impression of the prepared master cast & pouring the impression in a refractory material.
A stone cast may be duplicated for the following
purposes:
1. To preserve the original master cast from abrading its surface & from fracture.
2. For processing a temporary prosthesis3.Formation of an investment cast for framework fabrication.
Duplicating materials: Two types
1.Colloidal materialReversible colloidal material e.g. Agar Agar which is fluid by heating & return gel while cooling.
Irreversible hydrocolloid e.g. alginate.
Cast to be duplicated placed in suitable flask called duplicating flask
2.Silicone material (rubber base)Duplication using agar agar
Equipments:1-duplicating flask
2-automatic duplicating machine for preparing and storing agar agar.
3-Relieved and blocked out master cast
4-Hydrocolloid duplicating material(agar agar)
Care must be taken that the temperature of duplicating material is not too high because it will melt the wax.
Duplication using agar agar
investment materials
The property of this material is the resistance to very high temperatures
Refractory or investment cast a cast made of a material that will withstand high temp. without disintegration.
Types of investment material:
1.Gypsum bonded investments(low heat investment)
This refractory material can be burned out at 704 C ° without causing breakdown of the investment.2.Phosphate-bonded investment (High heat investment)
material burned out at temperature 1037 C °
The colloid mold is poured immediately with investment material (refractory material) to get the refractory or investment cast.
3.silica-bonded investment
refractory cast
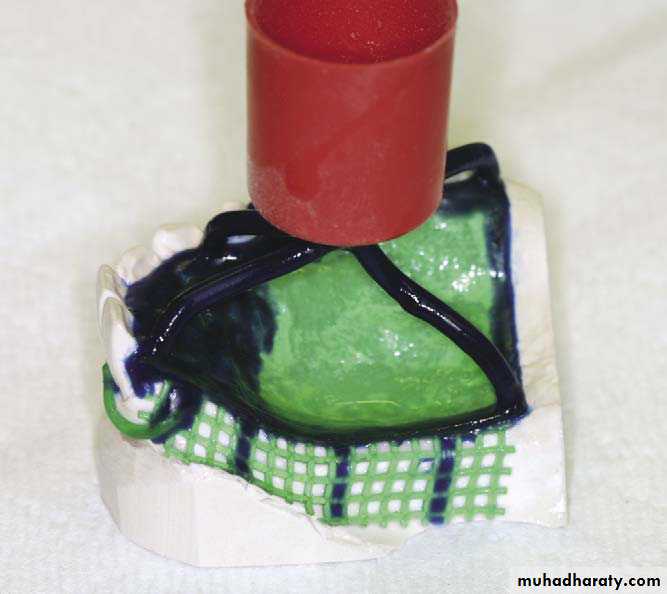
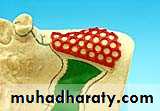
Waxing the frameworkWaxing the framework
The design of framework is transferred to the refractory cast using lead pencilWaxing is done by using :
1.performed plastic or wax pattern
2. Free hand waxing
Preformed plastic patterns
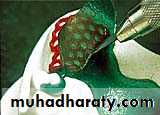
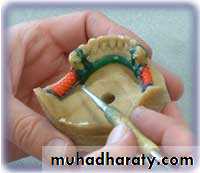
Sprue technique
Universal funnel form
Wax pattern sprued and ready to invest
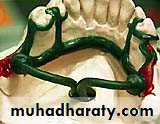
Types of sprue1.multiple sprue
2. single sprue
Spruing the framework
The sprue channel is the opening leading from the crucible to the cavity in which the framework is to be cast & through it the metal travel.General rules or Principles for spruing:
1.The sprue should be large enough so that the molten metal in them will not solidify until after metal in the casting proper has frozen2. The sprues should lead into the mold cavity as direct as possible.
3.The sprues should leave the crucible from a common point & be attached to the wax at its bulkier sections.
Casting from the
top
Casting from the bottom
Wax pattern sprued and ready to invest
Important points in multiple spruing11.use a few sprues of large diameter rather than several small sprues.
2.Keep all sprues as short & direct as possible.3.Avoid sudden or abrupt changes in direction ,avoid T- shape junctions as much as possible.
4.Reinforce all junctions with additional wax to prevent constrictions in the sprue channel & to prevent V- shaped sections of investment that may be breakaway during the casting
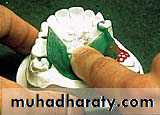
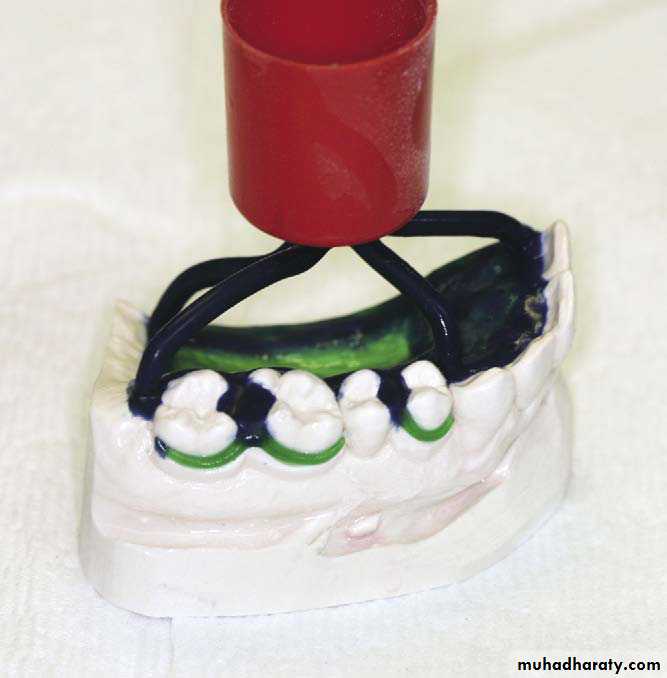
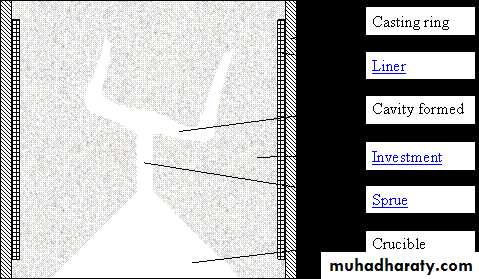
Investing The sprued pattern
The investment for R.P.D casting consist of two parts:-1.investment cast on which the pattern is formed.
2.outer investment surrounding the cast & pattern
This is done using (metal ring)
The metal ring is lined with layer of asbestos substitute to allow for both setting & thermal expansion of the mold in all directions.
Investing The sprued pattern
Purposes of the investment are:
1.it provides the strength necessary to hold the forces exerted by the entering stream of molten metal.2. it provide smooth surface for the mold cavity so that the final casting require as little finishing as possible.
3.it provides an avenue of escape for most of the gases entrapped in the mold cavity by the entering stream of molten metal.
4. provide necessary compensation for dimensional changes of the alloy from molten to solid state.
Investing The sprued pattern
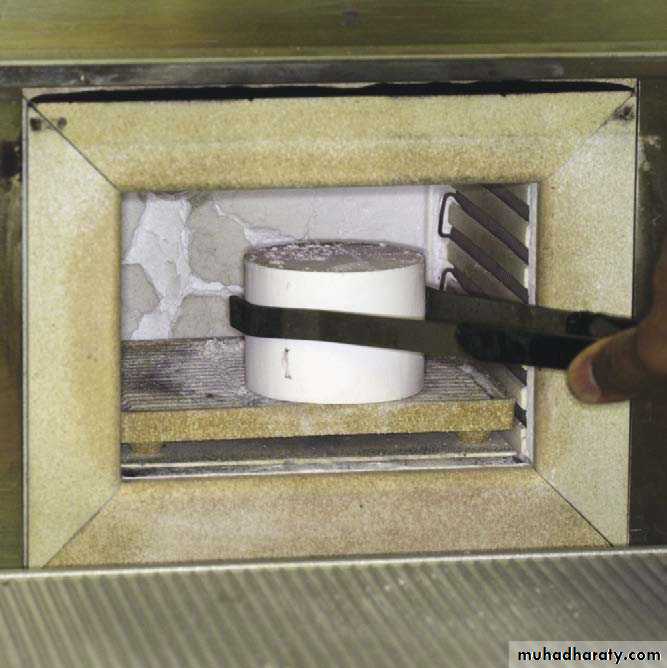
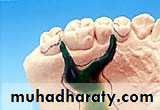
Burnout
Three purposes of burnout1.drying moisture in the mold.
2.Vaporizes & eliminates the wax pattern , leaving a cavity in the mold.3.expands the mold to compensate for contraction of the metal on cooling.
An invested pattern in the burnout oven for complete elimination of the wax pattern.
Casting
All methods that uses force to quickly inject the molten metal into the mold cavity.The force may be
1. Centrifugal ….commonly used
2. air-pressure
*If too little force is used the mold is not completely filled before the metal begins to freeze.
*If too much force is used excessive turbulence may result in the entrapment of gases in the casting.
Centrifuge for casting
The metal is melted by1.Gas-oxygen torch
2.Electrical machineFinishing & Polishing
Rules for finishing and polishing1.High speed is preferable to low speed.
2. Avoid excessive pressure which heats the work, crushes the abrasive particles.
3.Sequencing for finishing.
4.Clean polishing wheels should be used to avoid embedding of foreign particles which lead to discoloration.
5. Be sure each finishing operation completely removes all scratches left by the preceding one.
Nonstop high-speed
grinderDiamond grinding stones - sintered
Finishing & Polishing equipments
Air-blasting unitThe framework is divested with aluminum oxide