Fifth Stage
Internal Medicine
Dr. Aamer – Lecture 3
1
vWF diseases
Case
: 30 years old female presented with:
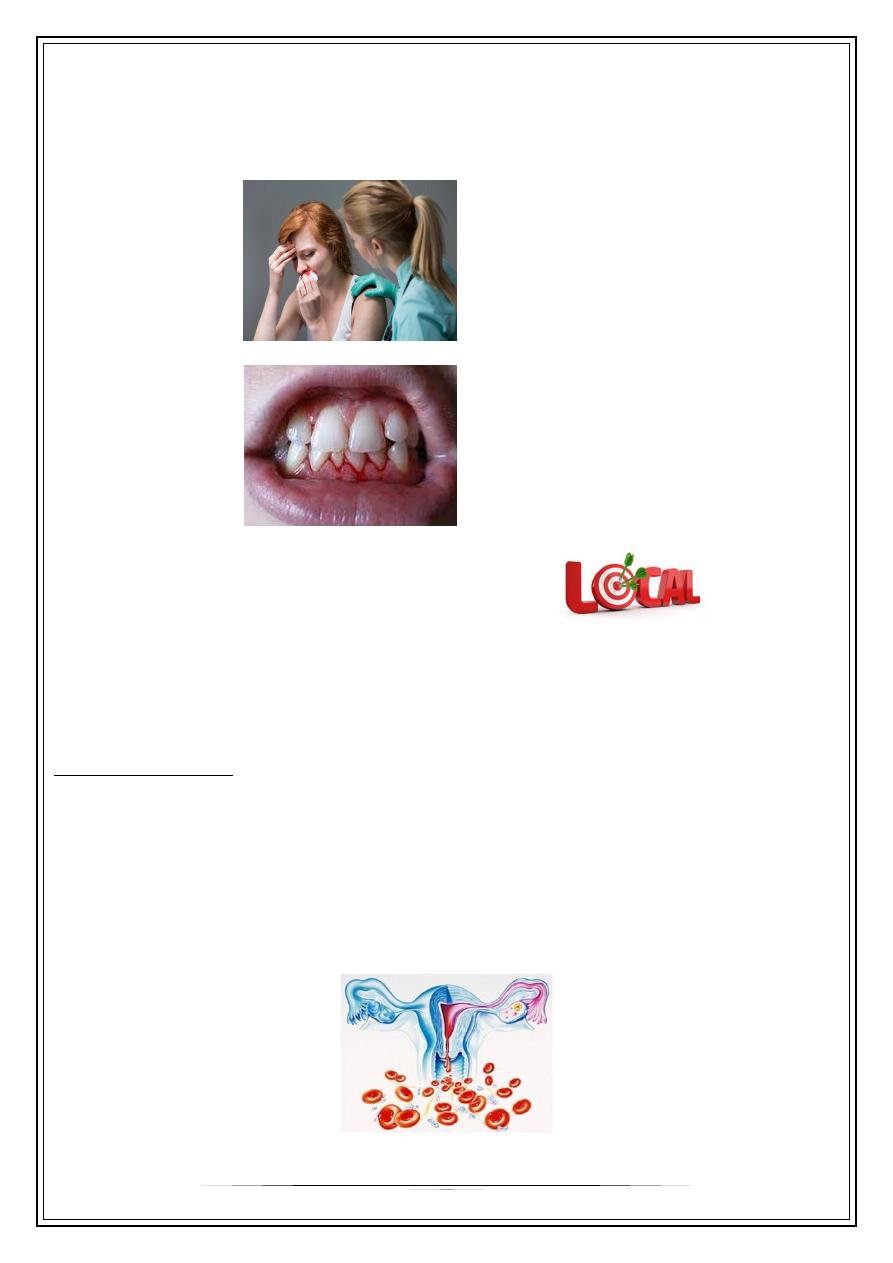
+Epistaxis:
+Bleeding gums:
This exclude local causes (i.e. ENT causes, trauma …)
So, this is primary hemostatic defect (mucocutaneous bleeding)
While secondary hemostatic defect usually presents with deep seated bleeding like arthritis, arthrosis …
Primary hemostasis: is formation of platelet plug, it requires:
•
Functional blood vessels
•
Good platelets (number+function)
•
Von Willebrand factor
History details:
+Heavy menstrual bleeding:

2
-No Fever! :
+Family history, (Consanguinity,relative marriage) is positive!
Examination
-No Organomegaly:
-No Lymohadenoapthy in
cervical, axillary or inguinal!
Investigation
-Complete blood count & blood film:
-All are normal (RBC, WBC & platelets)!
+Bleeding time is + prolonged!
•
Bleeding time is a test of platelet function (which depends
on both platelets & vWF, so it is a crude test)

3
•
It is the time it takes for bleeding to stop (time for a platelet plug to form)
•
The template bleeding time is used when the test is performed by standard
template method
+Alternative to bleeding time is: Platelet function analyzer
(Both the above two tests are not specific for platelets)
+Von Willebrand Factor Antigen (i.e. count): Low!
+Ristocetin Cofactor: assess vWF activity: abnormal!
So, Diagnosis is,
von Willebrand diseases!
•
It is the commonest inherited bleeding disorder
(autosomal dominant), equal in male/female.
•
Presented with mucocutaneous bleeding, and all
initial tests are normal.
•
Diagnosed by low or inactive vWF.
In general, vWF is double agent:
•
Works in primary hemostasis (glue factor)
•
And also in secondary hemostasis, as a shield
(chaperon) for factor VIII.
So, the presentation can be hemophilia-like bleeding.

4
Classification
It depends on quality and quantity of vWF.
The quality is more important.
Type 1:
•
Most common
•
Quantitative
•
Partial reduction of quantity of vWF antigen (count), it is
not completely absent.
Type 3:
•
Quantitative
•
Total absence of vWF antigen.
•
This type may falsely diagnosed as hemophilia (low factor
VIII due to absence of its protective chaperon: vWF)
Type 2:
•
Qualitative
•
Non-functioning (Crazy) vWF despite normal quantity
A secret: There is type 4, i.e. acquired vWF disease.
(Summary of types) :

5
Treatment
Tranexamic acid (anti-fibrinolytic)
•
It helps the vWF in his job.
Desmopressin
•
It works by squeezing the residual amounts of vWF
that exist in the endothelium of the vessels.
•
So, it works in Type 1 (Partial vWF quantity)
•
It is contraindicated in type 2 (Crazy vWF)
Cryoprecipitate
•
It contains vWF, Factor VIII and fibrinogen.
•
Replenish the functioning amount of vWF
•
It is not preferable, (transmissible viral infection)
•
So, an alternative is
recombinant vWF

6
Summary of lecture:
Thank you,,,
Notes were written from real-time lecture…
