Lect. 6
FLUOROQUINOLONES\ Quinolones
Introduced in 1980Nalidexic acid derivative
Quinolones and fluoroquinolones are chemotherapeutic bactericidal drugs, eradicating bacteria by interfering with DNA replication
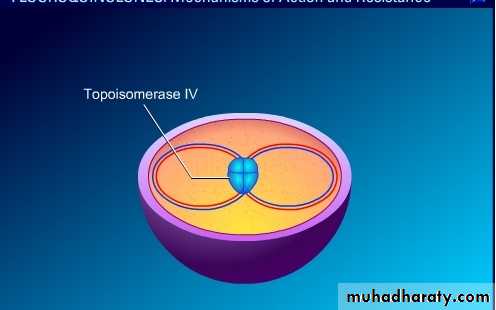
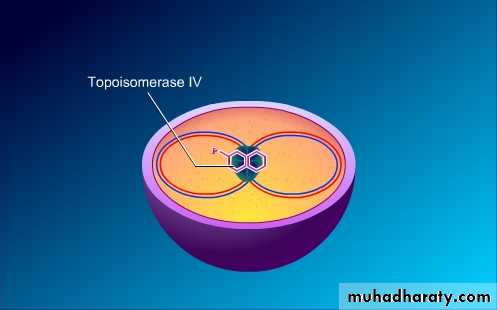
Quinolones inhibit the bacterial DNA gyrase or the topoisomerase IV enzyme, thereby inhibiting DNA replication and transcription
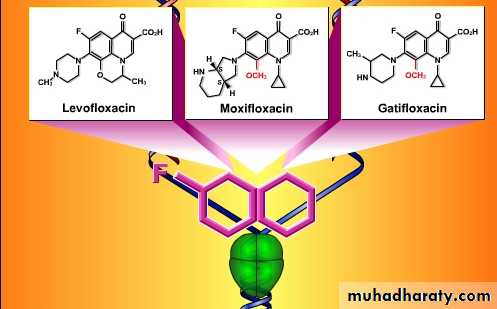
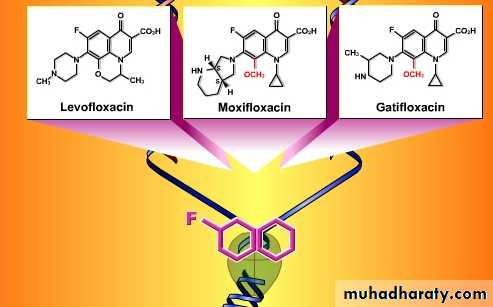
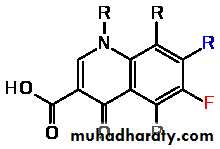
if the connection contains fluorine (red), it is a fluoroquinolone.
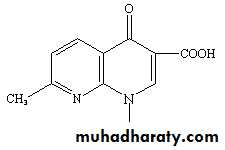
Parent drug: nalidixic acid (Quinolones )
• Generation• Drug Names
• Spectrum
• 1st
• nalidixic acid
• cinoxacin
• Gram- but not Pseudomonas species
• 2nd
• norfloxacin
• ciprofloxacin
• enoxacin
• ofloxacin
• Gram- (including Pseudomonas species), some Gram+ (S. aureus) and some atypicals
• 3rd
• levofloxacin
• sparfloxacin
• moxifloxacin
• gemifloxacin
• Same as 2nd generation with extended Gram+ and atypical coverage
• 4th
• *trovafloxacin
• Same as 3rd generation with broad anaerobic coverage
*withdrawn from the market in 1999
Therapeutic uses
UTI
Diarrhea
RTI
Dentistry
Not indicated for acute orofacial infectionCiprofloxacin for aggressive periodontitis
Ciprofloxacin
• - useful in treating infections caused by many Enterobacteriaceae and other gram-negative bacilli.Moxifloxacin
has enhanced activity against gram-positive organisms (for example, S. pneumoniae) but also has excellent activity against many anaerobes. It has very poor activity against P. aeruginosaDrug interactions:
↓ absorption: Al3+, Mg2+, and Ca2+ antacidsCYP450 inhibition potential drug interactions for ciprofloxacin
Adverse effects
-GI: Nausea, vomiting
CNS: HA, dizziness, confusion, insomnia, delerium, hallucinations, seizure (rare)
Cardiovascular: Torsades de pointes (rare)
Musculoskeletal: Rupture of tendon (rare)
Neurologic: Polyneuropathy (rare)
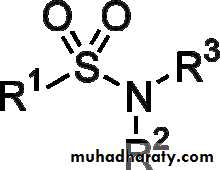
Sulfonamides
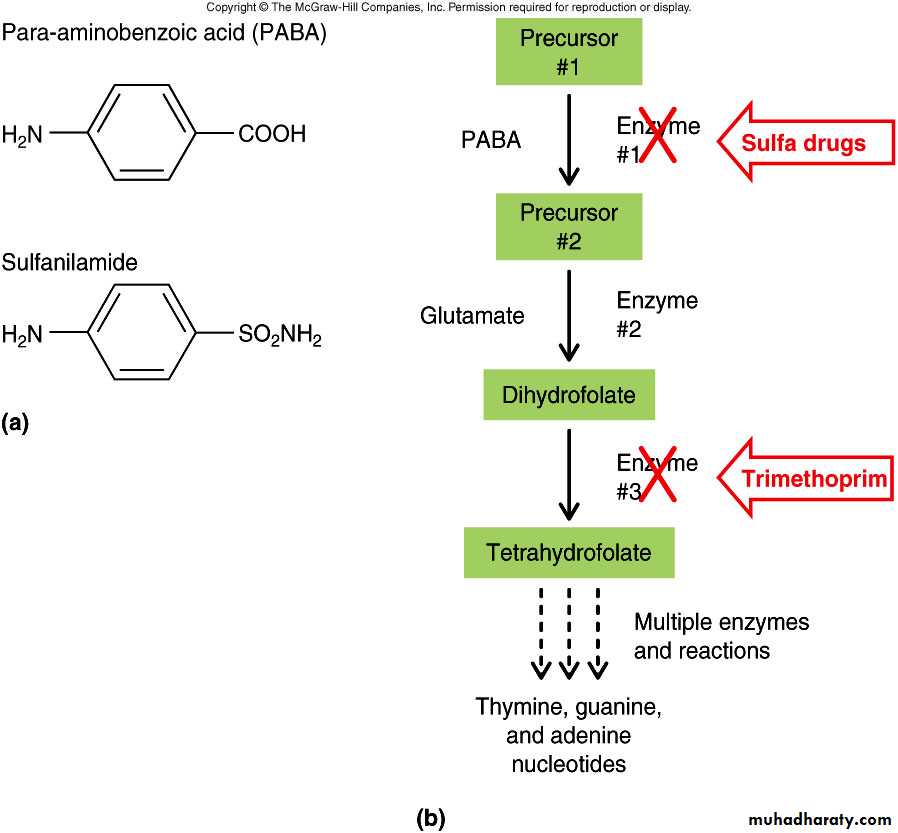
Sulfonamide or sulphonamide is the basis of several groups of drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides (sometimes called sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs) are synthetic antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group.Sulfonamides uses
Sulfonamides are infrequently used as single agents.The fixed-drug combination of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the drug of choice for infections such as
Pneumocystis pneumonia,
acute bronchitis, toxoplasmosis,
nocardiosis, and occasionally other bacterial infections
No uses in dentistry
Sulfonamids for topical use
Sulfacetamide
- Used for ophthalmic infection in very high aqueous concentration which is not irritating to the eye.
Poorly absorbed sulfonamides
SulfasalazineVery poorly absorbed from GIT
Used for Rx of ulcerative colitis and crohn´s disease.
Sulfonamides adverse effects
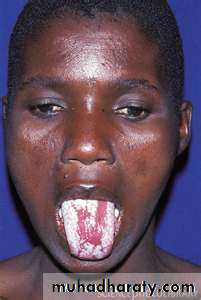
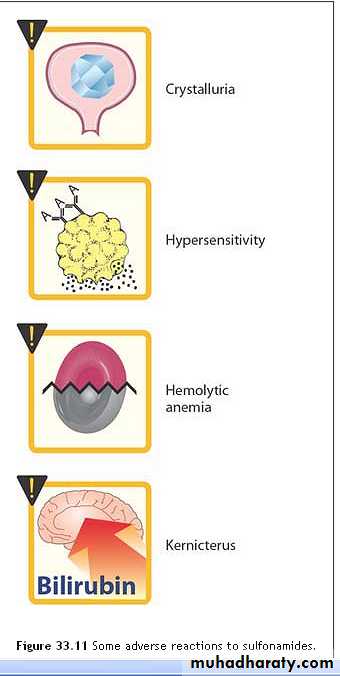
All sulfonamides, have been considered to be partially cross-allergenic.The most common adverse effects are allergy( fever, skin rashes, exfoliative dermatitis).
photosensitivity, urticaria, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and difficulties referable to the urinary tract (crystal urea).
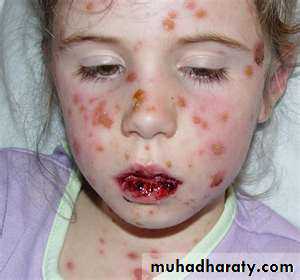
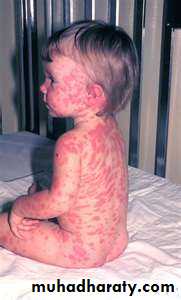
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, although relatively uncommon , is a particularly serious and potentially fatal type of skin and mucous membrane eruption associated with sulfonamide use.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
• Kernicterus this disorder may occur in
• newborns, because sulfa drugs displace bilirubin from binding sites on serum albumin.• The bilirubin is then free to pass into the CNS, because the baby's blood-brain barrier is not fully developed
Trimethoprim
Often used synergistically with sulfonamideInhibits folic acid production
Interferes with activity of enzyme following enzyme inhibited by sulfonamides
trimethoprim
Mechanism of actionInhibit tetrahydro folate reductase enzyme which is requir for purin and pyrimidine amino acid its similar to sulfamethoxazole but it (20- 50) fold more potent .
Therapeutic uses
• Pneumocystic pneumonia• Respiratory infection
• GIT infection: use to treat non typhoid salmonella .
• Prostate and urinary tract infection
Adverse effect
• Megaloplastic anemia• Leucopenia
• Granulcytopenia
CO-TRIMOXAZOLESTRIMETHOPRIM+SULFAMETHOXAZES
Mechanism of actionSynergistic antimicrobial activity result from inhibition of 2 step in synthesis of tetrahydro folic acid .
Sulfamethoxazole inhibit incorporation of PABA into folic acid and trimethprim inhibit reduction of dihydrofolate .
It has broad spectrum of antibacterial actions than sulfa drug
Clinical uses
has a broader spectrum of antibacterial action than the sulfa drugsIt is effective in treating UTIs and respiratory tract infections as well as in Pneumocystis pneumonia and ampicillin- or chloramphenicol-resistant systemic salmonella infections
Adverse effect
• Dermatologic• GIT: glositis and stomatitis
• Hematologic : megaloblastic anemia, leukopenia , thrombocytopenia and it reversed by administration of folic acid.
• Drug inter action: prolong prothrombine time in patient receiving both trimethprim and warfarin , plasma half life of phenytoin may be increased due to inhibition of metabolism .