
Intrauterine fetal growth
restriction
By
Asmaa. Kadhim

Definitions
• Small for gestational age SGA
• Fetal growth below 10
th
centile
• Fetal growth restriction
• Failure of fetus to achieve its growth potential
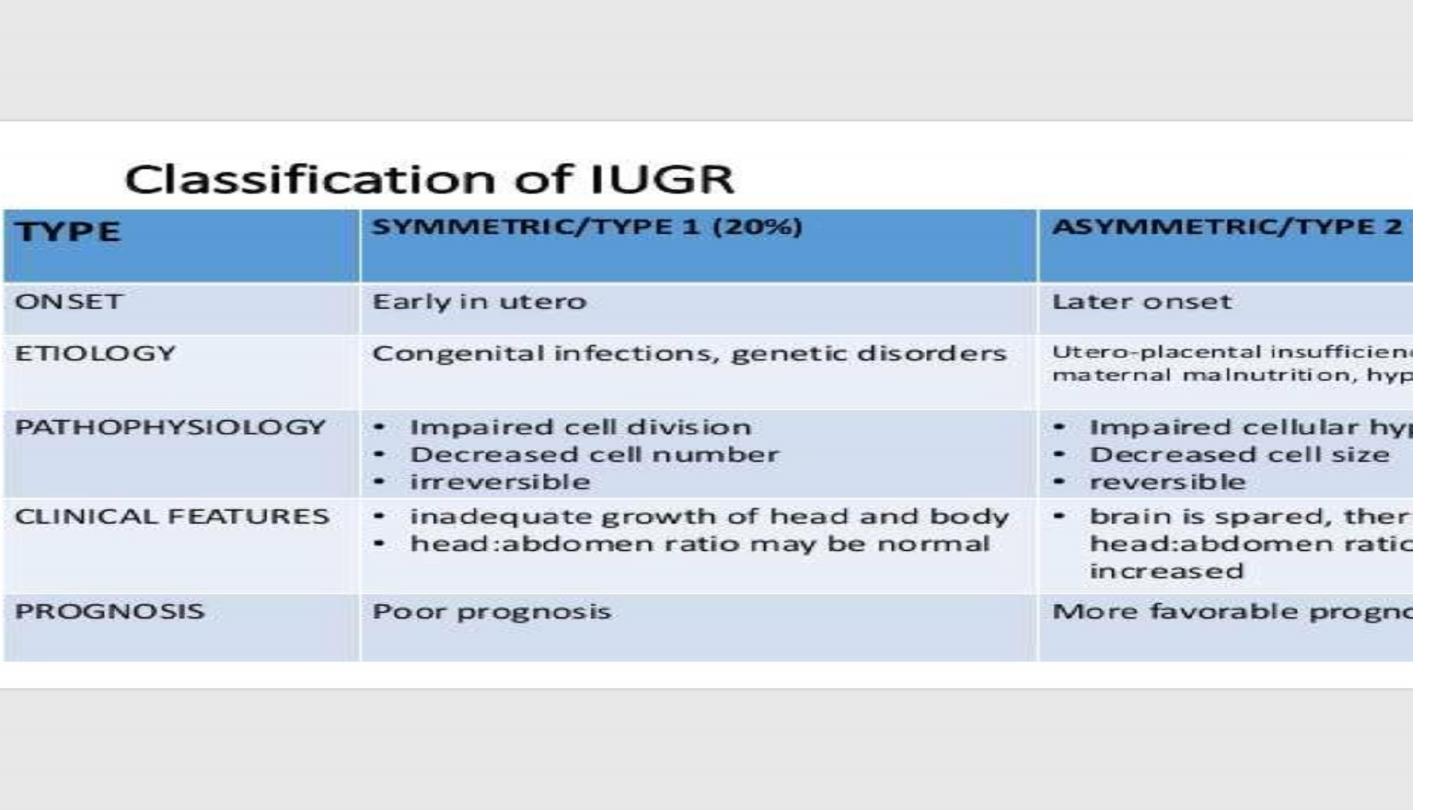
• Types of IUGR
• Symmetrical
• Asymmetrical

Causes of IUGR
• Maternal causes
• Nutritional status. , smoking , drug abuse , alcohol , maternal disease ,
therapuetic medications
• Fetal causes
• Fetal anomalies and fetal infection
• Placental cause
• Defective angiogenesis. , conditions result in uteroplacental
insufficiency

Prediction and screening
• History to identify any risk factors like ,,
• Age , parity , previous history of IUGR , any pregnancy complications
,…..
• Examination
• Assessment of SFH
• Maternal serum screening ( AFP , HCG ,E3)
• U/S abnormal uterine artery doppler ,, echogenic bowel

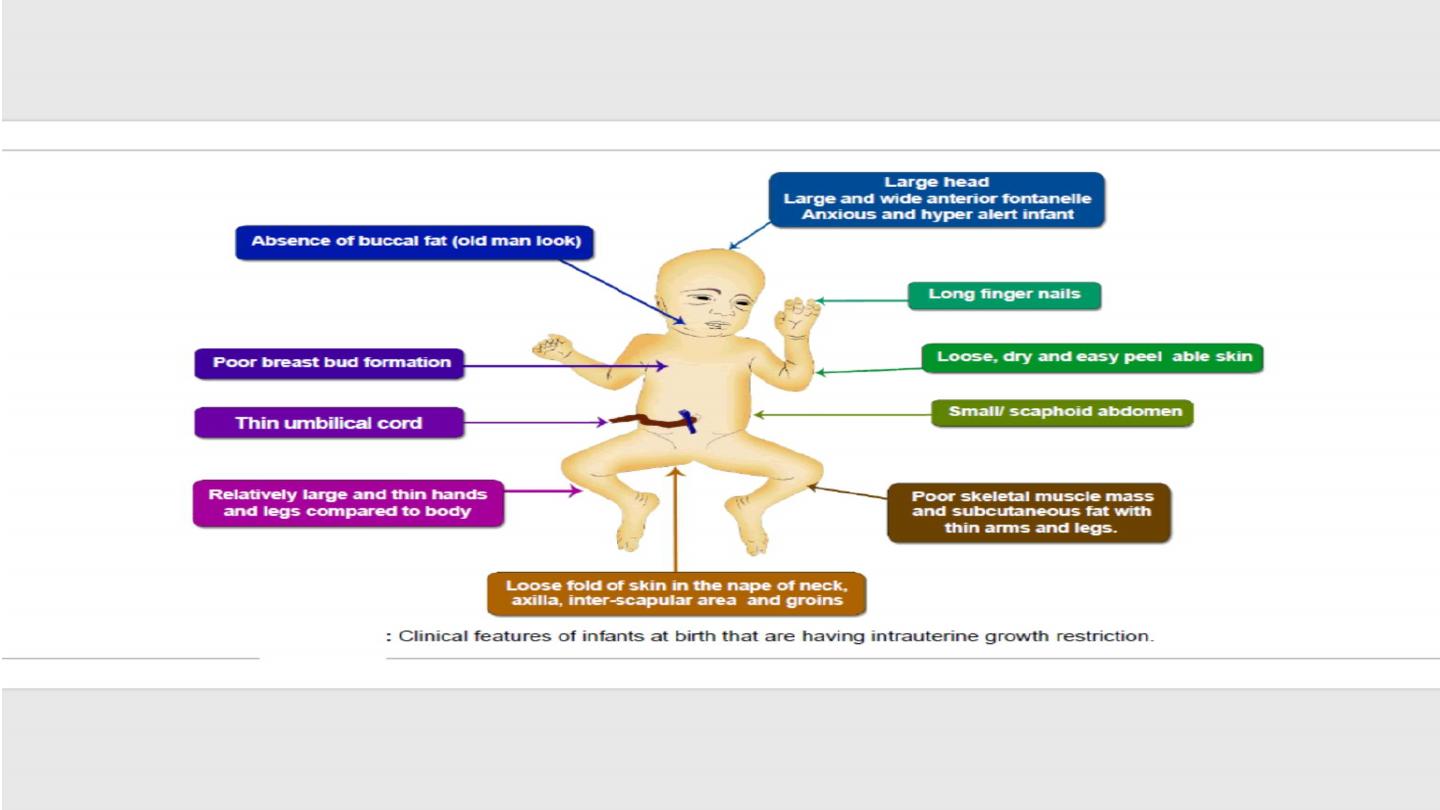
Diagnosis of IUGR
• Clinical assessment by serial measurement of SFH
• Ultrasound
• Serial biometric assessment of fetus ( BPD. , FL ,AC , EFW )
• Assessment of amount of amniotic fluid
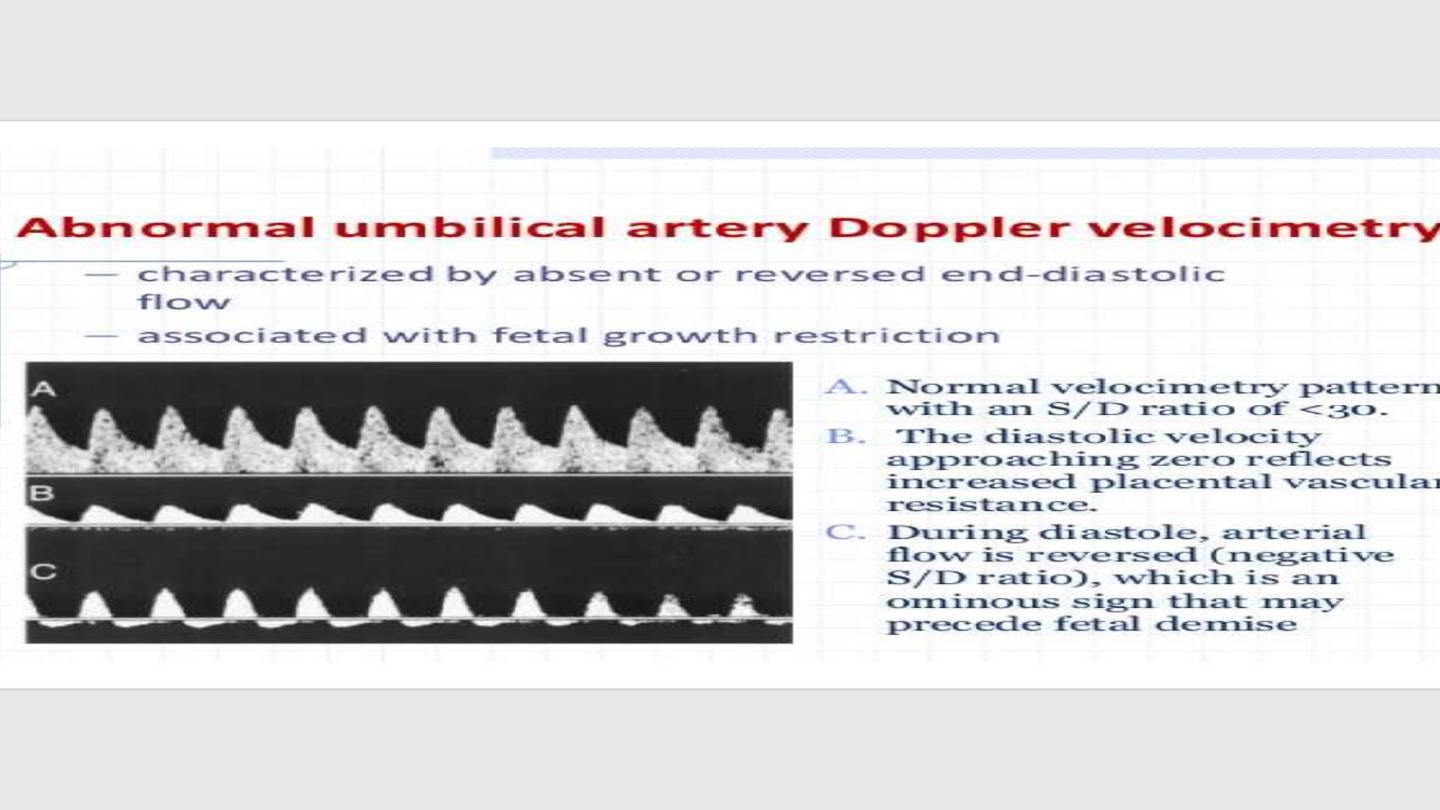
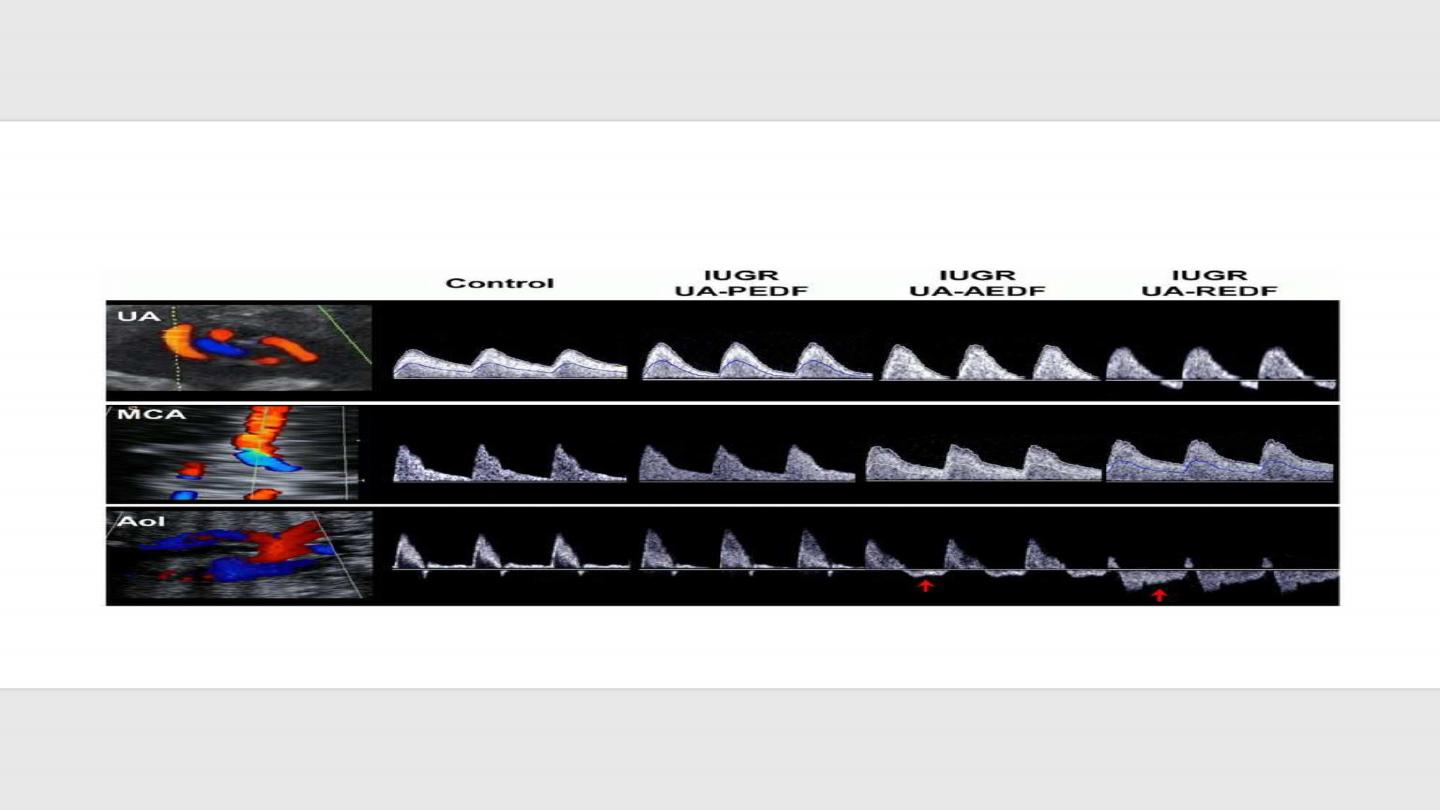
• Doppler study of umblical cord vessels
• Frequency of assessment every 2-4 weeks




Management of IUGR
• Prophylaxis
• Before pregnancy
• Identify at risk patient
• Stop smoking. ,
• Improve nutritional state if patient is malnurtioned
• Optimize maternal health and control her disease if present prior to
pregnancy
• During pregnancy
• Low dose Aspirin 75 mg
• Vit C and E

Treatment
• SGA fetus
• Conservative by observation of fetal biometry , doppler and liqour volume
• IUGR
• If diagnosed after 34 weeks ,,,,,, delivery
• Before 34 weeks
• Steroid to enhance lung maturity
• Serial observation , once there is Abnormal result (abn doppler) ,,,, delivery
• Mode of delivery
• If GA < 37 wks ,,,,,CS
• GA >37 wks ,,,, vaginal deliver is possible but with carful use of oxytocin and PG
• Continous monitoring by CTG

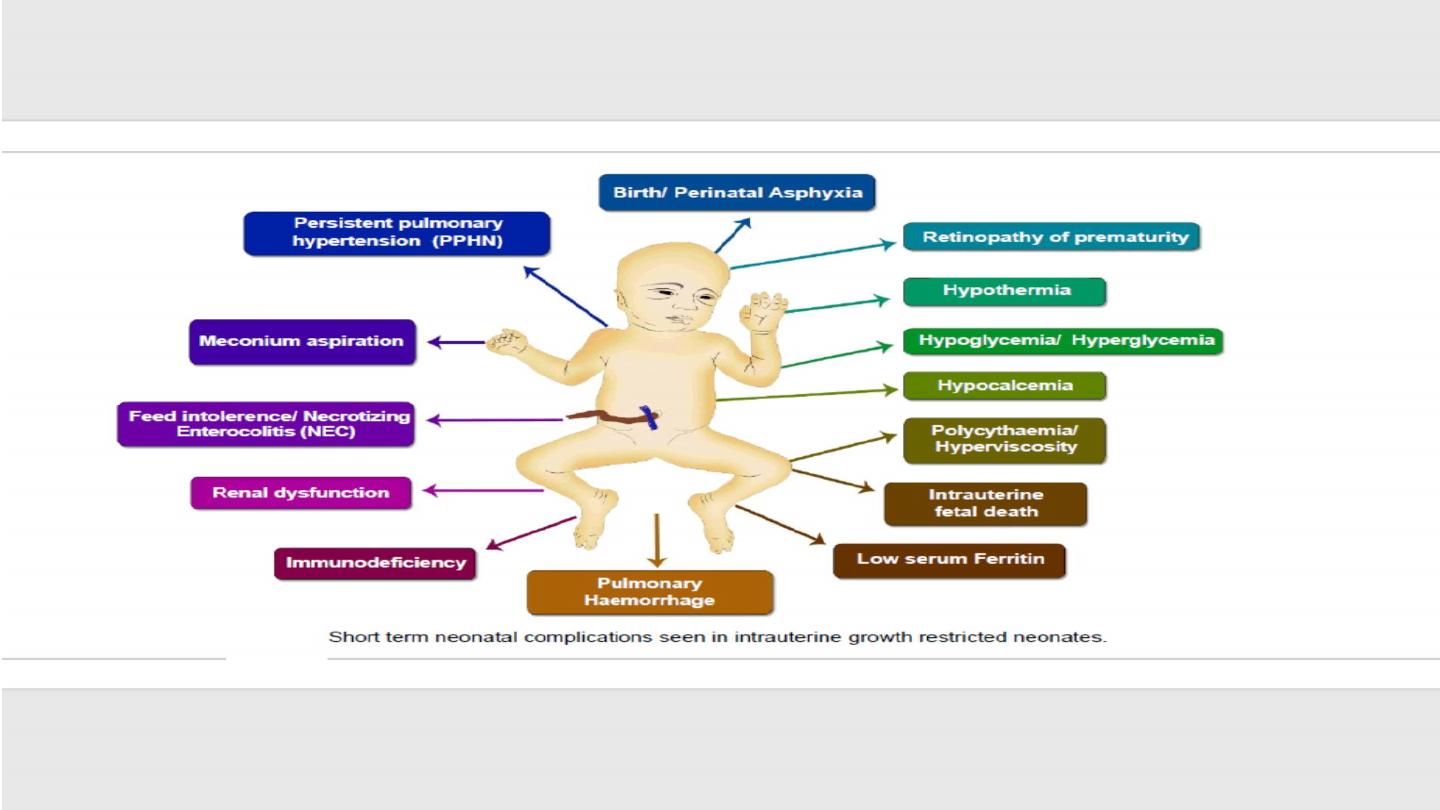
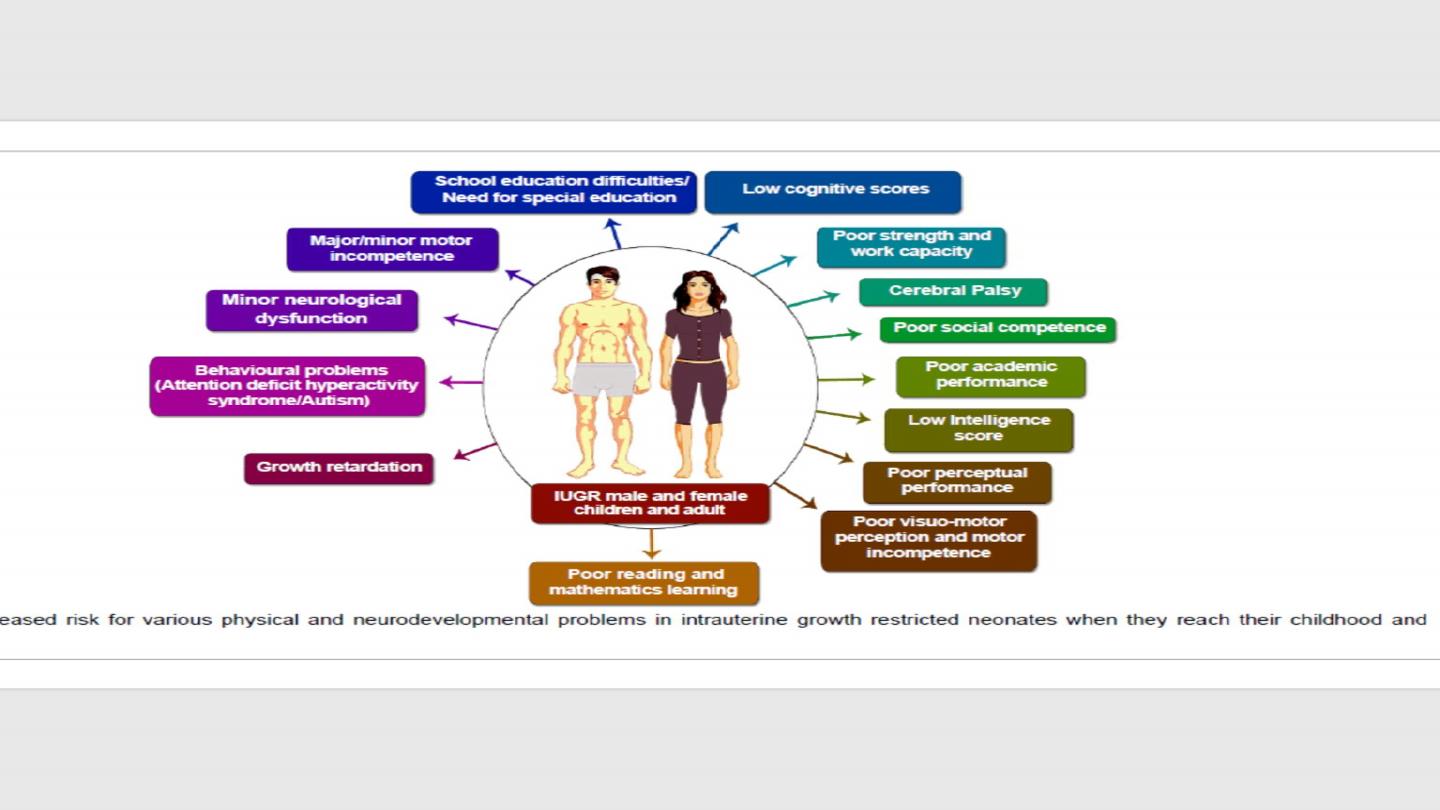

Intrauterine fetal death (IUFD)
• Definition
• Death of fetus of more than 20 weeks gestational age or fetal weight
more than 500 gm when the gestational age is unknown

Causes
• Antepartum
• Maternal
• Fetal
• Placental
• Intrapartum
• Asphyxia during labour
• Cord prolaps
• Abruptio placenta
• Rupture uterus
• Abnormal labour


Diagnosis
• History
• Loss of fetal movement
• Examination
• Fundal height less than normal
• Fetal heart can not be detected by auscultation
• Investigation
• Ultrasound (absence of fetal heart activity )
• Doppler study
• Spalding sign

Complications
• Infection and sepsis
• DIC
• PPH
• Thrombosis
• Maternal death

Management
• Psychological support to the patient
• Conservative treatment
• Patient could wait spontaneous delivery within 2-4 weeks when she
is stable and her serum fibrinogen is normal
• Active management by Termination of pregnancy
• Induction of labour
• Adequate analgesia , carful use of oxytocic drugs ,avoid amniotomy
as much as possible ,active management of 3
rd
stage of labour
• Operatve delivery. When vaginal delivery can not be conducted

Investigations
• Maternal
• Blood sample
• Urine sample
• Genital tract sample ( HVS)
• Fetal
• Blood sample
• Skin sample
• X ray
• Placental ( histop


•Thank you
