Fifth Stage
Gynecology
Dr. Sumeya – Lecture 4
1
Assisted Reproductive Technology
History of ART
►
1978- first successful birth using In Vitro Fertilization
►
1984- first successful birth using Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer
►
1986-first successful birth using Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer
Assisted Reproductive Technology
The term ART describes clinical and laboratory techniques used to achieve pregnancy
in infertile couples for whom direct correction of underlying causes are not feasible .In
principle ,IUI meets this definition .
All fertility treatments in which both eggs and sperm are handled. In general, ART
procedures involve surgically removing eggs from a woman's ovaries, combining them
with sperm in the laboratory, and returning them to the woman's body or donating them
to another woman.“
Procedures are in vitro fertilization (IVF) ,OCR, AZH, ICSI, ZIFT, PGD, GIFT, SSR
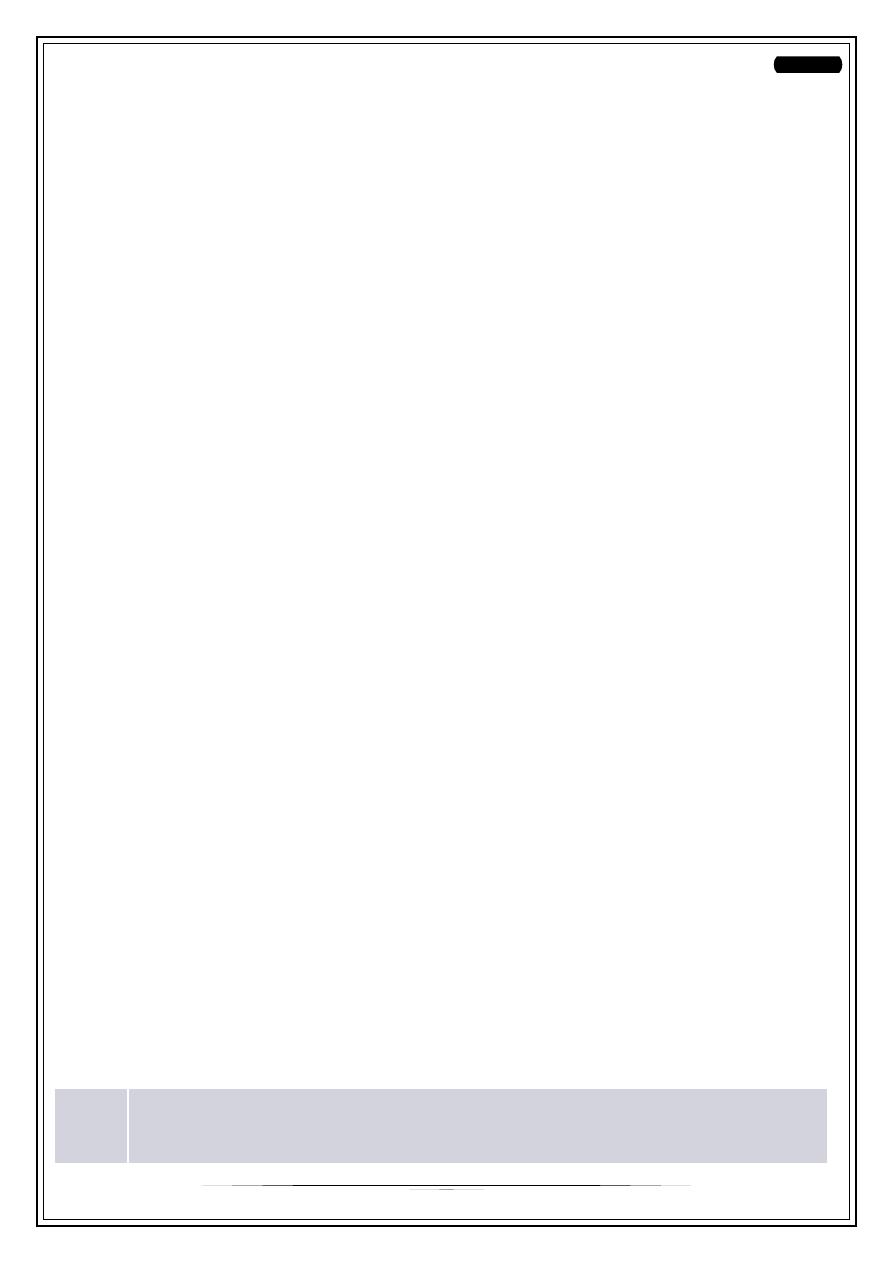
Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is performed by introducing a small sample of
prepared sperm into the uterine cavity with a fine uterine catheter. This process
usually requires mild stimulation with FSH to produce 2–3 mature follicles.
Follicular tracking is essential to avoid over or under stimulation.
The success rate of this procedure ranges between 15 and 20 per cent in top
fertility units.
This type of artificial insemination can be performed in a natural or induce cycle;
with clomid alone, Clomid and FSH injection or purely with FSH. If any form of
ovulation induction has been used it is also quite H.C.G injection approximately
36 hours prior to the insemination to ensure optimal timing with ovulation .All IUI
cycles were accompanied by ovarian stimulation with CC, HMG or recombinant
FSH, Ovarian response was monitored by plasma E2, LH concentrations and by
ovarian ultrasonography .
Indications for intrauterine insemination
1.
2.
Gross male infertility or sub fertility ( severe oligo-asthenoteratozoospermia),
for couples who cannot afford IVF or reject IVF for other reasons
2
3. Ejaculatory failure is the classical indication, since the male partner is unable
to ejaculate into the vagina
4. Cervical factor, while cervical mucus hostility is a logical indication for IUI, as
it bypasses the mucus in the cervical canal.
5. Idiopathic/unexplained infertility
6. Immunological infertility
7. Endometriosis
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
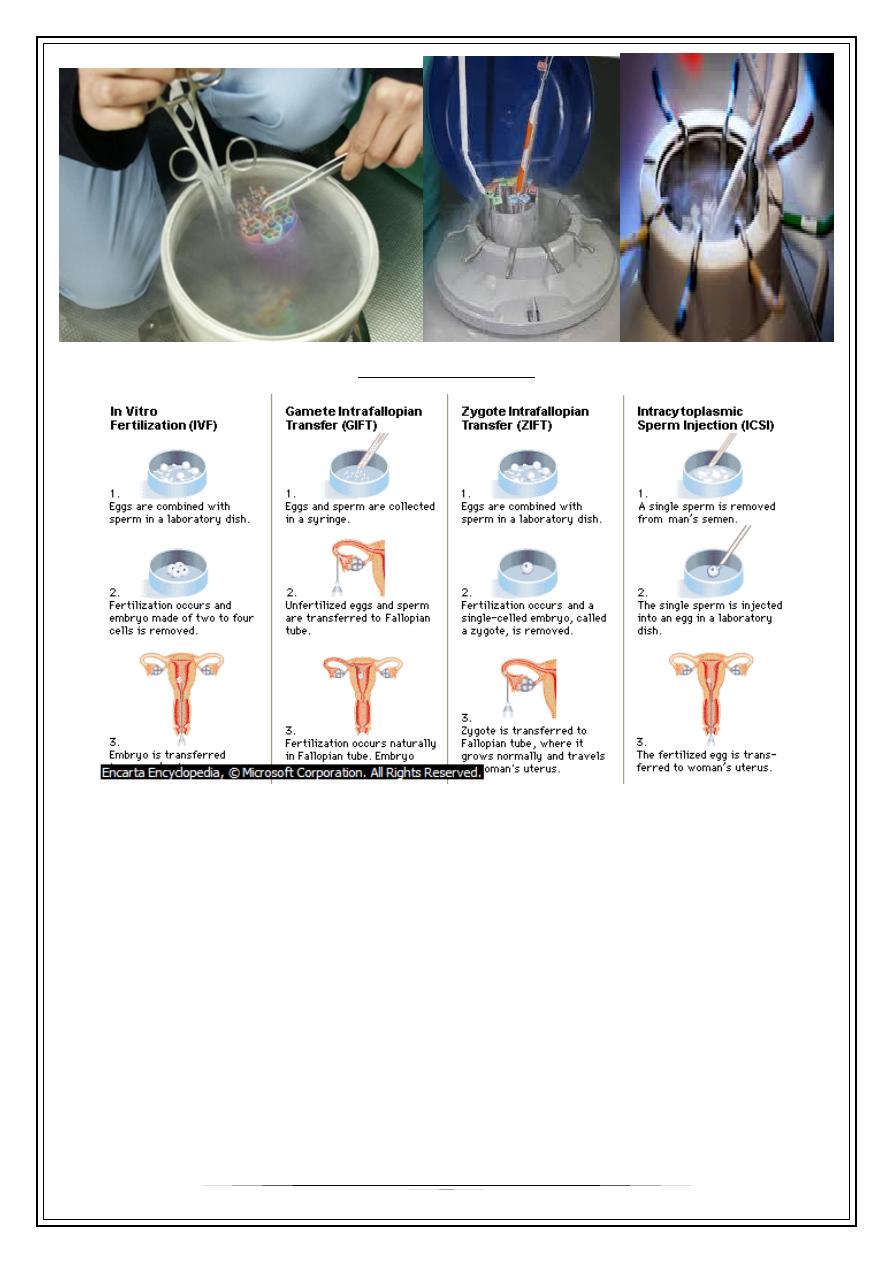
In Vitro Fertilization
This technique has been used extensively in animal
embryological research for decades, but only since 1978 has
it been successfully applied to human reproduction
Indications of IVF
Originally, IVF was designed for the treatment of severe tubal disease .
Another common indication for IVF is low sperm count.
Unexplained infertility; when unexplained infertility does not respond to traditional
treatments (clomid or stronger fertility medications combined with artificial
insemination) IVF can be an option.
IVF may also be used in conjunction with pre-implantation genetic diagnosis, PGD,
to determine the presence of certain genetic disorders in embryos. This allows for
only the unaffected embryos to be transferred back to the mother.
3
The Stimulation Phase
-
Fertility medication :Most fertility medications are agents that stimulate the
development of follicles in the ovary. Examples are gonadotropins .
-
In human reproduction the process involves stimulation of the growth of multiple
eggs by the daily injection of hormone medications.
Monitoring the cycle
There are five reasons for monitoring the cycle:
1- Beforehand, predict the ovarian response to gonadotropins.
2- Monitor the effect of pituitary down-regulation.
3- During the stimulation, evaluate whether the dose of gonadotropin is adequate.
4- Avoid the ovarian hyper stimulation syndrome( OHSS)
5-Identifying adequate follicular development during such stimulation and finally
optimizing the time of HCG administration,..
There are five methods for monitoring follicular maturation in ART cycles:
1- Serum E2.
2- Ultrasound measurements of follicular growth and endometrial thickness.
3- Ultrasound and serum E2 combined.
4- Perifollicular blood flow by means of power doppler imaging.
5- Perifollicular blood flow using three-dimensional ultrasound.
Ultrasonography in the management of ovulation induction and intrauterine
insemination
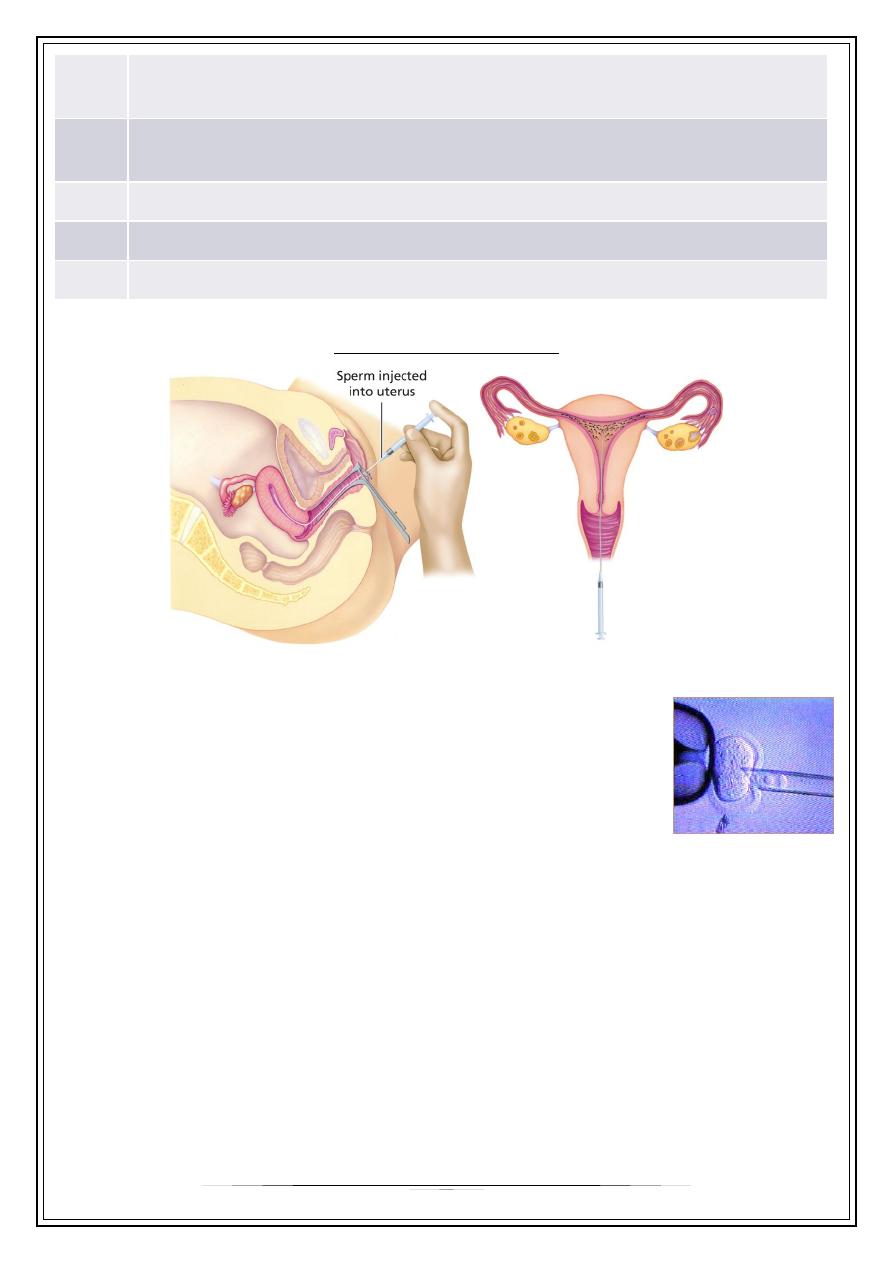
Endometrial thickness is defined as the maximal distance between the echogenic
interfaces of the myometrium and the endometrium, it is an easily measurable
ultrasonic parameter and it represents a bioassay of estrogenic activity.
On the day before H.C.G injection it is
postulated that it may predict the likelihood
of implantation, pregnancy rates were
significantly higher in the patients with an
endometrial thickness > 9 mm compared
with those of < 9 mm.An increased rate of
early miscarriage with very thin (<6 mm) or
thick endometrium (>13) .
4
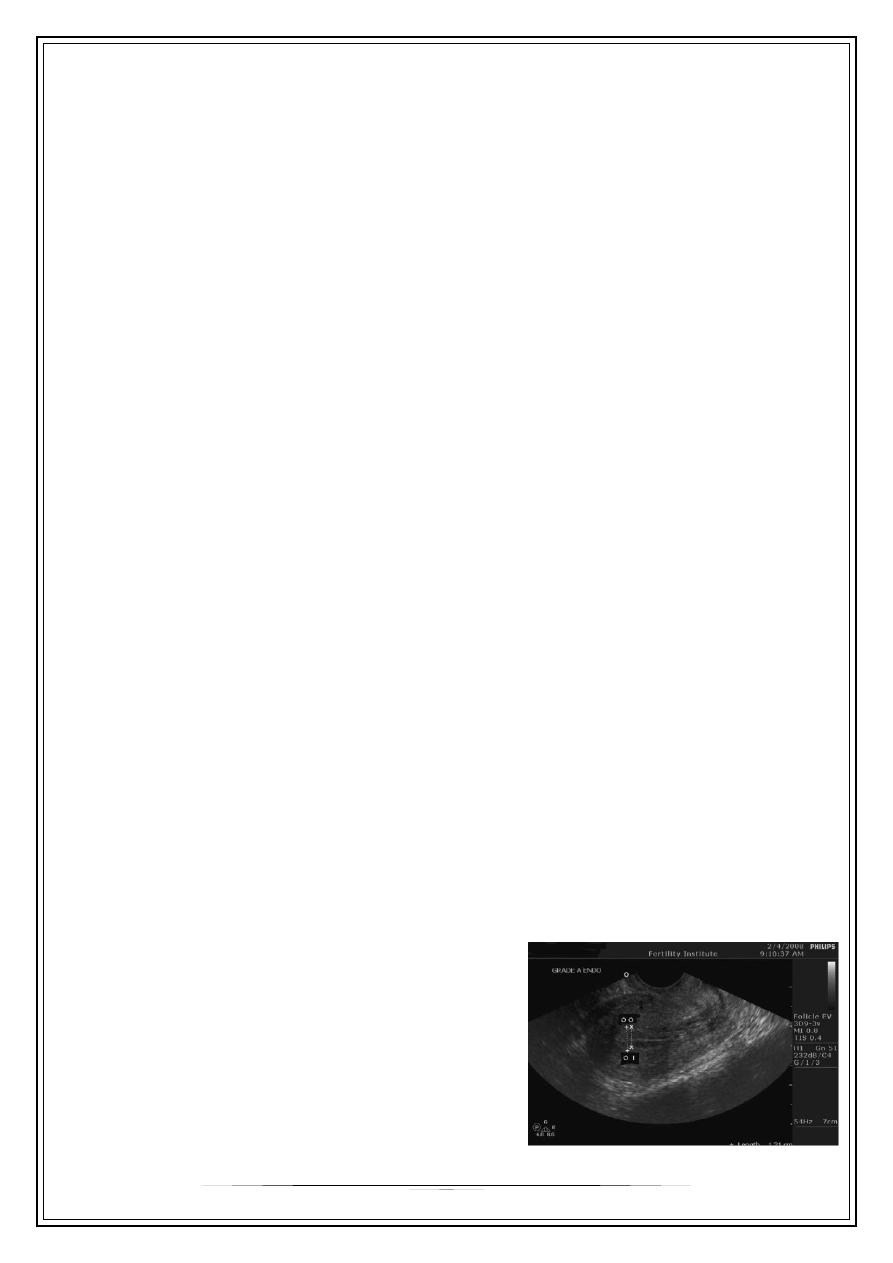
Ultrasound scan for ovaries
Examination of ovaries follows the
assessment of the uterus.. When ovaries are
examining attention should be paid to:-
ovar¬ian size, structure and relation to the
uterus. Ovarian volume should be measured
searching for ultrasonic features of polycystic
ovaries and the presence of ovarian cysts.
Sperm preparation
The ideal sperm preparation technique is to achieve the largest number of
morphologically normal motile spermatozoa in a small volume of physiological
culture media free from seminal plasma, leukocytes and bacteria.
Techniques usually used in in vitro fertilization
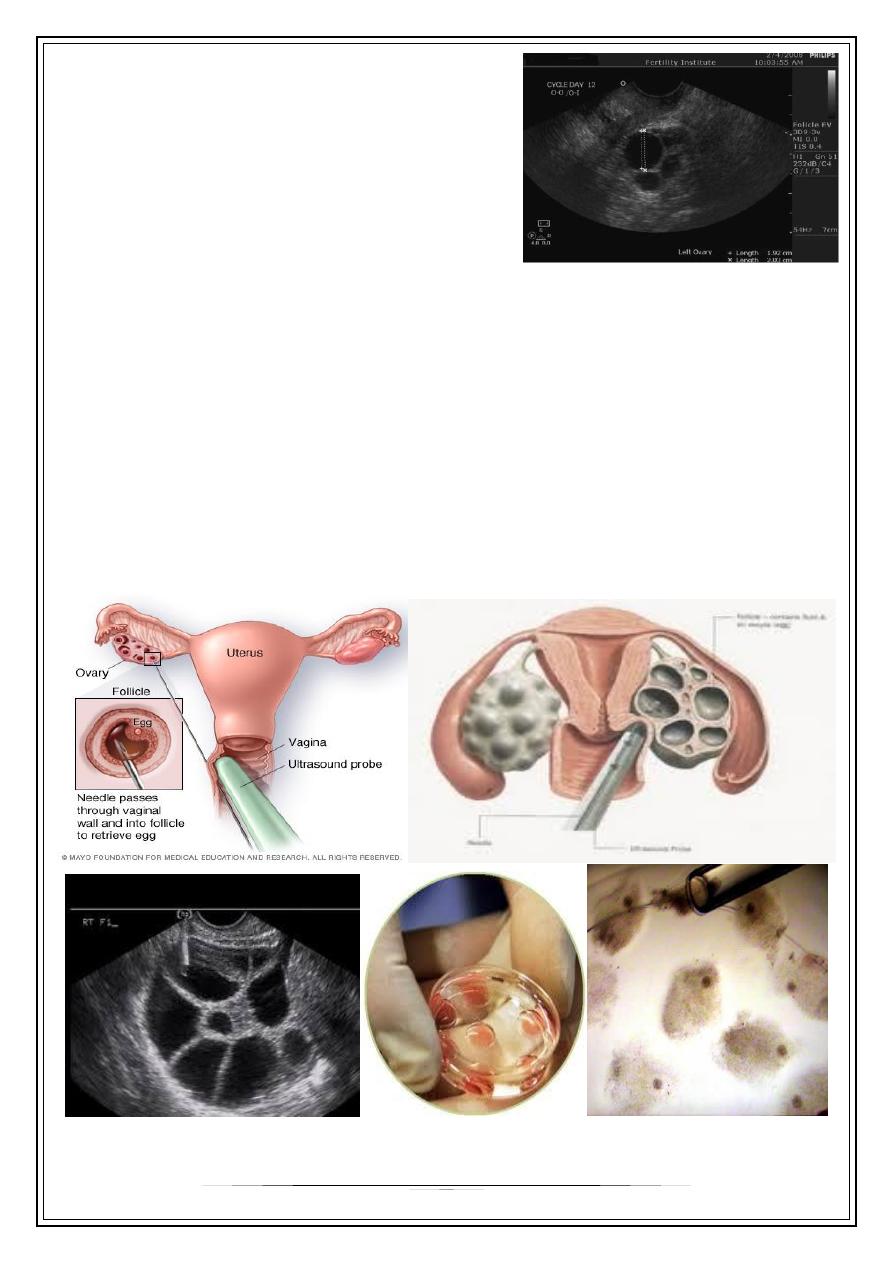
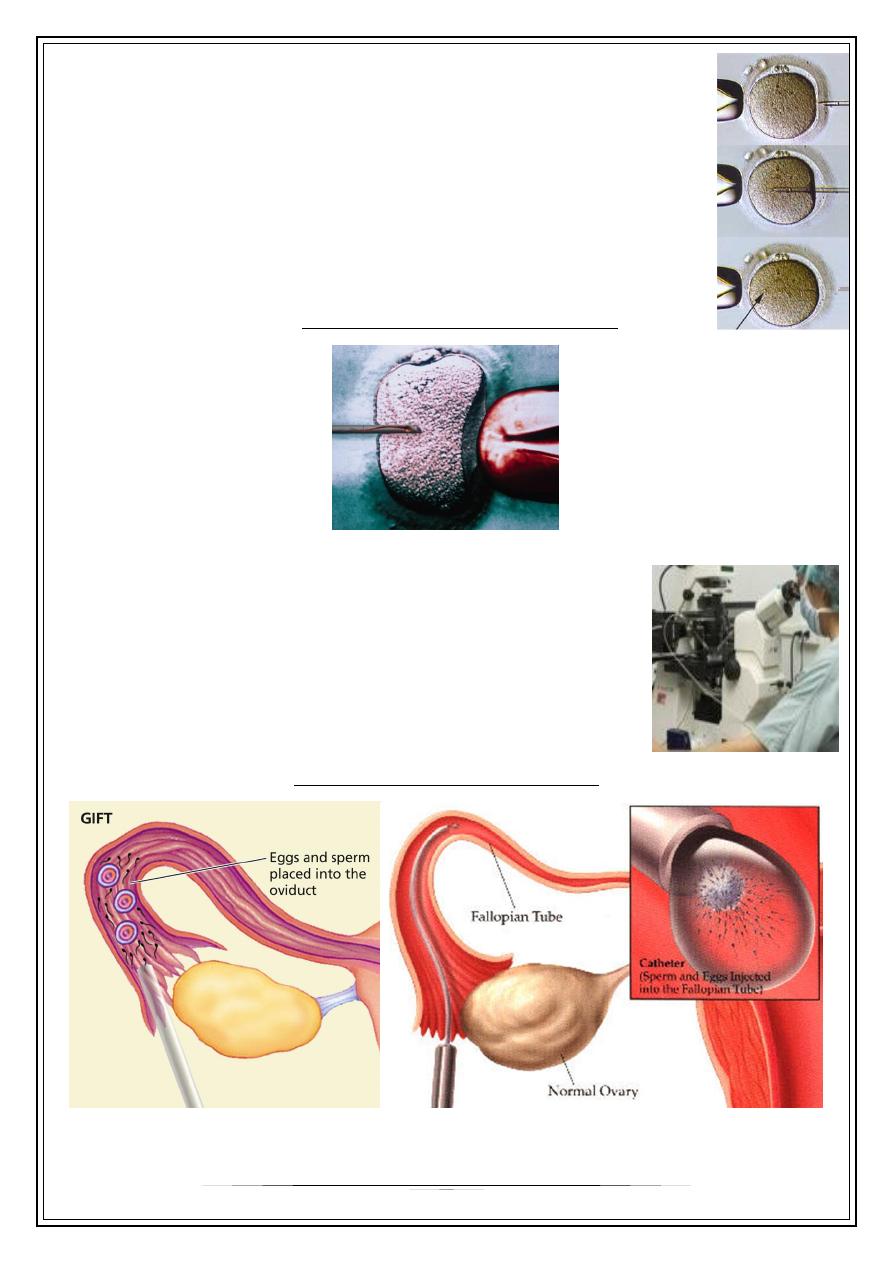
Transvaginal ovum retrieval
(OCR) is the process whereby a small needle is inserted through the back of the vagina
and guided via ultrasound into the ovarian follicles to collect the fluid that contains the
eggs.
5
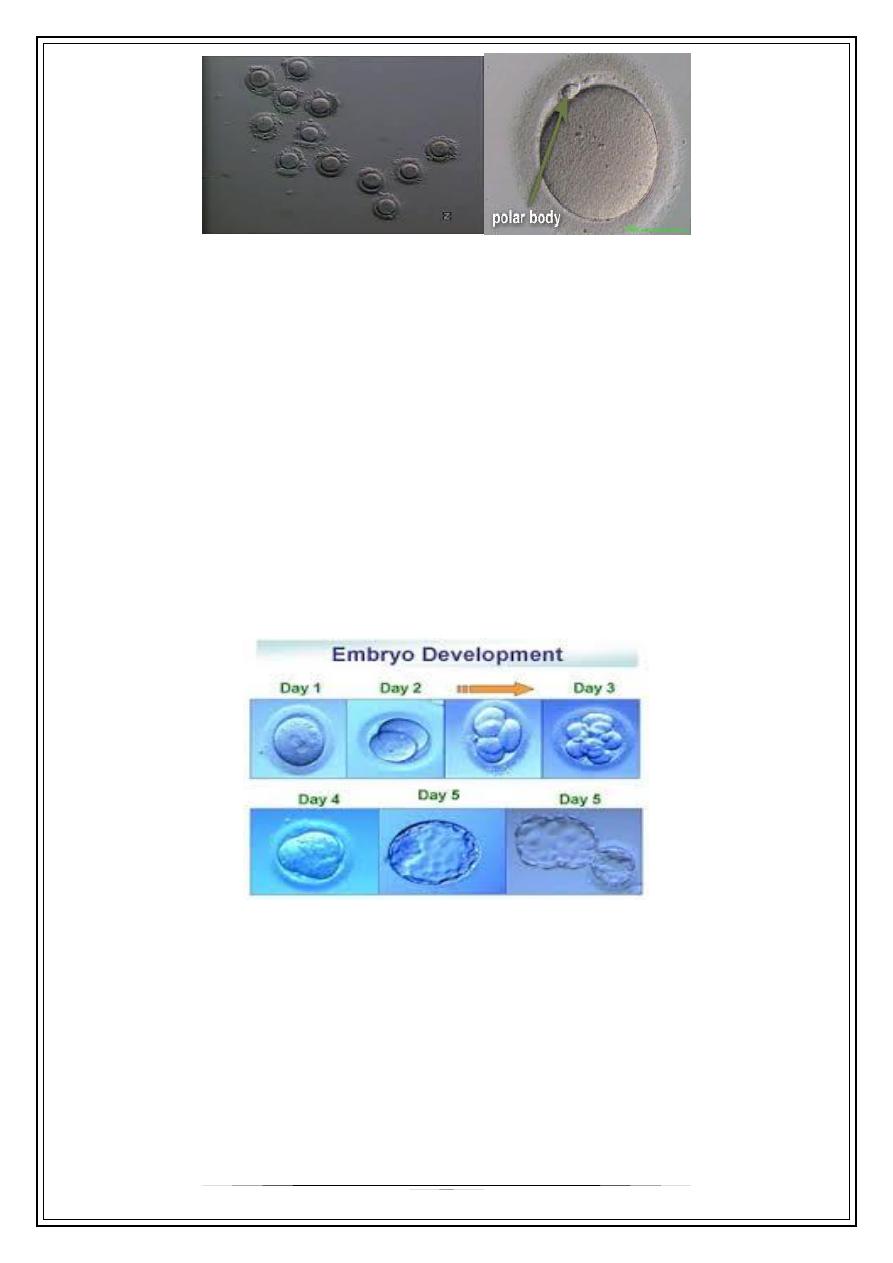
Fertilization And Culture Of The Embryos
Within a few hours after retrieval embryologist will be preparing to fertilize the
eggs.
This may be done with either traditional IVF or with ICSI.
In the former a high concentration of sperm is placed around each egg and they
are left together overnight to allow “natural” fertilization to take place. With ICSI –
intracytoplasmic sperm injection – actually inject a single sperm into each egg.
Embryo transfer
over the next 48 hours the fertilized eggs – now called embryos – will be left alone
in the incubator.. However, embryos will only grow in incubators for 3 to 5 days. At
this time, they must be transferred back into the uterus. Embryo transfers may be
done either on the third day after retrieval (day 3 transfer) or on the fifth day
(referred to as a blastocyst transfer).
Less commonly used techniques in in vitro fertilization are:
Assisted zona hatching (AZH) is performed shortly before the embryo is
transferred to the uterus. A small opening is made in the outer layer surrounding
the egg in order to help the embryo hatch out and aid in the implantation process
of the growing embryo.
Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection
6
(ICSI) is beneficial in the case of male factor infertility where
sperm counts are very low or failed fertilization occurred with
previous IVF attempt(s).
The ICSI procedure involves a single sperm carefully injected into
the center of an egg using a microneedle. With ICSI, only one
sperm per egg is needed. Without ICSI, you need between 50,000
and 100,000. This method is also sometimes employed when
donor sperm is used.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT)
In gamete intrafallopian transfer is a the technique is
similar to IVF, but the harvested eggs and sperm are placed
directly into the fallopian tubes, with fertilization occurring
in the woman's body
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT)
7
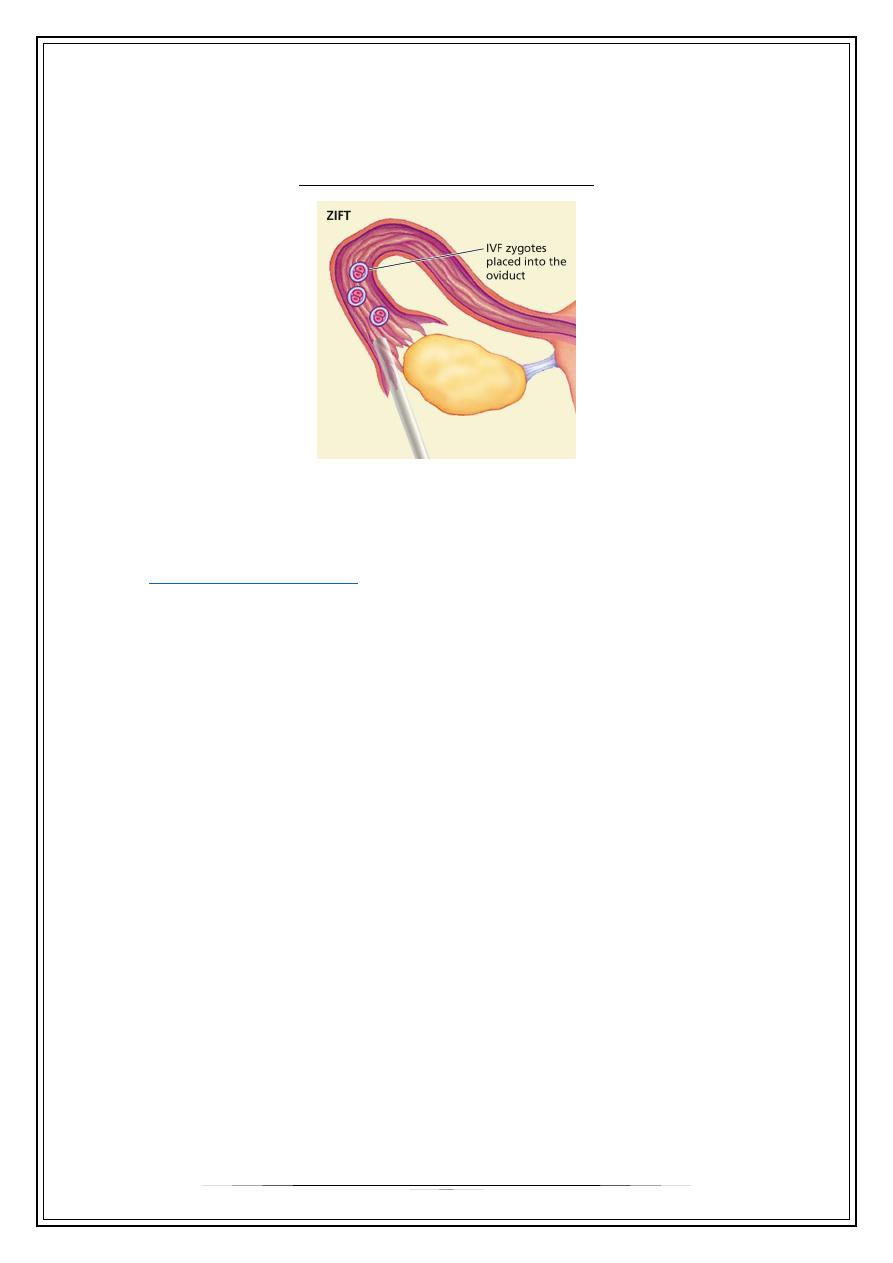
Zygote Inrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
The eggs are mixed with partner’s sperm,
but wait until fertilization occurs to place the embryos inside fallopian tube.
Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT)
Egg donors
•
are resources for women with 1- no eggs due to surgery, chemotherapy, or
genetic causes; or with 2- poor egg quality, 3-previously unsuccessful IVF cycles
or 4-
•
In the egg donor process, eggs are retrieved from a donor's ovaries, fertilized in
the laboratory with the sperm from the recipient's partner, and the resulting
healthy embryos are returned to the recipient's uterus.
Sperm donation
•
may provide the source for the sperm used in IVF procedures where the male
partner produces1- no sperm or has 2- an inheritable disease, or where the
woman being treated has 3-no male partner.
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis
•
(PGD) involves the use of genetic screening mechanisms such as fluorescent in-
situ hybridization (FISH) or comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) to help1-
identify genetically abnormal embryos and 2-improve healthy outcomes.
•
Removal and genetic analysis of a single cell from a 3- to 5-day old embryo
•
Used to select embryos free of genetic disorders for implantation and
development.
•
Removal of one cells does not affect growth of the embryo in any way—the
cells have not yet been activated to become a specific organ of the body

8
Surgical sperm retrieval
Where the sperm quality is low but sperm are present, ICSI is required to help
achieve a pregnancy.
However, in the absence of naturally ejaculated sperm, patients will have to
undergo surgical sperm retrieval (SSR). SSR can be performed under sedation or
general anaesthetic. A fine needle is inserted into the epididymis or the testicular
tissue to obtain sperm or testicular tissue with sperm, respectively.
The retrieved sperm can then be cryopreserved or injected into the oocyte as
part of a fresh IVF/ICSI cycle.
Cryopreservation of gametes
Sperm or oocyte can be cryopreserved for later use.
Often this process is very useful in preserving fertility for patients undergoing
chemo/radiation therapy for cancer.
Currently, the pregnancy rate for thawed sperm/egg in top fertility centres is very
near to that of normal IVF cycles.
This process can also be used for storage of gametes from donors who wish to
donate their sperm or eggs for altruistic reasons to help couples with fertility
problems.
Frozen Embryos
Frozen embryos: Specialists may freeze additional
embryos from a woman's cycle for later use. They
may also freeze embryos of a donor in order to have
them ready to place in a surrogate mother's uterus at
the appropriate moment in the surrogate's natural or
hormone-replaced cycle.
9
ART Procedures:
The Complications Of IVF
Serious complications from IVF are rare. In general, complications can be divided into 4
categories:
complications from retrieval,
hyperstimulation,
multiple pregnancies, and
emotional stress.
Thank you
