
LECTEURE # 2 :
STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING
Complete C++ Program
Dr. Abdalrahman R. Qubaa
Systems & Control Department
Electronics Engineering college
Nineveh University
First Stage
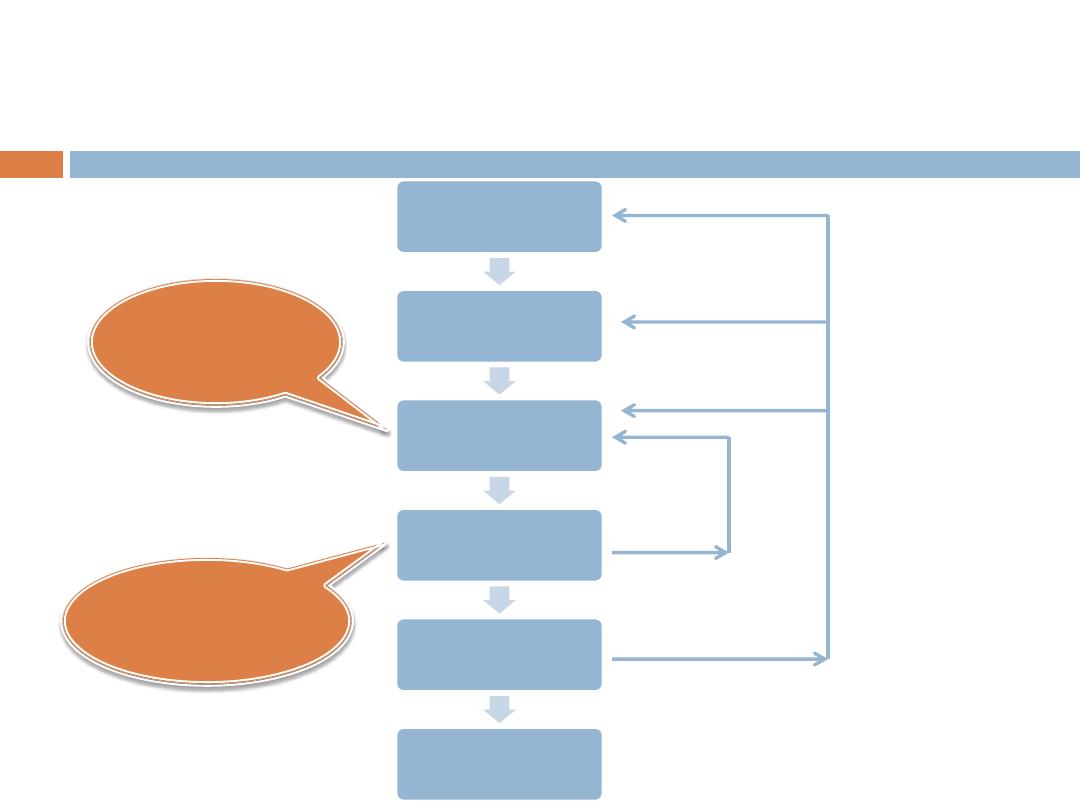
The Problem Cycle
Analysis–Coding–Execution
2
Problem Analysis
Algorithm Design
Coding
Complier
Execution
Get Results
Errors
Errors
Using Any
Programming
Language
Translate Code To
Machine
Language

The famous
Hello world program
When learning a new language, the first program people
usually write is one that salutes the world :
Here is the Hello world program in C++.
#include <iostream.h>
int main()
{
cout << “Hello world!”;
return 0;
}

A C++ program
//
include headers; these are modules that include functions that you may use in your
program; we will almost always need to include the header that defines cin and
cout; the header is called
<iostream.h>
1.
#include <iostream.h>
2.
int main()
3.
{
4.
//variable declaration
5.
//read values input from user
6.
//computation
7.
//and print output to user
8.
return 0;
9.
}
After you write a C++ program you compile it; that is, you run a program called compiler
that checks whether the program follows the C++ syntax,
if it finds errors, it lists them, If there
are no errors, it translates the C++ program into a program in machine language which execute.
.1
ةٌوناثلا جماربلا فٌرعت
(
من المكتبة
)
ًالت
عملٌ ًكل جمانربلا اهجاتحٌ
.
.2
ًسٌئرلا جمانربلا مسا فٌرعت
(
ةٌسٌئرلا ةلادلا
.)
.3
عالمة االبتداء
,
لكتابة اوامر البرمجة بعدها
.
.4
راتٌغتملا فٌرعت
.5
م من المستخدمٌق ةءارق وا
.6
نةٌعم تاباسح ءارجاوا
.7
او طباعة المخرجات
.
.8
مة صفرٌقلا ةداعاب جمانربلا ءاهتنا ىلع لٌلد
.
.9
عالمة انتهاء اوامر البرمجة
(
اي حصر اوامر
تٌكاربلا ةملاع لخادب ةجمربلا
)
Complete Program
5
1
// Fig. 2.1: fig02_01.cpp
2
// Text-printing program.
3
#include
<iostream.h>
// allows program to output data to the screen
4
5
// function main begins program execution
6
int
main()
7
{
8
cout <<
"Welcome to C++!\n"
;
// display message
9
10
return
0
;
// indicate that program ended successfully
11
12
}
// end function main
Welcome to C++!
comments
statement
main function
preprocessor directive
braces
string literal
output on screen
#include <iostream>
int
main()
{
Cout << “welcome to
c++!\n”
return
0;
}
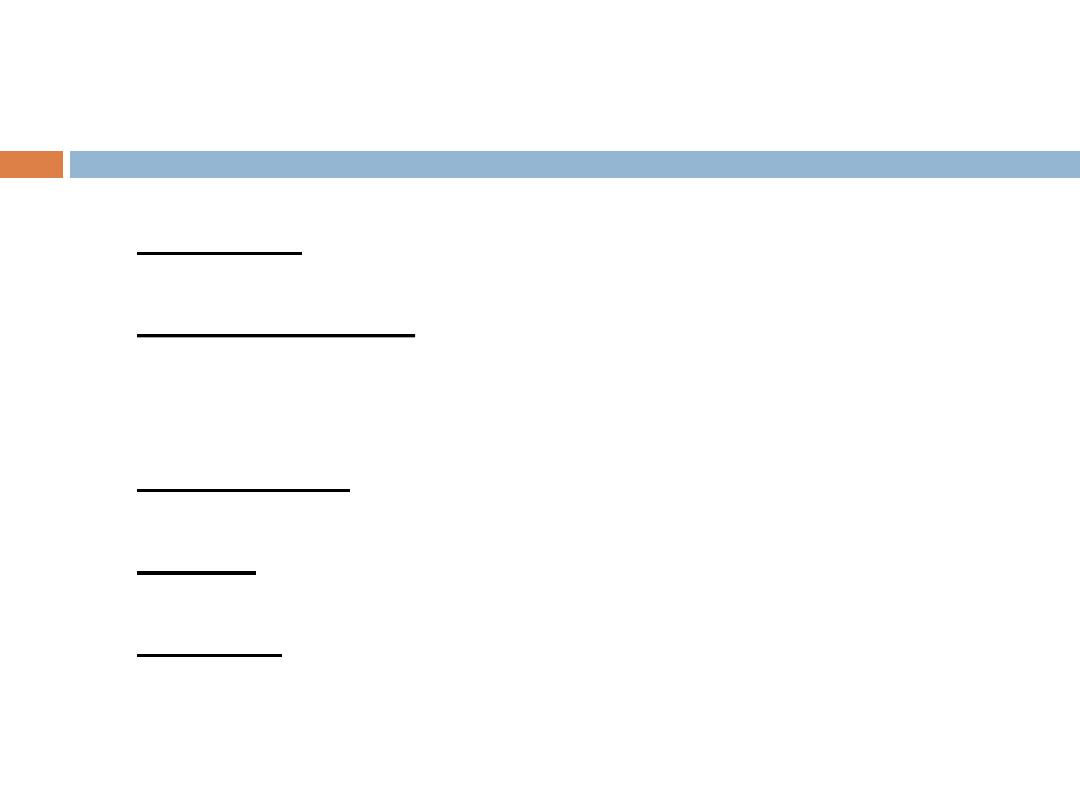

C++ Program Structure
1.
Comments: remarks that are ignored by the compiler
2.
Compiler directives: commands for compiler, which are needed
to compile and run program effectively
3.
Main function: where every program begins
4.
Braces: mark the beginning and ending code blocks
5.
Statement: a line of C++ code
6

1. Comments
Explain programs, their purpose, authors names and future
modification notes to other programmers
Improve program readability
Ignored by compiler
Single-line comment
Begin with (
//
)
Multi-line comment
Start with /*
End with */
7
// Fig. 2.1: fig02_01.cpp
// Text-printing program
/* Fig. 2.1: fig02_01.cpp
Text-printing program */
2. Preprocessor Directives
Instructions to the compiler rather than part of C++ language
Tells preprocessor stage to include the input/output stream header
file
<iostream.h>
Begin with
#
It tells the compiler to put code from
iostream
into the program
before actually creating the executable.
Forgetting to include the file will result in a compilation error.
8
#include
<iostream.h>
name of header file
3.
main
Function
Block of codes carries out a specific task
Part of every C++ program
ONLY one function in a program must be
main
Can or can’t be “return” a value
Returns an integer; once return
Body is delimited by braces { }
return
statement
The value 0 indicates the program terminated successfully
9
int
main()
{
return
0;
}

Rules of building a program in C++
10
1.
Must include
<
iostream.h>
for
cout
to work properly
2.
C++ is case sensitive.
1.
Make sure you don’t capitalize any of the letters in C++ keywords.
(Main is different that main)
3.
Every statement ends with a statement terminator: semicolon(
;
).
1.
except for function header, function braces and preprocessor directives.
4.
String literals must be enclosed in “ ”.
5.
Main function must return a value to the OS.
6.
Every opening brace { must have an enclosing brace }.
7.
Indentation is for the convenience of the reader; compiler ignores all spaces and
new line; the delimiter for the compiler is the semicolon (
;
).
Variable declaration
Type-name variable-name
Meaning: variable <variable-name> will be a variable of type
<type>
Where type can be:
int
//integer
double
//real number
char
//character
Example:
int a, b, c;
double x;
int sum;
char my-name;
Declaration Stage
Input statements
Standard Input stream object
cin >> variable-name;
Connected to the Keyboard
Defined in input/output stream header file
<
iostream.h>
Meaning: read the value of the variable called <variable-name>
from the user,
Example:
cin >> a;
cin >> b >> c;
cin >> x;
cin >> my-name;
Input Stage

Output statements
Standard output stream object
cout
<<
“Connected” to screen
Defined in input/output stream header file
<
iostream.h>
Example
cout << "Hello";
Inserts the string "Hello" into the standard output then
displays to the screen
13
Output statements
cout << variable-name;
Meaning: print the value of variable <variable-name> to the user.
cout << “any message “;
Meaning: print the message within quotes to the user.
cout << endl;
Meaning: print a new line.
Example:
cout << a;
cout << b << c;
cout << “This is my name: “ << my-name ;
cout << endl;
Output Stage
Escape Sequences
15
Escape
sequence
Description
\n
Newline. Position the screen cursor to the beginning of the next line.
\t
Horizontal tab. Move the screen cursor to the next tab stop.
\r
Carriage return. Position the screen cursor to the beginning of the current
line; do not advance to the next line.
\a
Alert. Sound the system bell.
\\
Backslash. Used to print a backslash character.
\'
Single quote. Use to print a single quote character.
\"
Double quote. Used to print a double quote character.
Escape characters
A character preceded by a backslash
"\"
Indicates “special” character output.
Example:
"\
n”
Cursor moves to beginning of next line on the screen.
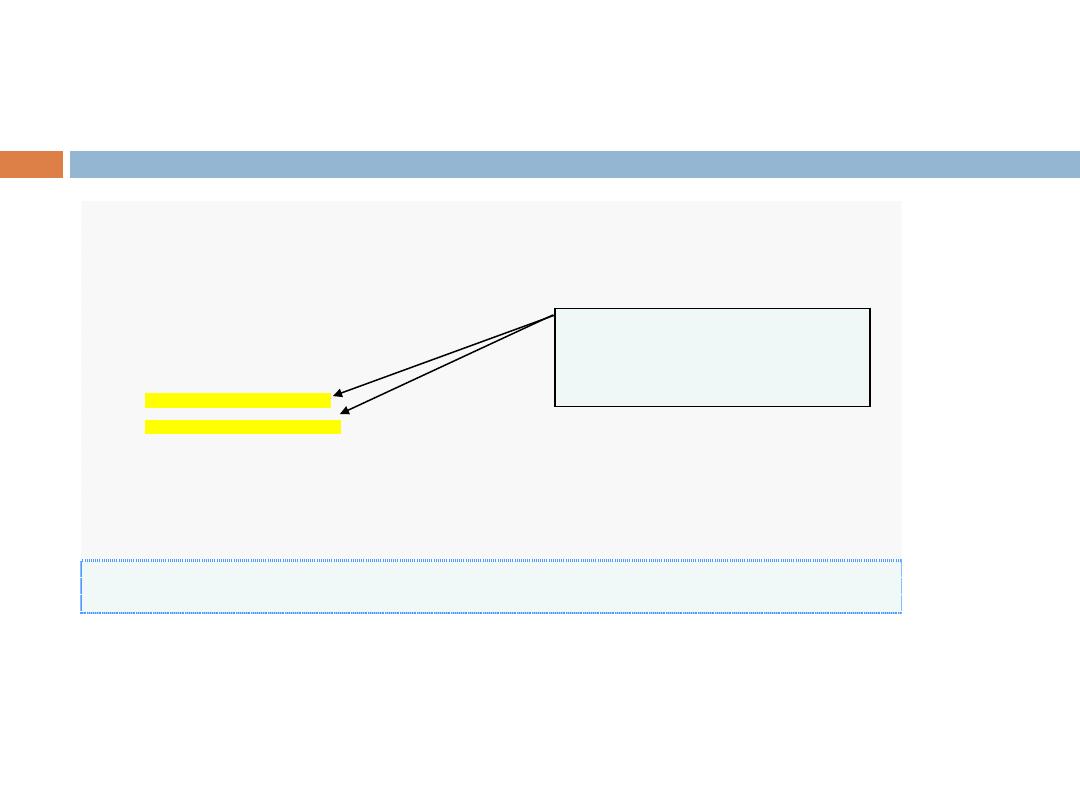
Modifying First Program - 1
16
1
// Fig. 2.3: fig02_03.cpp
2
// Printing a line of text with multiple statements.
3
#include
<iostream.h>
// allows program to output data to the screen
4
5
// function main begins program execution
6
int
main()
7
{
8
cout <<
"Welcome "
;
9
cout <<
"to C++!\n"
;
10
11
return
0
;
// indicate that program ended successfully
12
13
}
// end function main
Welcome to C++!
Multiple stream insertion
statements produce one line
of output
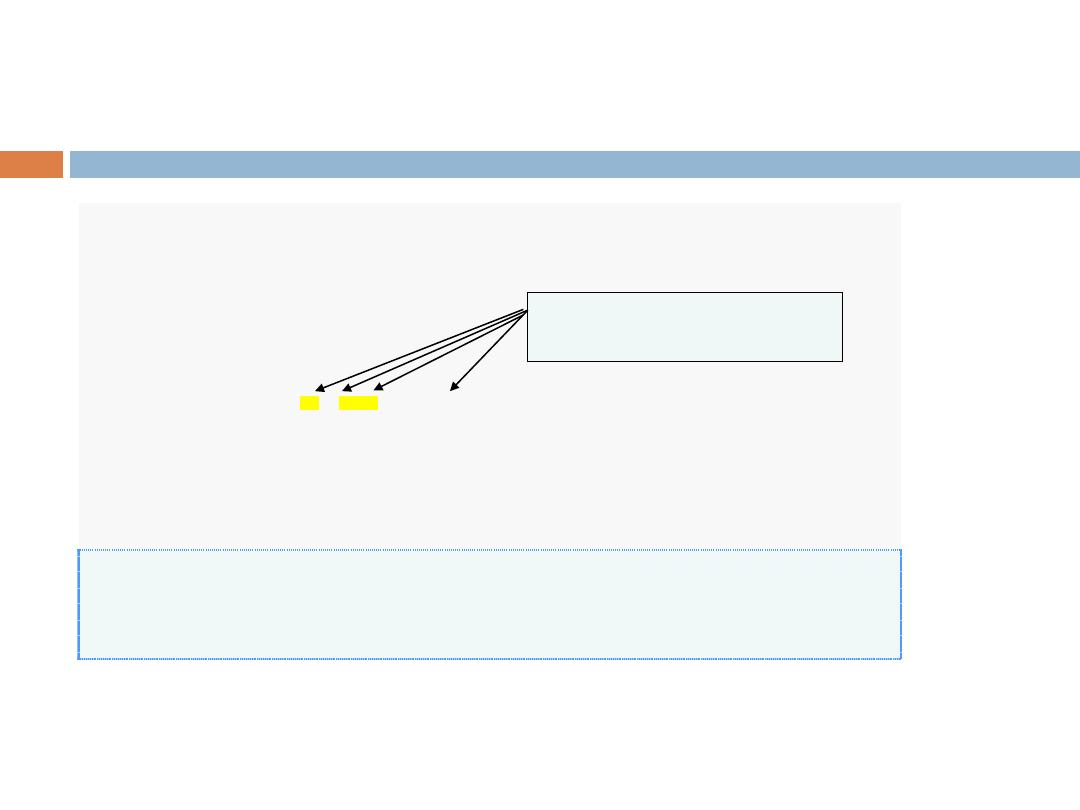
Modifying First Program - 2
17
1
// Fig. 2.4: fig02_04.cpp
2
// Printing multiple lines of text with a single statement.
3
#include
<iostream.h>
// allows program to output data to the screen
4
5
// function main begins program execution
6
int
main()
7
{
8
cout <<
"Welcome\nto\n\nC++!\n"
;
9
10
return
0
;
// indicate that program ended successfully
11
12
}
// end function main
Welcome
to
C++!
Use newline characters to
print on multiple lines

Exercise - 1
18
Write a program that display your name, class, section,
computer science degree, and your age.
Example (screen output):
Ahmad Ali
First year/Group A
Systems & Control Department
My computer science degree= 70.5
My age= 20
