
LECTURE # 7 :
STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING
Repetition Statements
(while)
D. Abdalrahman R. Qubaa
First Class, System and Control Engineering Dep.

Content
2
Types of repetition statements
while repetition statement
Counter-controlled repetition
do..while repetition statement
Nested control statements

Loop : Repetition statements
Some times we need to repeat a specific course of actions either a specified
number of times
or
until a particular condition is being satisfied.
For example :
To calculate the Average grade for 10 students.
To calculate the bonus for 10 employees.
To sum the input numbers from the user as long as he/she enters positive
numbers.
A loop statement:- allows us to execute a statement or group of statements
multiple times.
There are three methods of which we can repeat a part of a program. They are:
while
statement
do
..
while
statement
for
statement
3
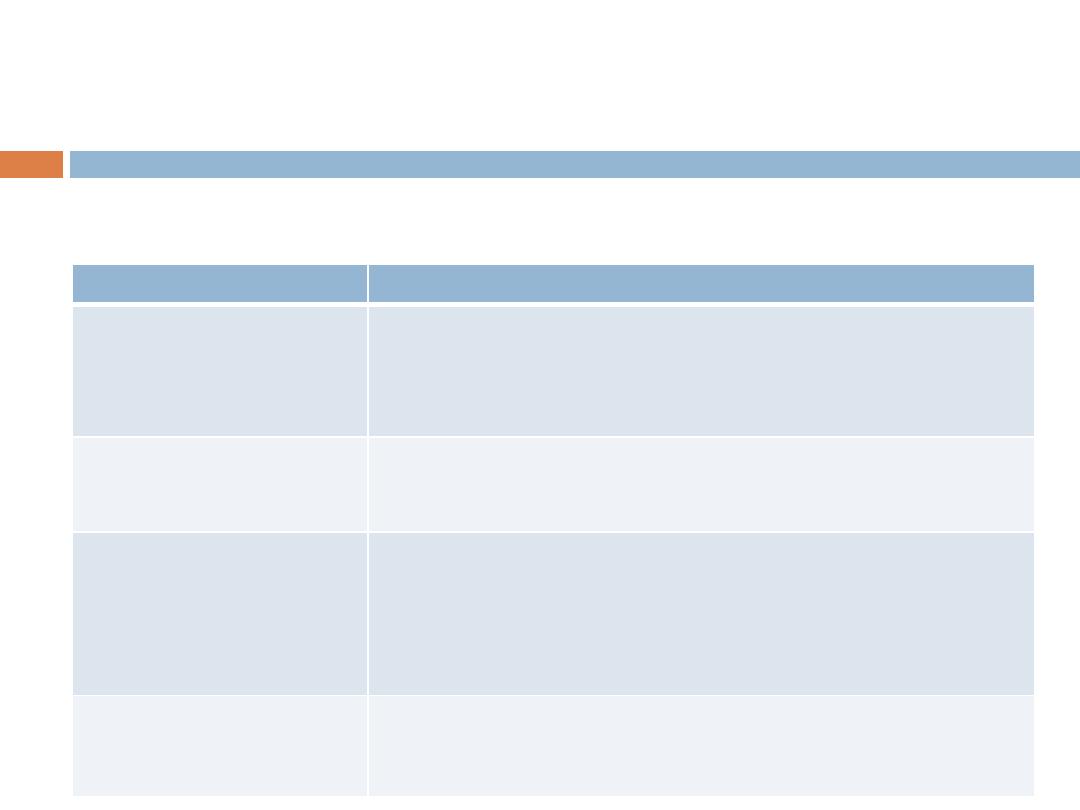
LOOP TYPES
Description
Loop Type
Repeats a statement or group of statements while a given
condition is true. It tests the condition before
executing the loop body.
while
loop
Like a ‘while’ statement, except that it tests the
condition at the
end
of the loop body.
do...while
loop
Execute a sequence of statements multiple times and
abbreviates the code that manages the loop variable.
for
loop
You can use one or more loop inside any another
‘while’, ‘for’ or ‘do..while’ loop.
nested loops
4
C++ programming language provides the following type of loops to handle
looping requirements.
while
Repetition Statements
Actions repeated while condition remains true
Syntax
One of the actions should causes condition to becomes false
Example
5
while
(condition)
{
action1;
action2;
.
.
actionN;
}
int
product = 3;
while
( product <= 30 )
{
product *= 3;
}
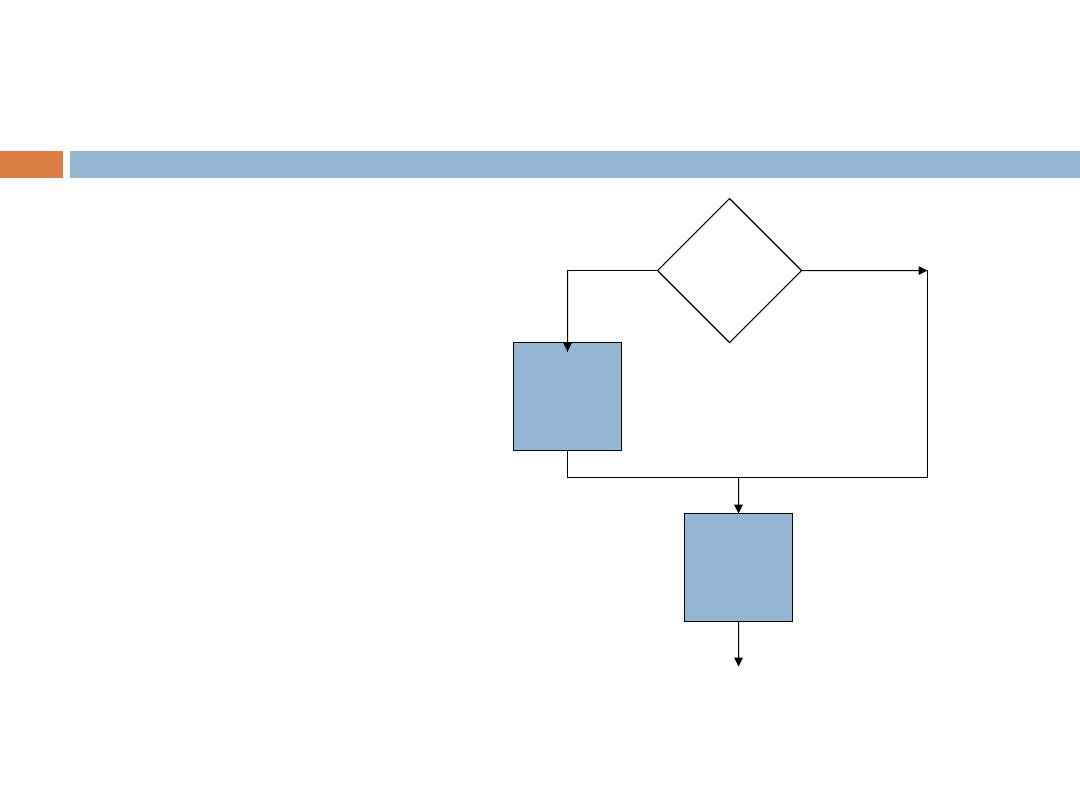
while
Repetition Statements (cont.)
while (condition)
{
S1;
}
S2;
condition
S1
S2
True
False

Counter-controlled Repetition
Uses a variable to control number of loops
’ iterations
Also known as definite repetition
Number of repetitions known beforehand
Requires
1.
Name
of loop control variable
2.
Initial value
of loop control variable
3.
Condition
to test of reaching final value
4.
Update
loop control variable
7
control var Name;
Initialize control var ;
while
(condition)
{
action1;
action2;
.
.
actionN;
update control var;
}

8
Counter-controlled Repetition
(cont.)
1- loop counter is any numeric variable ( int , float ,….).
2- when using a counter , the while loop is called counter–controlled loop.
3- The initial value of the loop counter is up to you, but you have to increment it to
avoid endless loops.
While ( continuation condition)
{
Action statement 1 ;
Action statement 2 ;
.
.
Action statement n ;
}
•
Example
: Write a program that calculates and prints out
the Average grade for
6
students.
int
counter = 1;
int
grade=0 , sum=0;
while
(
counter <=6
)
{
cout <<"Enter grade for student no " << counter <<"\n";
cin >>grade;
sum += grade;
counter ++;
}
cout <<"Average Grade is " << sum/counter <<"\n";
9
1-Name 2-Initial for counter
3- Condition to test the counter
4- Update control variable
Counter-controlled Repetition
(cont.)
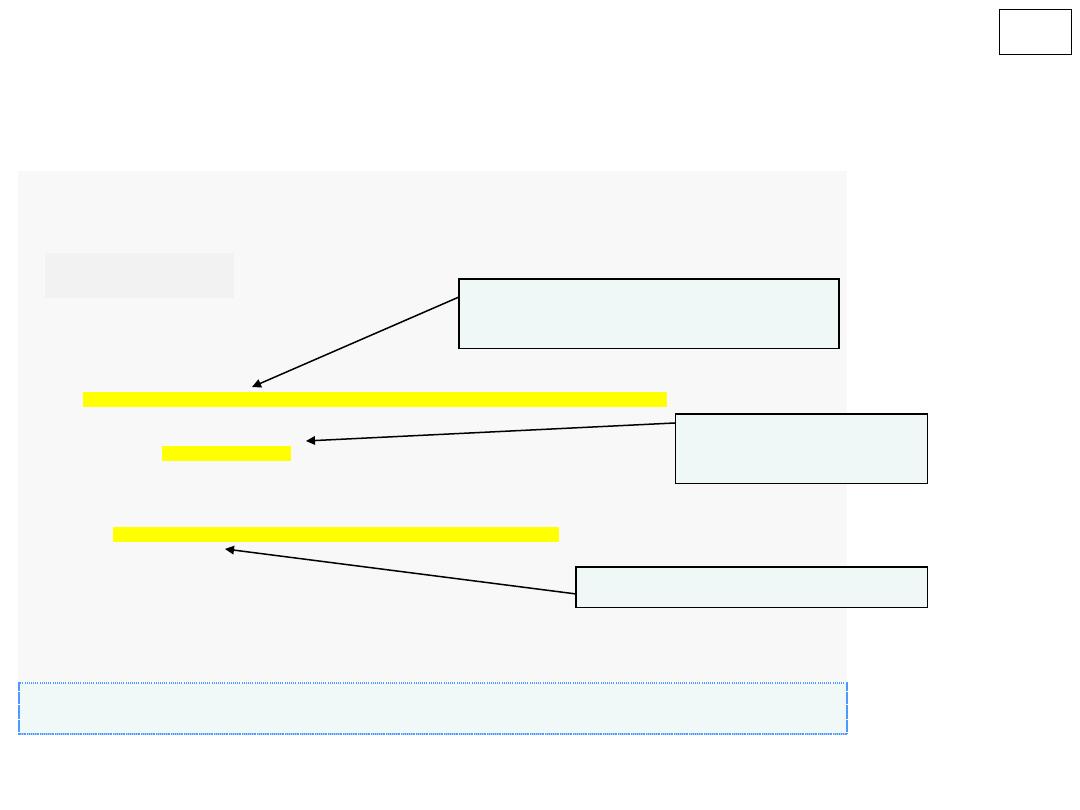
10
Example:
Write C++ program to type numbers from 1 to 10 using while
statement.
10
1
// Fig. 5.1: fig05_01.cpp
2
// Counter-controlled repetition.
3
#include
<iostream>
4
using
std::cout;
5
using
std::endl;
6
7
int
main()
8
{
9
int
counter =
1
;
// declare and initialize control variable
10
11
while
( counter <=
10
)
// loop-continuation condition
12
{
13
cout << counter <<
" "
;
14
counter++;
// increment control variable by 1
15
}
// end while
16
17
cout << endl;
// output a newline
18
return
0
;
// successful termination
19
}
// end main
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Control-variable name is counter
with variable initial value 1
Condition tests for
counter
’s final value
Increment the value in counter

do..while
Repetition Statement
Unlike for and while loops, which test the loop condition at the top
of the loop, the do...while loop checks its condition at the bottom of
the loop.
A do...while loop is similar to a while loop, except that a do...while
loop is guaranteed to execute at least
one
time.
11
do
{
action1;
action2;
.
.
actionN;
}
while
(condition)
Syntax

Consider the following two loops:
a/
i=11;
While (i<=10)
{
cout << i <<
“ ”;
i=i+5;
}
cout<< i <<endl;
Output: 11
b/
i=11;
do
{
cout<< i <<
“ ”;
i=i+5;
} While(i<=10);
cout << i << endl;
Output: 11 16
In a the while loop produces nothing . In b the do..while loop outputs the number 11
and also changes the value of I to 16
do..while
Repetition Statement
(cont.)

int
counter=1;
//(if counter=10)
int
grade=0 , sum=0;
do
{
cout <<"Enter grade for student no "
<< counter <<"\n";
cin >>grade;
sum += grade;
counter ++;
}
while
(
counter <=6
) ;
cout <<"Average Grade is " <<
sum/counter <<"\n";
do..while
Repetition Statement
(cont.)
•
Example
: Write a program that calculates and prints out the Average grade for
6
students.
int
counter = 1;
//(if counter=10)
int
grade=0 , sum=0;
while
(
counter <=6
)
{
cout <<"Enter grade for student no "
<< counter <<"\n";
cin >>grade;
sum += grade;
counter ++;
}
cout <<"Average Grade is " <<
sum/counter <<"\n";
Using do
…while Using while
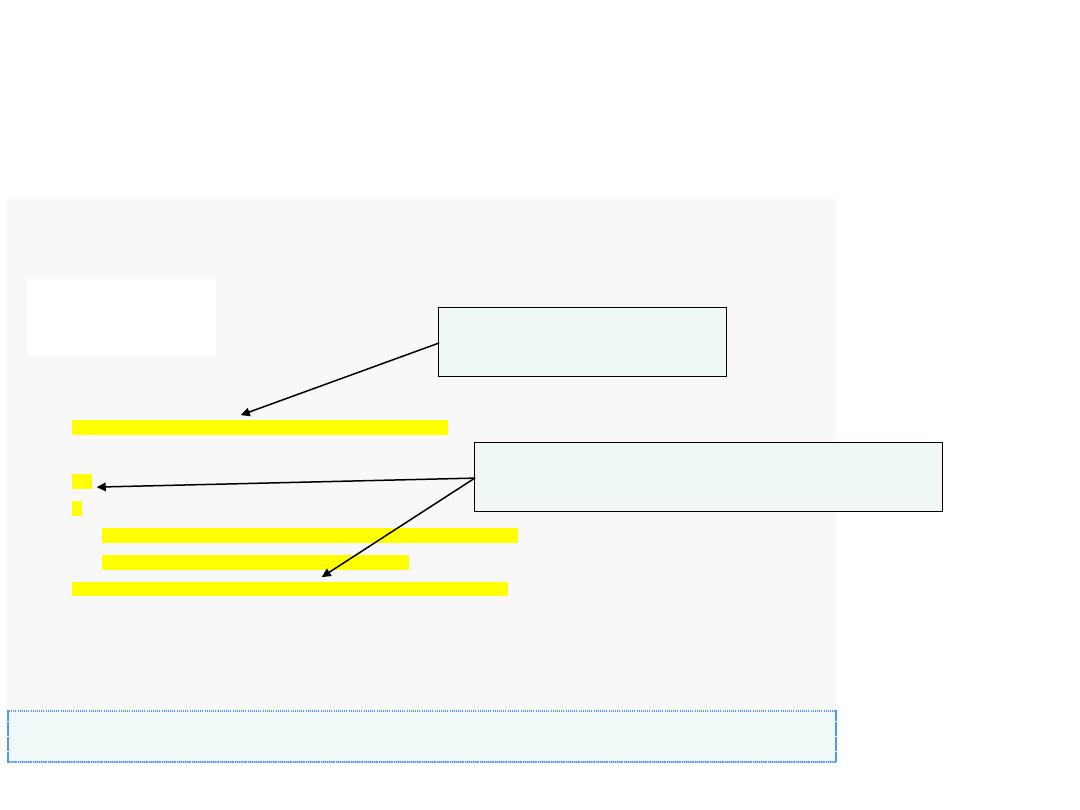
14
1
// Fig. 5.7: fig05_07.cpp
2
// do...while repetition statement.
3
#include
<iostream>
4
using
std::cout;
5
using
std::endl;
6
7
int
main()
8
{
9
int
counter =
1
;
// initialize counter
10
11
do
12
{
13
cout << counter <<
" "
;
// display counter
14
counter++;
// increment counter
15
}
while
( counter <=
10
);
// end do...while
16
17
cout << endl;
// output a newline
18
return
0
;
// indicate successful termination
19
}
// end main
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Declare and initialize
control variable counter
do…while loop displays counter’s value
before testing for counter’s final value
Example:
Write C++ program to type numbers from 1 to 10 using (do
…while ) statement.

Nested Control Statement
Control statements can be one inside the another
Nested building blocks
We can put loops one inside another to solve a certain
programming problems.
15

16
1
// Fig. 2.11: fig02_11.cpp
2
// Analysis of examination results.
3
#include
<iostream>
4
5
using
std::cout;
6
using
std::cin;
7
using
std::endl;
8
9
// function main begins program execution
10
int
main()
11
{
12
// initialize variables in declarations
13
int
passes =
0
;
// number of passes
14
int
failures =
0
;
// number of failures
15
int
studentCounter =
1
;
// student counter
16
int
result;
// one exam result
17
18
// process 10 students using counter-controlled loop
19
while
( studentCounter <=
10
) {
20
21
// prompt user for input and obtain value from user
22
cout <<
"Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): "
;
23
cin >> result;
24
Example # 1
A college has a list of test results (1 = pass, 2 = fail) for 10 students.
Write a program that analyzes the results. If more than 8 students pass,
print "Raise Tuition".

17
25
// if result 1, increment passes; if/else nested in while
26
if
( result ==
1
)
// if/else nested in while
27
passes = passes +
1
;
28
29
else
// if result not 1, increment failures
30
failures = failures +
1
;
31
32
// increment studentCounter so loop eventually terminates
33
studentCounter = studentCounter +
1
;
34
35
}
// end while
36
37
// termination phase; display number of passes and failures
38
cout <<
"Passed "
<< passes << endl;
39
cout <<
"Failed "
<< failures << endl;
40
41
// if more than eight students passed, print "raise tuition"
42
if
( passes >
8
)
43
cout <<
"Raise tuition "
<< endl;
44
45
return
0
;
// successful termination
46
47
}
// end function main
17
18
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 2
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 2
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 2
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 2
Passed 6
Failed 4
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 2
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Enter result (1 = pass, 2 = fail): 1
Passed 9
Failed 1
Raise tuition
Second Run
First Run
18

Nested Control Statement
(cont.)
Example # 2: Ask a teacher to enter a set of letter grades(5 letter), then
display a summery of the number of students who received each grade.
19
1
// Fig. 2.22: fig02_22.cpp
2
// Counting letter grades.
3
#include
<iostream>
4
5
using
std::cout;
6
using
std::cin;
7
using
std::endl;
8
9
// function main begins program execution
10
int
main()
11
{
12
int
grade;
// one grade
13
int
aCount =
0
;
// number of As
14
int
bCount =
0
;
// number of Bs
15
int
cCount =
0
;
// number of Cs
16
int
dCount =
0
;
// number of Ds
17
int
fCount =
0
;
// number of Fs
18
19
cout <<
"Enter the letter grades."
<< endl
20
<<
"Enter the EOF character to end input."
<< endl;
21
cin >> grade ;
char

20
22
// loop until user types end-of-file key sequence
23
while
( ( grade = cin.get() ) !=
EOF
) {
24
25
// determine which grade was input
26
switch
( grade ) {
// switch structure nested in while
27
28
case
'A'
:
// grade was uppercase A
29
case
'a'
:
// or lowercase a
30
++aCount;
// increment aCount
31
break
;
// necessary to exit switch
32
33
case
'B'
:
// grade was uppercase B
34
case
'b'
:
// or lowercase b
35
++bCount;
// increment bCount
36
break
;
// exit switch
37
38
case
'C'
:
// grade was uppercase C
39
case
'c'
:
// or lowercase c
40
++cCount;
// increment cCount
41
break
;
// exit switch
42
( grade != ‘Z' && grade != ‘z' )
{
20

21
43
case
'D'
:
// grade was uppercase D
44
case
'd'
:
// or lowercase d
45
++dCount;
// increment dCount
46
break
;
// exit switch
47
48
case
'F'
:
// grade was uppercase F
49
case
'f'
:
// or lowercase f
50
++fCount;
// increment fCount
51
break
;
// exit switch
52
53
case
'\n'
:
// ignore newlines,
54
case
'\t'
:
// tabs,
55
case
' '
:
// and spaces in input
56
break
;
// exit switch
57
58
default
:
// catch all other characters
59
cout <<
"Incorrect letter grade entered."
60
<<
" Enter a new grade."
<< endl;
61
break
;
// optional; will exit switch anyway
62
63
}
// end switch
64
65
}
// end while
66
43
case
'D'
:
// grade was uppercase D
44
case
'd'
:
// or lowercase d
45
++dCount;
// increment dCount
46
break
;
// exit switch
47
48
case
'F'
:
// grade was uppercase F
49
case
'f'
:
// or lowercase f
50
++fCount;
// increment fCount
51
break
;
// exit switch
52
53
case
'\n'
:
// ignore newlines,
54
case
'\t'
:
// tabs,
55
case
' '
:
// and spaces in input
56
break
;
// exit switch
57
58
default
:
// catch all other characters
59
cout <<
"Incorrect letter grade entered."
60
<<
" Enter a new grade."
<< endl;
61
break
;
// optional; will exit switch anyway
62
63
}
// end switch
64
65
}
// end while
66
cin >> grade ;
21
67
// output summary of results
68
cout <<
"\n\nTotals for each letter grade are:"
69
<<
"\nA: "
<< aCount
// display number of A grades
70
<<
"\nB: "
<< bCount
// display number of B grades
71
<<
"\nC: "
<< cCount
// display number of C grades
72
<<
"\nD: "
<< dCount
// display number of D grades
73
<<
"\nF: "
<< fCount
// display number of F grades
74
<< endl;
75
76
return
0
;
// indicate successful termination
77
78
}
// end function main

22
Enter the letter grades.
Enter the EOF character to end input.
a
B
c
C
A
d
f
C
E
Incorrect letter grade entered. Enter a new grade.
D
A
b
^Z
Totals for each letter grade are:
A: 3
B: 2
C: 3
D: 2
F: 1
Z
22
Home work
Update this program to display the total number of student.

Hom work:
23
1. Write C++ program to type numbers from 10 to 0 using
do/while statement.
2. Write C++ program to find the summation of even numbers
from 1 to 100 using do/while statement.
