Practical GIT Pathologyطب الاسنان
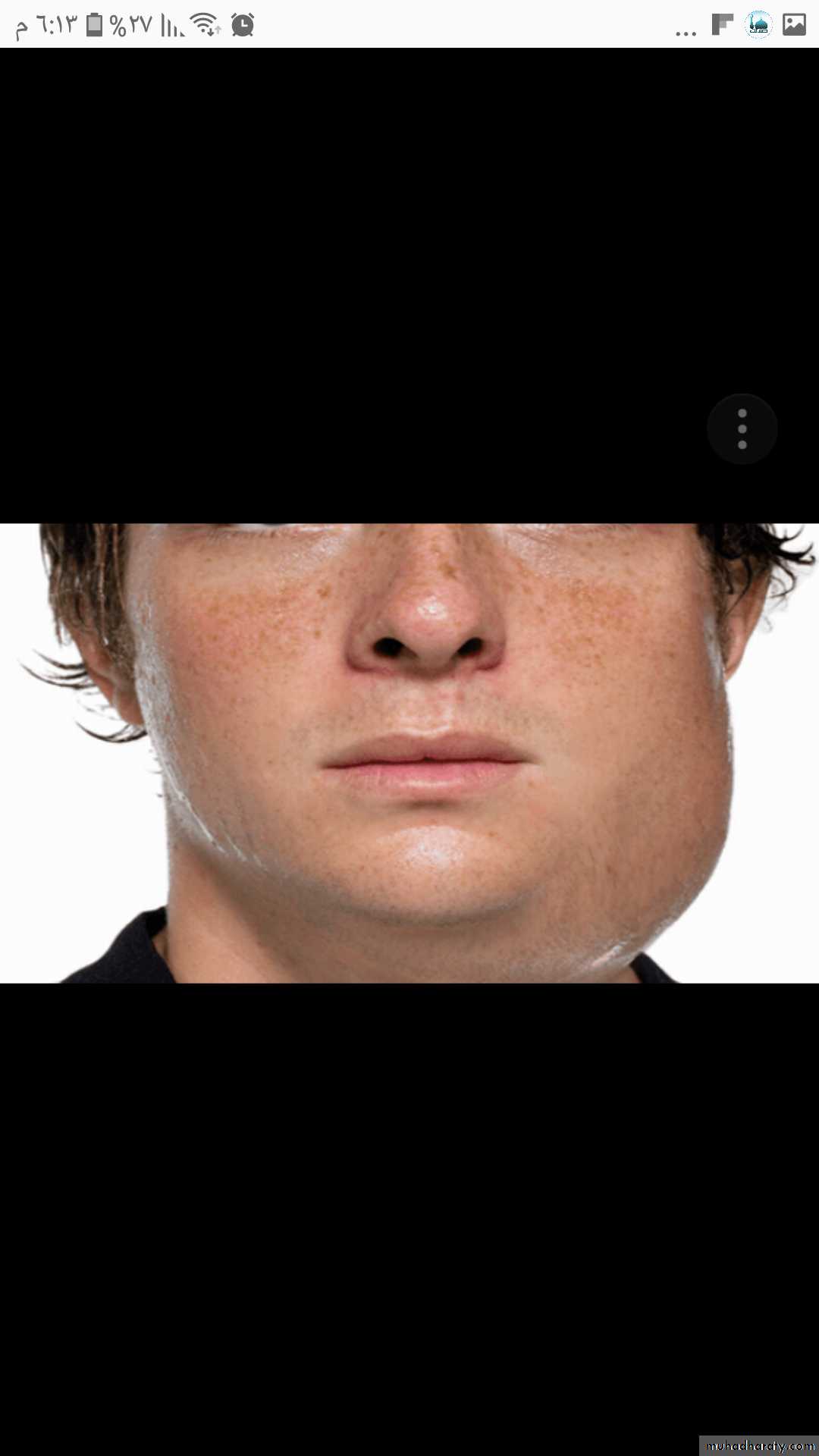
Mumps, there is a big swelling in the left cheek which locatedanterior to the ear and extend to cover the angle of the jaw
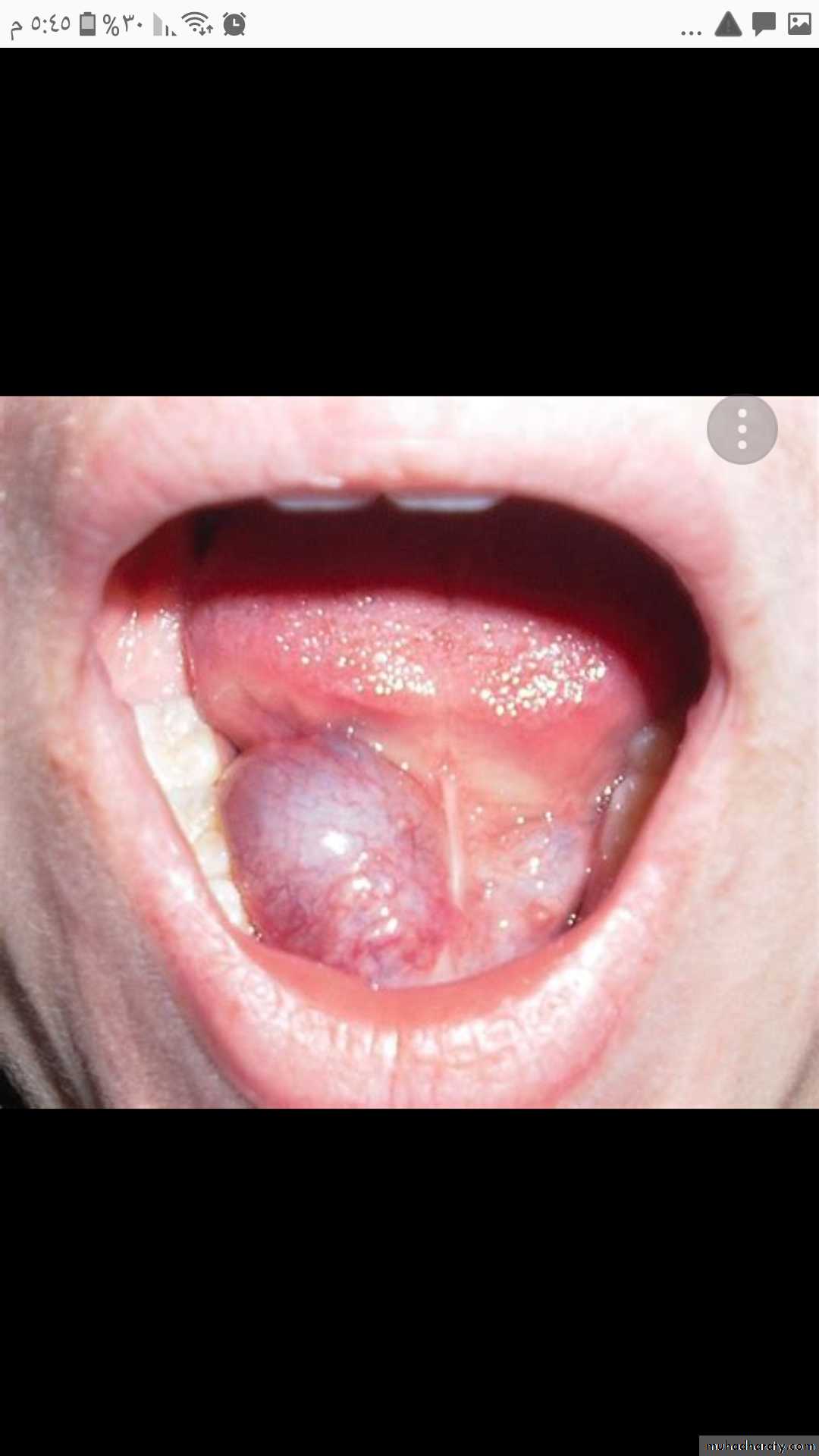
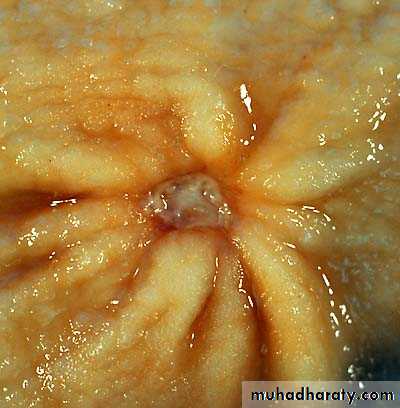
Ranula (mucocele) translucent blue , dome shaped swelling in the
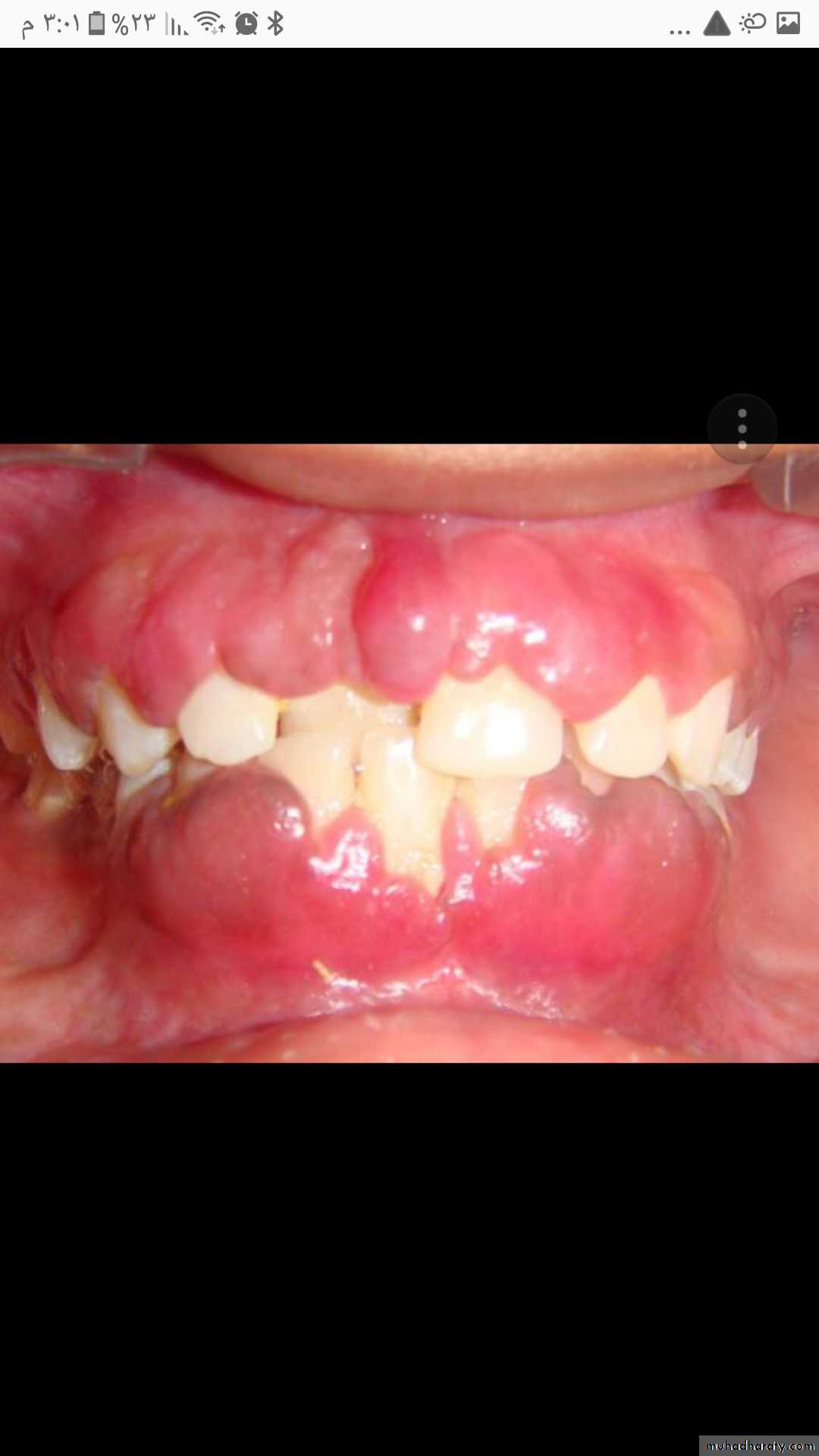
floor of the mouth , lateral to the midline.Gingival hyperplasia (gingival overgrowth) bright red gingival
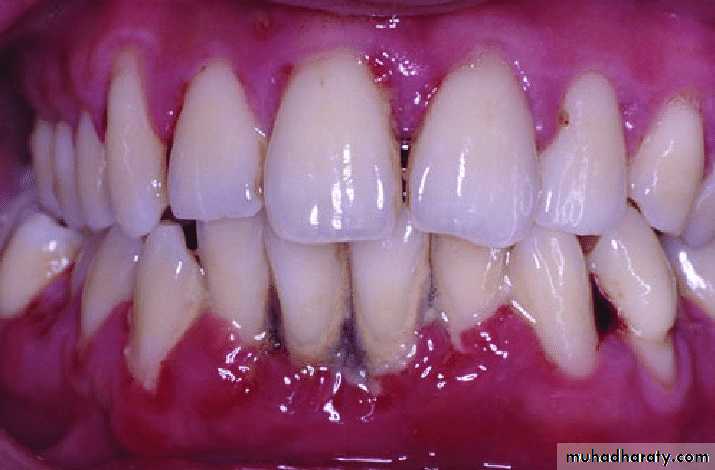
overgrowth around the necks of the teeth that bleed easilyPeriodontitis, the generalized inflammation, abnormal gingival anatomy owing to tissue destruction, gingival recession, swelling and inflammation, spontaneous bleeding and abundant plaque deposits.
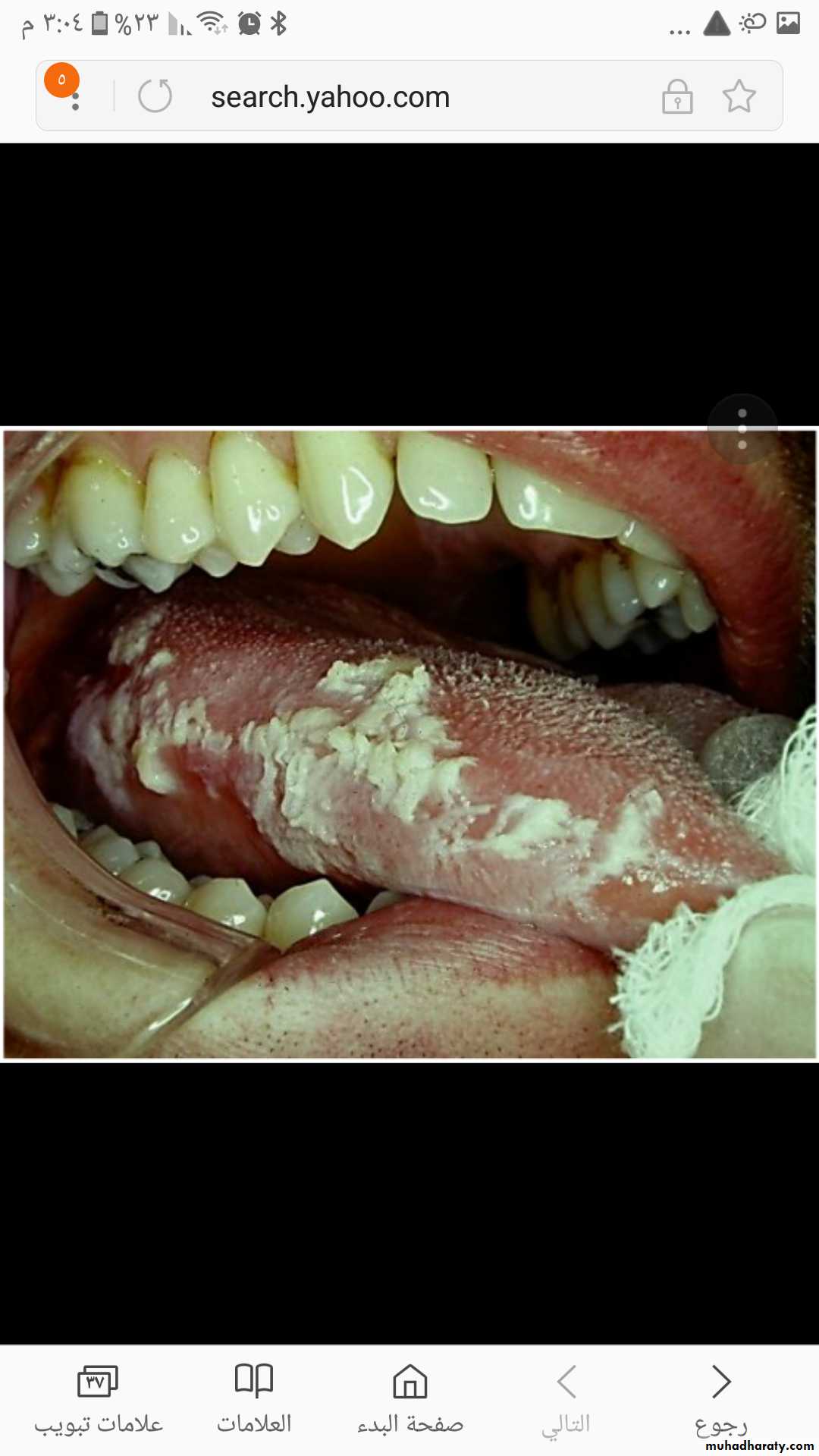
Leukoplakia, white thickened patches that cannot be scraped away
on the right border of the tongue, it is frequently mistakenfor oral thrush
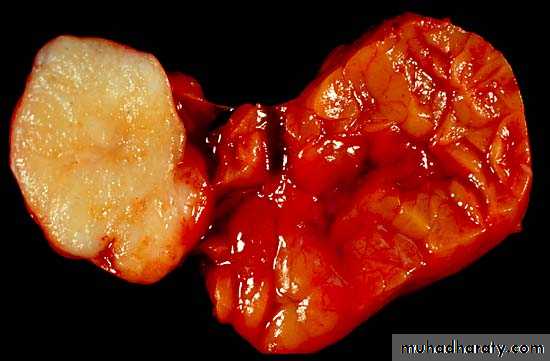
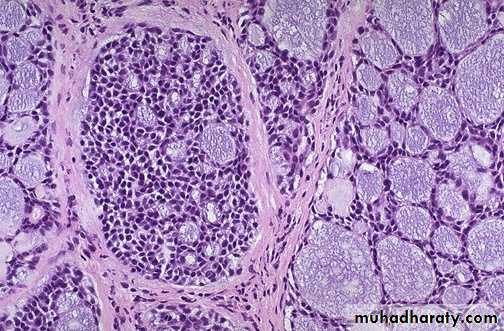
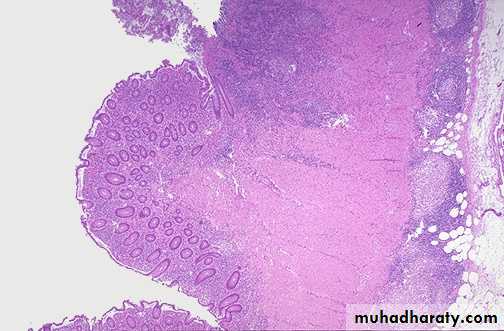
Pleomorphic adenoma, the tumor at the left side is white gray well circumscribe lobulated mass without hemorrhage or necrosis & encapsulated,(the normal lobulated gland (at the right
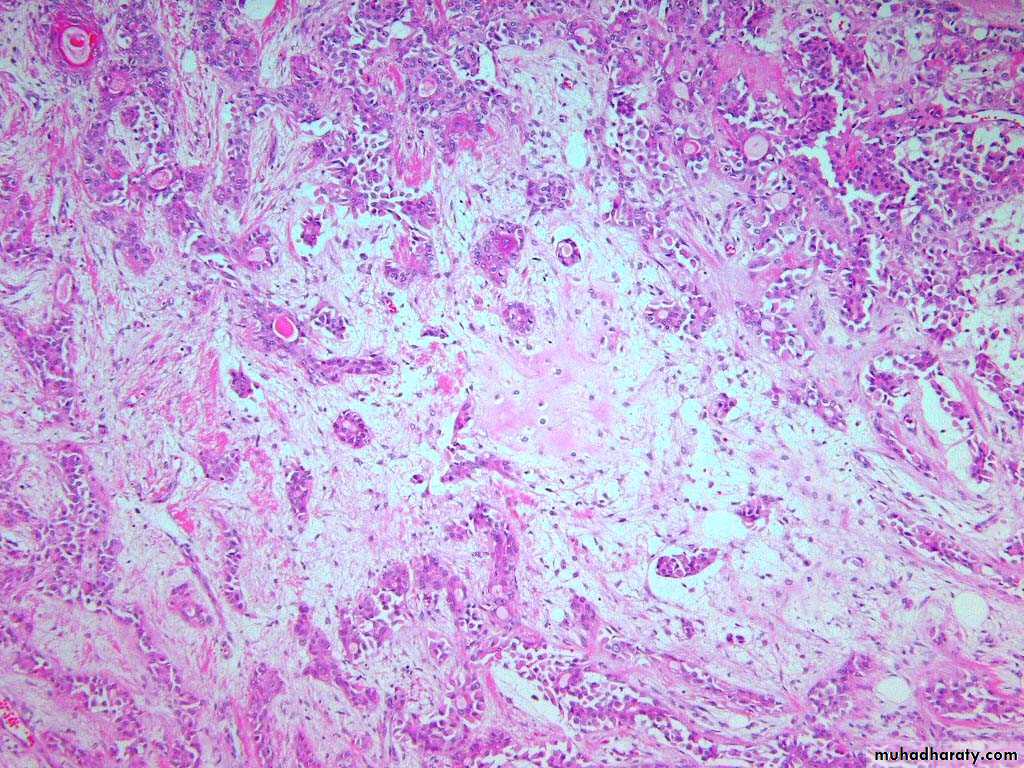
Pleomorphic adenoma, the myxoid stroma with proliferated ducts & scattered myoepithelial cells
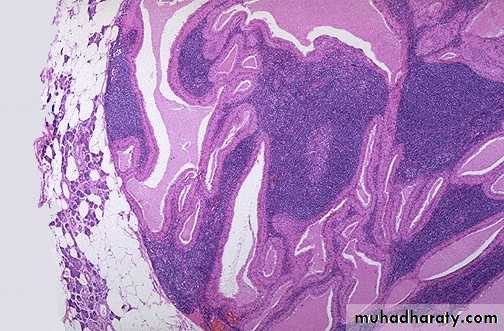
Benign papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, (Warthin's tumor) cystic spaces filled with serous fluid with papillary projections which are covered by double layers of oncocytic epithelium overlying lymphoid stroma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary gland, solid growth of small hyperchromatic neoplastic cells surrounding small (microcystic) spaces filled with mucinous secretions giving rise to cribriform appearance
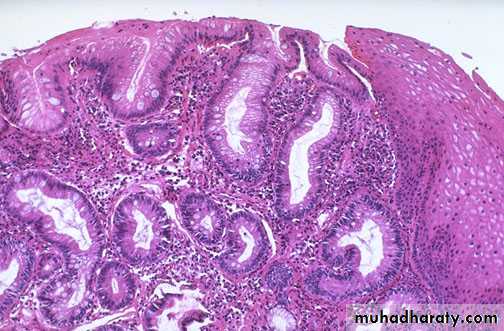
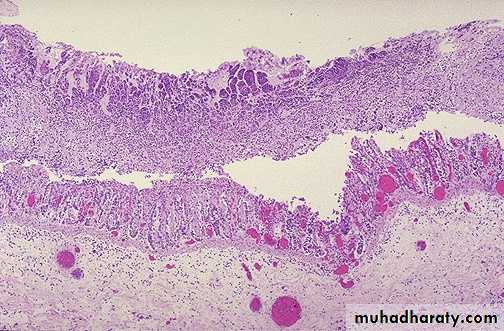
"Barrett's esophagus" in which there is gastric-type mucosa above the gastroesophageal junction with intestinal metaplasia .
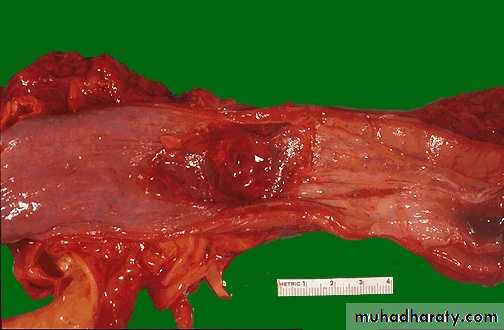
This irregular reddish, ulcerated exophytic mid-esophageal mass seen on the mucosal surface of the esophagusDiagnosis: Carcinoma of esophagus
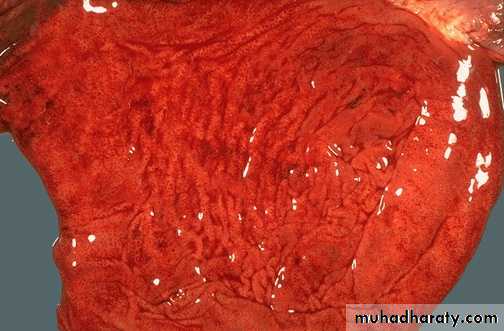
Acute gastritis: hyperemic edematous gastric mucosa with foci of superficial erosions. There are many causes for acute gastritis: alcoholism, drugs, infections, etc
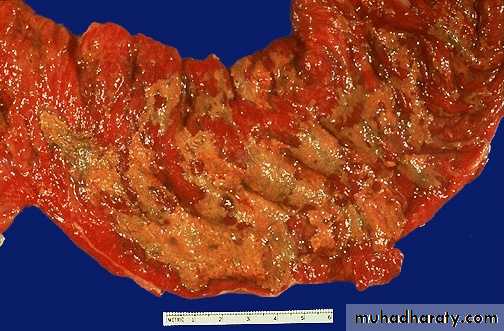
Chronic gastric ulcer: the ulcer is rounded covered by necrotic surface, note the radiating thickened mucosal folds due to underlying fibrosis.
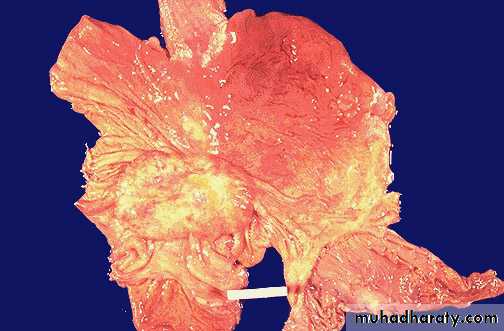
Gastric carcinoma: the mass is large fungating irregular whitish-gray mass within the body portion of the stomach
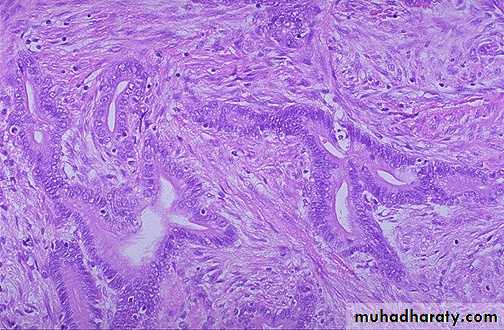
A moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma. There is still a glandular configuration lined by malignant glandular epithelial cells which demonstrate mitosis, high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratios & hyperchromatism, but the glands are irregular and very crowded.
Pseudomembranous enterocolitis.
The mucosal surface of the colon seen here is hyperemic and is partially covered by a yellow-green exudate. The mucosa itself is not eroded. It is due to overgrowth of bacteria such as Clostridium dificile or S. aureusMicroscopically, the pseudomembrane is seen to be composed of inflammatory cells, necrotic epithelium, and mucus in which the overgrowth of microorganisms takes place. The underlying mucosa shows congested vessels, but is still intact
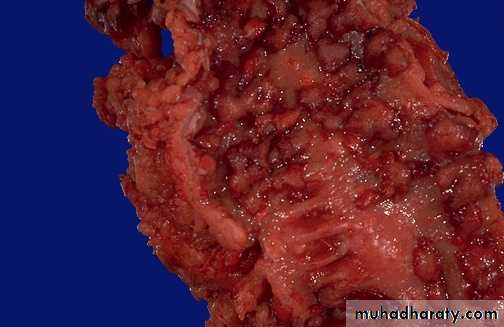
This portion of terminal ileum demonstrates the gross findings with Crohn's disease. The middle portion has a thickened wall and the mucosa has lost the regular folds. The serosal surface demonstrates reddish indurated adipose tissue that creeps over the surface
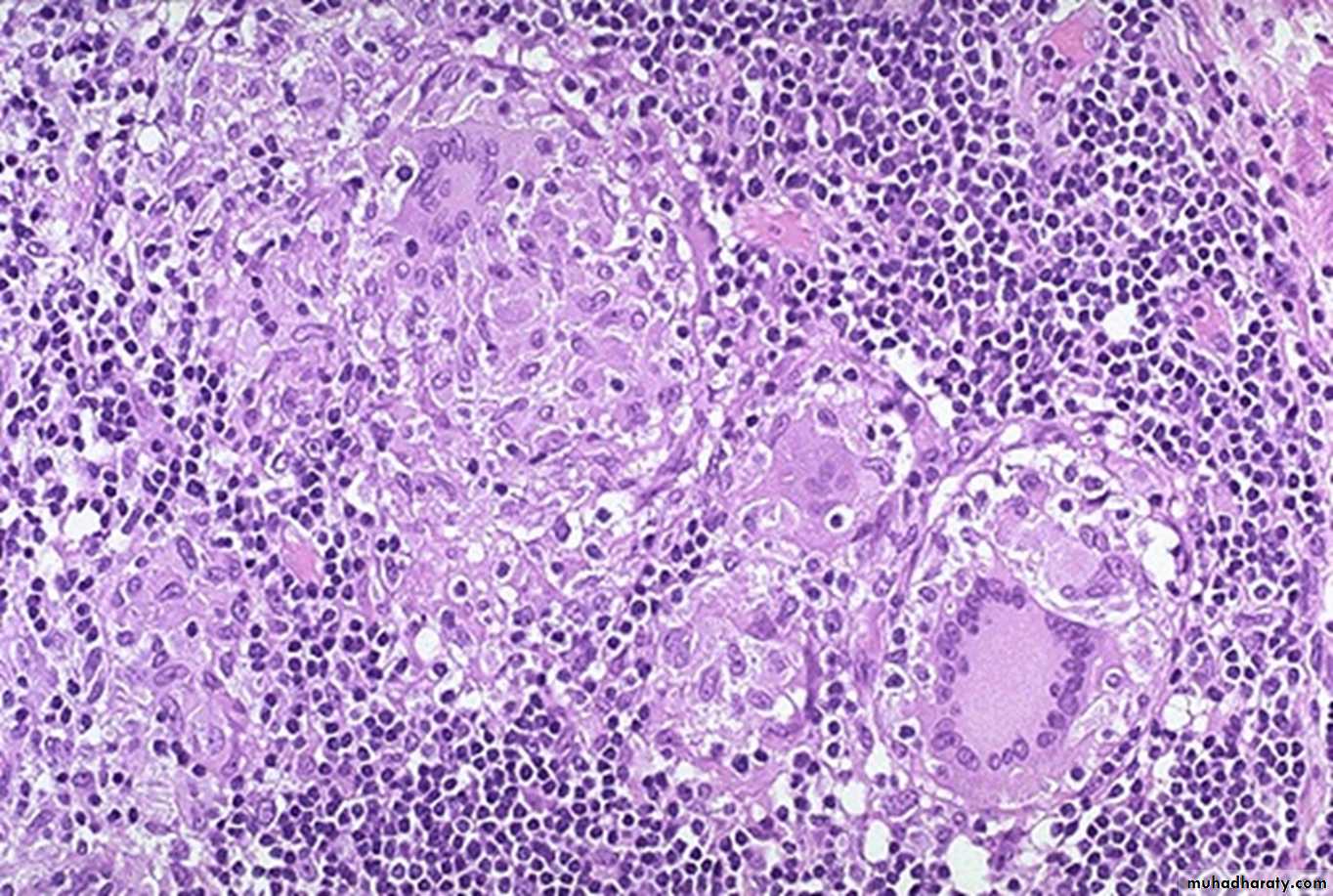
Crohn's disease is characterized by transmural inflammation. inflammatory cells (the bluish infiltrates) extend from mucosa through submucosa and muscularis and appear as nodular infiltrates on the serosal surface with pale granulomatous centers. non-caseating granuloma
Ulcerative colitis: pseudopolyps, The mucosa becomes eroded, the surrounding mucosa inflamed & edematous which bulged above the eroded areas giving rise to polypoidal appearance.
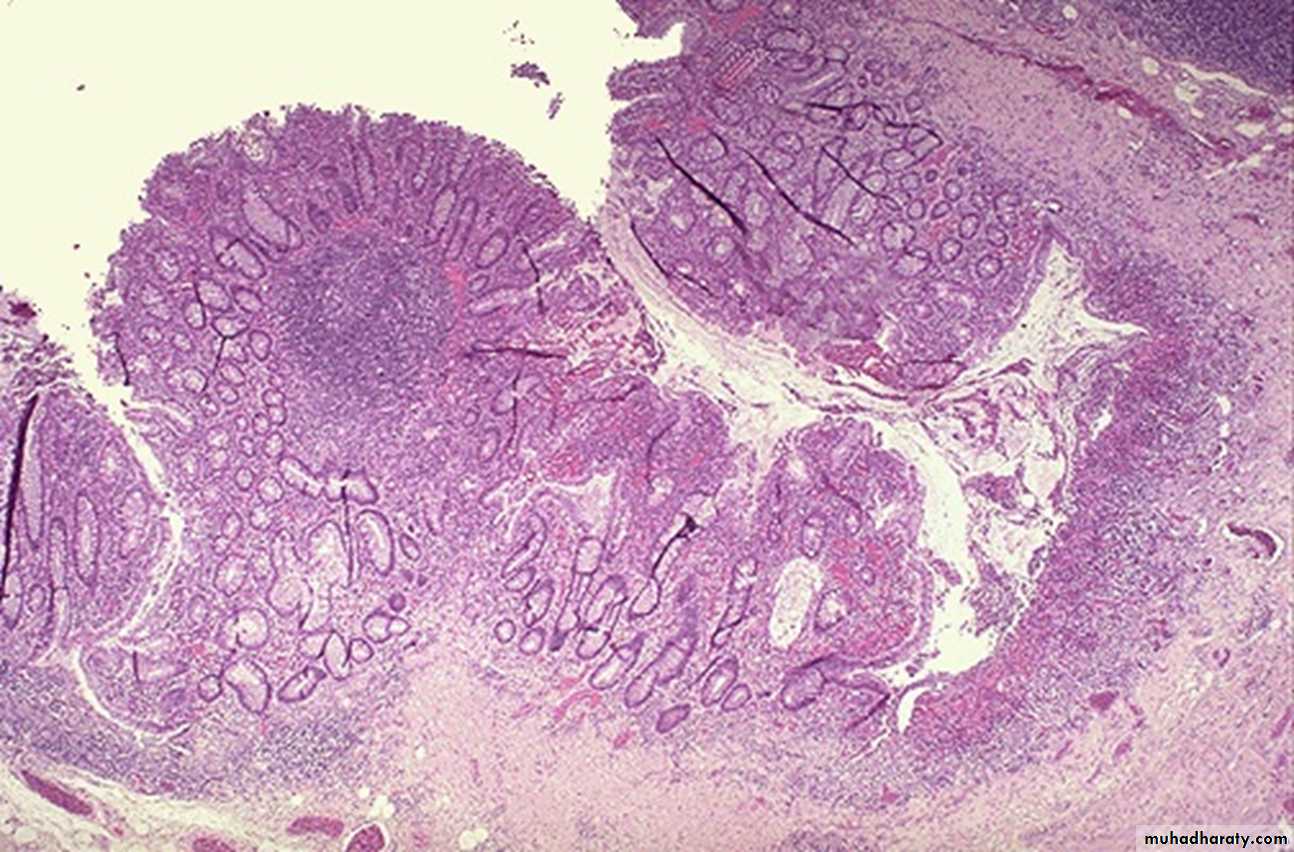
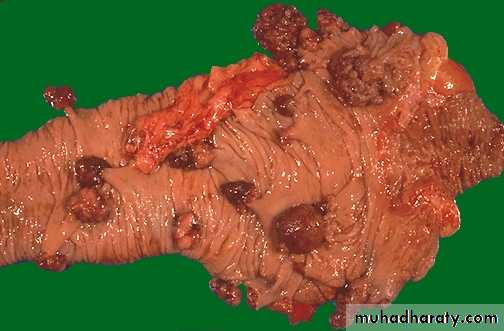
Multiple nodules of different sizes attached to colonic mucosa by a stalkDiagnosis: adenomatous polyp
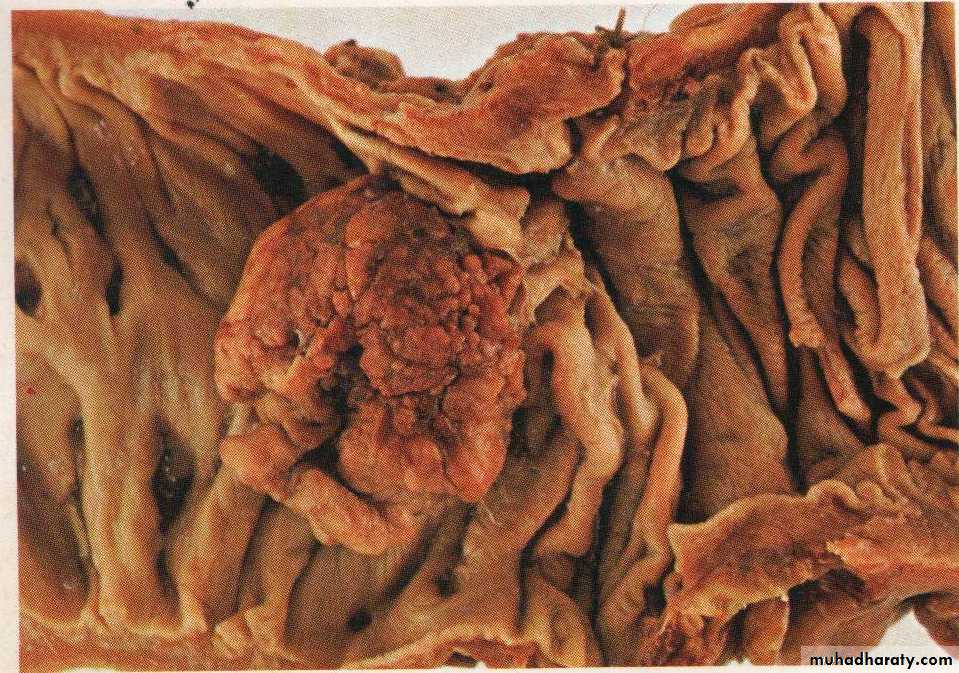
Adenocarcinoma of colon forming fungating irregular mass
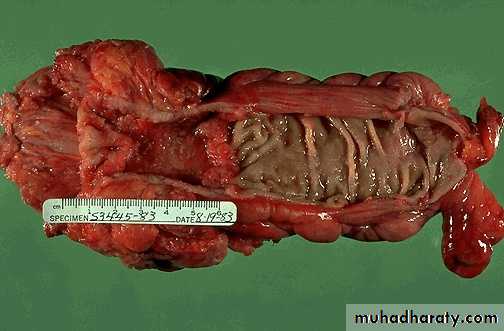
Carcinoma –colon, there is a heaped up margin of tumor at each side with a central area of ulceration.