Fifth Stage
Internal Medicine
Dr. Aamer – Lecture 6
1
Chronic Leukemia 's
Case 1
•
Middle / old age (30-50 years)
•
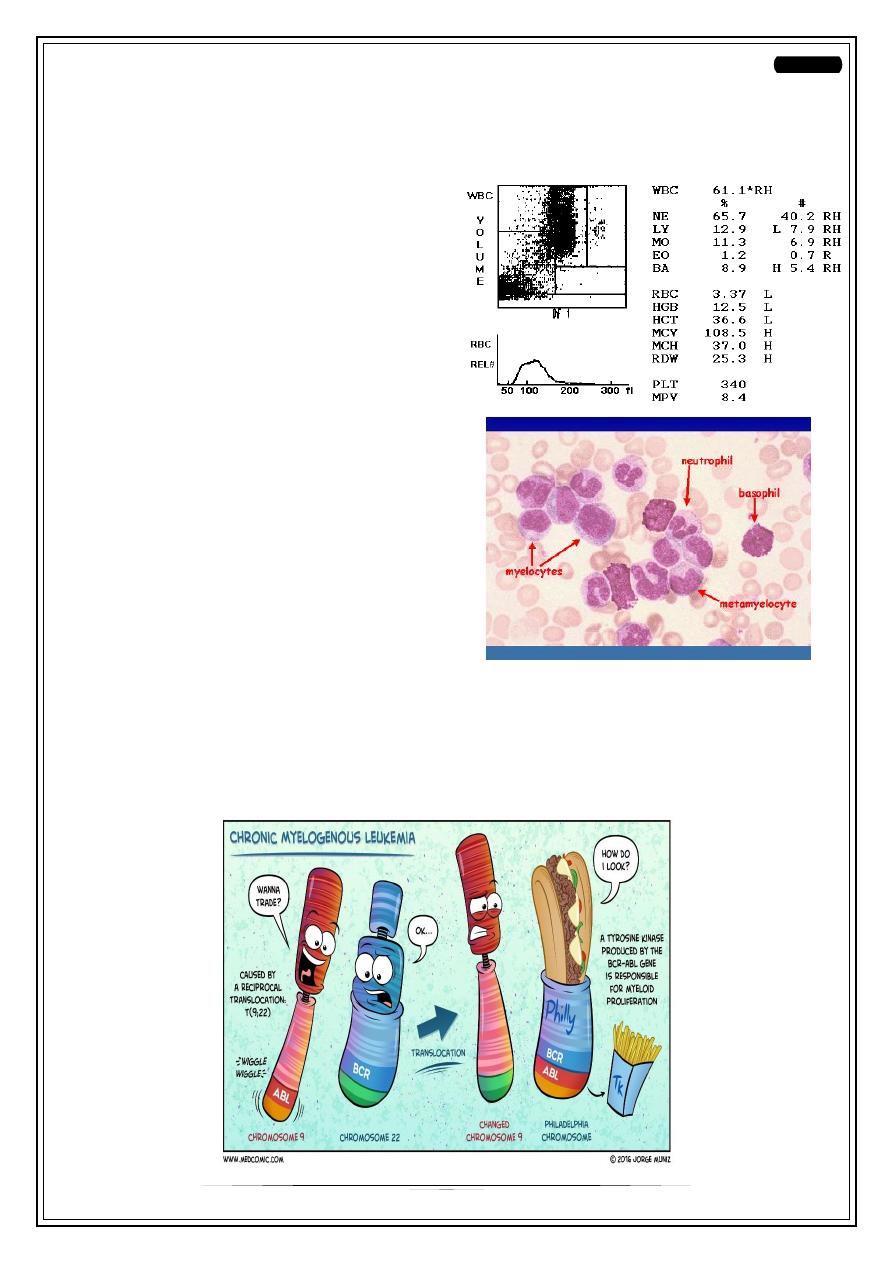
Incidental findings in CBC (e.g: During
blood donation)
o
Eosinophilia & Basophilia and
… etc.
o
I.e. all lineage are elevated
(leukocytosis)
•
In Blood film: filled with all maturation
sequences of granulocytic series.
•
Huge splenomegaly
This is,
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
!
•
Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome positive
•
It is translocation from chromosome 9 to chromosome 22 (t9:22). The new segment
in C22 is BCR-ABL, that produce tyrosine kinase.
2
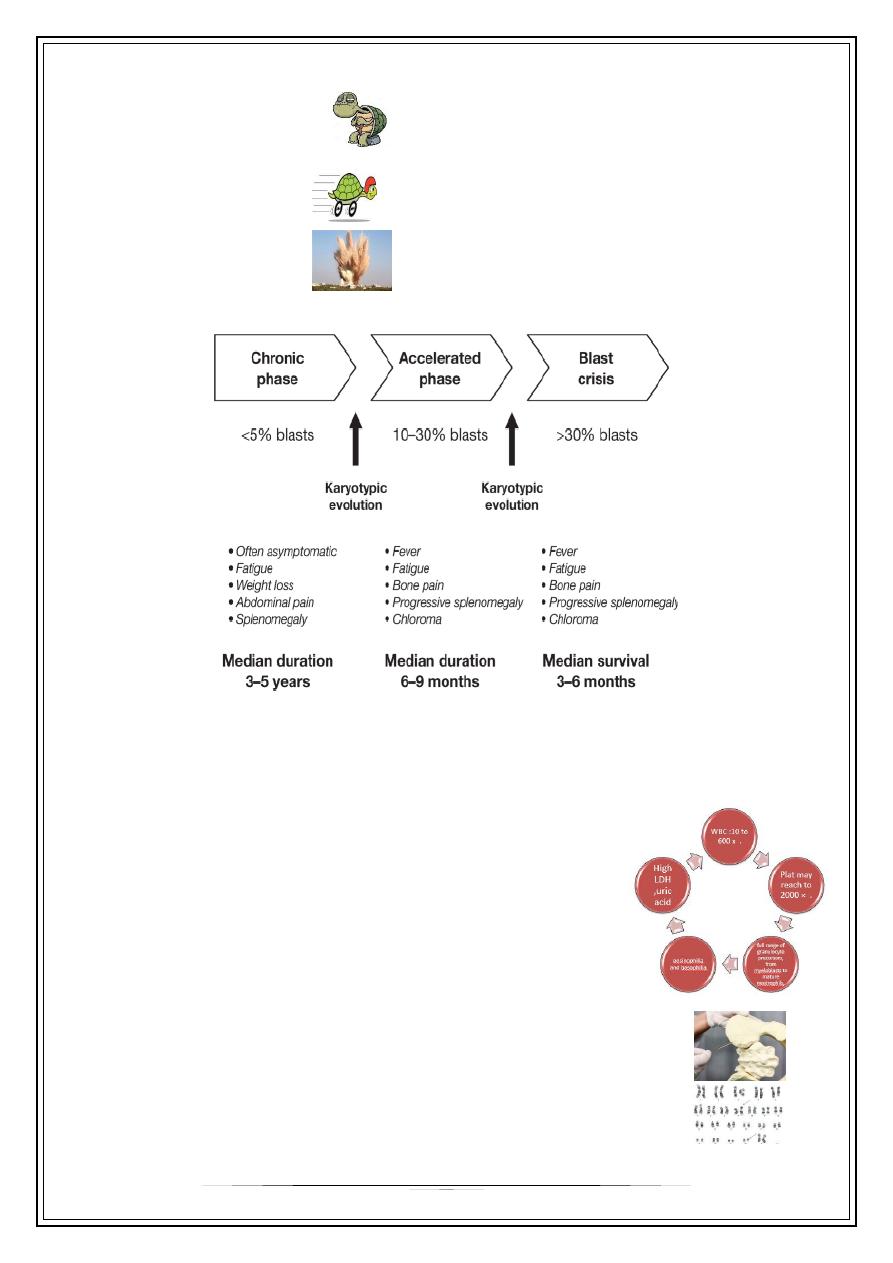
Phases
There are 3 phases
•
Chronic phase
o
< 5% blasts
o
Response very well to treatment
•
Accelerated phase
o
10-30% blasts
•
Blasting phase
o
>30% blasts
o
Very emergency
(Acute leukemia)
Q/Patient known of having chronic phase of CML, on treatment. He started to develop fever,
bone pain, spleen increased in size, these are symptoms of acceleration phase, next step?
Bone marrow to assess blast % to determine the phase.
Investigations
•
WBC: 10-600 x10
3
cell/mm
3
•
Platelets: 2000 x10
3
cell/mm
3
•
What are clues of blood film & CBC in CML?
o
Full range of granulocytes precursors.
o
Eosinophilia and basophilia (especially basophilia!)
•
High LDH, Uric acid (they are intra cellular component,
increase with number of cells)
Next investigations?
o
Bone marrow assessment is not used as diagnostic, it is
used to assess the phase (percent of blasts)
o
Karyotype for positive Philadelphia (translocation 9:22)
o
FISH / RT-PCR to search for BCR/ABL gene
Duration of survival
without treatment:
3
Treatment
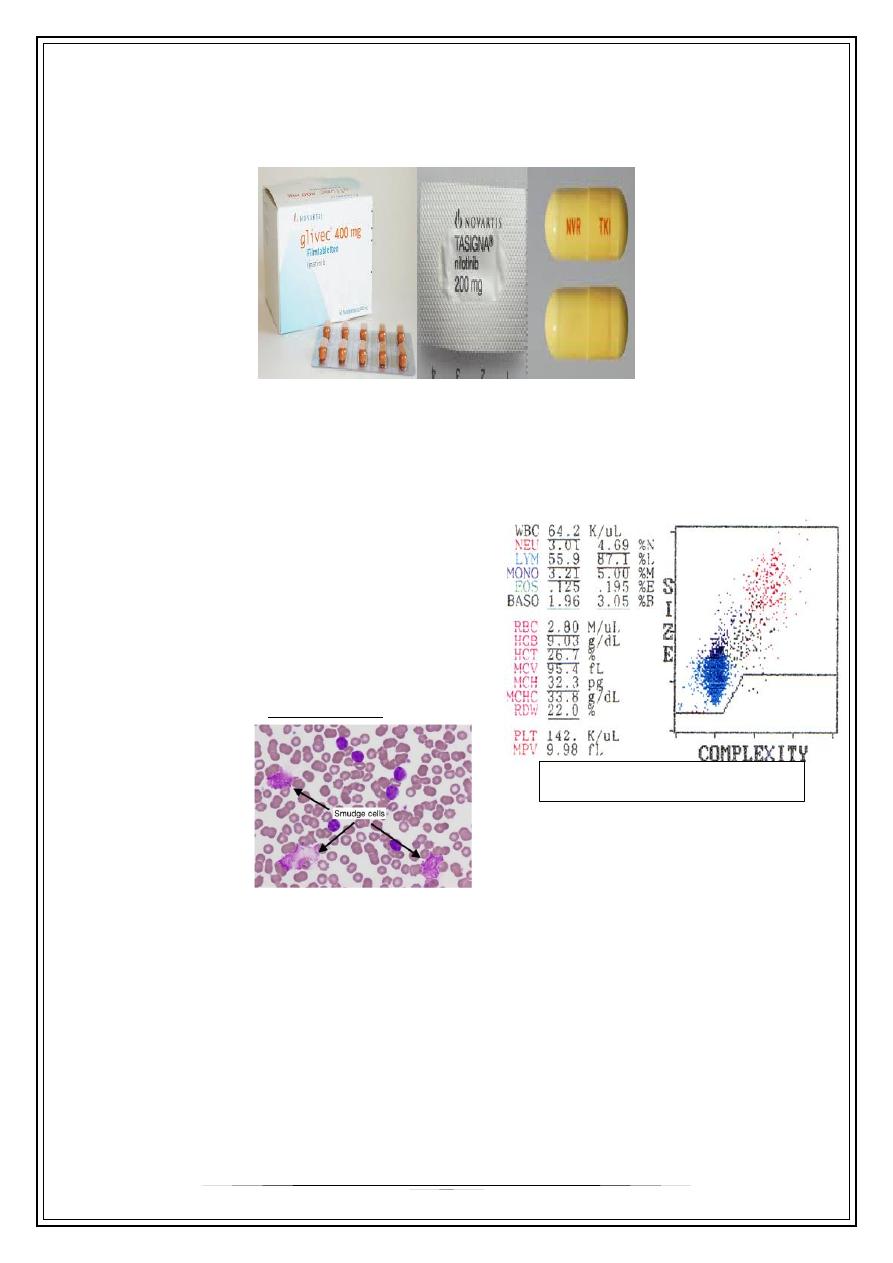
For Chronic phase:
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor: imatinib (glivec), nilotinib, dasatinib
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Case 2
Same guy in case 1. Asymptomatic during incidental blood film & CBC:
Investigations
•
Blood count
▸
WBC > 50 K.
▸
Lymphocytes > 85%.
• I.e isolated lymphocytosis.
•
Blood film
▸
Mature looking lymphocytes
▸
Ruptured cells (smudge cells).
This is
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
!
• When malignant clone is able to
differentiate
accumulation
of more
mature cells
of the affected cell type
• Differs from acute in that its clinical course is indolent.
Most are asymptomatic at
presentation
.
• Survival for several years after their initial diagnosis, even without treatment.
• In certain CL evolution to acute disease may occur, which may need d/t
management approach.
When WBC > 25, risk of leukemia is evident
When WBC > 50, usually it is leukemia

4
Clinical features
•
Asymptomatic lymphocytosis (> 50K)
•
Lymphadenopathy: painless, often symmetrical, splenomegaly 66%,
hepatomegaly.
•
BM failure due to infiltration causing:
o
Anemia
o
Neutropenia
o
Thrombocytopenia
o
And Fever (due to anemia)
•
Recurrent infection due to acquired hypogammaglobulinemia, specially herpes
zoster.
Staging
◦ Binet classification for CLL
▸
A: asymptomatic < 3 involved areas, Hb > 10g, Plt > 100 G/L
▸
B: asymptomatic but bulky disease (lymph node and spleen), > 3 involved
areas, Hb > 10g, Plt > 100 G/L
▸
C: bone marrow, any number of involved areas, Hb < 10g, Plt <100 G/L
We should Assess clonality by detecting CD markers by flow cytometry.
From blood count alone, we can determine acute or chronic by looking to state of
patient whether stable or not (toxic, fever… etc).
5
Treatment
• CLL is non-curative disease
◦ Stage A and B: only monitoring every month and discharge home. Watchful
waiting.
◦ Stage C: chemotherapy to make him back to stage A.
▸
If age < 60 years: Standard regimes FCR (episode every 2 for 6 months).
▸
If age is older: other regimes.
Thank you,,,
Some Notes were written from students…
Some Clues in cases:
• Clue in AML is Auer rods (stick like).
• Clue in CML is presence of all maturation sequences.
• Clue in CLL is smudge cell.
