3rd Stage
Proteus
Microbiology (Lab)
1
The genus is named after a Greek sea deity Proteus
The god is flexible, versatile and adaptable and , like the flowers assumes
many different forms .
General charachteristic:
Gram negative rods, facultative anaerobics.
Motile they have peritrichous flagella
Non capsulated
Non spore forming
Proteus sp. are most commonly found in the human intestinal tract as part
of normal human intestinal flora.
Non-lactose fermenting
The main species of medical importance are:
P. mirabilis
P. vulgaris
Proteus spp. are opportunist pathogens and may cause many types of infection.
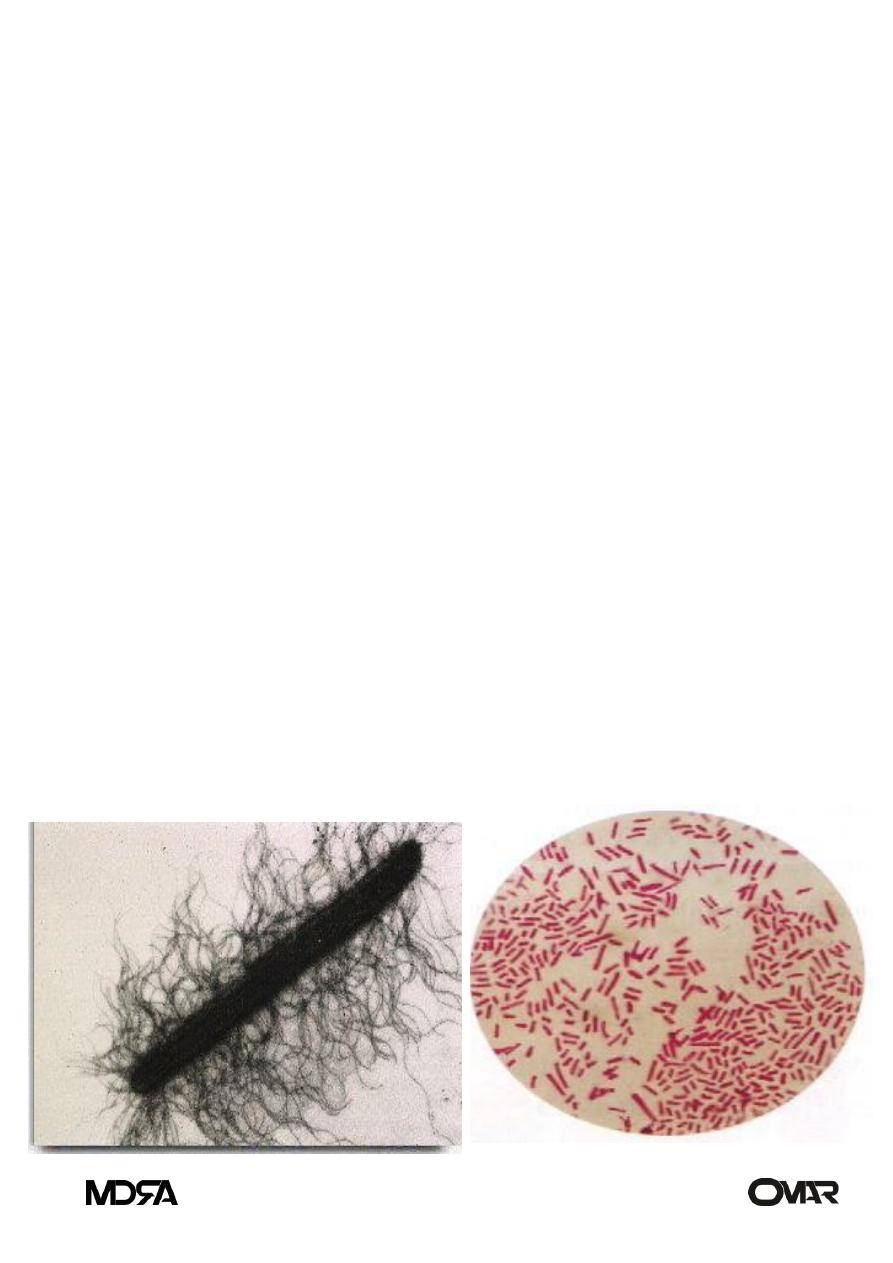
Morphology of proteus spp
Microscopical morphology
Gram negative bacilli, motile has flagella
3rd Stage
Proteus
Microbiology (Lab)
2
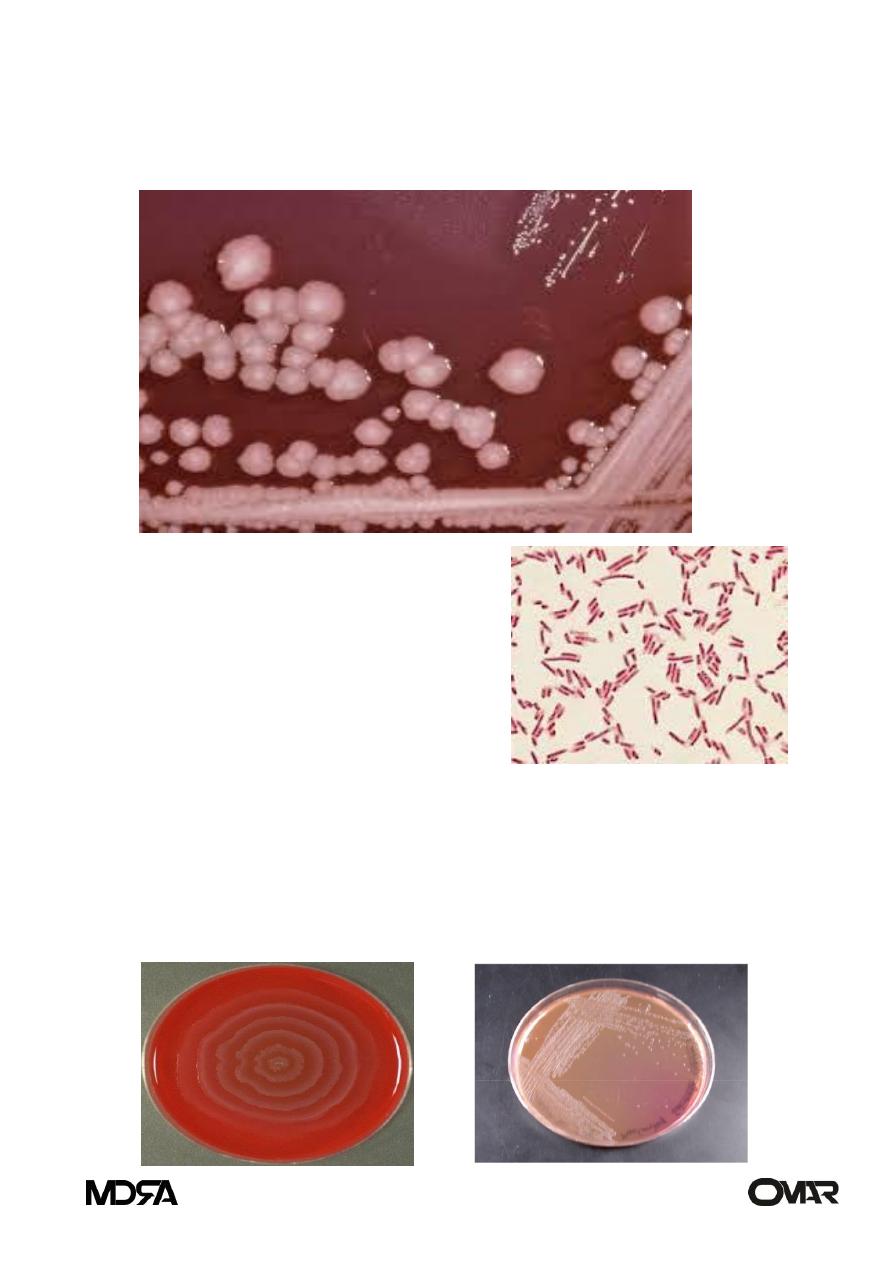
Colony morphology:
Large ,circular, gray ,smooth colonies
Diagnosis method of proteus spp.
Specimens:
Urine, pus and ear
Gram stain:
Rod shaped gram negative
Culture:
Blood agar: Swarming effect over blood agar plate as a consequence of the
organisms active motility.
Macconkey agar: Cultures give out an odour described as fishy, Non- lactose
fermenting colonies .
3rd Stage
Proteus
Microbiology (Lab)
3
Virulence Factors :
Urease activity
Protease
Fimbriae
Haemolysins
Motility
Swarming
Oxidase test:
The oxidase test is used to determine if a bacterium produces certain
cytochrome c oxidases. The reagent turns dark blue when oxidized (oxidase
positive). The reagent is colorless when reduced (oxidase-negative)
Proteus spp. Oxidase negative
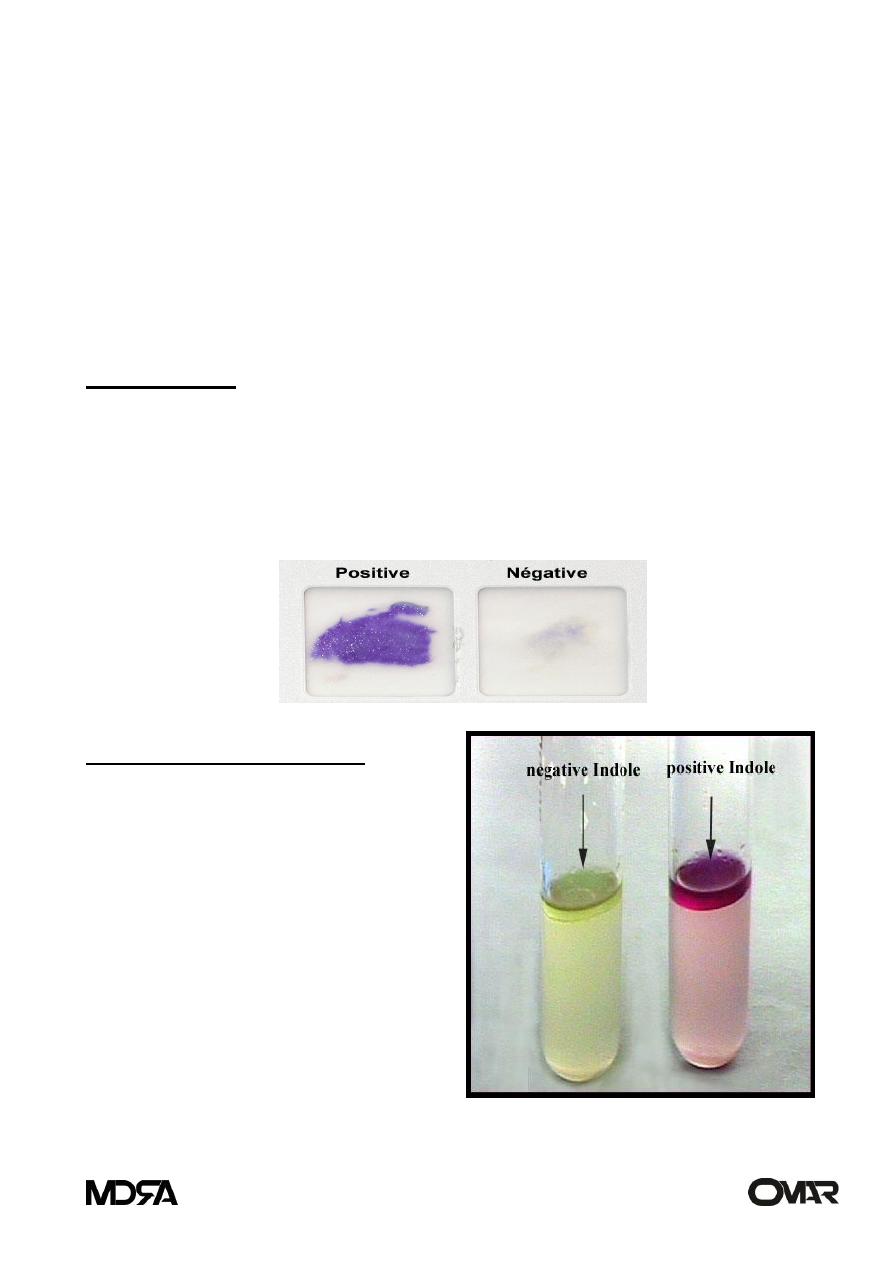
IMViC test1-indole test:
is used to determine the ability of
bacteria to convert tryptophan into
indole.
P. mirabilis can be differentiated from
p.vulgaris by indole test.
P. mirabilis → negative
P. vulgaris → positive

3rd Stage
Proteus
Microbiology (Lab)
4
Methyl red test:
The methyl red test is used to
identify bacteria to produce pyruvic
acid from glucose metabolism.
Proteus vulgaris:
Methyl red : posative
Proteus mirabils:
Methyl red: positive
Voges–Proskauer:
Is a test used to detect acetoin in
a bacterial broth culture. A red-
brown color indicates a positive
result, while a yellow-brown color
indicates a negative result.
p.Vulgaris : Negative
p.mirabilis:negative
Citrate test:
Ability
of
an
organism
to
use citrate as the sole source of
carbon and energy.
p.Vulgaris: Negative
p.mirabilis: posative

3rd Stage
Proteus
Microbiology (Lab)
5
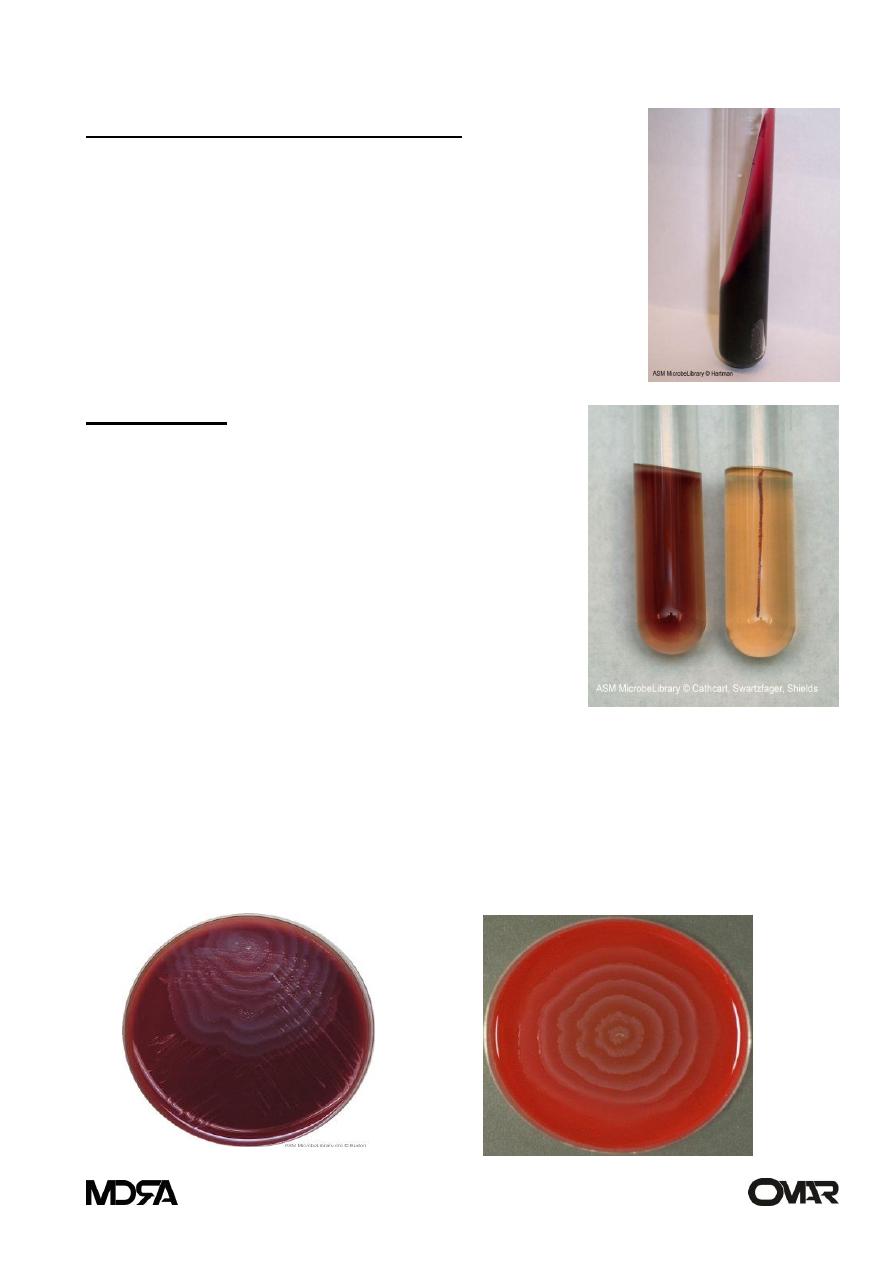
TSI test (Triple Sugar Iron test)
This test is used to determine the ability of bacteria to
ferment sugars and to produce hydrogen sulfide (H2S) or
other gases
Proteus spp.
(red/red with H2S production)
(black)
Motility test
used to determine whether an organism is equipped
with flagella and thus capable of swimming away
from a stab mark.
• Left tube
shows positive motility test for Proteus spp.
• Right tube
negative for S.aureus
Swarming phenomenon
swarming is described as the formation of concentric zones of bacterial
growth, able to cover th e whole surface of solid culture medium.
P.mirabilis & P.vulgaris are known for their swarming ability over (sheep
blood agar)
3rd Stage
Proteus
Microbiology (Lab)
6
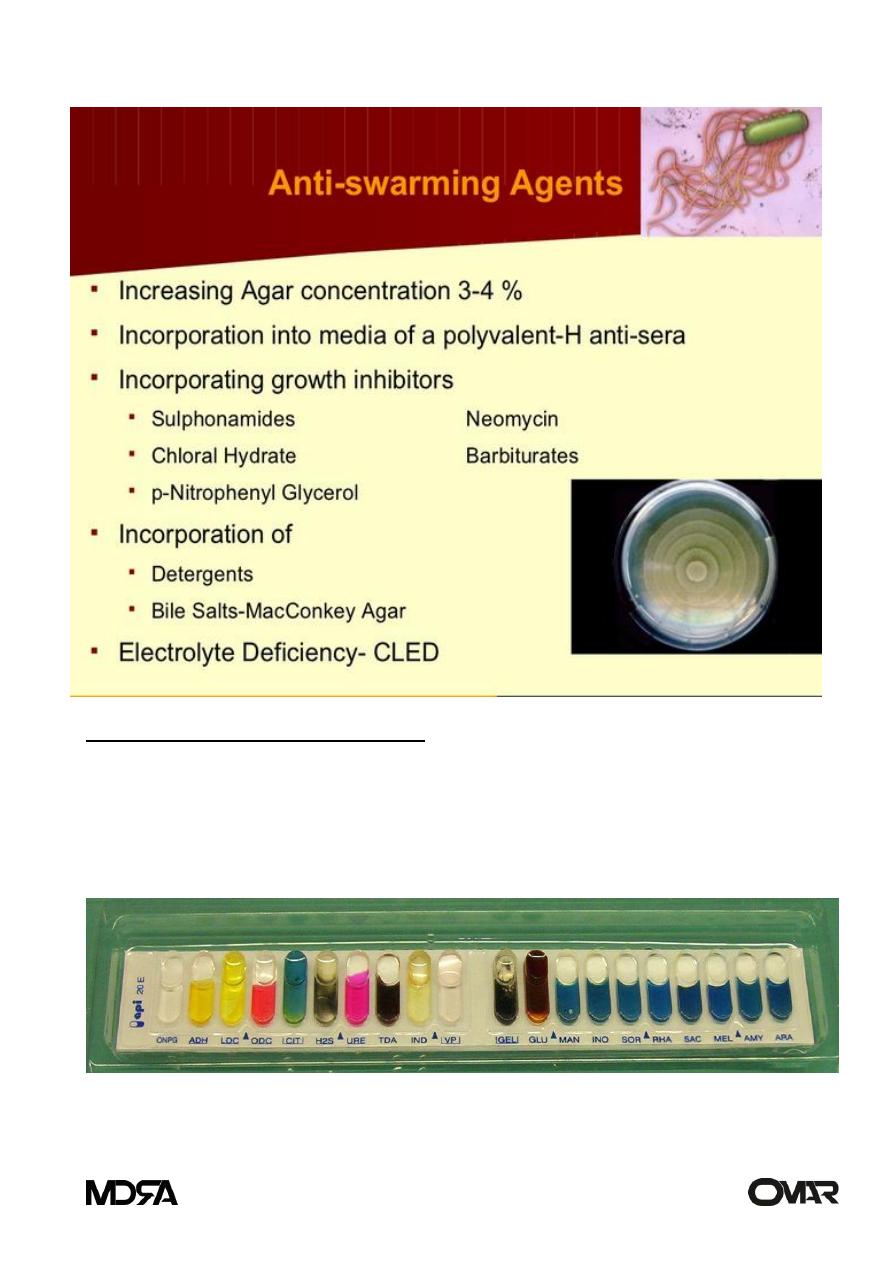
Analytical Profile Index (API)
By inoculating microorganism to a strip that has 20 tests on it. during
inoculation metabolic cause color change, to complete the identification of the
strains either identified to the genus only or that have multiple genera consist
of profile number

3rd Stage
Proteus
Microbiology (Lab)
7
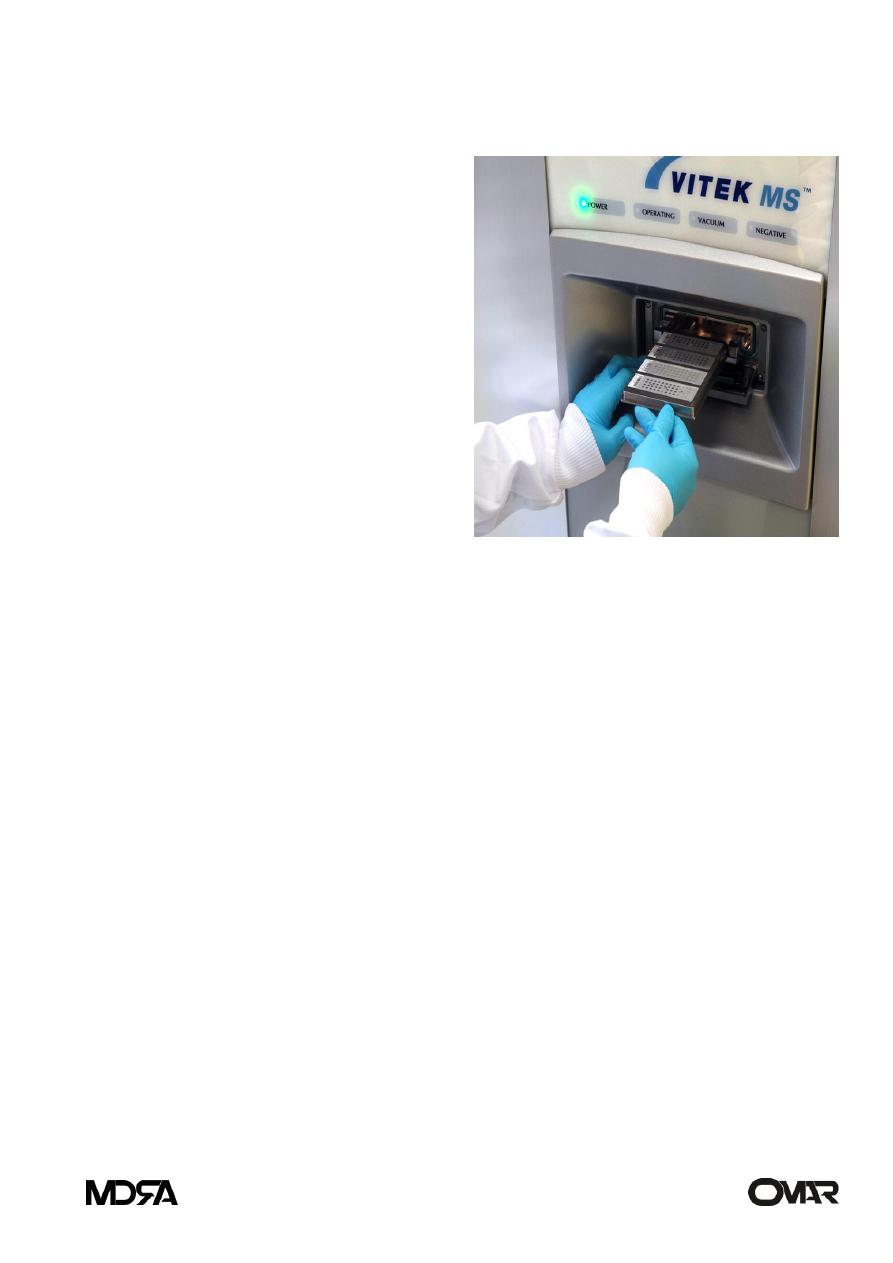
Vitek system
It is a new automatic system for
identification and susceptibility testing
for most of clinically important
bacteria.
It compromises:
-A filtter/sealer:enable
-inoculation of the card
within few minute.
-An inoculator /leader
- A computer and printer
Antimicrobial Susceptibility
P.mirabilis resistant to Polymyxin B and Colistin
P.mirabilis sensitive to
Nalidixic Acid and other Quinolones
Semi synthetic Penicillins-Mezlocillin , Azlocillin,Piperacillin,
Carbenicillin and Ticarcillin
Most Aminoglycosides
Carbapenems
P.vulgaris resistant to
Pencillin, Ampicillin and many Cephalosporins like Cefazolin and
Cefamandole
Inducible β-Lactamase (Cefuroximase)- Cefuroxime, Cefotaxime.
P.vulgaris sensitive to
Ceforoxime,Cefotaxime and Cefoxitin
Quinolones
Most Aminoglycosides
Carbapenems
