Course: Virology
Lecturer: Dr. Weam SaadLecture: Bacterial viruses (Bacteriophage)
Bacterial viruses (Bacteriophages):
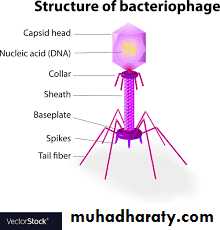
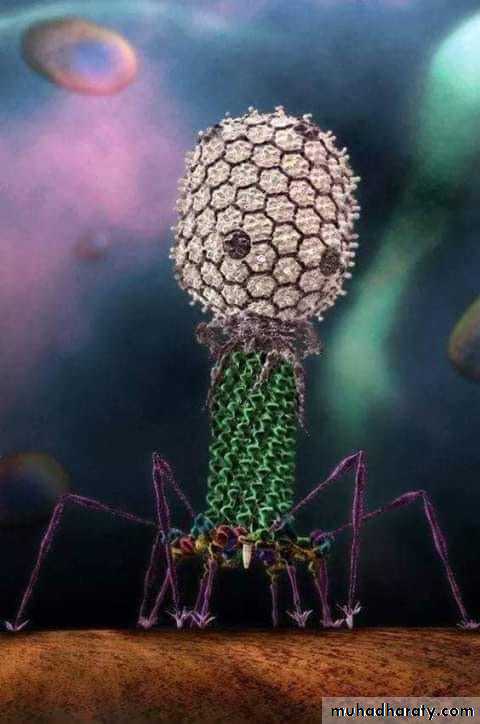
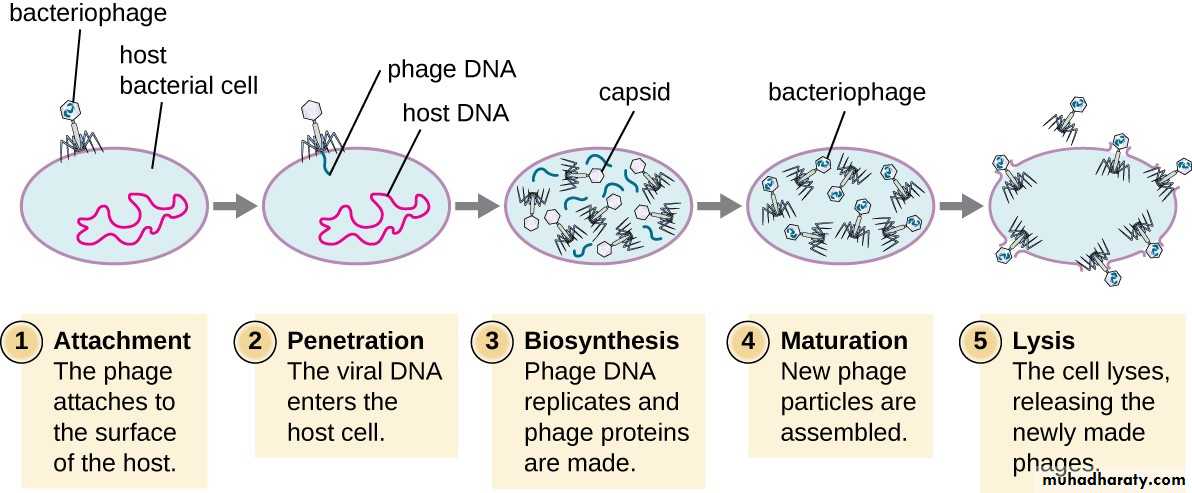
Bacteriophages are complex structure viruses that infect bacteria and HYPERLINK "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Archaea" archaea cells; they are everywhere and common in aquatic environments. These viruses infect specific bacteria by binding to surface receptor molecules and then entering the cell. Within minutes, bacterial polymerase starts translating viral mRNA into protein. These proteins help in assembly of new virions, or proteins involved in cell lysis due to viral enzymes that cause breakdown of the cell membrane. The role of tail fibers is the attachment of the phage to its host cell’s surface. For example; the Enterobacteria T4 phage, in just twenty minutes after injection inside Escherichia coli bacteria, over three hundred phages could be released.(Structure of bacteriophage)
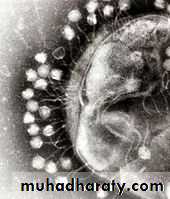
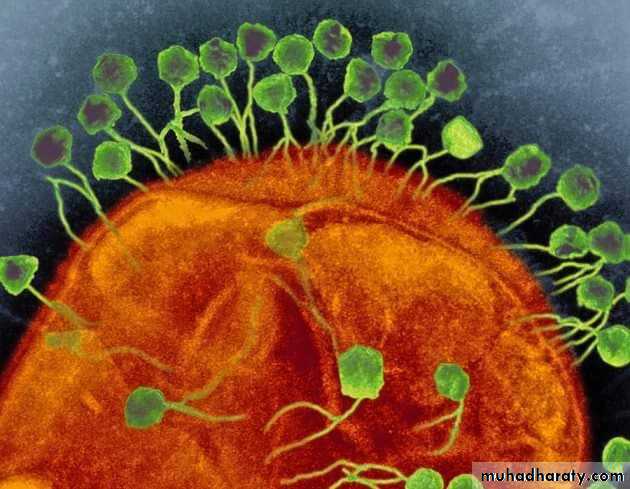
The bacteria defend themselves against bacteriophages infection by producing enzymes that destroy foreign DNA. These enzymes, called restriction endonucleases, cut up the viral DNA that injected by the bacteriophages into bacterial cells (host cell). Bacteria also contain a system that allows them to block the virus's replication through a form of RNA interference (a genetic system provides bacteria with acquired immunity to infection).Electron microscope pictures of many bacteriophages attached to a bacterial cell wall
(Bacteriophage mechanism of infection and life cycle)
Scientists developed phage therapy against multi-drug-resistant strains of bacteria; also some bacteriophages are used bacteriophage to diagnose bacteria; that is called phage typing system e.g. using specific bacteriophage for detecting MRSA or Multidrug resistance Staphylococcus aureus.Some bacteriophages play important role in the virulence of bacteria because they carry virulence genes and when infect bacteria, the bacteria will be more virulent e.g. the Corynebacterium diphtheriae toxin gene is encoded by the lysogenic bacteriophage and not encoded on the bacterial chromosome; also shiga-like toxin; this toxin is produced by E.coli and the genes are carried by a specific bacteriophage. Some bacteriophages represent a problem in food industries like fermentation failures of cheese and reduce the product quality when bacteriophage infects the starter cultures (lactic acid bacteria LAB, Streptococcus thermophiles and Lactobacillus sp.).
Life cycle of bacteriophages:
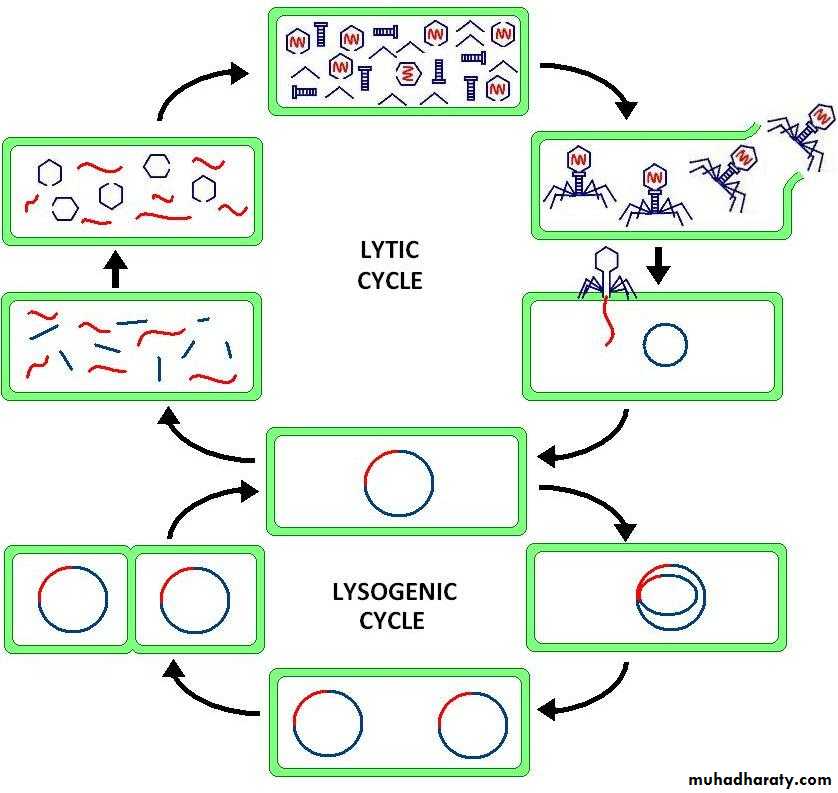
Life cycle of bacteriophages can be lytic or lysogenic cycle, the difference between the lytic cycle and the lysogenic cycle is that the lysogenic cycle does not lyse the bacterial host cell due to the integration of phage genome into the host bacterial cell genome. While lytic cycle leads to the death of the host cell due to destroy of cell plasma membrane. Phages that replicate only by the lytic cycle are known as virulent phages while phages that replicate using both lytic and lysogenic cycles are known as temperate phages.Examples of bacteriophages:
Temperate phages (mu and lambda):It is icosahedral double stranded linear DNA virus, infects Escherichia coli. The phage DNA may integrate itself into the host cell chromosome in the lysogenic pathway. In this state, the λ DNA is called a prophage and stays resident within the host's genome without apparent harm to the host bacterial cell.
Filamentous and spherical phages (FV):
Both phages having ssDNA (single stranded DNA). Their hosts are gram-negative bacteria that have sex pilli. They adsorb at the tips of the bacterial appendages or sex pilli and are released from growing and dividing cells without harming the bacterial host cells.
The series of T-even phages T2, T4 and T6 strains:
They are double-stranded DNA bacteriophages infect Escherichia coli. T-even phage is considered the best studied model organism in molecular biology because it contains five genes only.