
ANUS AND ANAL CANAL
By Dr. Ali K.Shaaeli
MBChB, FIBMS, FACS

THE OBJECTIVES
To understand the management of anal
pathologies.
Understand the anatomy of the anal canal and
their relationship to surgical disease and its
treatment.
Anal diseases are common and its treatment
tends to be conservative, although surgery may
be required.

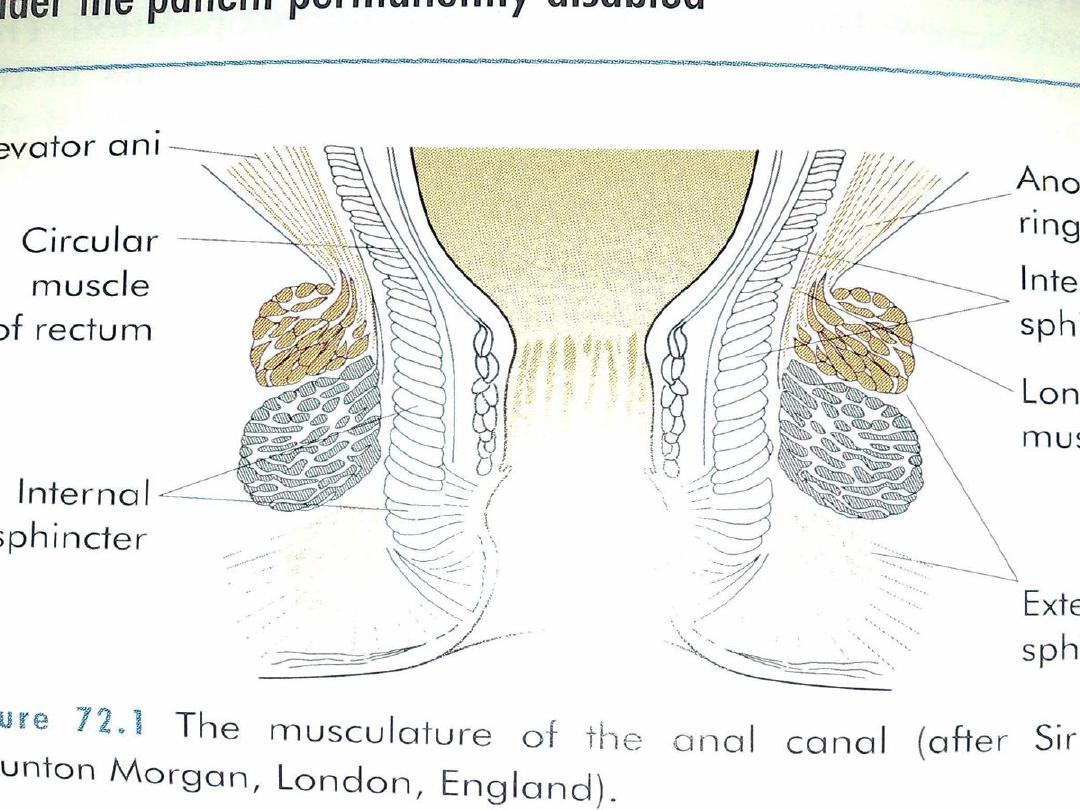
Surgical anatomy
Anal canal extends from pelvic floor to the anal
verge.
Internal sphincter is white in color and its fiber is
white .
External sphincter is voluntary muscle red fiber.
Dentate line is line between mucus membrane
and squamous epithelium

• Anal fissure
It is an longitudinal ulcer extend from anal verge
to dentate line.
It is associated with skin tag and sentinel papillae.
Posteriorly located in more than 90%
Affect female more than male
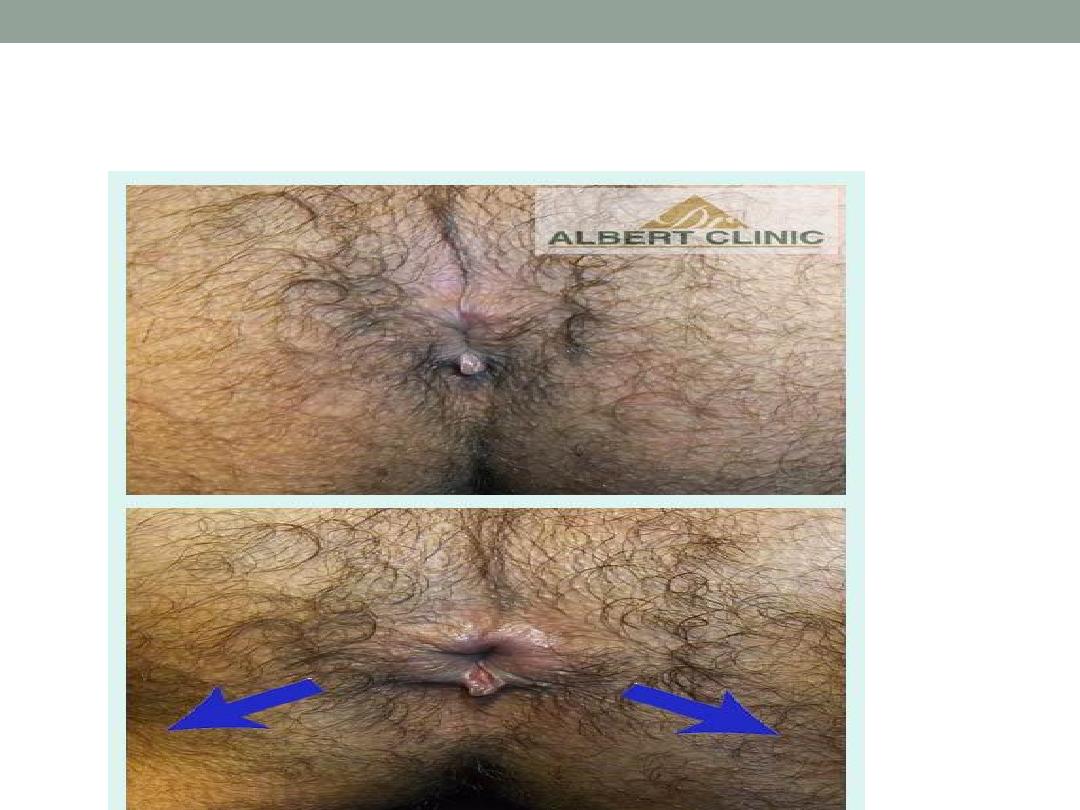
Fissure in ano

Etiology
•
Trauma
•
Ischemia
•
Stricture after hamorrhoidectomy
•
Inflammatory bowel disease (crohns disease )
•
Sexually transmitted disease

Clinical features
•
It is common in young age group, it is not rare in
children
•
Pain is sharp, agonizing, during defecation.
•
Bleeding, it is slight and may appear as streaks
•
Might be slight discharge.
•
On Exam, we found longitudinal ulcer with skin
tag and sentinel papillae
•
PR. Exam, is very painful better to be avoided
unless there is especial indication.

Treatment
•
Conservative treatment ;
•
a- glyceryl trinitrate ointment
b-diltiazem(ca.channel blocker)
c-laxatives
•
Surgical treatment;
•
a-lateral sphinctrotomy
b-anal advancement flap

Pilonidal sinus
•
It is acquired disease due to broken hair
accumulate at the natal cleft
•
It also occur at interdigital fold
•
It also occur at umbilicus
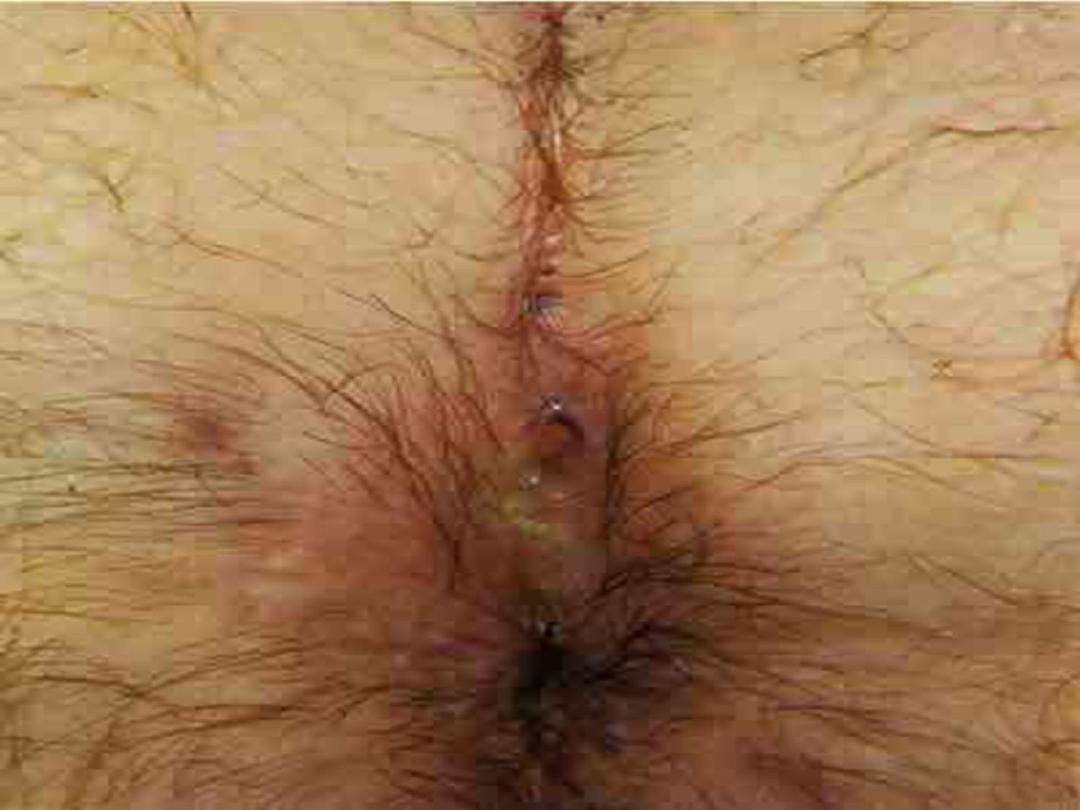

Clinical features
•
Affects male more than female, at the third
decade of life
•
Discharging sinus at level of coccyx, with one or
more opening.
•
Contains hair tuft in the opening.
•
Might be associated infection (abscess )

Treatment
•
1- conservative; a-cleaning of the tracks and
remove hair,
b- frequent washing
c- avoid long sitting

Treatment
•
Surgical treatment;
a- Abscess; should be drained
b-open the tracks and suture the skin to the
edge .
c-excise the tracks, drain and direct suture.
d- excise sinus area and packing followed by
daily change of dressing and bath till closure by
granulation tissue.
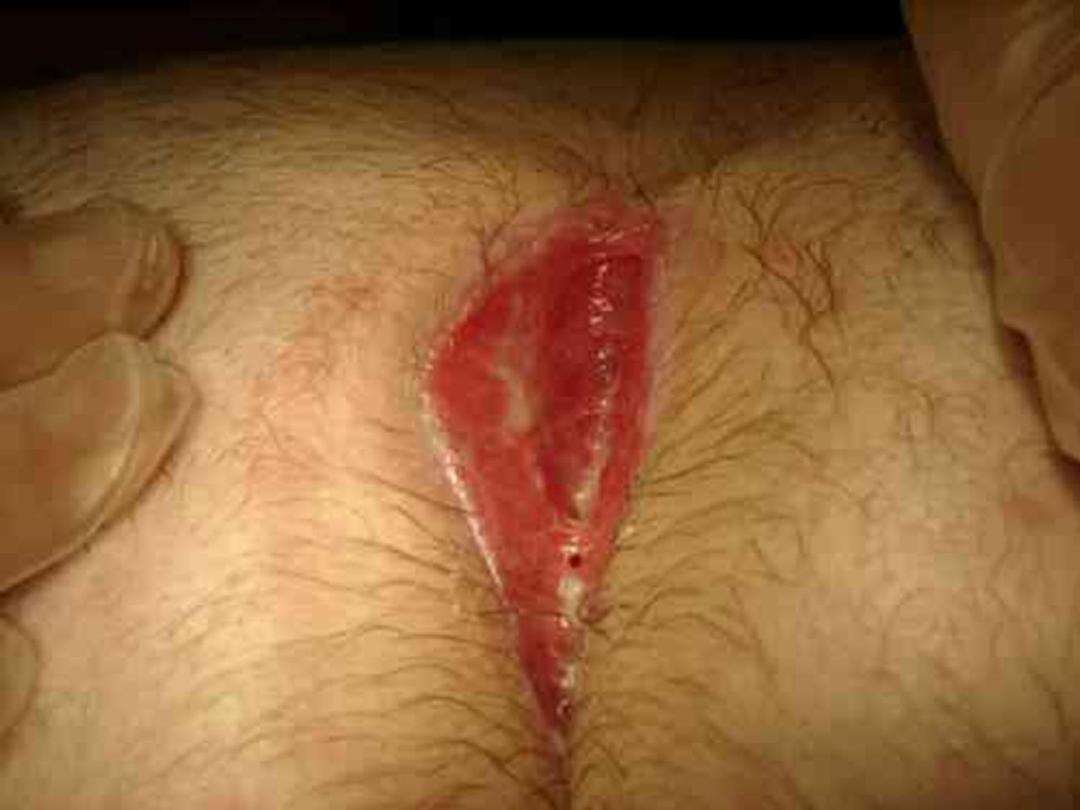
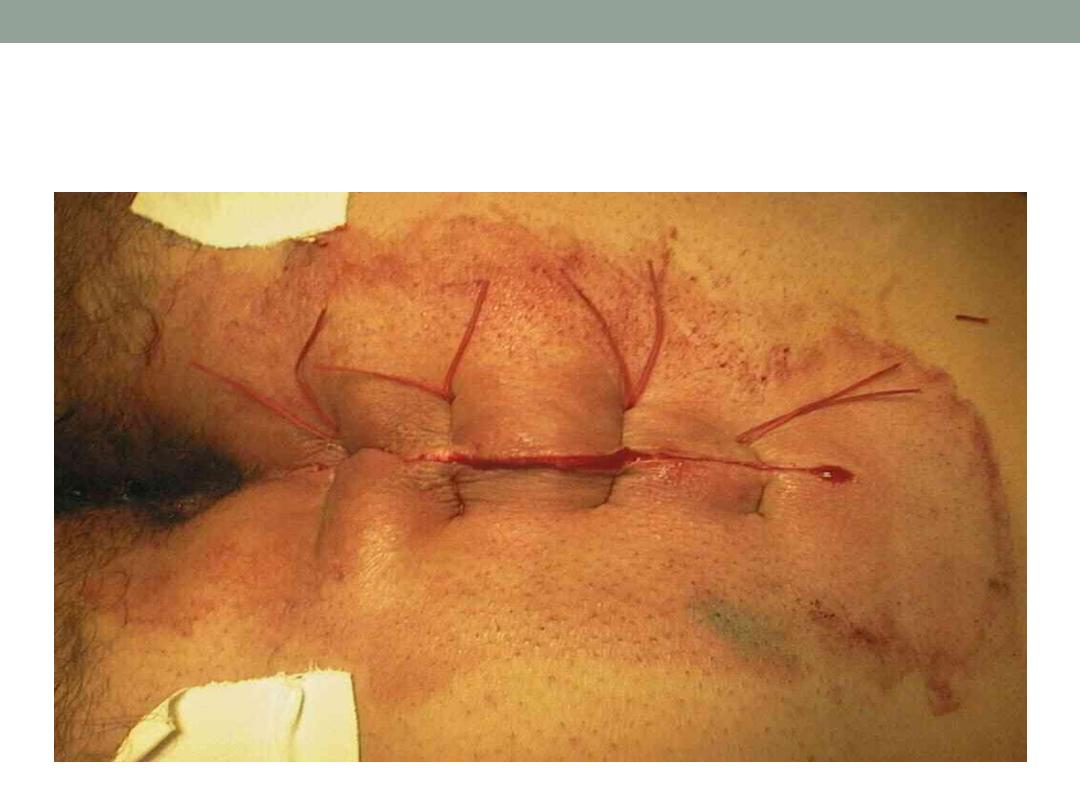
Closure by suturing
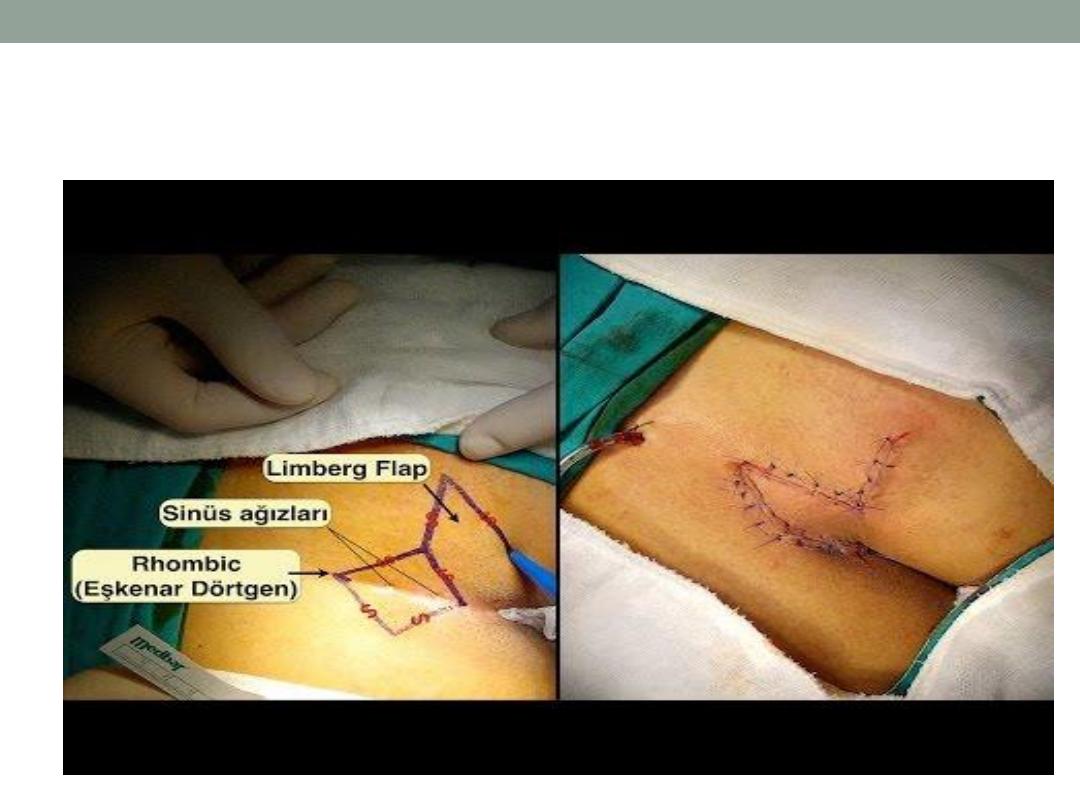
Limberg flap

Heammorhoids
•
May be symptom of other diseases;
1.
Carcinoma of rectum.
2.
Pregnancy.
3.
Straining at micturition.
4.
Constipation.

Pathology
•
They are arrange in three groups at 3,7,and 11
o’clock sites while patient in lithotomy position.
•
These are related to the superior rectal artery
branches.
a-pedicle
b- internal hemorrhoid
c-external hemorrhoid.
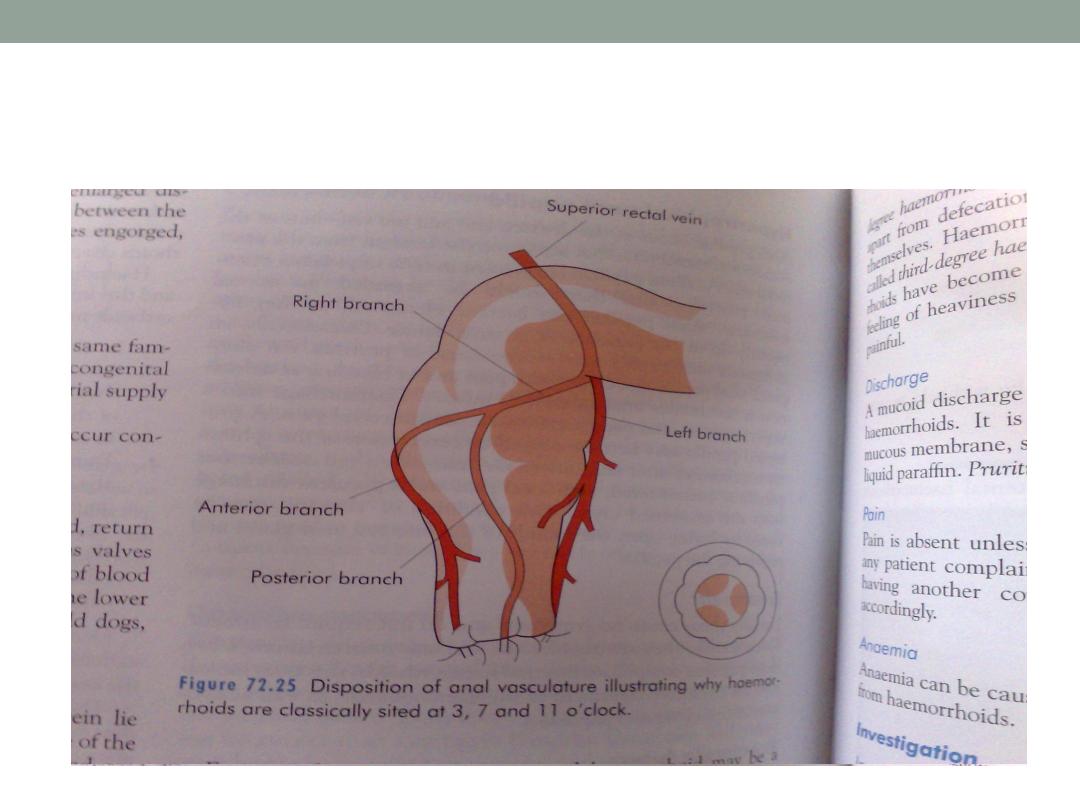
Hemorroidal arteries

Clinical features
1.
Bleeding
2.
Prolapse
3.
Discharge
4.
Pain
5.
anemia

Findings On Examination
•
Inspection
•
Digital examination
•
Proctoscopy
•
segmoidoscopy
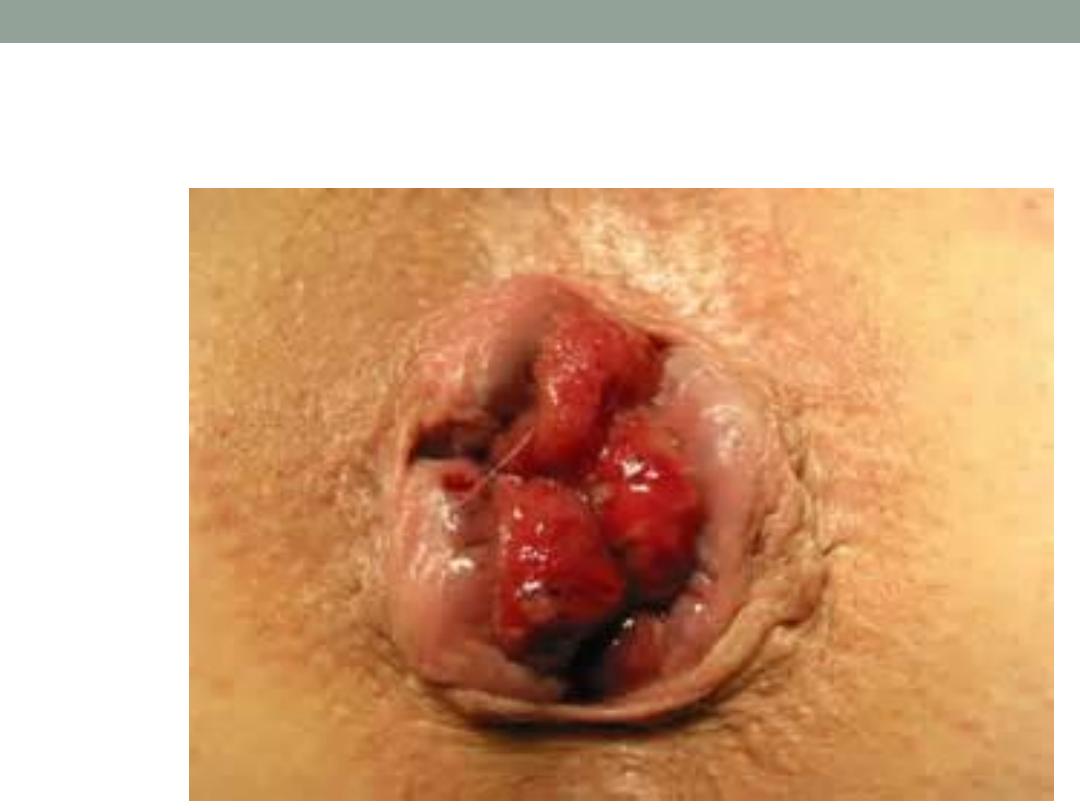
Prolapsed heamorrhoid

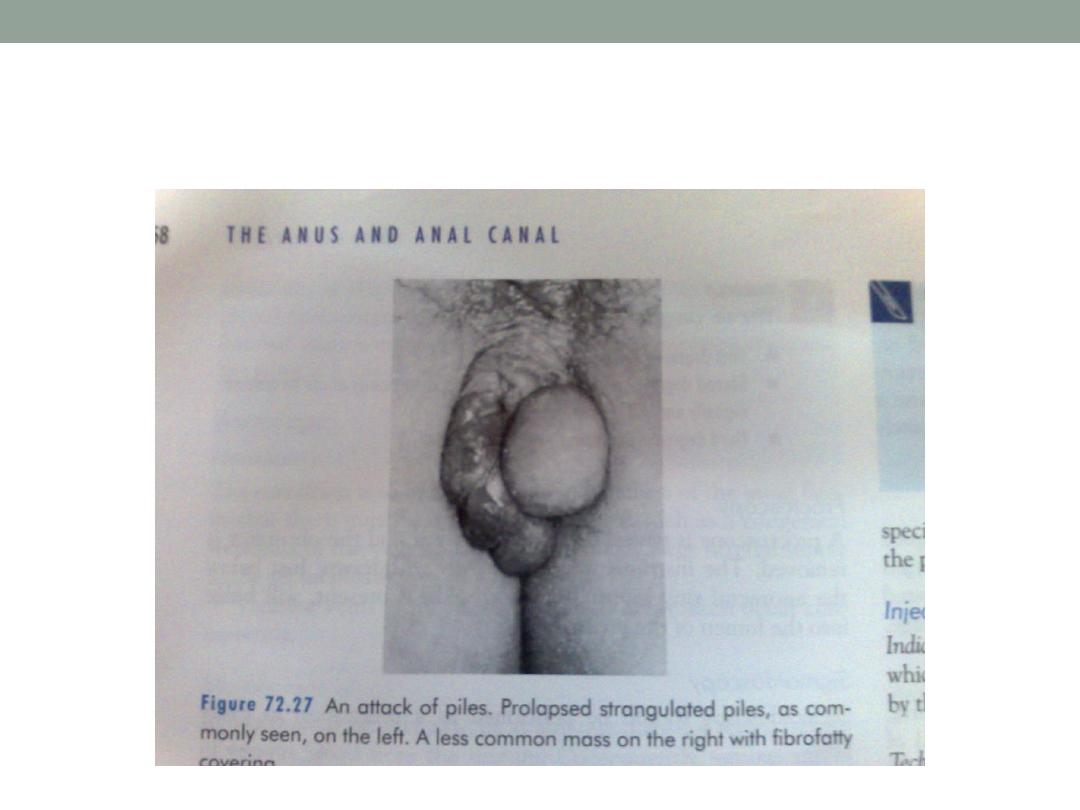

complications
1.
Strangulation
2.
Thrombosis
3.
Ulceration
4.
Gangrene
5.
Fibrosis
6.
Suppuration
7.
Pyophlebitis(portal pyaemia )
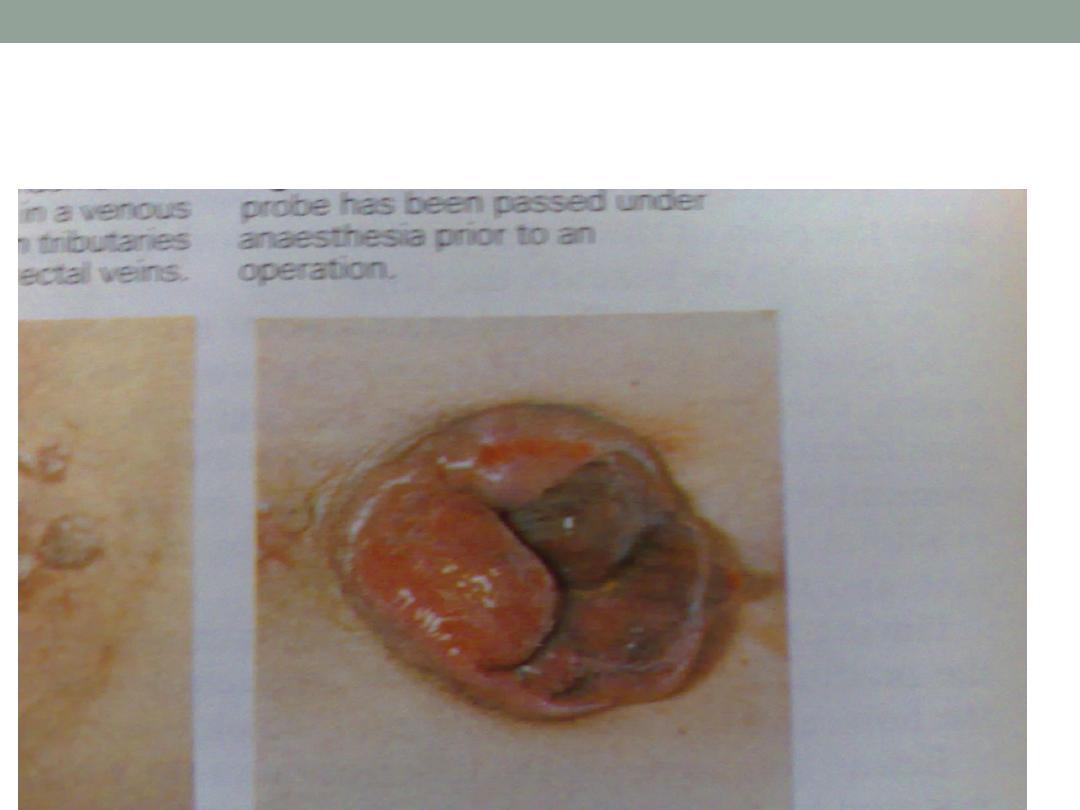
Strangulated haemorrhoids
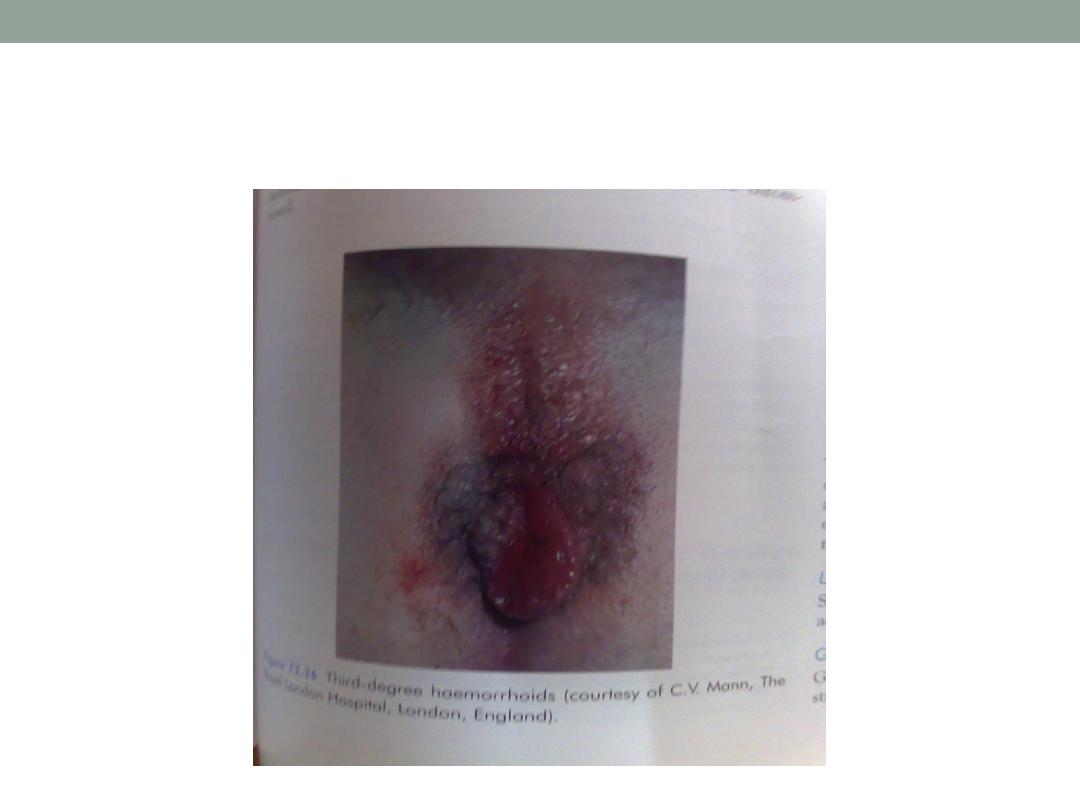
Third degree haemorrhoids

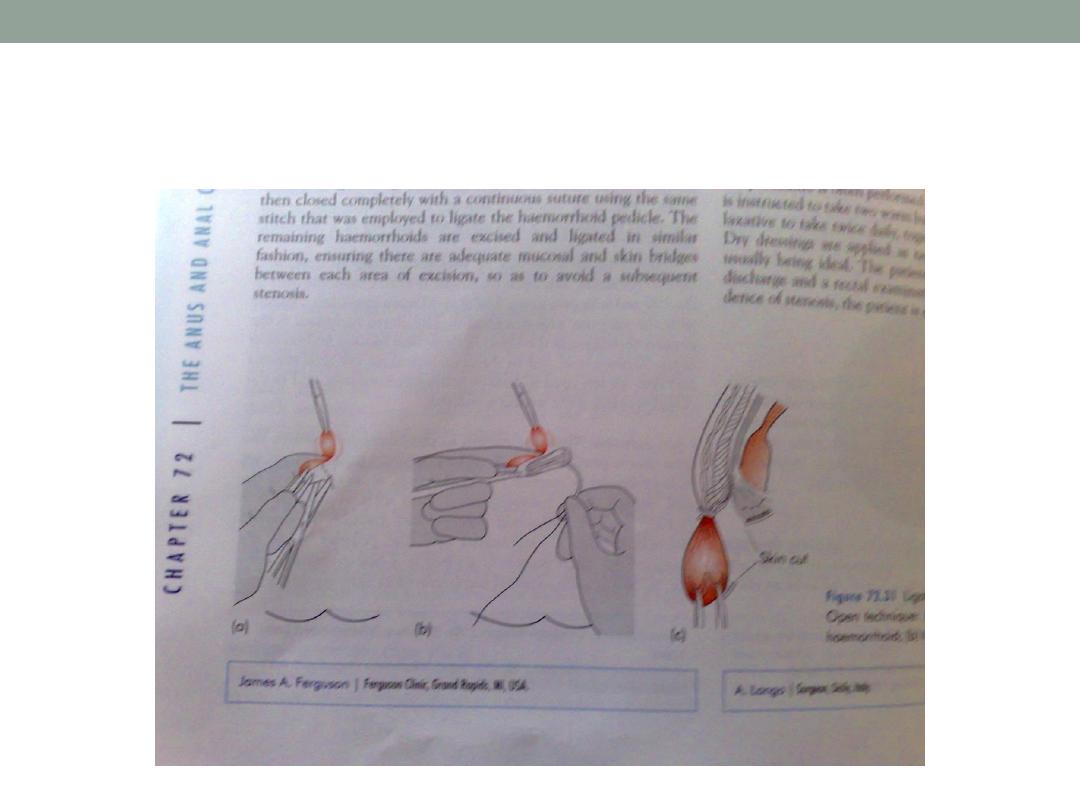
Treatment
•
Symptomatic treatment
•
Active treatment
1-injection
2-banding (barrons band )
3-cryosurgery
4-photocoagulation
5-surgery (transfixation and excision )
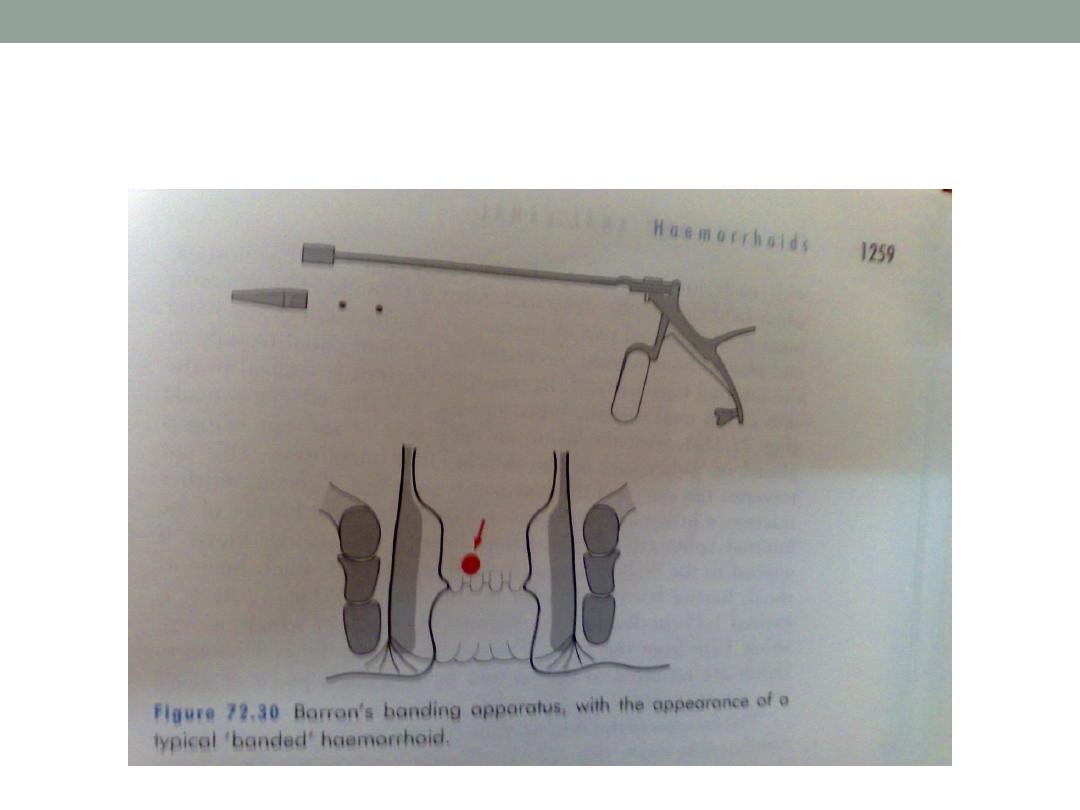
Barron’s banding


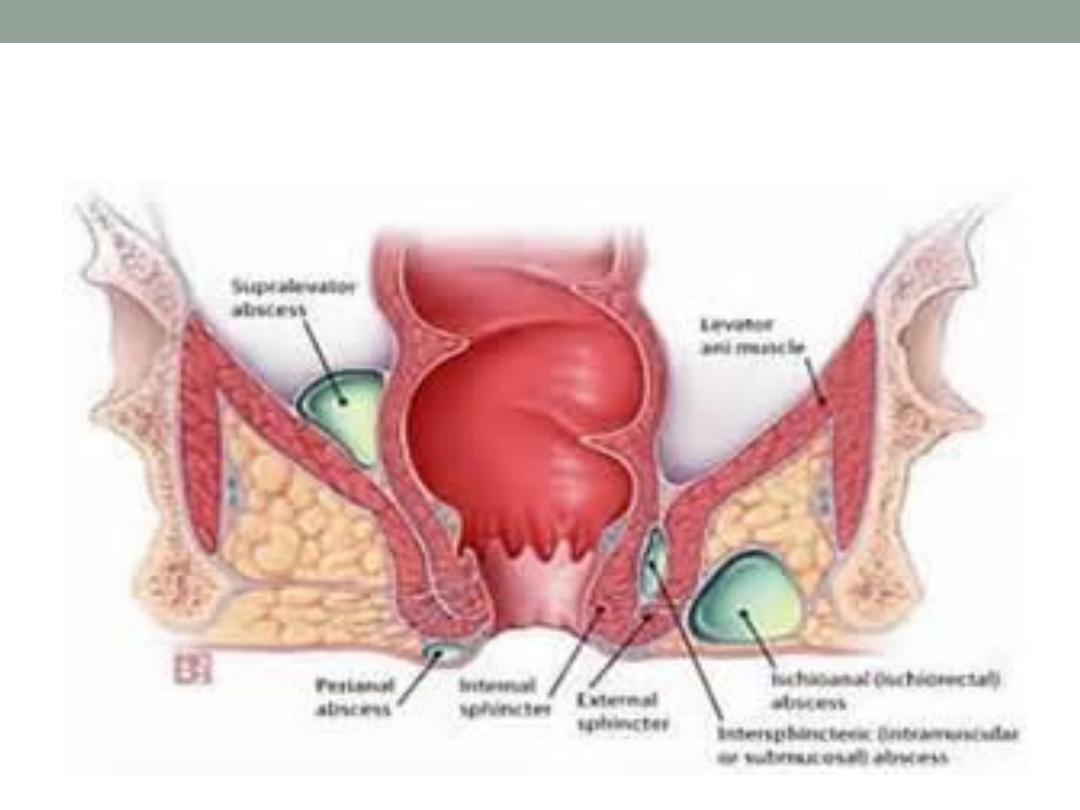
Anorectal abscess
•
Perianal 60%
•
Ischiorectal 30%
•
Submucus
•
pelvirectal
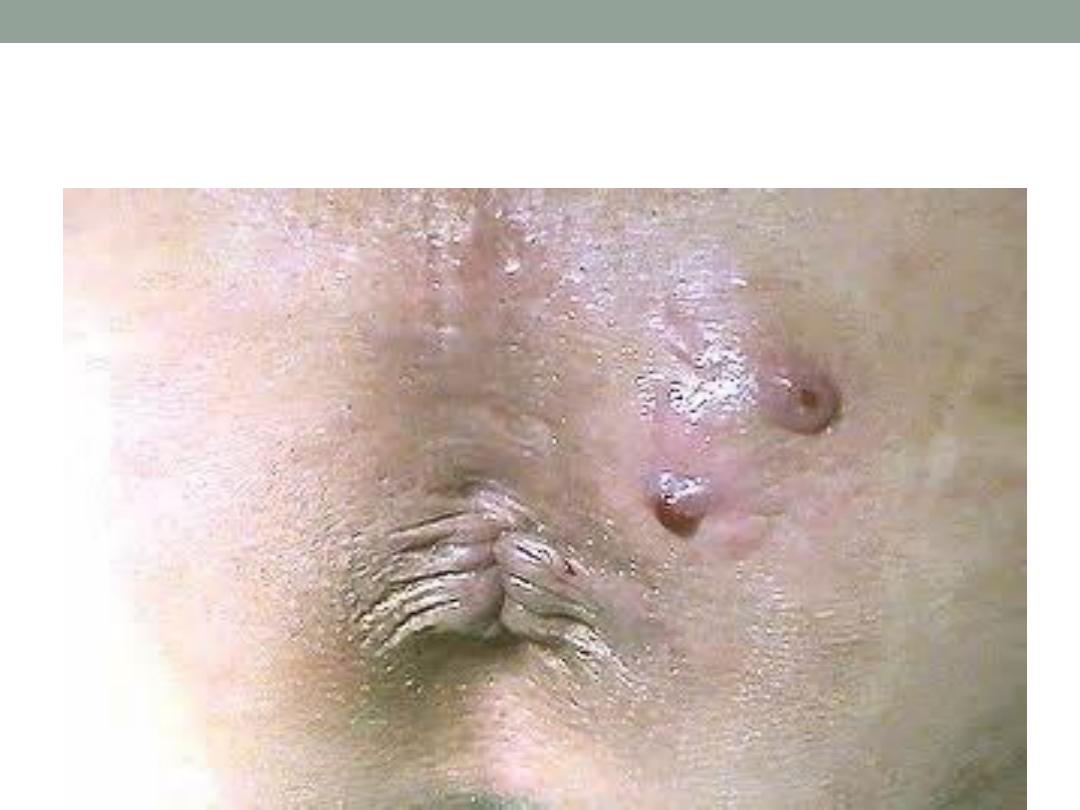
Perianal abscess


Fistula in ano
It is a track connecting two epithelial
surface (skin and anal or rectal
mucosa )

Classifications
Low or high fistula according to the
internal opening wethere below or
above the ano-rectal ring.

Classifications
Anatomical ; subcutaneous,
submucous, low anal, high anal,
pelvirectal.
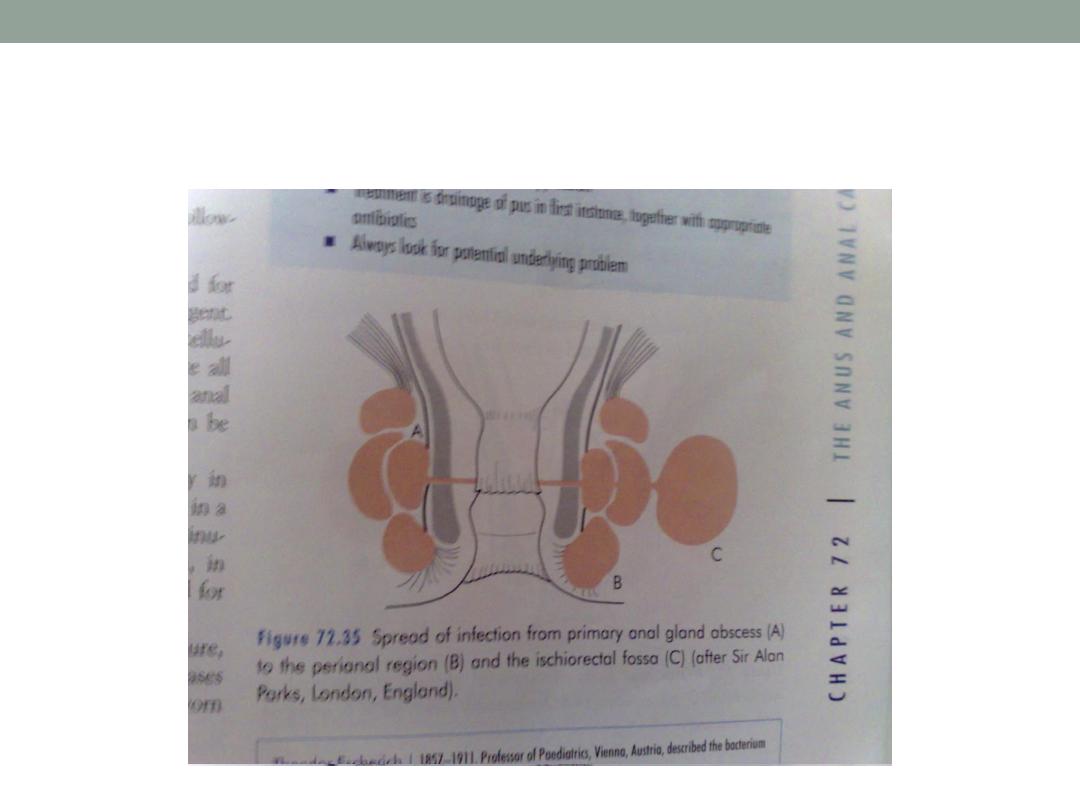
Park classification; a-intersphincteric
b-transsphincteric
( low or high )
c-supralevator
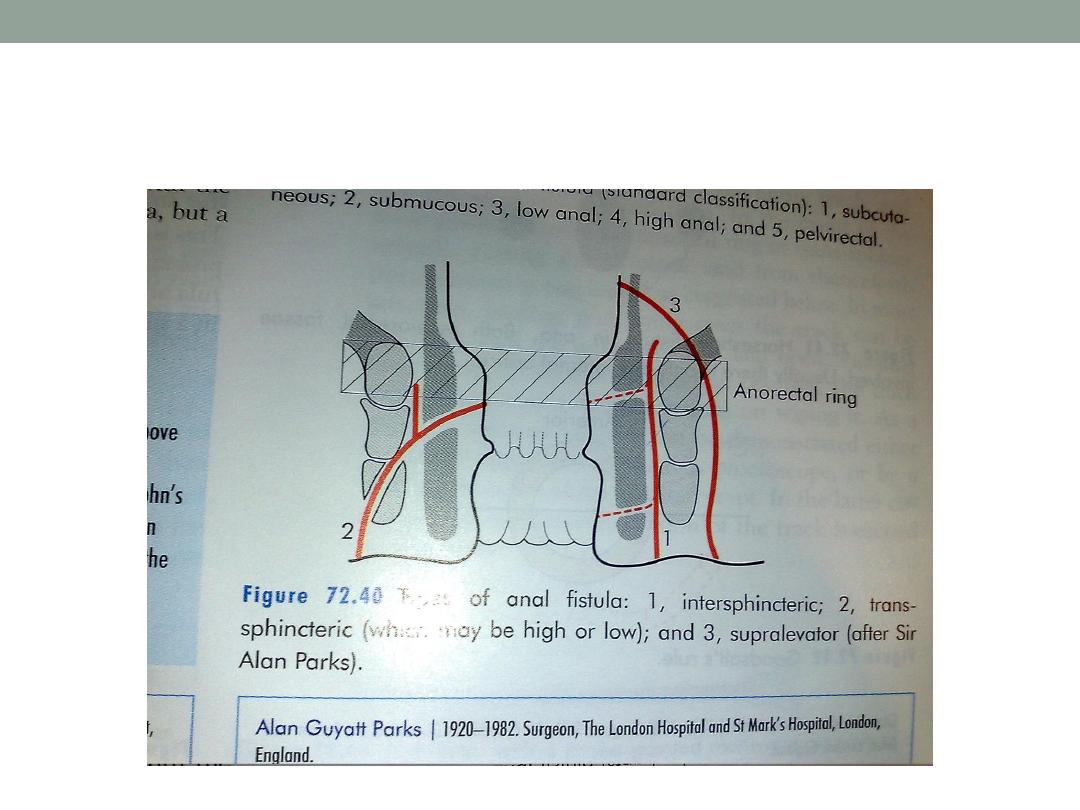
Park classification of fistula
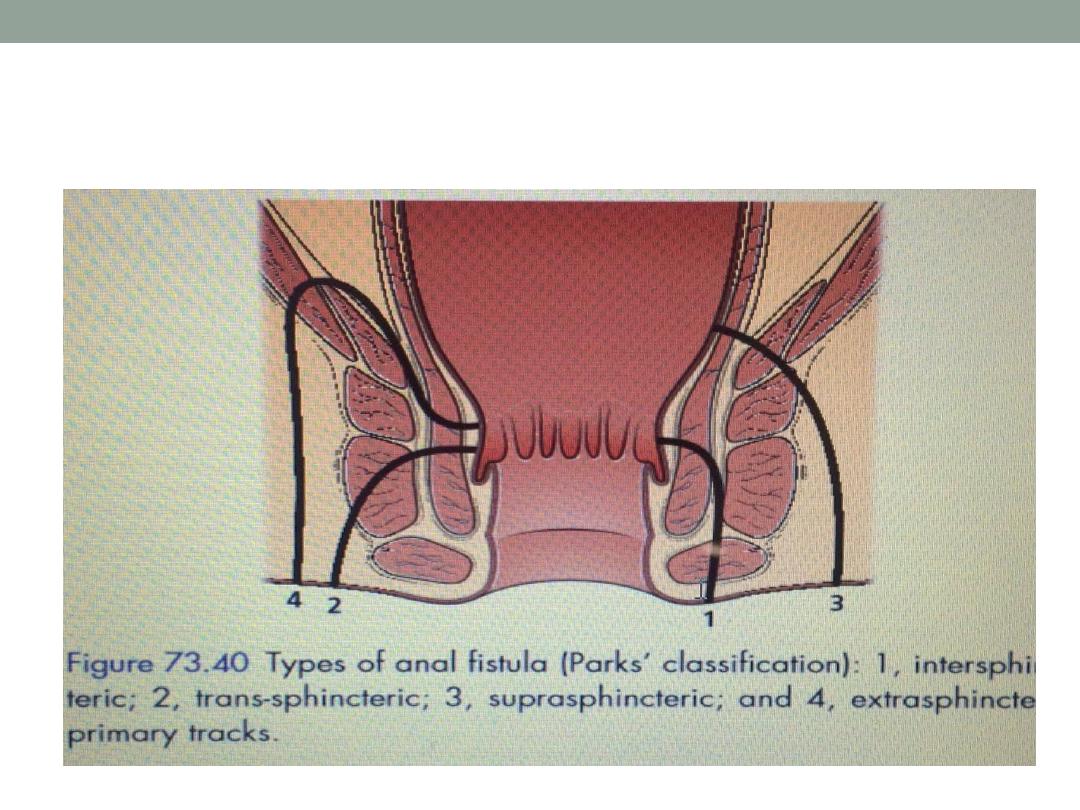
Parks classification of fistula in ano

Goodsoll’s rule

Clinical features
Continuous seroperulent discharge
Attacks of pain followed by discharge of pus
Orifice usually small, 3-4 cm from anus
Goodsall’s rule ; orifice at the anterior half are
direct while that at posterior half have curved
track.
PR. Examination
Proctoscopy

Treatment
Low type; lay open ( fistulatomy )
High type; staged operation
seton
colostomy

Options in the management of perianal
abscess, include all except
1.
Early operative treatment with drainage of
pus
2.
De-roofing of abscess cavity sometimes
with excision of overlying skin
3.
Checking for a fistula opening once a cute
inflammation had subsided
4.
Conservative treatment with suitable
broad spectrum antibiotics.

In the surgical treatment of a high anal
fistula, all are options EXCEPT:
•
A-the tract is completely laid open and
allowed to heal by granulation
•
B- the tract is partially laid open and
partially cored
•
C- A seton is applied
•
D- A colostomy is made
