Lec 2
كورس ثاني
الدكتور حسن سالم الجميلي
باطنيه
؛
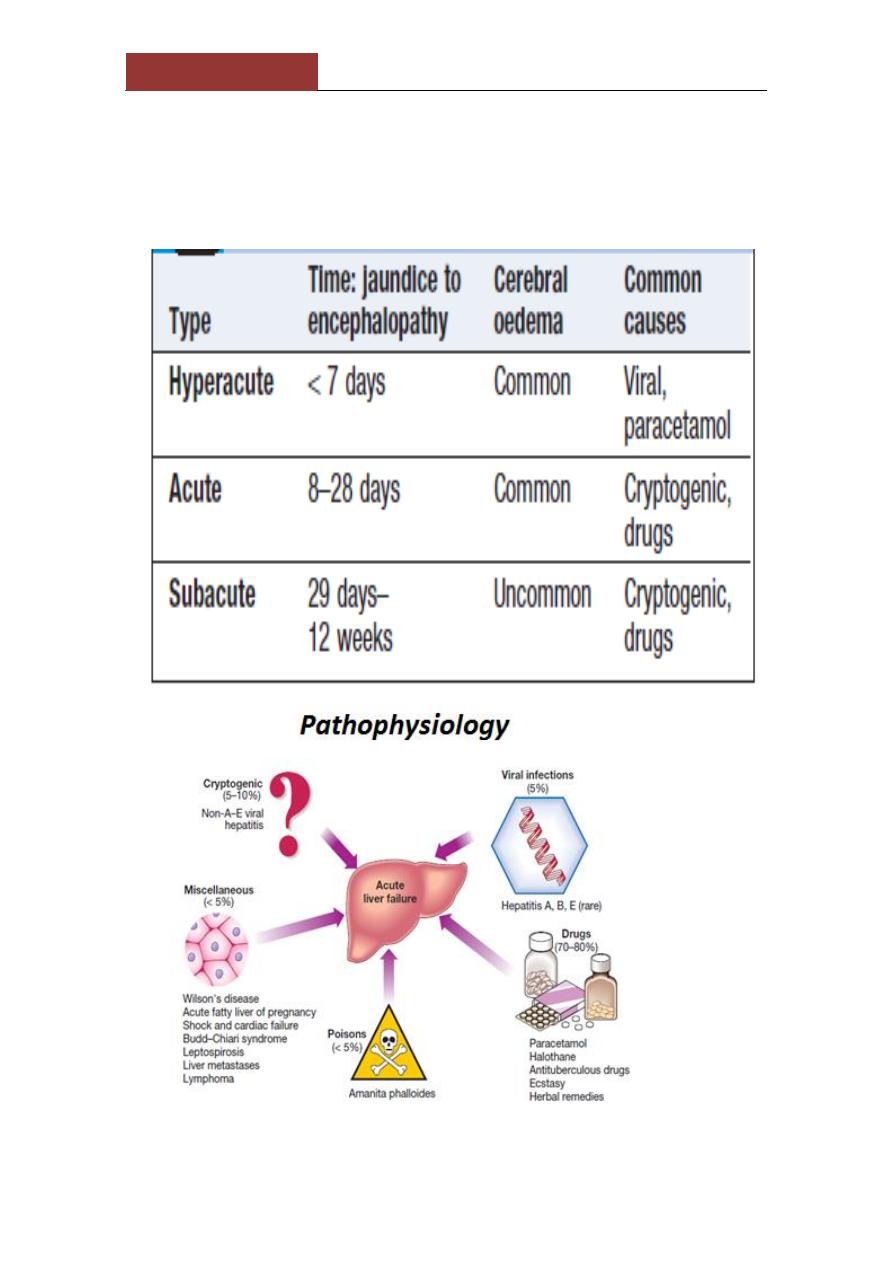
Acute liver failure:
progressive deterioration in liver function and mental changes
progressing from confusion to coma in absence of evidence of
preexisting liver disease.
Lec 2
كورس ثاني
الدكتور حسن سالم الجميلي
باطنيه
؛
. Clinical assessment
1-Cerebral disturbance
(hepatic encephalopathy and/or cerebral
oedema) is the cardinal manifestation of acute
liver failure. Cerebral oedema may occur due to increased intracranial
pressure
-unequal or abnormally reacting pupils, fixed pupils
- hypertensive episodes bradycardia, hyperventilation, profuse
sweating, local or general myoclonus, focal fits or decerebrate
posturing.
-Papilloedema occurs rarely and is a late sign.
2-
nausea and vomiting. Right hypochondrial discomfort
. The patient may be
jaundiced
.
- death may occur in fulminant cases of acute liver failure before
jaundice develops.
-
Fetor hepaticus
can be present.
-The
liver
is usually of normal size but later becomes smaller.
- Hepatomegaly is unusual and, in the presence of a sudden onset of
ascites, suggests venous outflow obstruction as the cause (Budd–
Chiari syndrome.
Splenomegaly is uncommon
and never prominent.
-
Ascites and oedema
are late due to fluid therapy.
West haven classification of H.Encephalopathy

Lec 2
كورس ثاني
الدكتور حسن سالم الجميلي
باطنيه
؛
invex:
PT, bilirubin, Plasma aminotransferase.
Plasma albumin remains normal unless the course is
prolonged. Percutaneous liver biopsy is contraindicated
because of the severe coagulopathy, but biopsy can be
undertaken using the transjugular route if appropriate.
Management
1-high-dependency or intensive care unit
2-Conservative treatment ..GW, mannitol,bowelsterlization by
metronidazole and neomycin.
3- N-acetylcysteine therapy may improve outcome, particularly in
patients with acute liver failure
due to paracetamol poisoning.
4-earlytransfer to a specialized transplant unit . Survival following
liver transplantation for acute liver failure
is improving, and 1-year survival rates of about 60%
can be expected.
Adverse prognostic criteria in acute liver failure:
-Indication for transplant in paracetamol poisoning

Lec 2
كورس ثاني
الدكتور حسن سالم الجميلي
باطنيه
؛
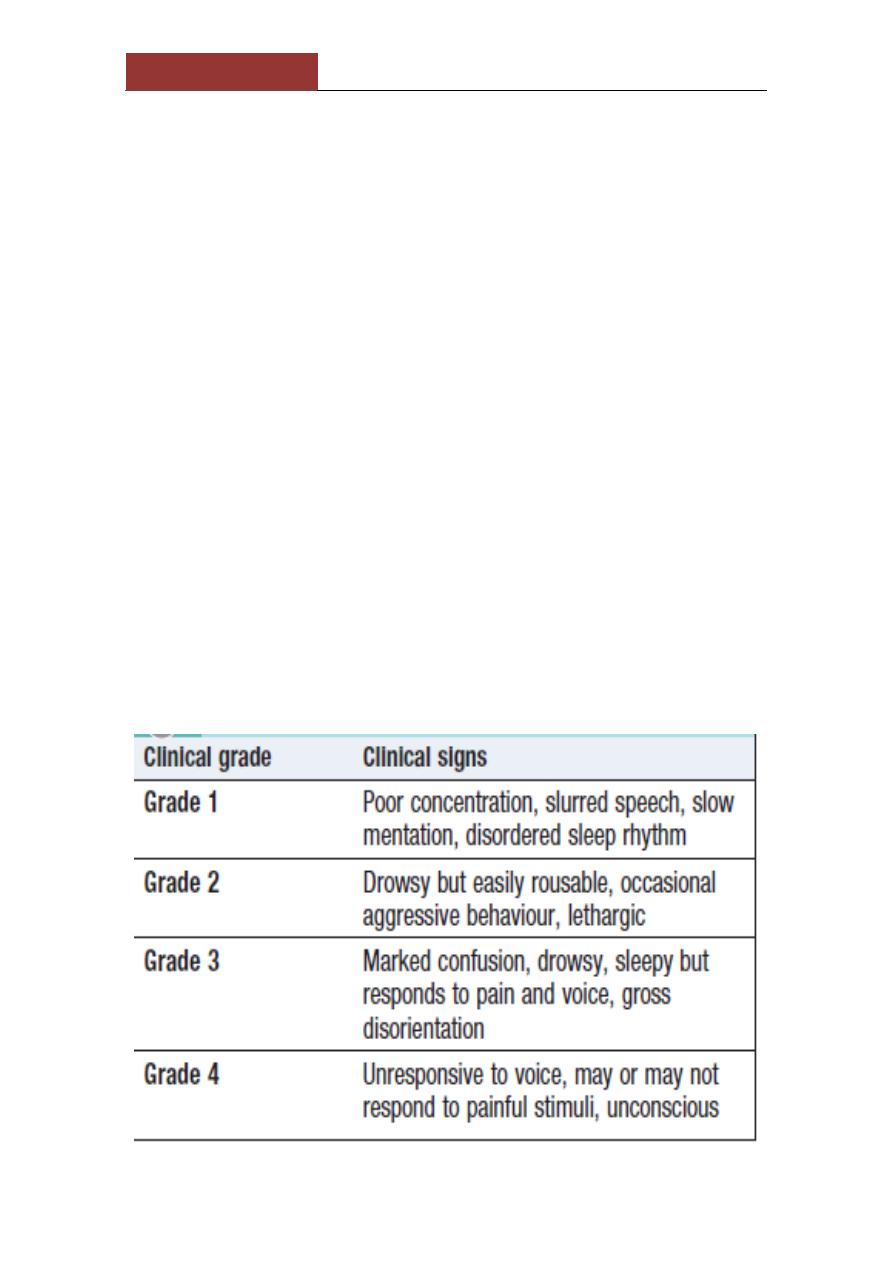
Hepatic encephalopathy
neuropsychiatric syndrome caused by liver disease. As it progresses,
confusion is followed by coma. The
degree of encephalopathy can be graded from 1 to 4,
Examination --a flapping tremor (
asterixis)
,
inability to perform simple mental arithmetic tasks or
to draw objects such as a star (
constructional apraxia
;
and, as the condition progresses,
hyper-reflexia
and
bilateral extensor plantar responses
.
When an episode develops acutely, a precipitating factor may be found :
• Drugs (especially sedatives antidepressants)
• Dehydration (including diuretics paracentesis)
• Infection
•Hypokalaemia
• Constipation
• TIPS
•↑Protein load (including GI bleeding)

Lec 2
كورس ثاني
الدكتور حسن سالم الجميلي
باطنيه
؛
Pathophysiology
disturbance of brain function by neurotoxins that are normally
metabolised by the liver. mainly nitrogenous substances produced in
the gut,
Ammonia
has traditionally been considered an important
factor.
Other:
γ-aminobutyric acid
(GABA) as a mediator
octopamine,
amino acids, mercaptans and fatty acids
that can act as
neurotransmitters.
Investigations
1-clinical
2-(
EEG
)shows diffuse slowing of the normal alpha waves with
eventual development of delta waves.
3-The arterial ammonia is ↑
Rx;
1-precipitatingfactors
2-suppress the production of neurotoxins by bacteria in the bowel.
Rifaximin
(400 mg 3 times daily) is a well tolerated,
non-absorbed antibiotic that acts by reducing
the bacterial content of the bowel and has been shown
to be effective..
3-
Lactulose
(15–30 mL 3 times daily) is increased gradually until the
bowels are moving twice daily. It produces an osmotic laxative effect,
reduces the pH of the colonic content, thereby limiting colonic
ammonia absorption,. -
4-Chronic or refractory encephalopathy is one of the main
indications for liver transplantation.

Lec 2
كورس ثاني
الدكتور حسن سالم الجميلي
باطنيه
؛
Viral hepatitis
Clinical features of acute infection
-prodromal illness --headache, myalgia, arthralgia, nausea and
anorexia usually precedes the development of jaundice by a few days
to 2 week.
-Vomiting ,diarrhoea ,abdominal discomfort is common.
-Dark urine and pale stools may precede jaundice.
Exam:. The
liver
is often tender but minimally enlarged. mild
splenomegaly and cervical LAP
:
Complications
• Acute liver failure
•Cholestatic hepatitis (hepatitis A)
• Aplastic anaemia
• Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis (hepatitis B and C)
• Relapsing hepatitis
Investigations
1-A hepatitic pattern of LFTs
,transaminases
between 200 and 2000 U/L in an acute infection (usually lower and
fluctuating in chronic infections)
2-
bilirubin
reflects the degree of liver damage.

Lec 2
كورس ثاني
الدكتور حسن سالم الجميلي
باطنيه
؛
3-
ALP
rarely exceeds twice the upper limit of normal
4-
PT
Prolong indicates the severity of the hepatitis but rarely exceeds
25 seconds
5-
WBC
=normal with a relative lymphocytosis.
6-
Serological tests
confirm the aetiology of the infection.
Management
→
Most individuals do not need hospital care
.
→
sedatives and narcotics, which are metabolised in the
liver, should be avoided
.
→
No specific dietary modifications are needed
.
→Alcohol should be avoided during the acute illness.
→
Elective surgery should be avoided in cases
of acute viral hepatitis, as there is a risk of post-operative
liver failure.
→Liver transplantation is very rarely indicated for
acute viral hepatitis complicated by liver failure
Hepatitis A
hepatitis A virus
-picornavirus group of enteroviruses.
-highly infectious , spread by the faecal–oral route.
-asymptomatic, excrete the virus in faeces
for about 2–3 weeks before the onset then for a further 2 weeks.
-Infection is common in children
-common in areas of overcrowding and poor sanitation.
- In contrast to hepatitis B, achronic carrier state does not occur.
Investigations
▲
HAV is only present in the
blood
transiently during the incubation
period. Excretion in the
stools
occurs for only 7–14 days after the
onset of the clinical symptoms
▲
Anti-HAV IgM is diagnostic of an acute HAV infection.
▲
Titres of this antibody fall to low levels within about 3 months of
recovery
▲
Anti-HAV IgGis marker of previous HAV infection. Its presence
indicates immunity to HAV.
Lec 2
كورس ثاني
الدكتور حسن سالم الجميلي
باطنيه
؛
MX:
▲
-prevented
by improving social conditions
, especially
overcrowding and poor sanitation
▲
-
inactivated virus vaccine
..immunization should be considered for
1- chronic hepatitis B or C infections.
infected
-
close contacts of HAV
those at particular risk, such as
-
2
patients, the elderly, those with other major disease &pregnant
women.
3- People travelling to endemic areas
▲
Immediate protection by
immune serum globulin
---
1- after exposure
2-outbreak of hepatitis, in a school or nursery those at risk prevents
secondary spread to families.
Three imp.notes:
-
no role
for antiviral drugs in the therapy of HAV infection
-Acute liver failure is rare in hepatitis A (0.1%) and chronic infection
does
not occur
.
In adults, a cholestatic phase with elevated ALP levels may
-
.
complicate infection
\
Hepatiti s E
RNA virus
-The clinical presentation and management of hepatitis
E are similar to that of hepatitis A.
- faecal–oral route;
-does
not usually
cause chronic liver disease, although some cases
have been described, usually in immunocompromised patients
epatitis A in that infection
Hepatitis E differs from h
during pregnancy is associated with the development of
.
acute liver failure, which has a high mortality
-IgM antibodies to HEV are positive.
