BREECH PRESENTATION
Breech presentation is defined as a foetus
in a longitudinal lie with the buttocks or
feet closest to the cervix.

• This occurs in 3-4% of all deliveries.
• The percentage of breech deliveries
decreases with advancing gestational
age
• 22-25% of births prior to 28 weeks
gestation .
• 7-15% of births at 32 weeks' gestation .
• 3-4% of births at term.

• Peri-natal mortality is increased
• Two - to four fold with breech
presentation.
• Regardless of the mode of delivery.

• Deaths are most often associated with:
• malformations.
• prematurity.
• and intrauterine fetal demise.

Predisposing factors for breech
•
.
• fetal abnormalities ( CNS malformations, neck
masses,aneuploidy)
• Fetal abnormalities in 17% of preterm and in 9%
of term breech deliveries.
•

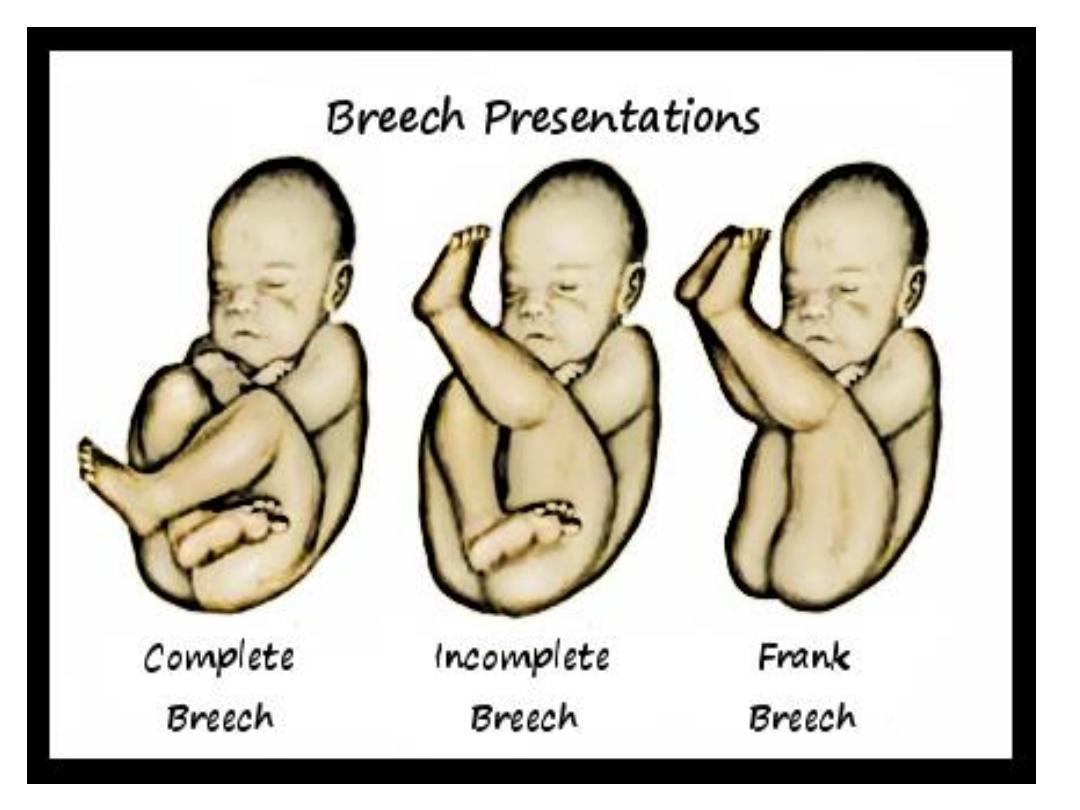
Types of breeches
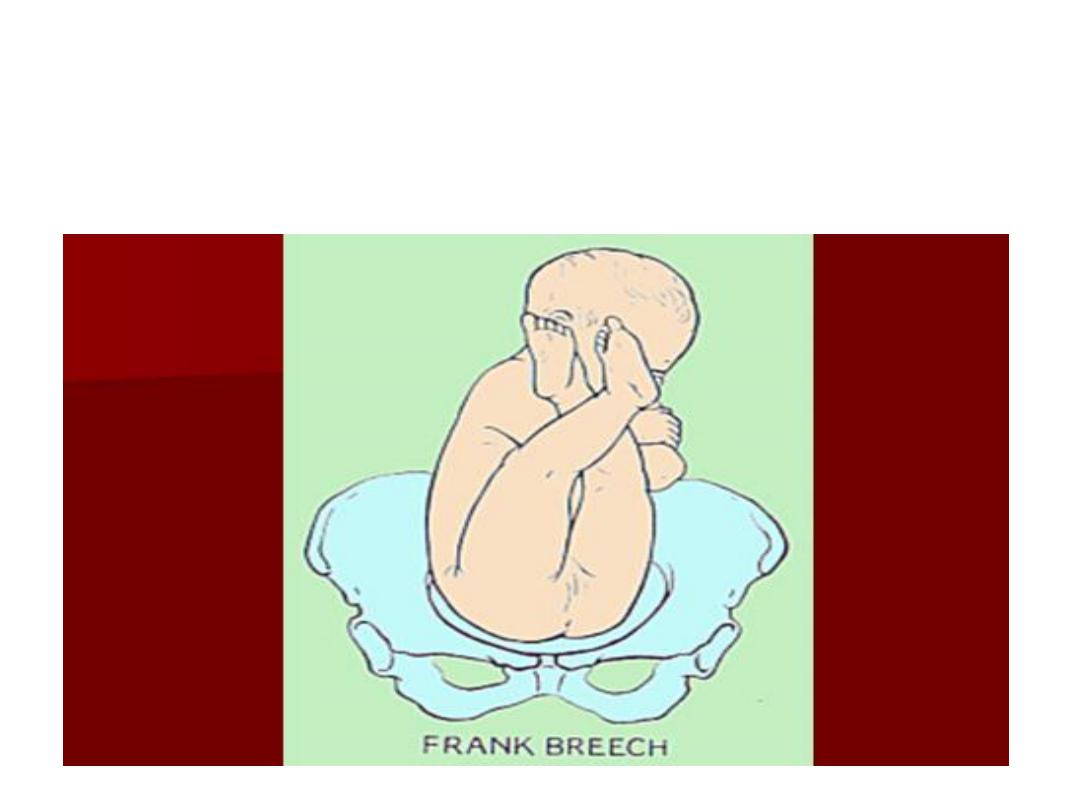
• Frank breech (50-70%) - Hips flexed,
knees extended (pike position)
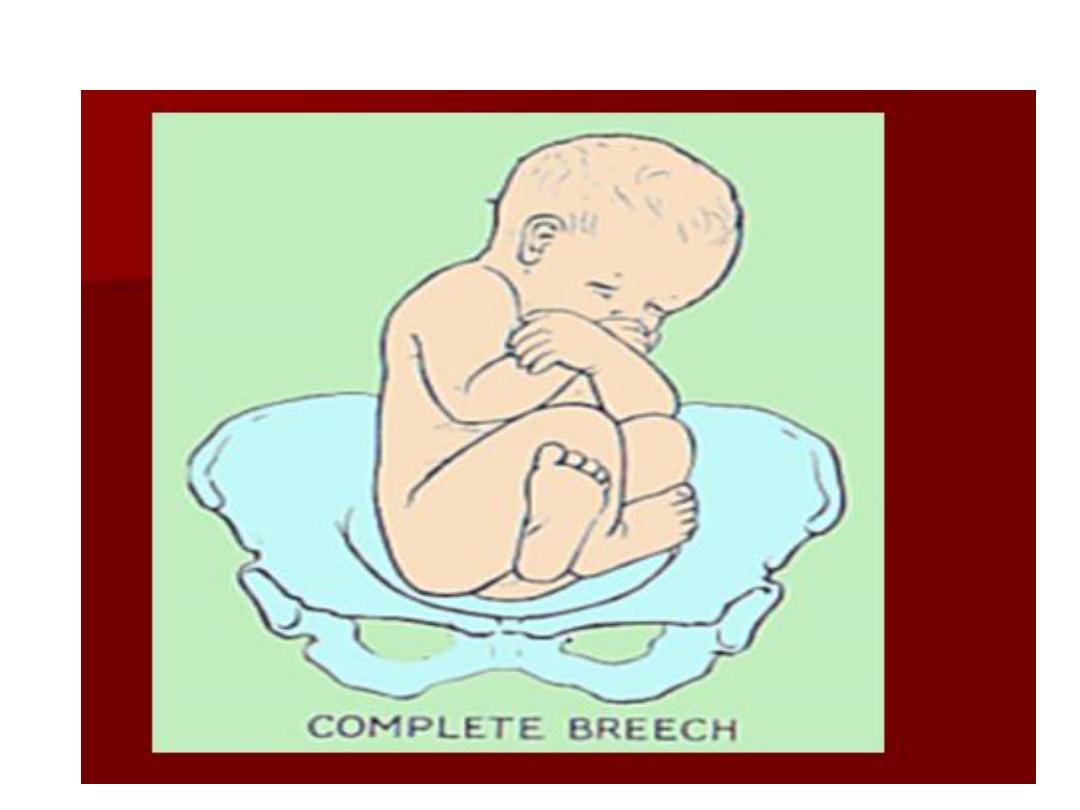
• Complete breech (5-10%) - Hips flexed,
knees flexed (cannonball position)
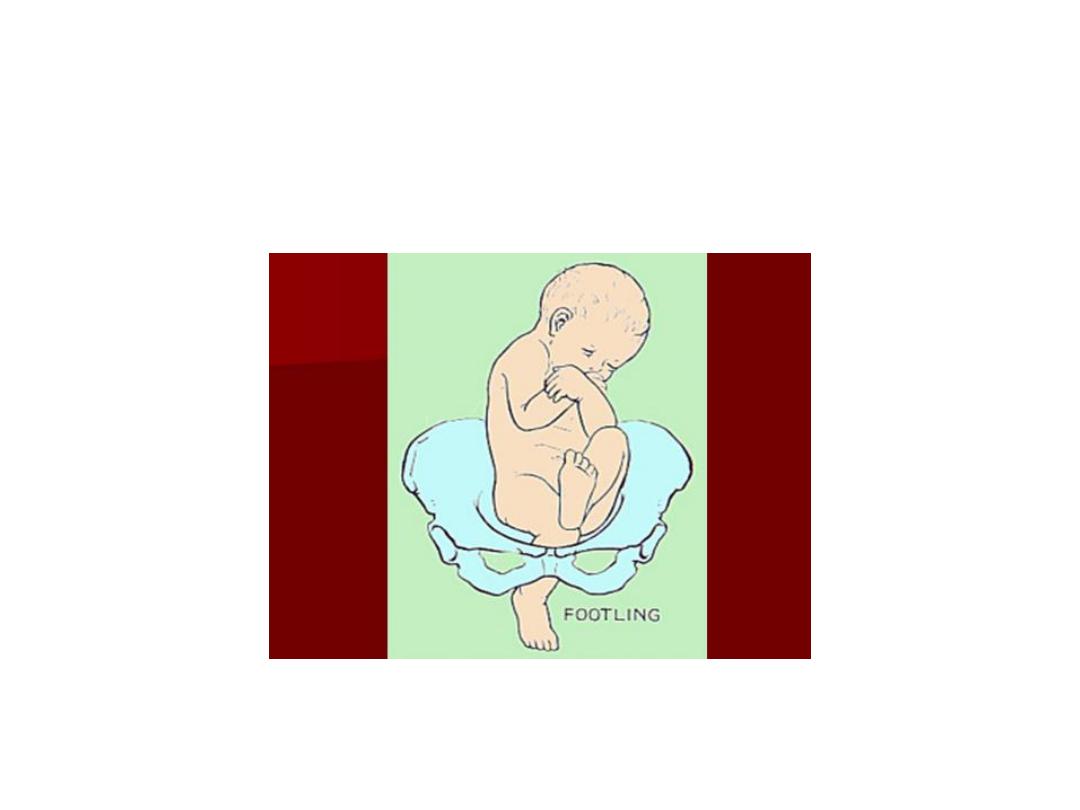
• Footling or incomplete (10-30%) - One
or both hips extended, foot presenting

DIAGNOSIS:
• HISTORY.
• Physical Exam.
• Investigations.
Abdominal exam:
Pelvic exam:

Options of Management:
• External Cephalic Version.
• Assisted vaginal delivery.
• Operative delivery.

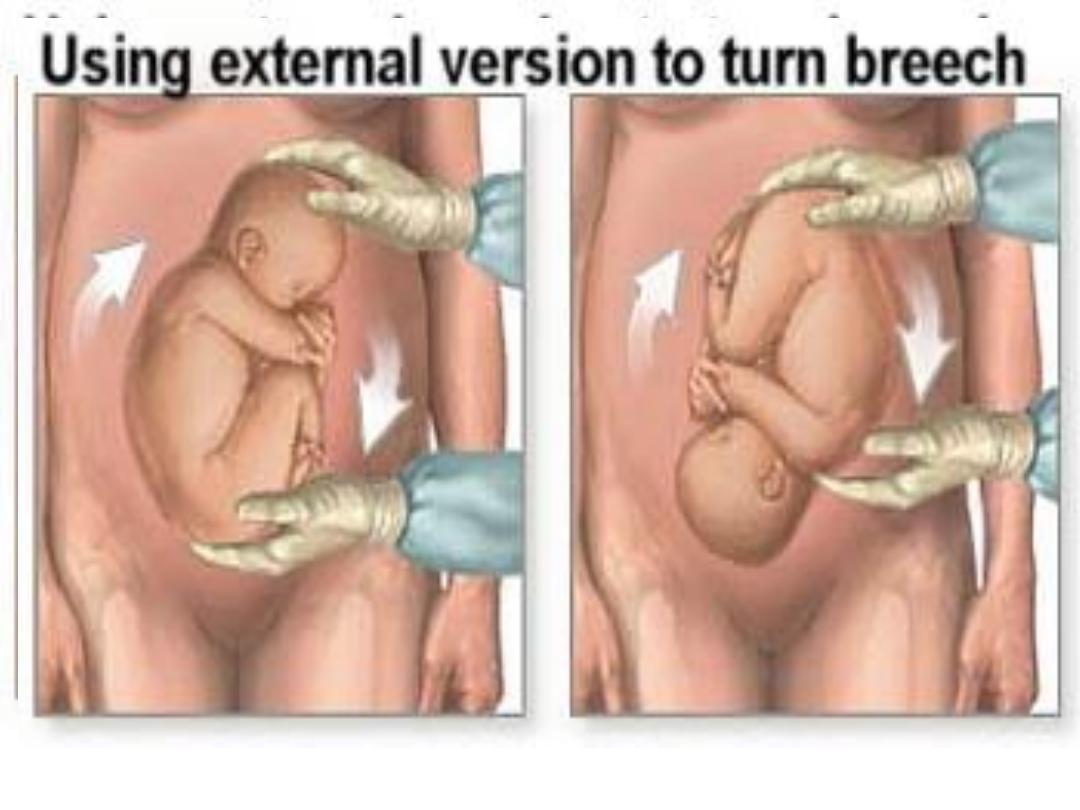
• External Cephalic Version(ECV):
is the trans-abdominal manual rotation of
the foetus into a cephalic presentation,
around 36 weeks.
• ECV should be performed where facilities
for monitoring and immediate delivery
are available.

• ECV should be offered from 36 weeks in nulliparous
women and from 37 weeks in multiparous women
• Absolute contraindications for ECV that are likely to
be associated with increased mortality or
morbidity:
● where caesarean delivery is required
● antepartum hemorrhage within the last 7 days
● abnormal cardio-tocography
● major uterine anomaly
● ruptured membranes
● multiple pregnancy (except delivery of second
twin).

Relative contraindications
● small-for-gestational-age fetus with
abnormal Doppler parameters
● proteinuric pre-eclampsia
● oligohydramnios
● major fetal anomalies
● scarred uterus
● unstable lie.

Risks
• Uncommon risks of ECV include fractured
fetal bones, precipitation of labor or
premature rupture of membranes
, fetomaternal hemorrhage (0-5%),
and cord entanglement (< 1.5%). A more
common risk of ECV is transient slowing of
the fetal heart rate

Vaginal Delivery:
• Frank
• GA>34w
• FW=2000-3500gr
• Adequate pelvis
• Flexed head
• Nonviable fetus
• Good progress labor

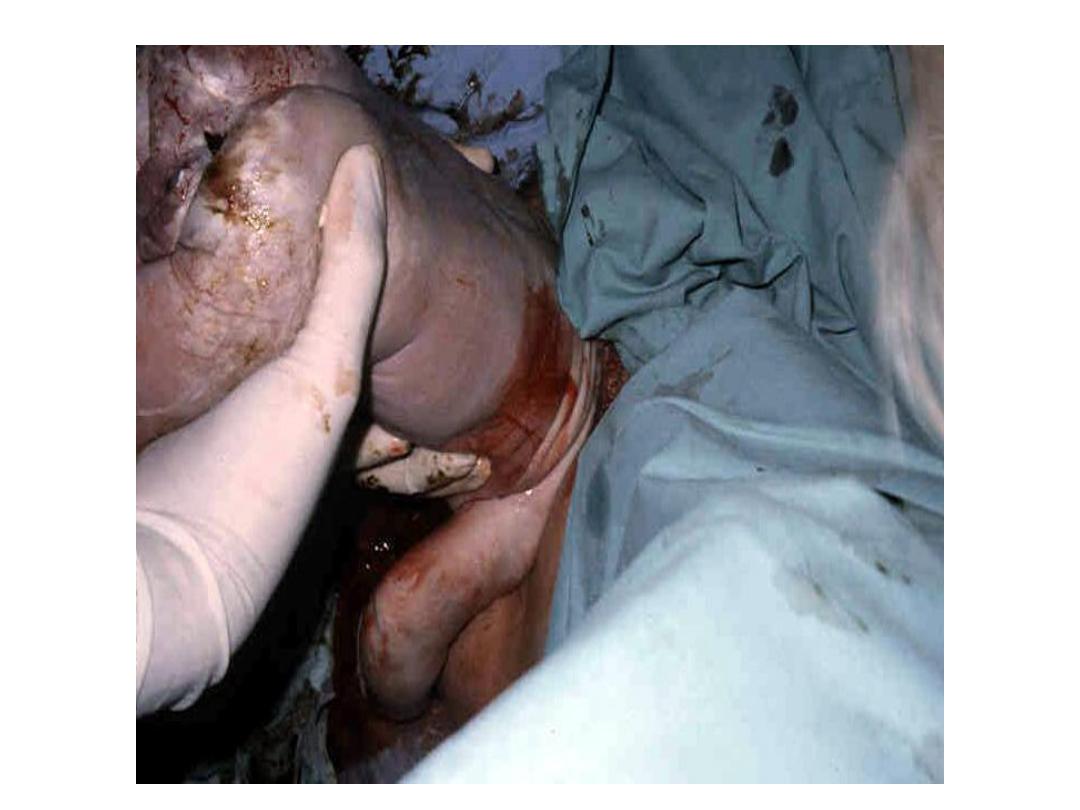
Vaginal breech delivery
Three types :
• Spontaneous breech delivery:
No traction or manipulation is used. This is for
very preterm, often previable, deliveries.
• Total breech extraction:
• The fetal feet are grasped, and the entire fetus is
extracted. It should be used only for a
noncephalic second twin.

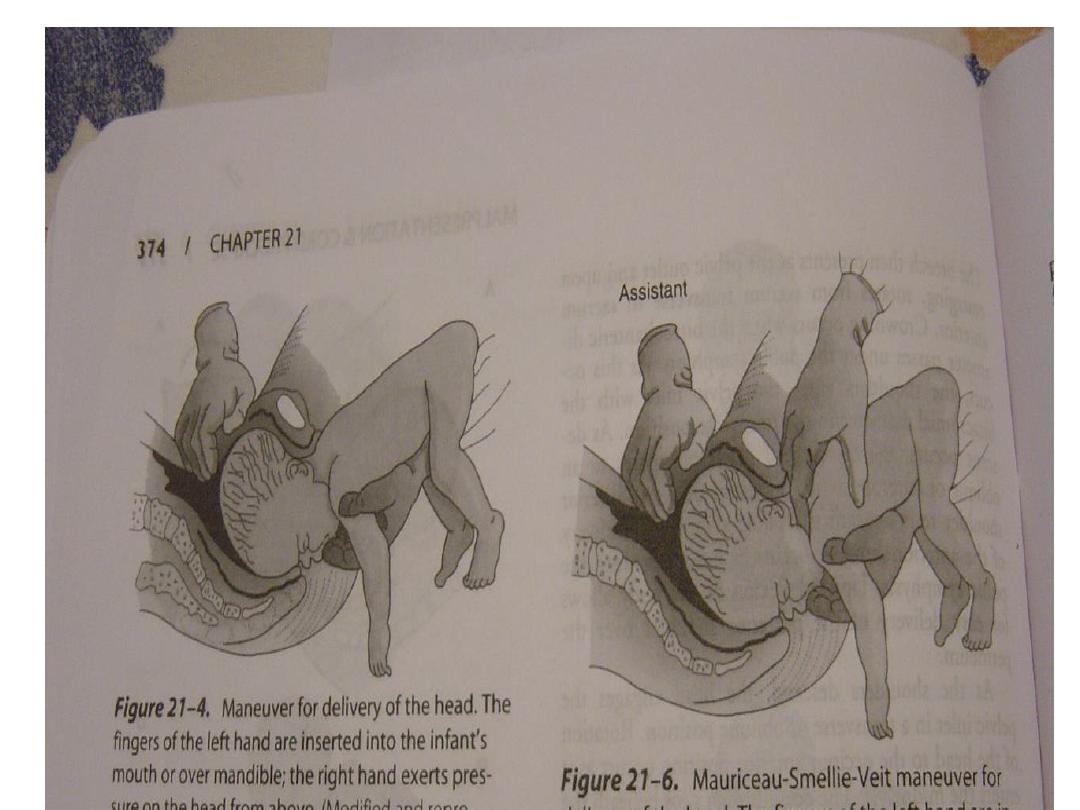
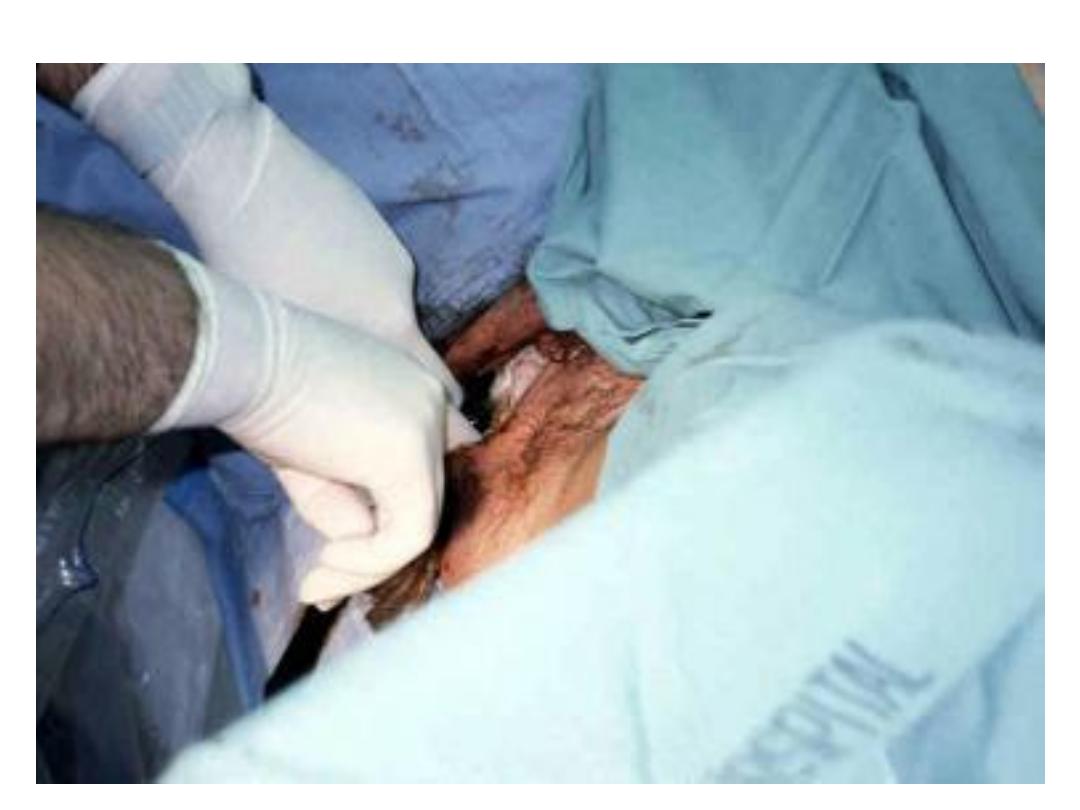
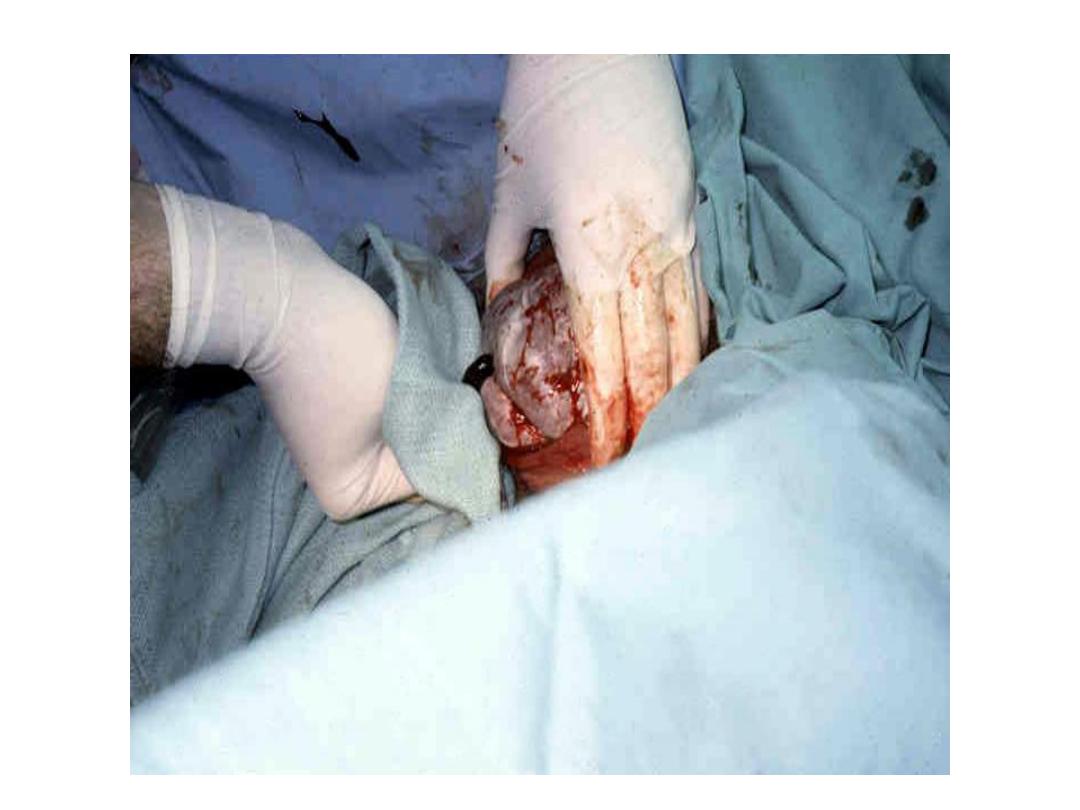
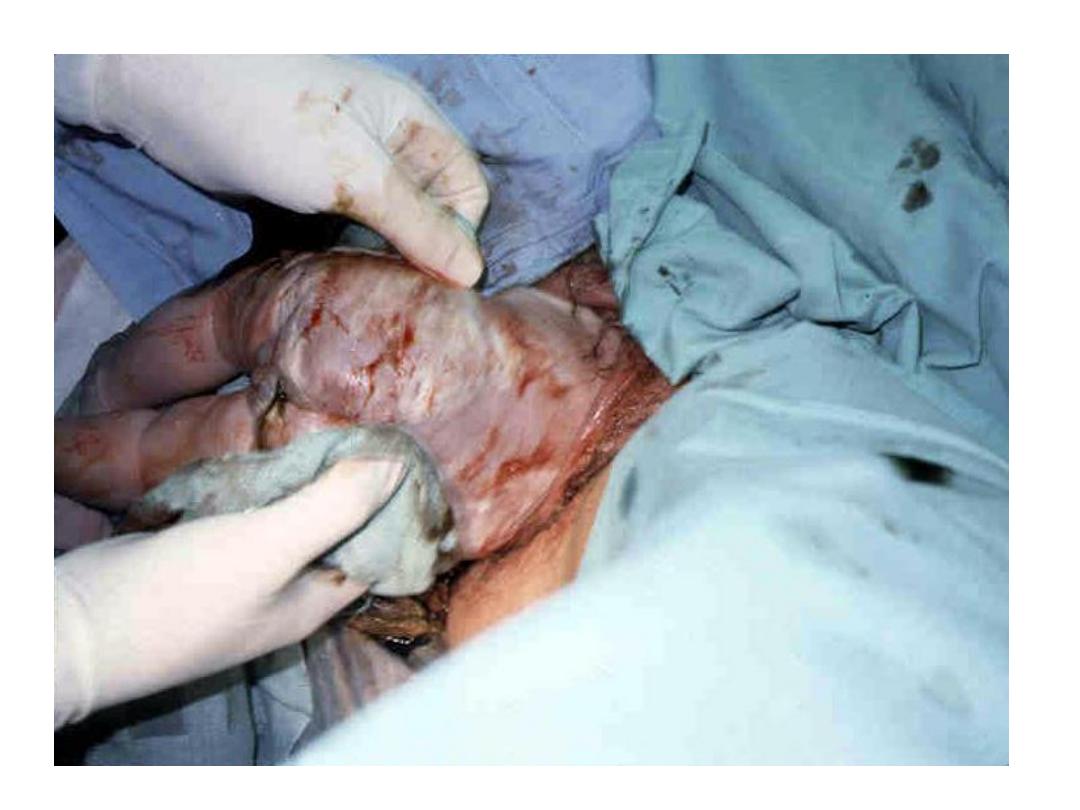
Assisted breech delivery:
• the most common type. The infant is allowed
to spontaneously deliver up to the umbilicus,
and then maneuvers are initiated to assist in
the delivery of the body, arms, and head.

First stage :
• Oxytocin contraversial.
• ARM not done.
• An anesthesiologist and a pediatrician
should be immediately available for all
vaginal breech deliveries.

Second stage:
• Assisted vaginal delivery


Caesarean Delivery
• FW<1500or> 3500gr
• Footling
• Small pelvis
• Deflexed head
• Arrest of labor
• Elderly Primigravida.
• Bad obstetrical history
• Fetal distress