• SALIVARY GLAND DISORDERS
Dr. Lana Shabur Talabani
• INTRODUCTION
• Four main salivary glands• Two parotid glands
• Two submandibular glands
• Multiple minor salivary glands in the upper respiratory track
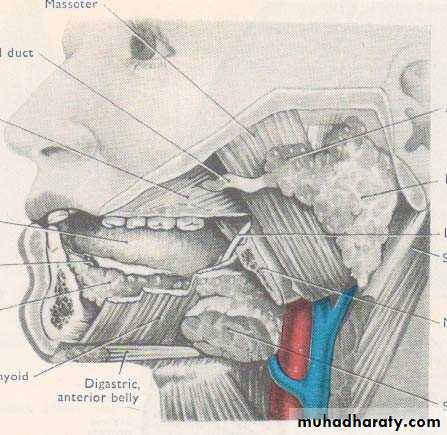
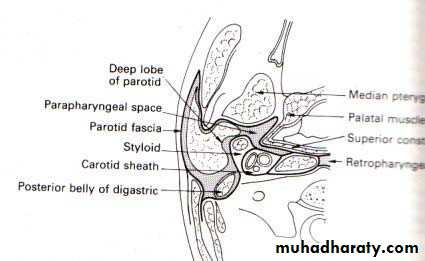
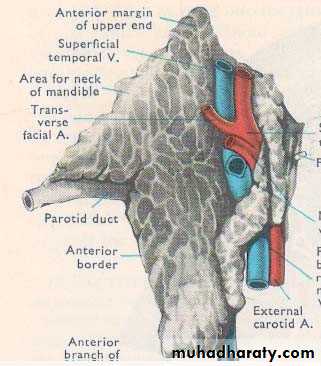
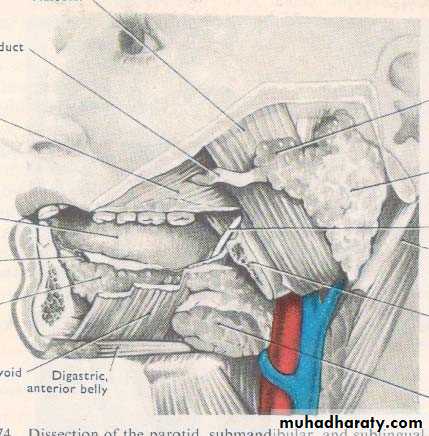
• ANATOMY
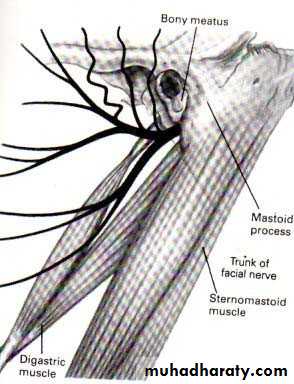
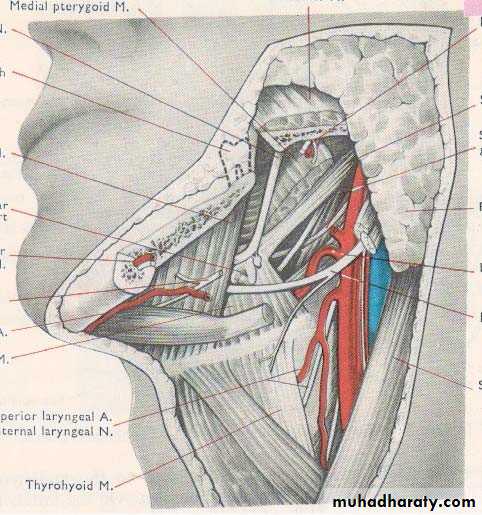
• IMPORTANT STRUCTURES THAT PASS THROUGH PAROTID GLAND
• Facial nerve• Terminal part and branches of external carotid artery
• Maxillary artery
• Superficial temporal artery
• Retromandibular vein
• Intra parotid lymph nodes
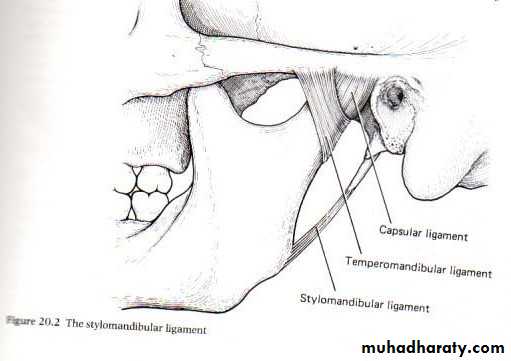
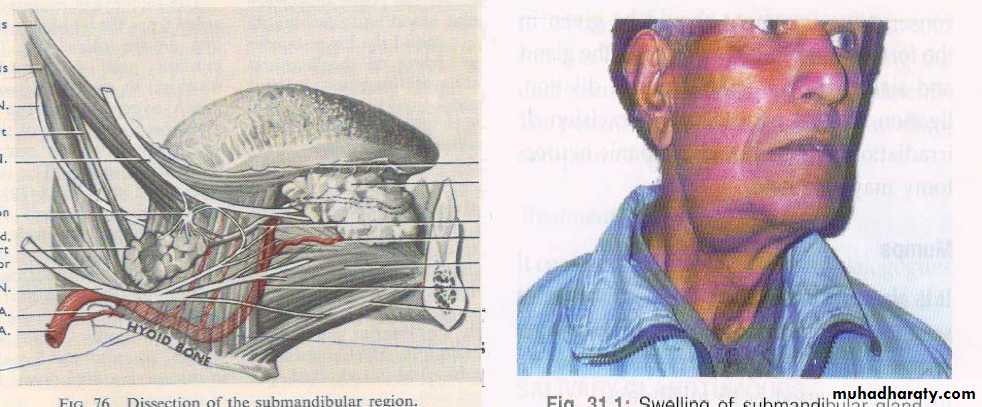
• SUBMANDIBULAR GLAND
•
• SALIVARY GLANDS LESIONS
• Congenital• Inflammatory
• Viral
• Bacterial
• Traumatic
• Neoplasm
• Benign
• Malignant
• INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS
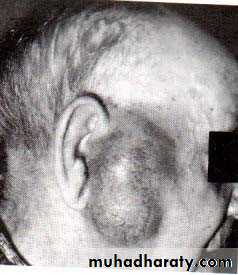
• Viral infections (Mumps)• acute painful parotid swelling
• children
• airborne droplet infection
• ex on meals
• Complications
• Orchitis ,oophritis, pancreatitis ,SNHL, meningoencephlitis
• TREATMENT
• Analgesics
• Fluid intake
• Life long immunity
• BACTERIAL INFECTION
• Acute Suppurative Sialadenitis• May involve parotid or submandibular gland
• Ascending infection
• Staph aureus , strep.
• Dehydrated old / young children
• ACUTE SUPPURATIVE SIALADENITIS
• Clinical Features :• Malaise, pyrexia , cx LAP
• Examination : pus from duct opening Management :
• USG
• I.V Antibiotics
• Drainage
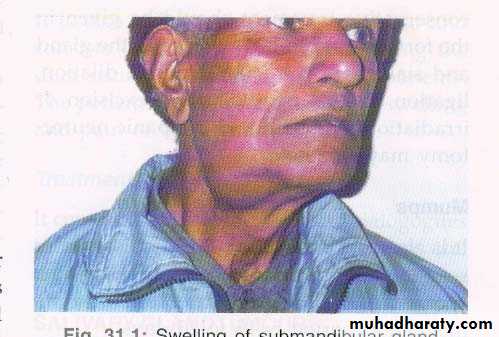
• CHRONIC SIALADENITIS
• Chronic infection of salivary gland can lead to firm, mild enlargement of the gland with repeated acute infection
• More in parotid gland followed by submandibular gland
• History of recurrent mildly painful enlargement of gland. Massage of gland produces scanty secretions at the opening of the duct
• MANAGEMENT
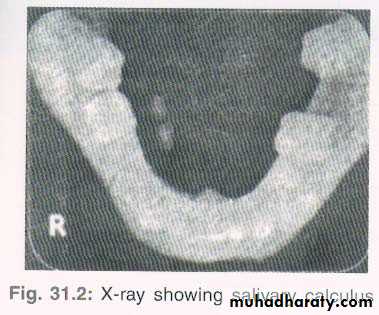
• USG• Papillotomy
• Removal of calculus
• Antibiotic
• Massage of the gland
• Total gland excision
• Tympanic neurectomy
• SALIVARY GLAND TUMOURS
• Tumours of salivary glands represent a complex and histopathologically diverse group of tumour• Diagnosis and management is complicated by the fact that they are in frequent
• Making up only 1% of head and neck tumour
• Proper management require and accurate diagnosis by the pathologists and physicians
• Salivary gland tumours
• Benign
• malignant
• Parotid
• 80-90%
• 10-20%
• Submandibular
• 50%
• 50%
• Sublingual
• 5%
• 95%
• Minor
• 10%
• 90%
• PAROTID TUMOURS
• Most common site of salivary neoplasm• Mainly arise from superficial lobe
• Slow growing painless mass below or infront of pinna
• Deep lobe tumours present as parapharyngeal mass
• Dysphagia / snoring / mass in oropharynx
• CLASSIFICATION OF PAROTID TUMOURS
• Adenoma• Carcinoma
• pleomorphic / warthin, adenolymphoma
• acinic cell ca / adenoid cystic ca adenocarcinoma / scc
• PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA
• Most common benign tumour• Can arise from parotid, submandibular or other salivary gland
• In the parotid it usually arises from tail
• Slow growing tumour
• Seen in 3rd or 4th decade
• More in female
• Both epithelial and mesenchymal elements are seen
• DIAGNOSIS
• History• Clinical examination
• FNAC
• Ultrasonography
• CT Scan
• MRI
• TREATMENT
• Surgical Excision
• Superficial parotidectomy
• Total parotidectomy with preservation of facial nerve• WARTHIN’S TUMOUR
• More common in male (5:1)• Seen between 5th & 7th decade
• Mostly involve tail of parotid
• Bilateral in 10%
• May be multiple
• Rounded, encapsulated at time cystic
• Treatment : Superficial parotidectomy
• CLINICAL FEATURES OF MALIGNANT SALIVARY TUMOURS
• Facial palsy• Rapid increase in size
• Hard mass / ulceration• Cervical lymphadenopathy
• SIALADENOSIS
• Non inflammatory swelling affecting salivary glands• Diabetes mellitus
• Alcoholism , pregnancy
• Bulemia
• Drugs
• idiopathic
• DEGENERATIVE CONDITIONS
• Sjogren syndrome
• Autoimmune
• Progressive destruction of salivary and lacrimal glands
• xerostomia
• Primary
• Secondary
• connective tissue disorders
• DISEASES OF SUBMANDIBULAR GLAND
• Inflammatory conditions• Viral
• Bacterial
• Obstructive
• Calculus
• trauma
• Tumours