Definition
• Jaundice came from the French
word “jaune” which means yellow.
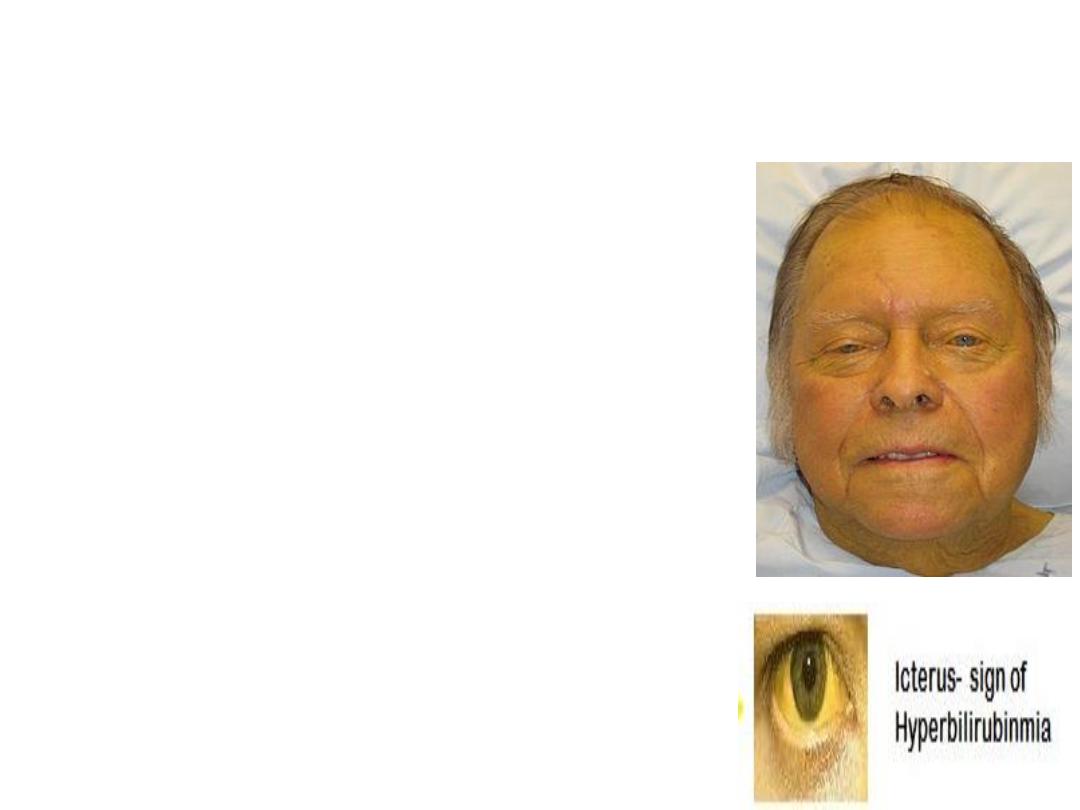
• Yellowish discoloration of sclera,
skin mucous membranes due to
increased serum bilirubin level.
Typically can be detected if serum
bilirubin level above 3 mg/dl (51.3
μmol/L.
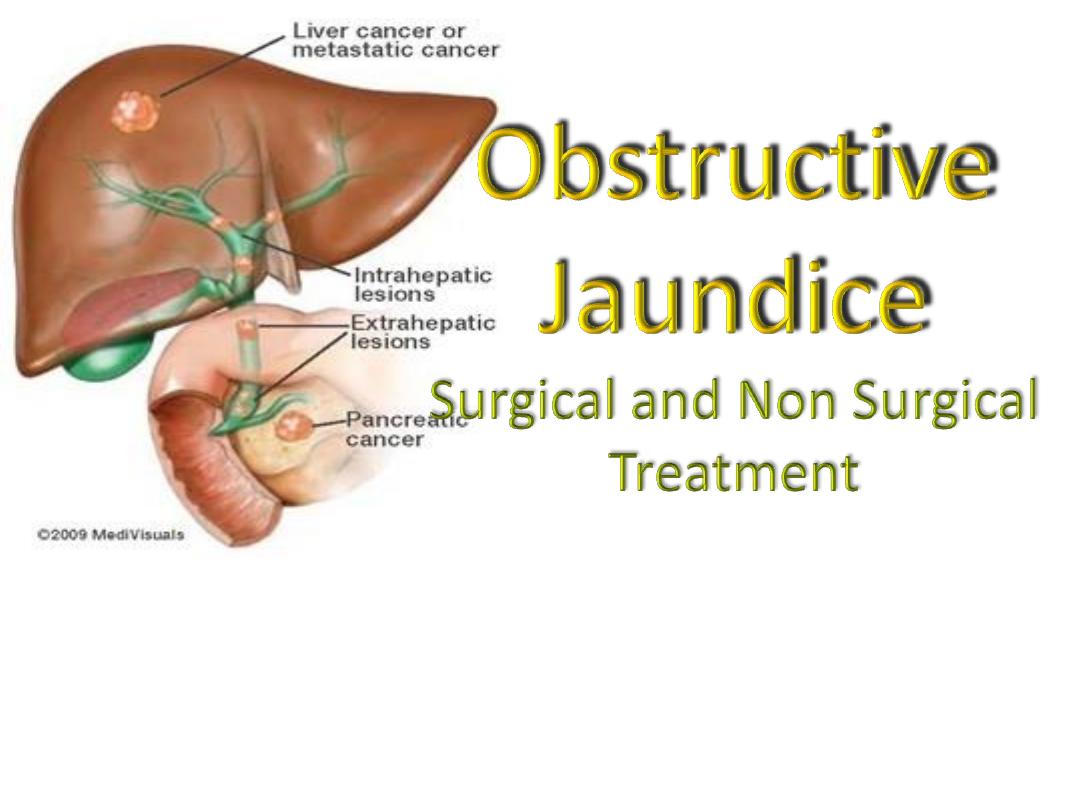
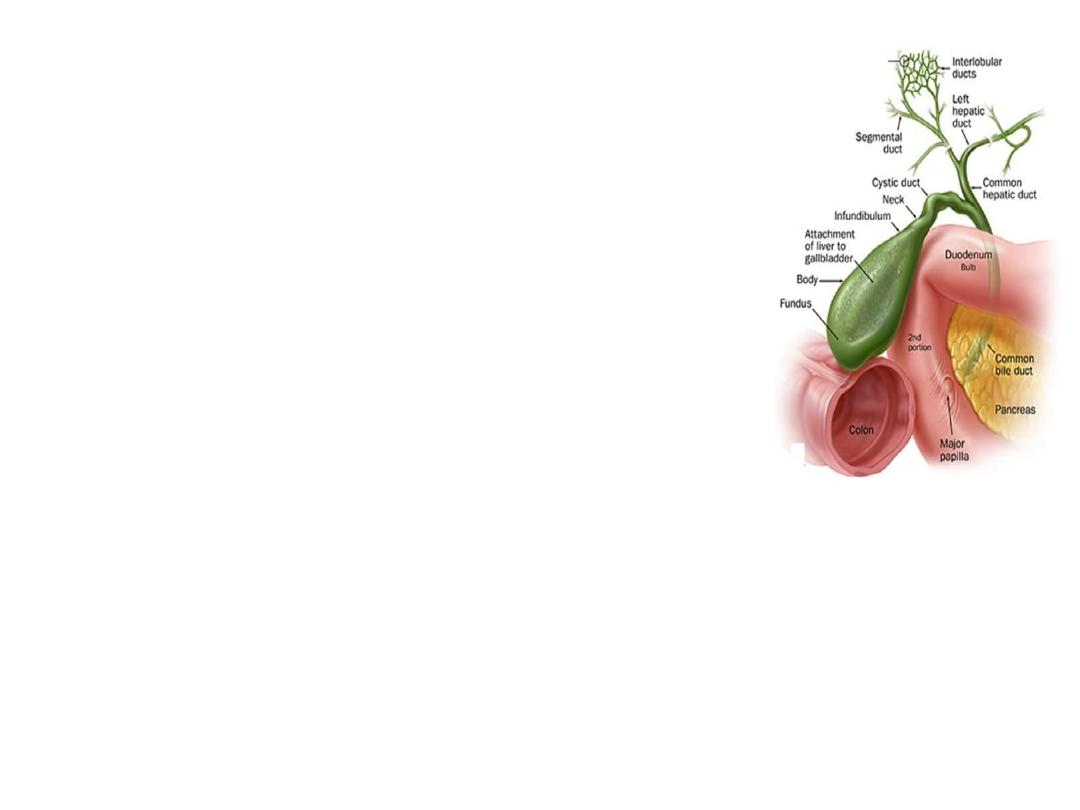
• Obstructive jaundice is interruption
to the drainage of bile in the biliary
system
Classifications:
I.
Prehepatic
II. Hepatic
III. Posthepatic (Obstructive)
• Intraluminal- Transmural- Extramural
• Common- Infrequent- Rare
• Complete (type 1)- Intermittent (Type 2)- Chronic incomplete
(Type 3)- Segmental obstruction (Type 4
)
• Etiology (congenital, inflammatory, traumatic, neoplastic, parasitic
etc ).
Obstructive Jaundice
Alteration in:
• Systemic and renal
hemodynamics
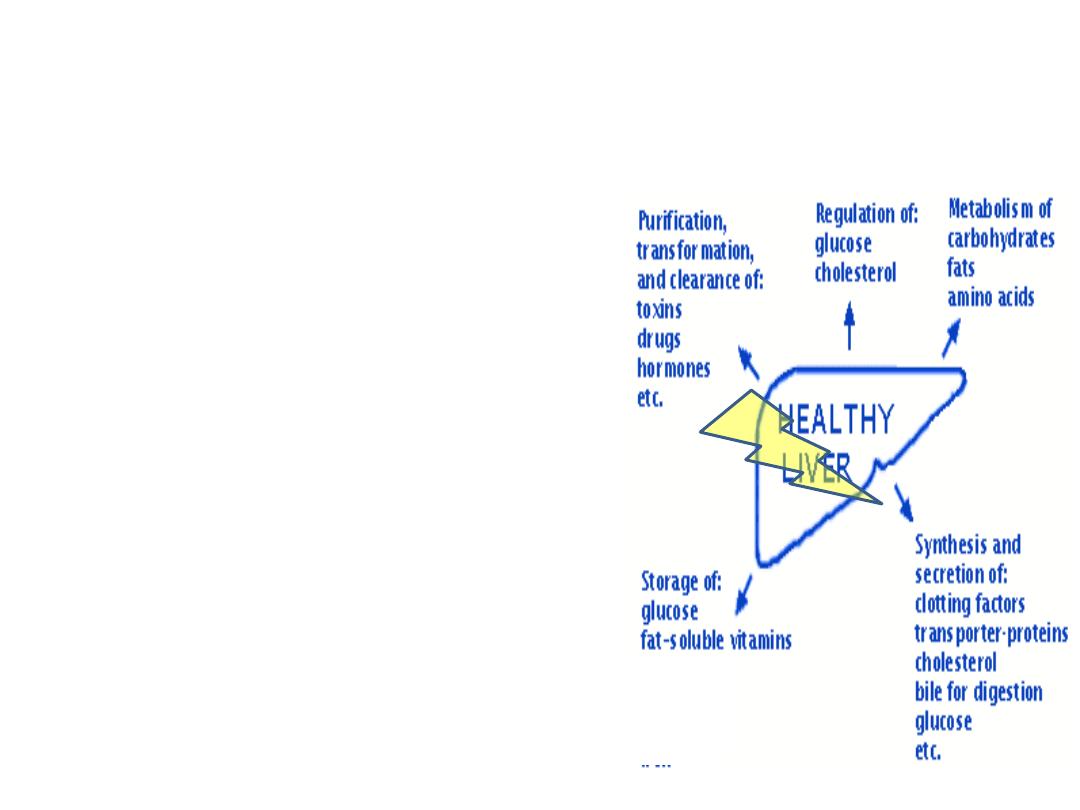
• Hepatic function ( protein
synthesis, reticuloendothelial
function,hepatic metabolism)
• Hemostatic mechanism
• Gastointestinal barrier
• Immune function
• Wound healing

Managment
Objectives:
• To identify pts who need relief of obstruction
To establish cause, to plan appropriate
intervention, prevent complications, prevent
recurrence.

S&S for urgent surgical interventions :
• Abdominal pain ( 70%
)
• Jaundice ( 60%
)
• Tea colored urine/ pale stool
• Altered mental status ( 10-20%
)
• Hypotension ( 30%
)
• Fever, persistent ( 90%
)
• RUQ tenderness

Imaging Studies
• Ultrasound
• CT scan, Spiral CT scan
• MRI, MRCP
• Digital substraction angiography
• Cholangiography ERCP, PTC
• IDUS
• PET
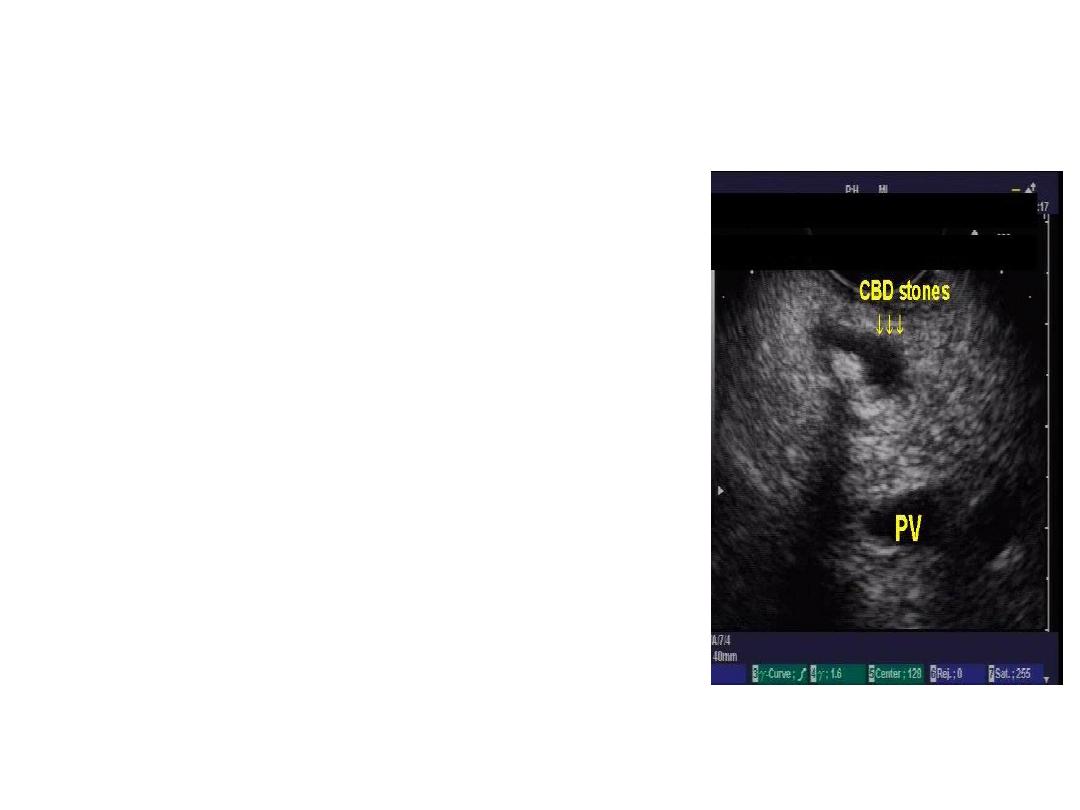
Ultrasonography
• 1
st
choice in O.J.
• Non invasive, cheep, bed side
• Size of bile duct, level of
obstruction, identify the cause in
some cases, liver parenchyma,
• Limitation: obese, Exessive bovel
gases, retroduodenal and
intraduodenal CBD
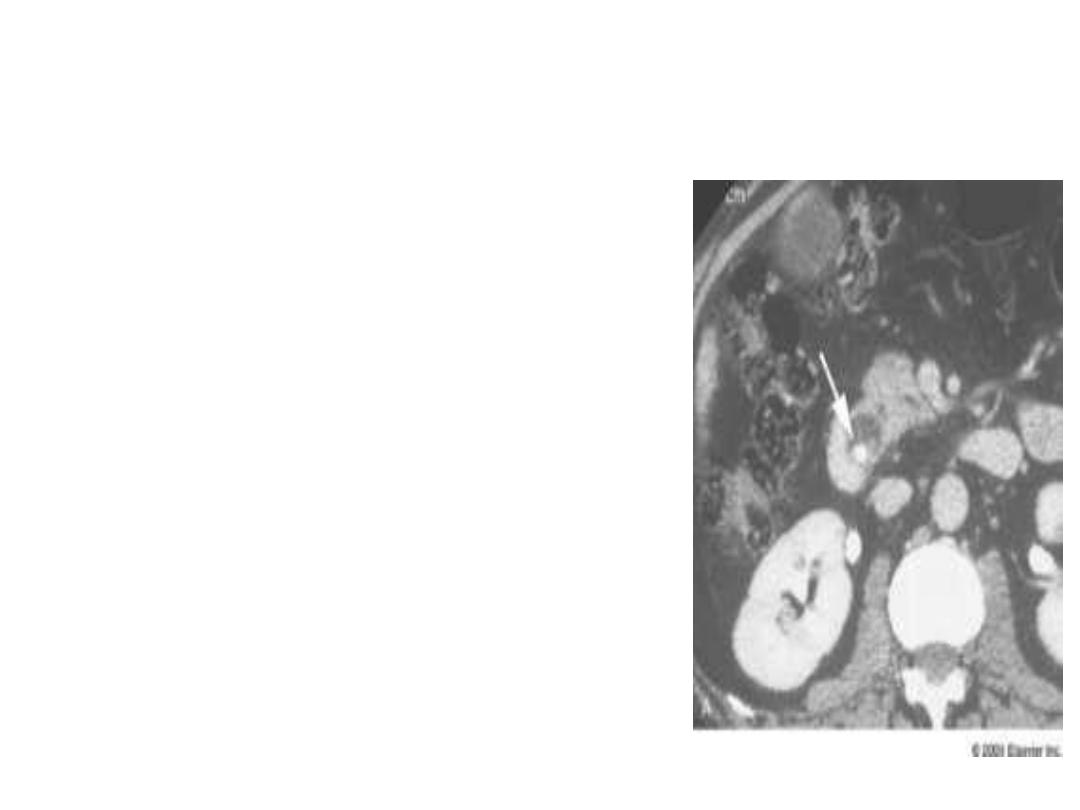

CT scan of Abdomen
• Very useful for assessment of
malignancy
• Intrahepatic biliary dilatations,
• Level of obstruction
• Spiral CT allows : relationship
vascular and bile duct anatomy
at the hilum
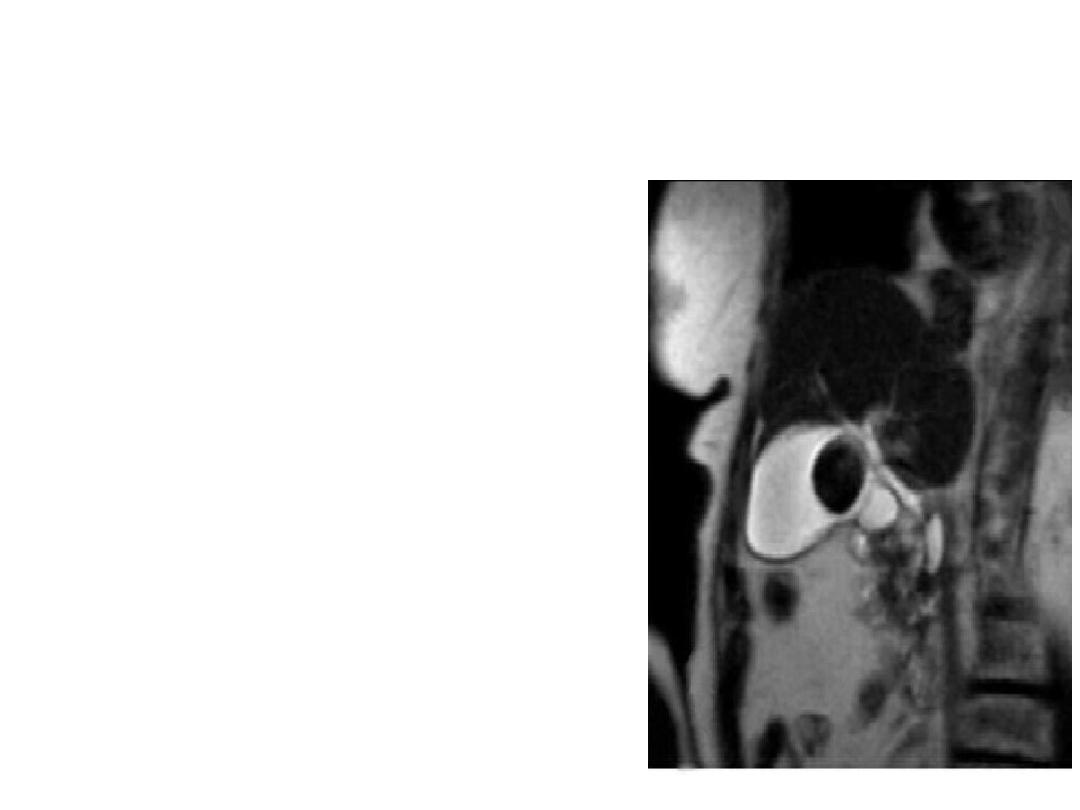
MRCP
• Non invasive
• Useful when ERCP
contraindicated
• No intravenous contrast
• Purely diagnostic
• C/I pt with pacemaker,
cerebral aneurism clips,
other metal implants
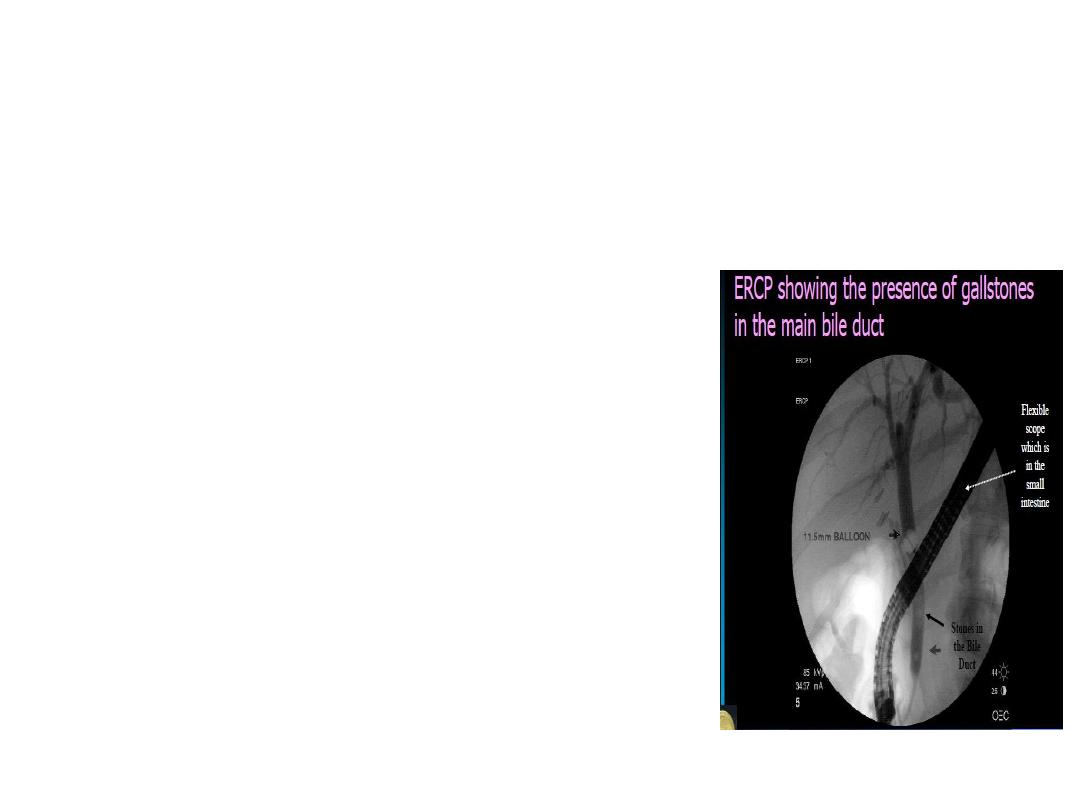
ERCP
• Diagnostic and therapeutic
• Find out obstruction especially in
the lower part of biliary passage
• Invassive
• Cannot reliabily distinguish
betweenbenign and malignant
features
• Opportunity to take tissue sample
• Endoprosthesis
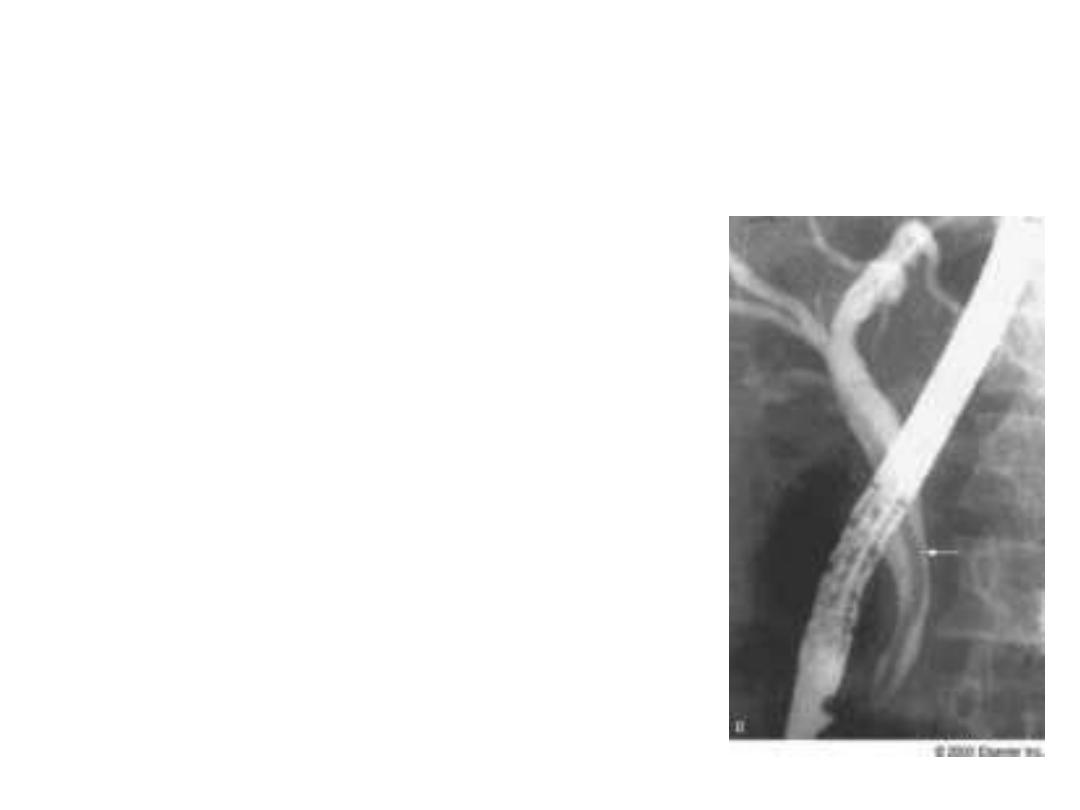
ERCP
• Diagnostic and therapeutic
• Find out obstruction especially in
the lower part of biliary passage
• Invassive
• Cannot reliabily distinguish
betweenbenign and malignant
features
• Opportunity to take tissue sample
• Endoprosthesis
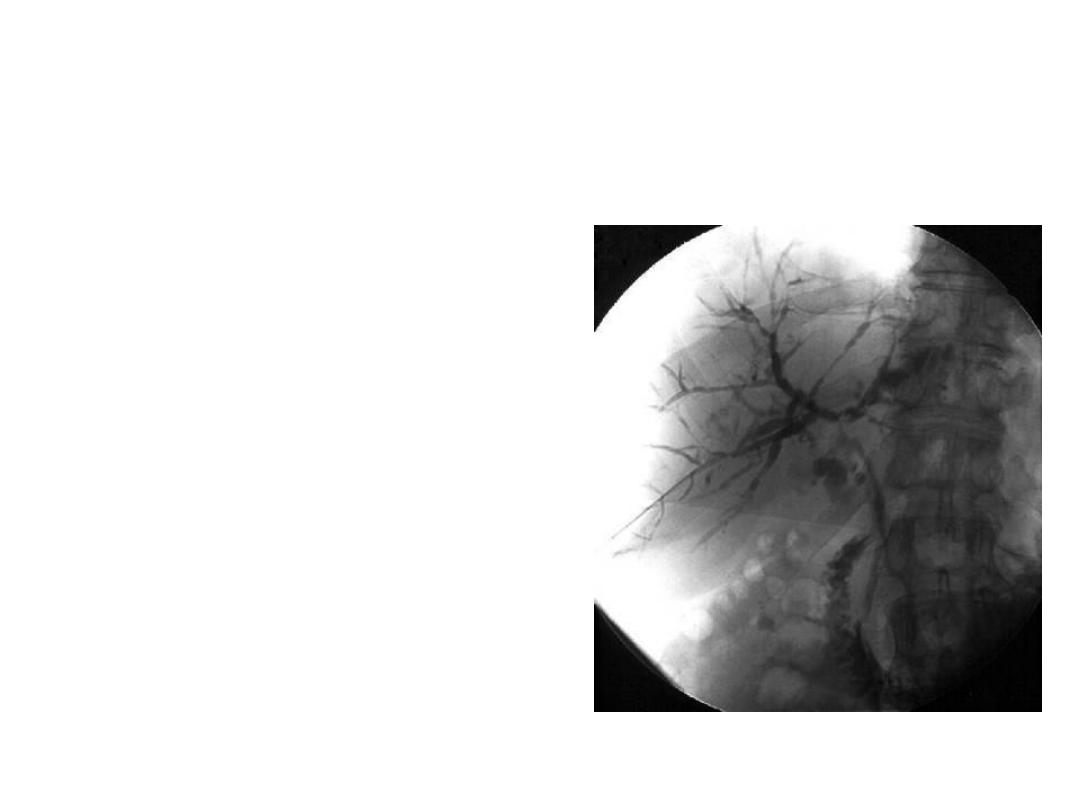
PTC
• Diagnostic and therapeutic
• Best suited for leisions
proximal to the bifurcation
of hepatic duct
• Invasive
• Complications similar to
ERCP
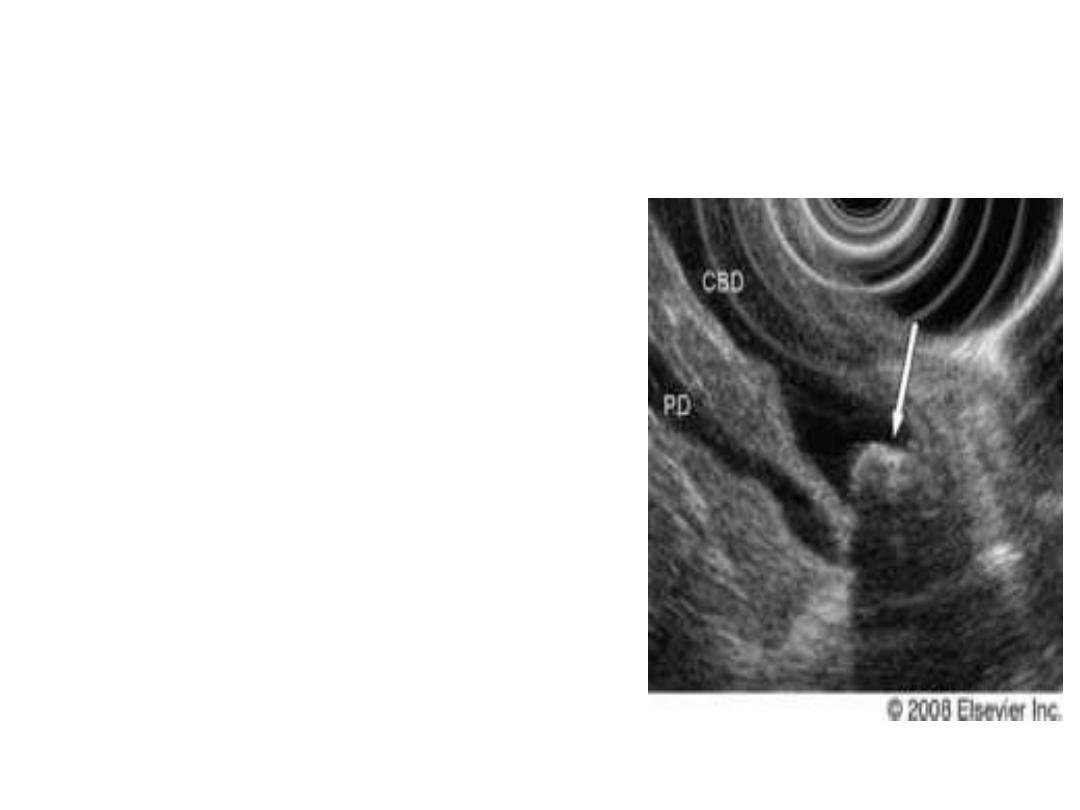
Endoscopic Ultrasound
• Assessment bile duct and
proximal pancreatic
pathology
• Recently IDUS in ERCP
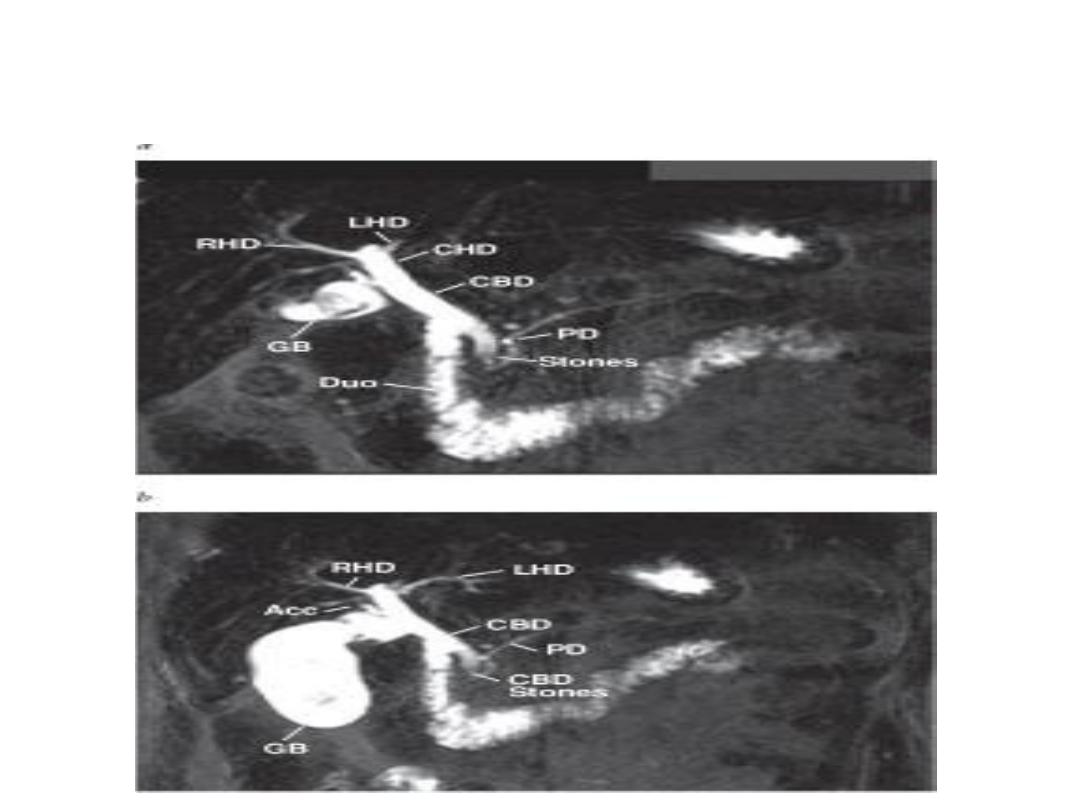
Laparoscopic cholangiography
Treatment
Conservative 1
• Fluid and electrolytes
• Urine output monitoring
• Correction of coagulation defects
• Prevention of infection
• Prevention of hepatorenal syndrome
• Nutrition

Conservative 2
• Bile acid binding resins, Cholestyramine (4g) or
cholestipol (5g) disolved in wter or juice × TDS
• Individualized regime for replacement of vitamines
A, D, E and K as needed.
• Antihistamine for pruritus
• Naloxone or nalmefene has improved pruritus
• Discontinuation of medications that cause or
exacerbate cholestasis

Surgical Options
By Pass Surgeries
• Roux-en-y hepaticojejunostomy
• Roux-en-y Choledochojejunostomy
• Roux-en-y Cholecystojejunostomy
Choledochoduodenestomy
Whipple’s operation
Pylorus Preserving Pancreaticoduedenectomy
Choledochotomy + T-tube drainage
Transduodenal sphincterotomy and sphinteroplasty
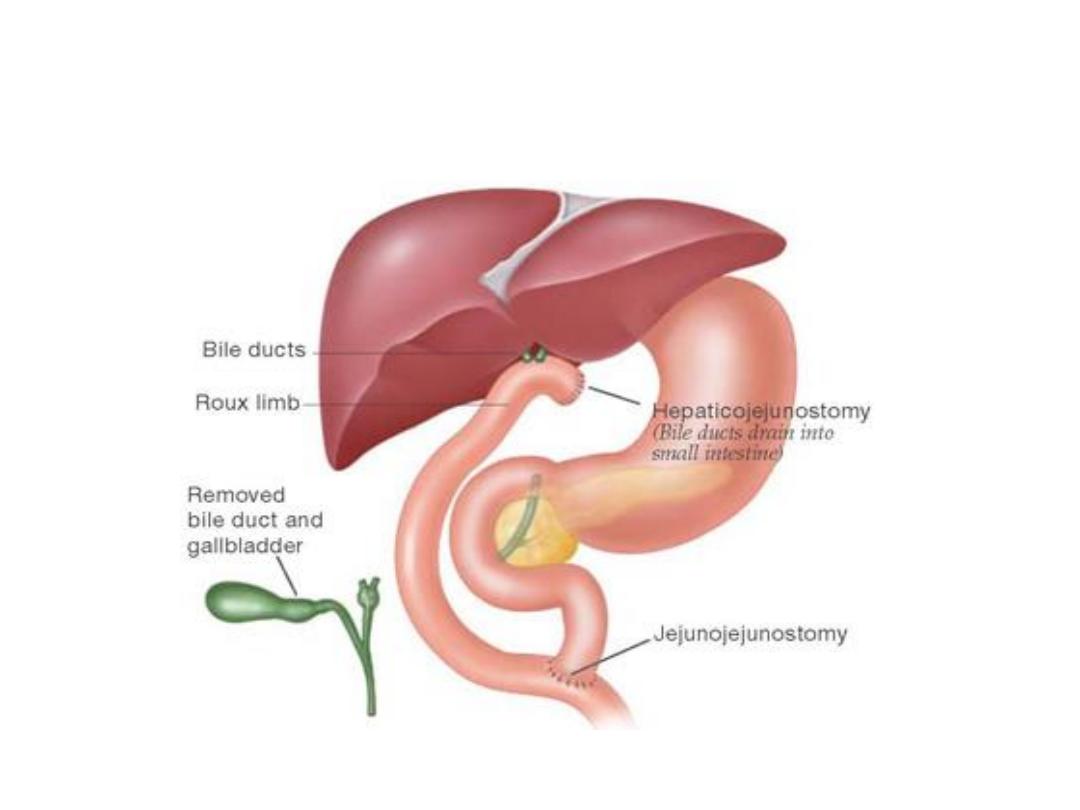
Roux-en-Y Hepaticojejunostomy
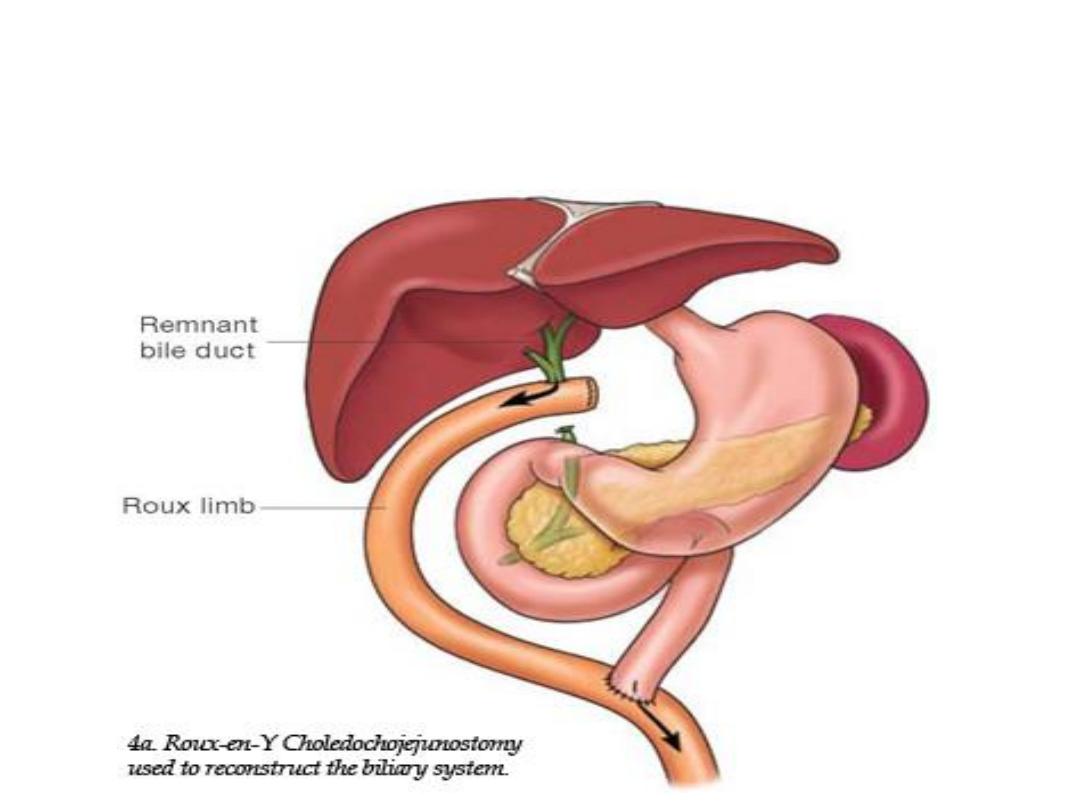
Roux-en-Y Choledochojejunostomy
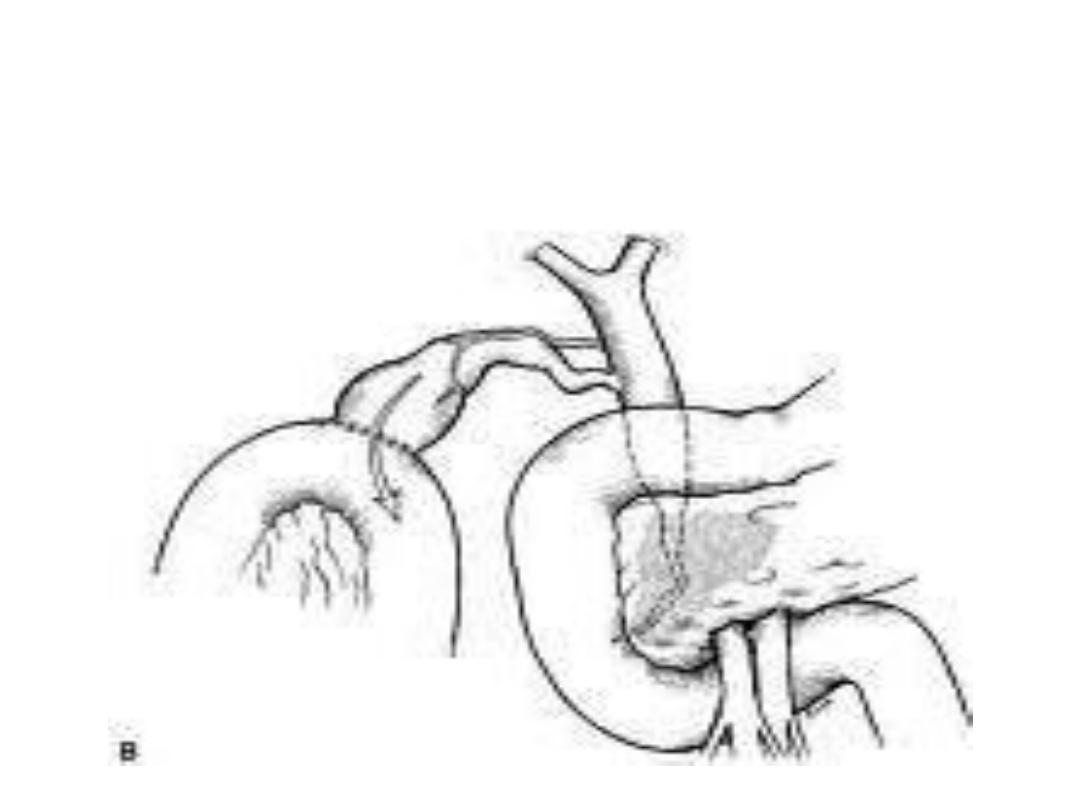
Cholecystojejunostomy
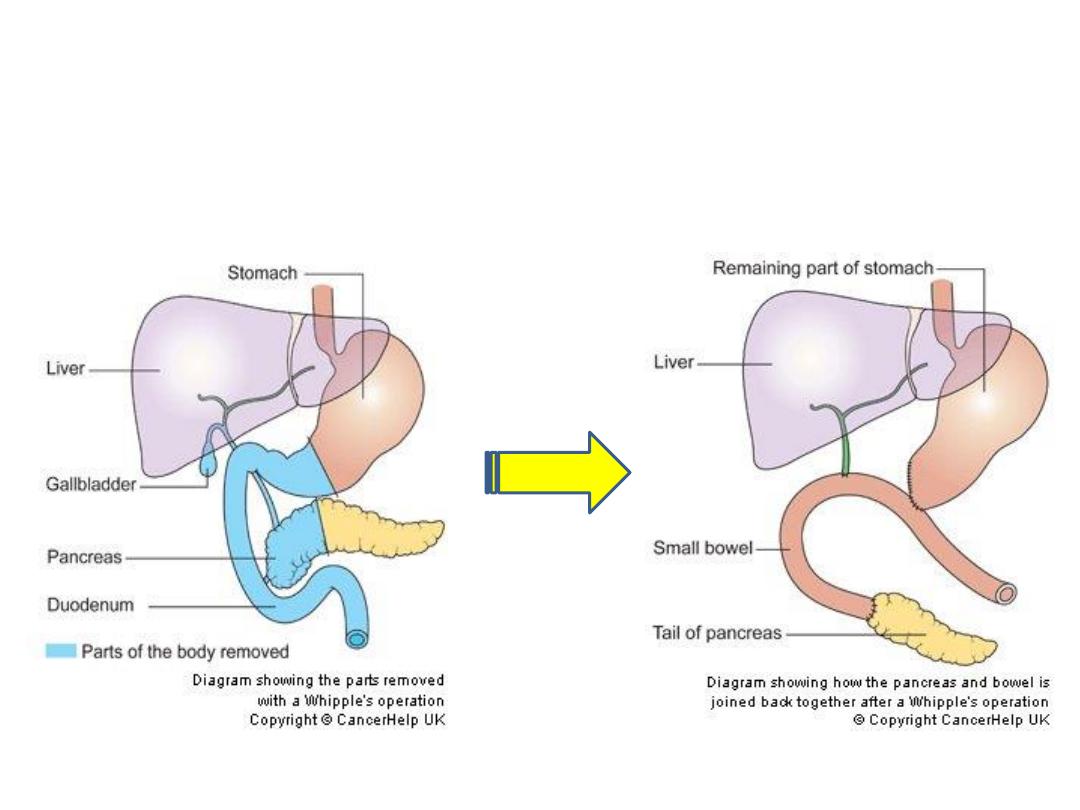
Whipple’s Operation
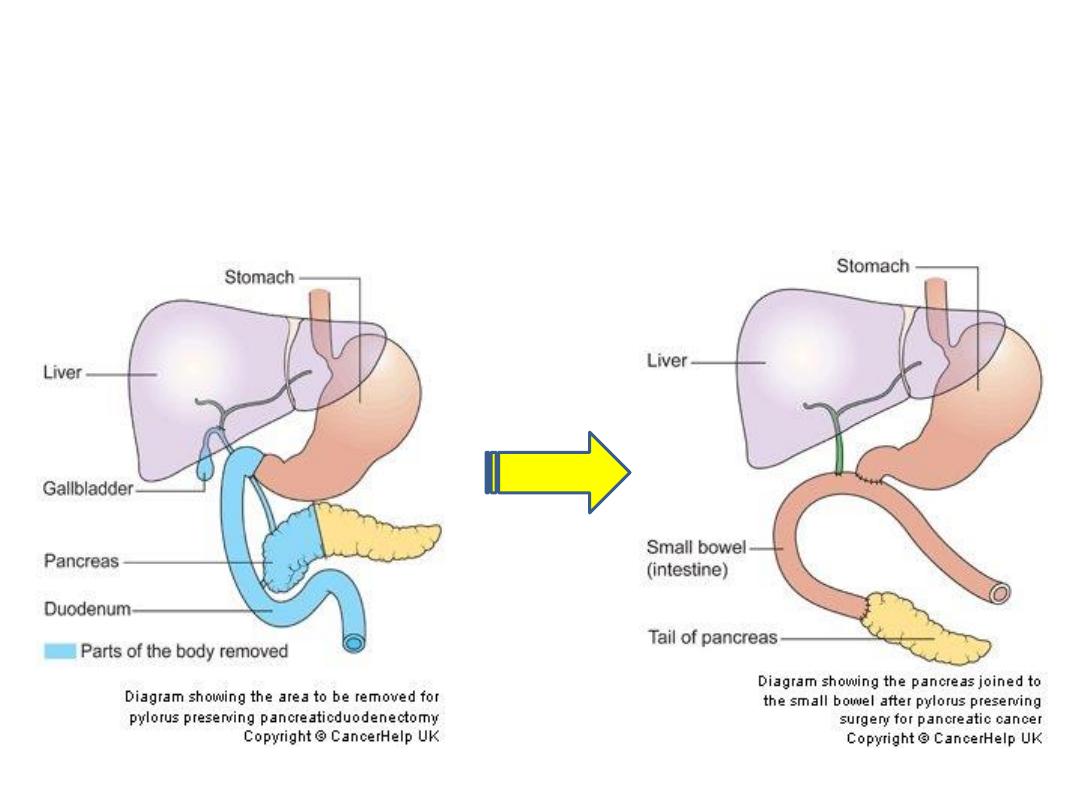
Pylorus Preserving Pancreaticoduedenectomy
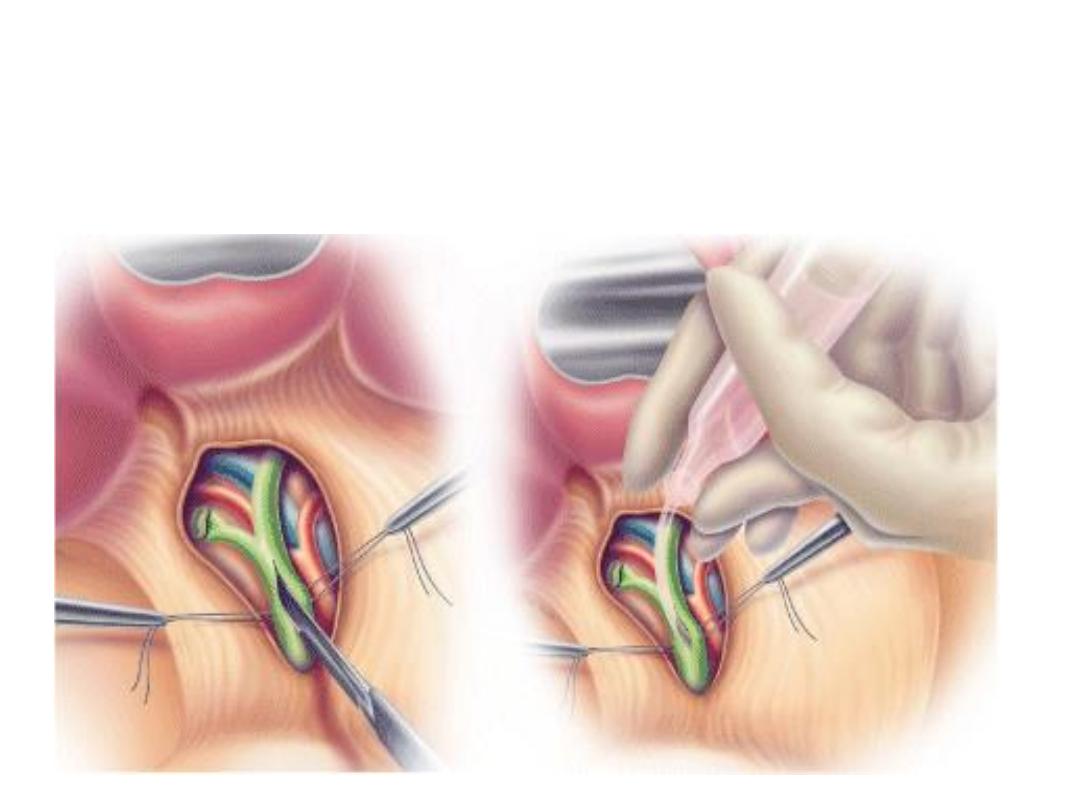
Open Exploration of CBD
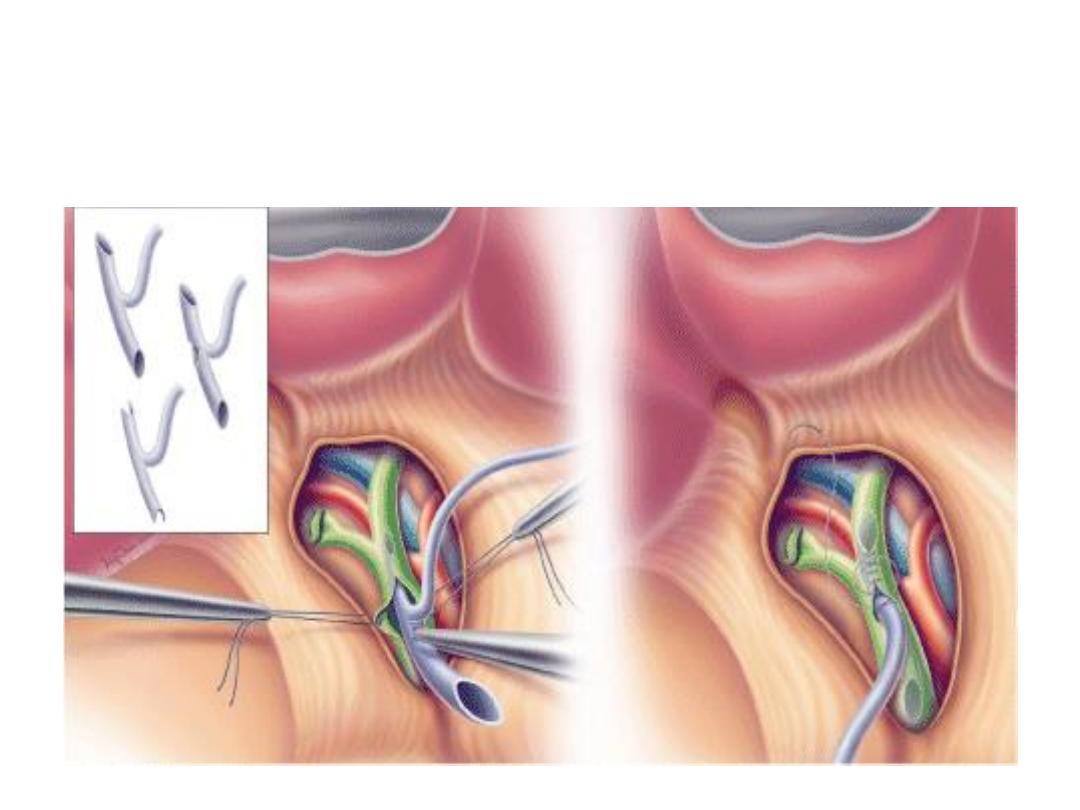
T- tube
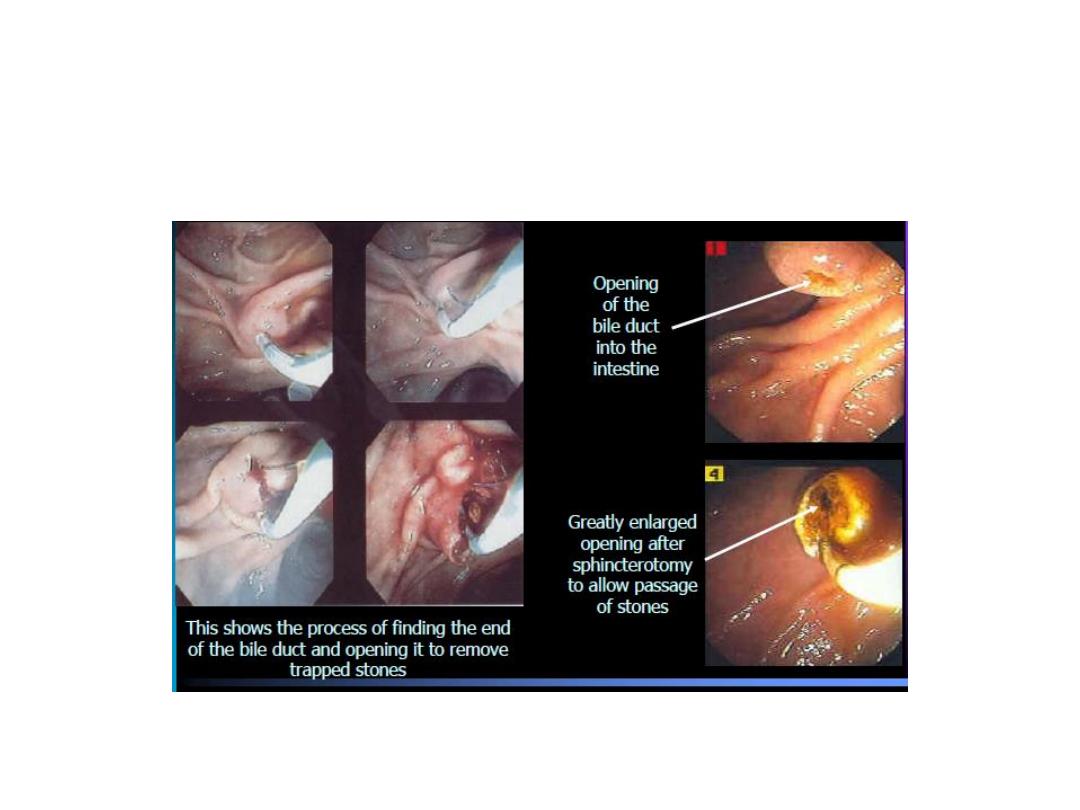
ERCP with Sphincterotomy
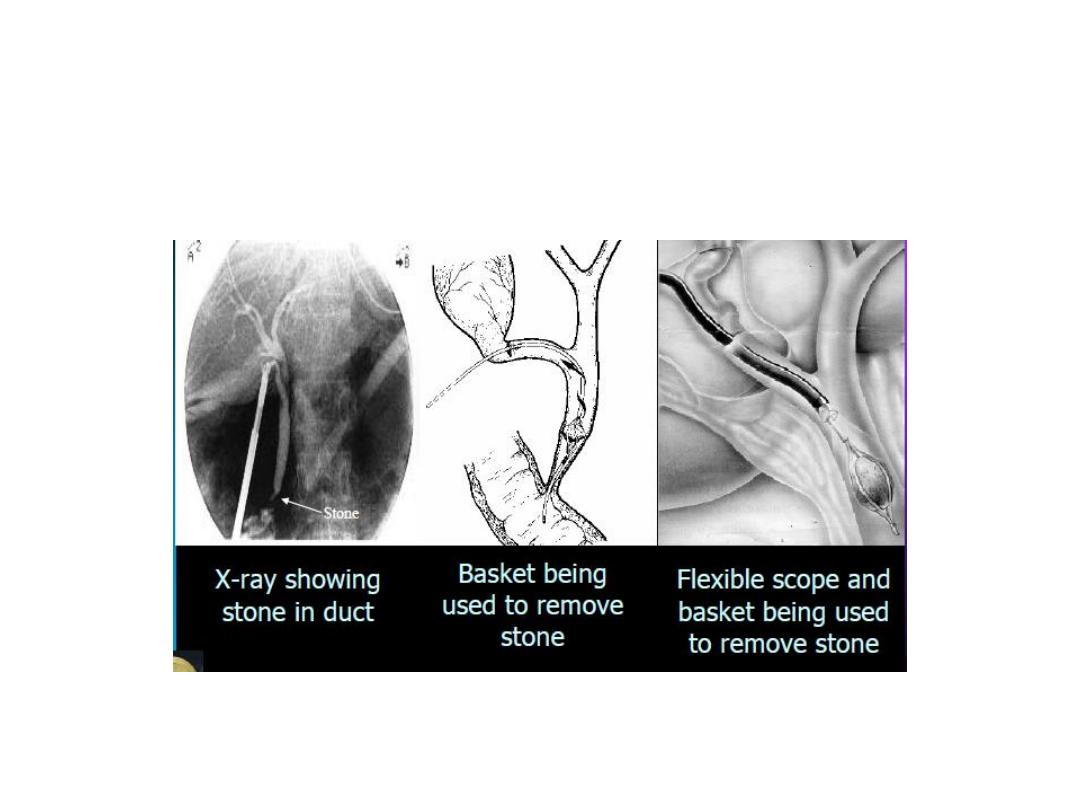
Transcystic CBD Exploration

Indications for Open CBD Exploration
• Multiple stones > 5
• Stones > 1 cm
• Multiple intrahepatic stones
• Distal bile duct sticture
• Failure of ERCP
• Recurrence of CBDS after sphinterotomy

CBD Exploration- Surgical Options:
• CBD exploration with T-tube decompression
• Choledochoduodenostomy
• Transduodenal sphincterotomy and
sphinteroplasty
• Roux-en-Y choledochojejunostomy

Criteria for Irresectability
• Extra hepatic metastasis
• Extrahepatic organ invasion
• Peripheral hepatic metastasis remote from
primary tumor
• Major vascular involvement

Palliative Procedures
• Interventional Endoscopy: Endoscopic stenting
• Radiology: Chemo radiation, Intralumial
brachitherapy
• Photo Dynamic Therapy
• High intensity intraductal ultrasound
• Palliative surgery: Cholecystojejunostomy,
choledochojejunostomy, Hepatojejunostomy +/-
gasrtojejunostomy ,
