Practical lung and pleura
Dr. Zainab.W. A. AlhayaliAtelectasis. The right lung of an infant is pale and expanded by air; the left lung is collapsed
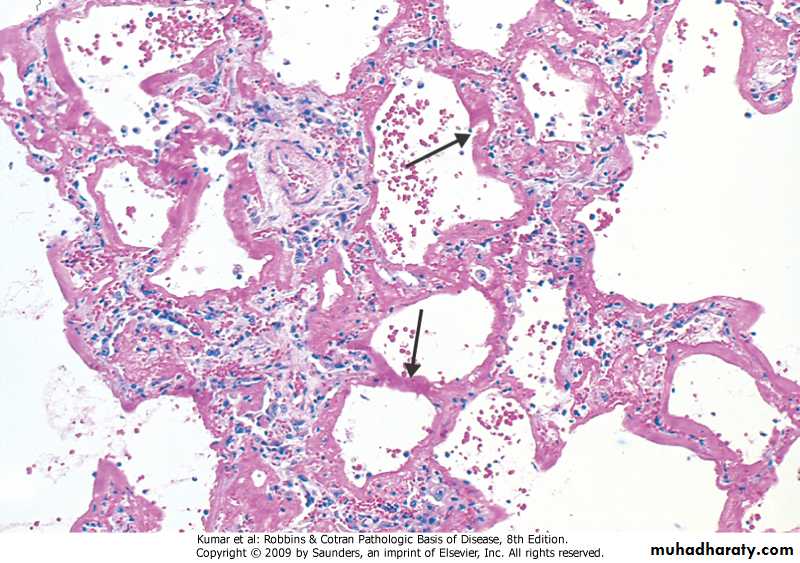
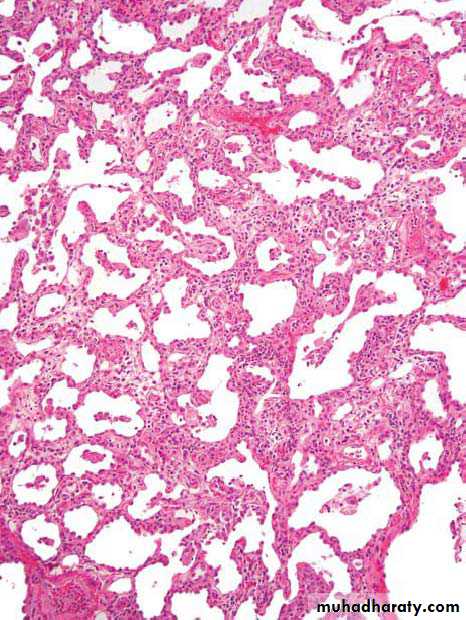
Diffuse alveolar damage, hyaline membrane
Emphysema
Residual strands of fibrovascular tissue in severe emphysema cross-spaces created by destruction of lung parenchymaBullous emphysema
Bronchial wall shows increased numbers of bronchial glands characteristic of chronic bronchitis.
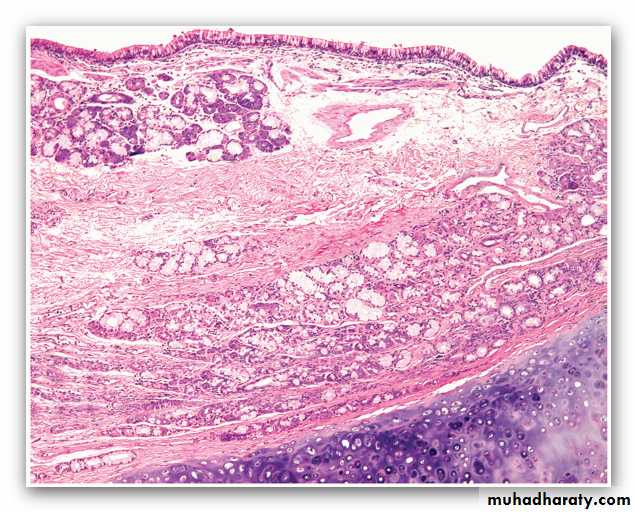
Morphology of asthma; .Gross, occlusion of bronchi and bronchioles by mucus plugs
Bronchial asthma, sub-basement membrane fibrosis, eosinophilic inflammation, muscle hypertrophy
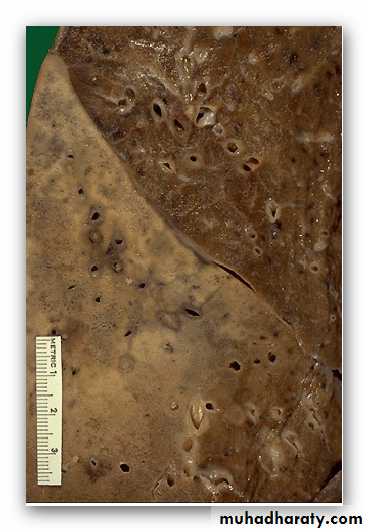
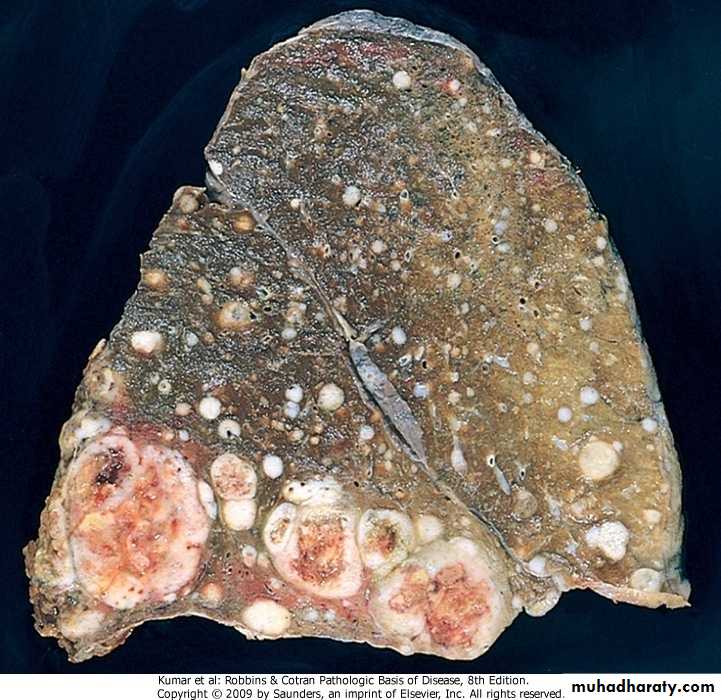
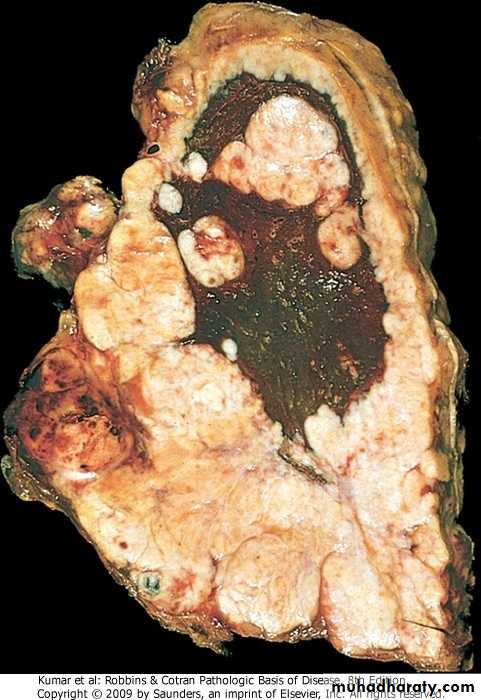
Bronchiectasis. The resected upper lobe shows widely dilated bronchi, with thickening of the bronchial walls and collapse and fibrosis of the pulmonary parenchyma.
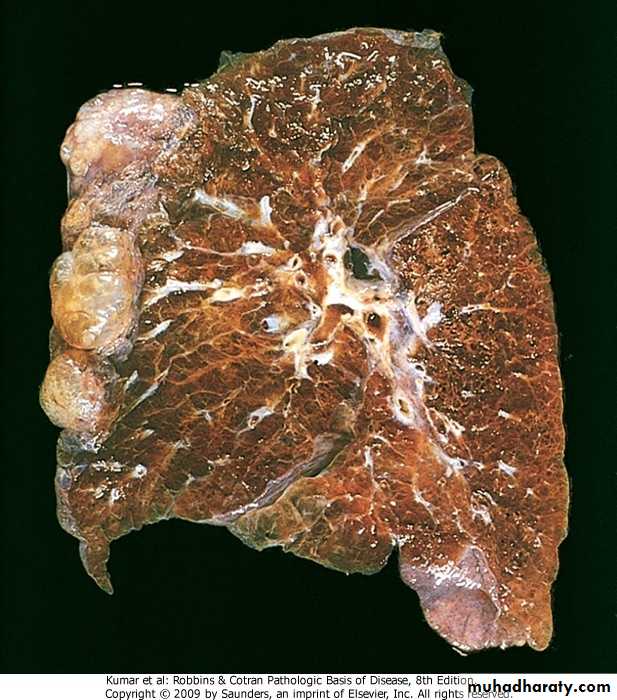
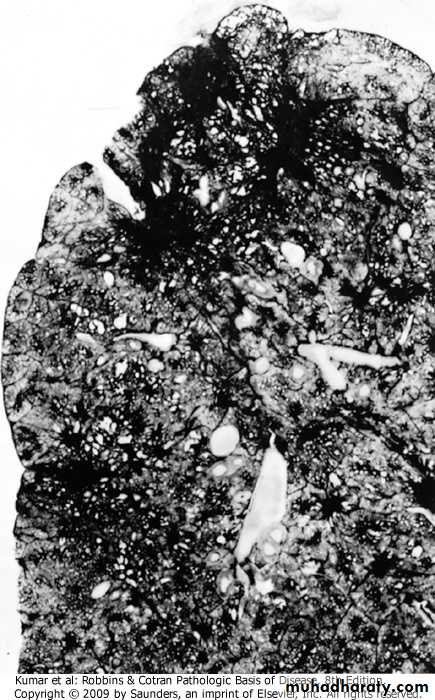
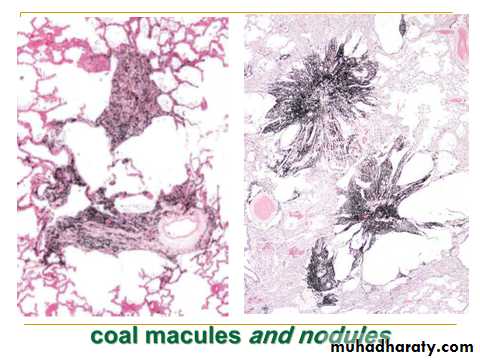
coal workers pneumoconiosis
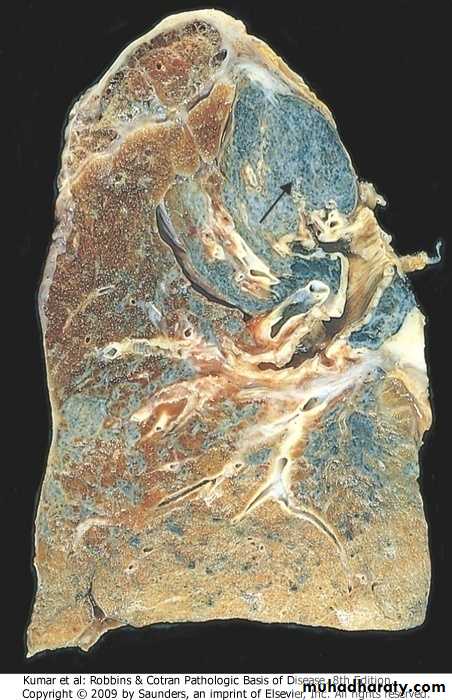
Advanced silicosis, fibrotic nodule, arrow
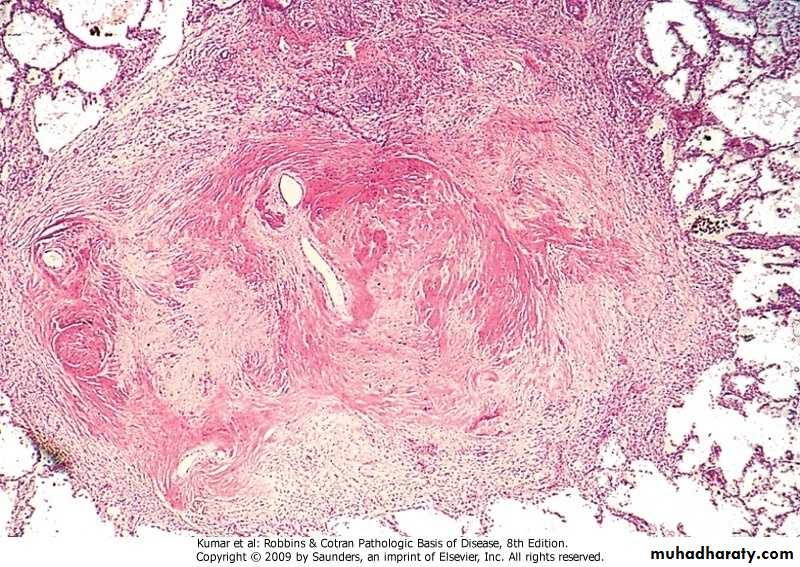
Several coalescent collagenous silicotic nodules
patchy distribution of a bronchopneumonia is seen. The consolidated areas here very closely match the pattern of lung lobules (hence the term "lobular" pneumonia)
lobar pneumonia demonstrates the distinct difference between the upper lobe and the consolidated lower lobe. Radiographically, areas of consolidation appear as infiltrates.
Lobar pneumonia, red hepatization. The alveoli are packed with an exudate composed of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and occasional macrophages.
Lobar pneumonia, grey hepatization
The fibrotic and inflammatory process within alveolar walls; this is the characteristic finding in atypical pneumonia
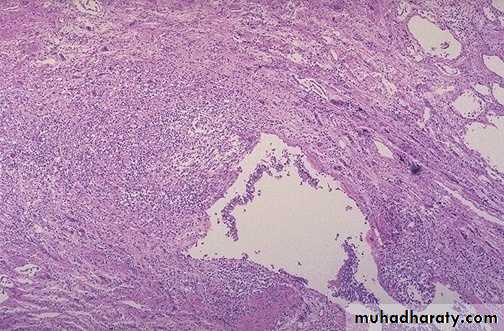
Lung abscess
suppurative destruction of the lung parenchyma within the central area of cavitation
cystic abscess contains
a purulent exudate and is contained by a fibrous
wall
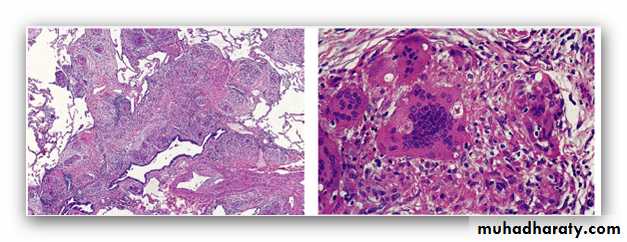
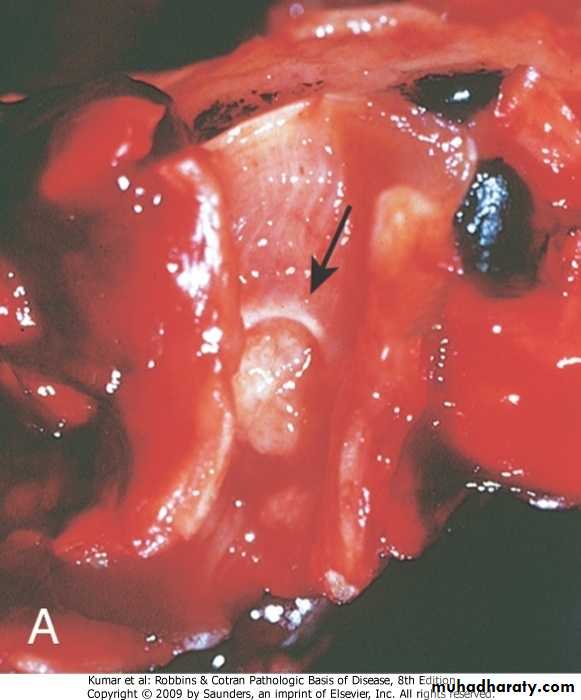
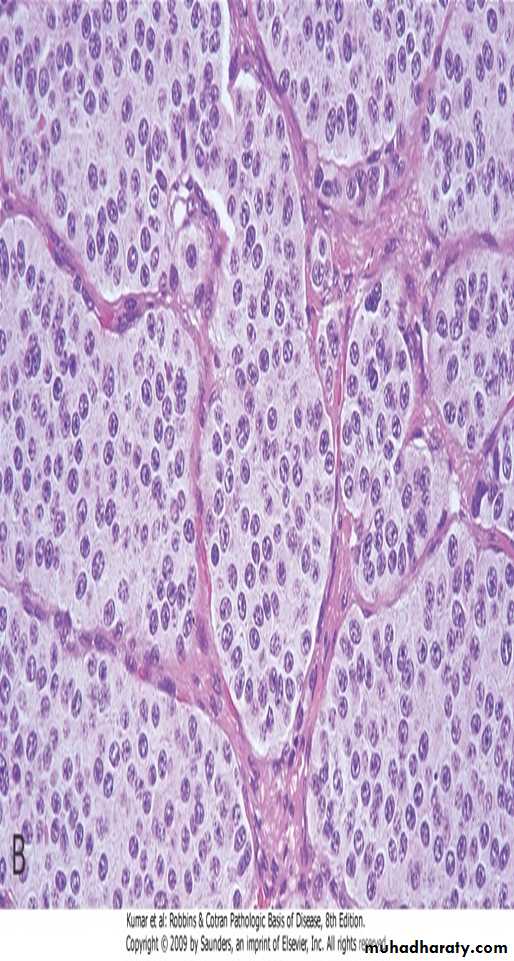
Histoplasmosis. A, Laminated Histoplasma granuloma of the lung. B, Histoplasma capsulatum yeast forms fill phagocytes in the lung of a patient with disseminated histoplasmosis, inset shows high power of pear-shaped thin-based budding yeasts (silver stain).
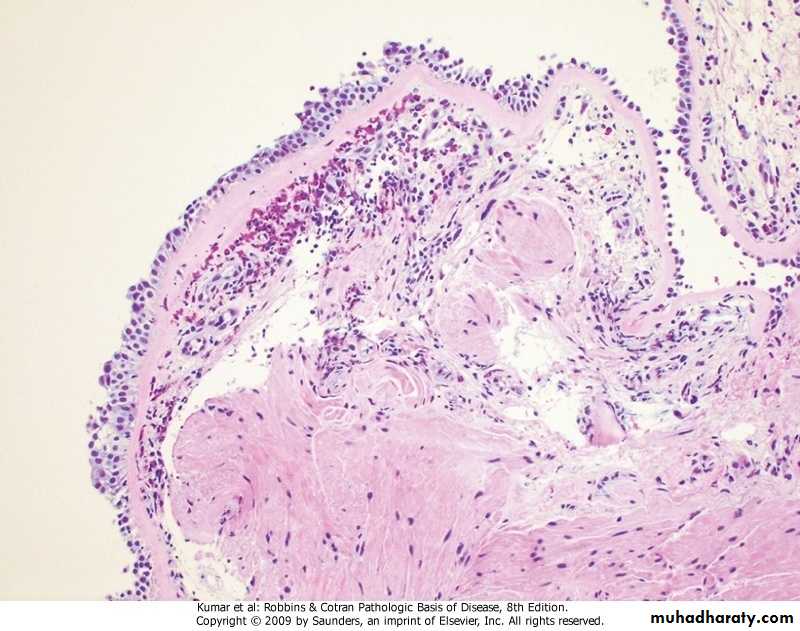
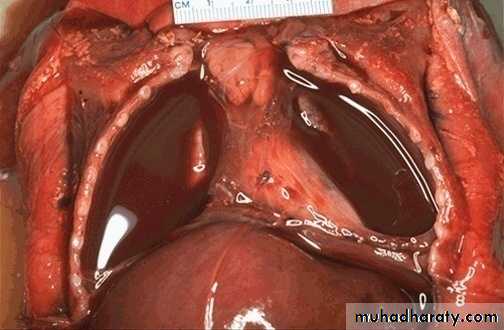
Empyema . The pleural surface left demonstrates thick yellow-tan purulent exudate and the pleural cavity is filled with purulent exudate.
Morphology:
squamous cell carcinoma with a keratin pearl composed of cells with brightly eosinophilic cytoplasm.
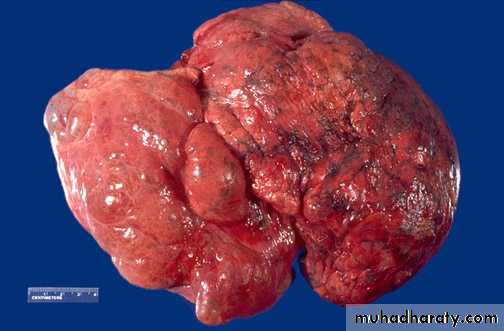
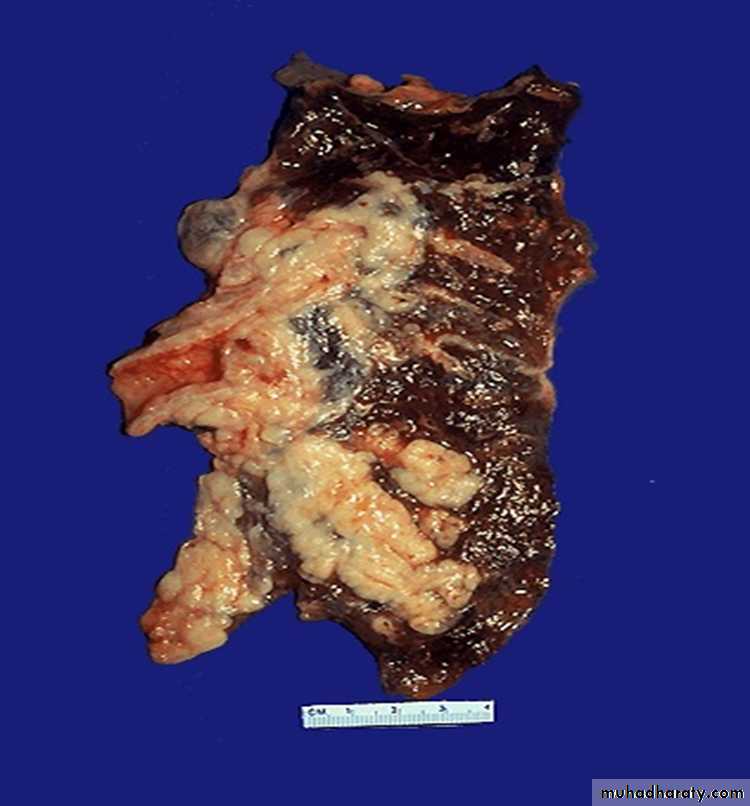
gray-white tumor
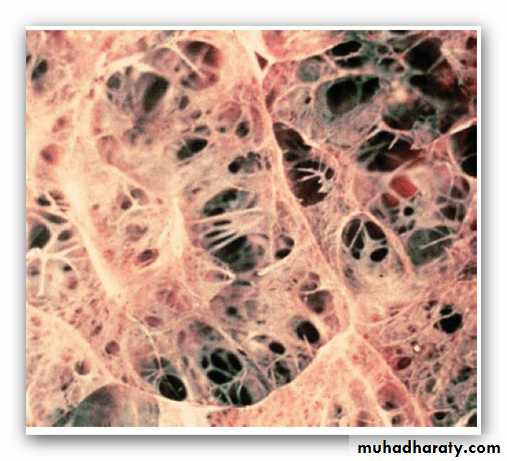
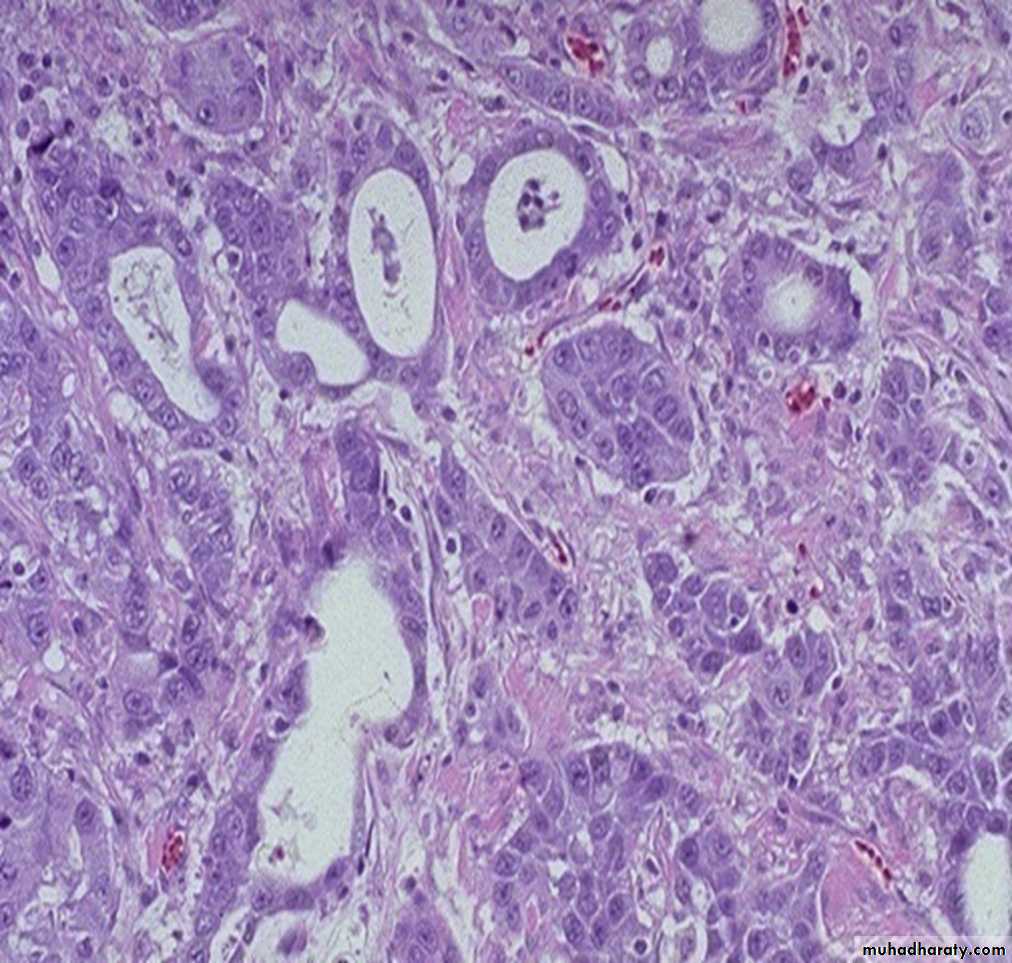
malignant epithelial cells of an acinar adenocarcinoma form glands
MORPHOLOGY
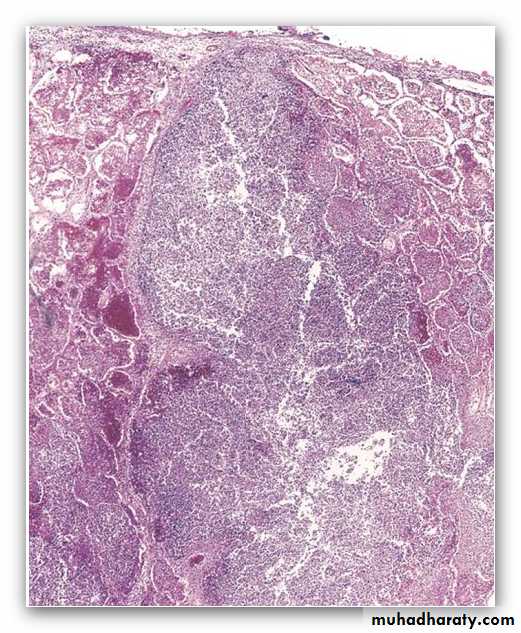
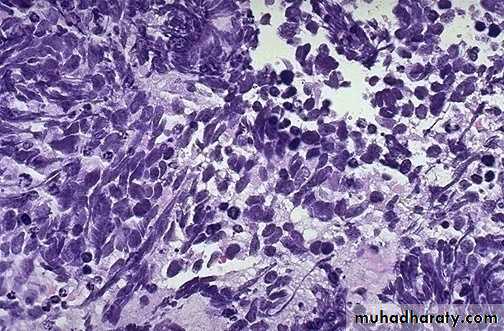
small oval to spindle-shaped cells with scant cytoplasm, finely granular nuclear chromatin, and conspicuous mitoses.