Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
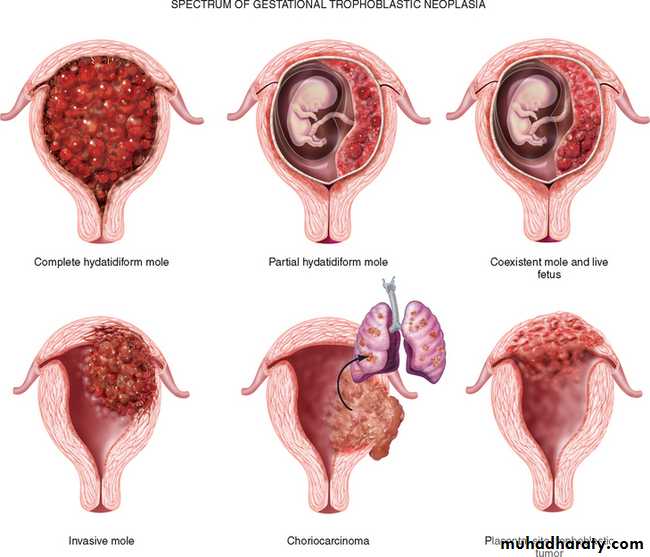
Gestational trophoblastic disease comprises a heterogeneous group of lesions arising from abnormal proliferation of trophoblast of the placenta.Classification of Gestational trophoblastic disease :
1. hydatidiform mole• Complete
• partial .
• invasive.
2 placental site trophoblastic tumor.
3 choriocarcinoma .
(Hydatidiform Mole )
Complete H. mole.This is an abnormal conceptus in which an embryo is absent and the placental villi are so distended by fluid that they resemble a bunch of grapes .
women with a mole has a 2-3% risk of eventually developing choriocarcinoma
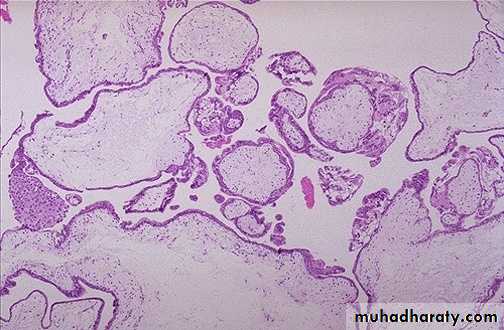
Microscopically :
The stroma of the villi is markedly edematous often with cistern formation .A constant feature is the presence o f a variable degree of atypical villous trophoblastic hyperplasia
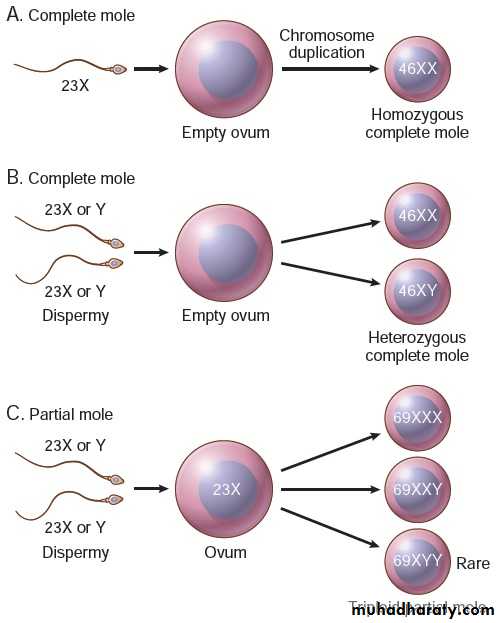
Complete H .Mole is caused by abnormal gametogenesis & fertilization .
The nuclei of the trophoblastic cells in this disease contain only paternal chromosomes & are therefore androgenetic in origin .Chromosomes are diploid 46,XX in 90% cases 46,XY in a small part
Partial H.Mole
About 15 - 35% of all moles are of the partial type.It is often associated with the presence of an embryo although is usually abnormal.
The risk for the development of choriocarcinoma following a partial mole is very low.
5 -10 % of partial mole progress to invasive mole
Grossly:The placenta contain mixture of normal & vesicular villi .These villi show focal edema leading to central “cisternal” formation .Many of the villi contain fetal (nucleated ) red blood cells .
Trophoblastic proliferation is present but in lesser degree than in complete H. mole .
Most partial moles are triploid (69xxx or 69xxy) & few show trisomy 16.
A partial mole is often accompanied
by a fetus that is usually grossly abnormal .
Pathogenesis of molar pregnancy
Invasive Mole
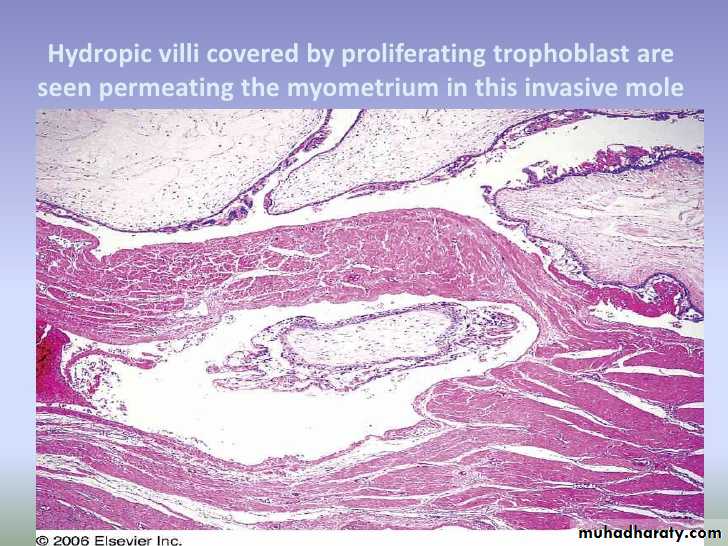
It refers to H.M. ( nearly always of the complete type but occasionally of the partial type ) in which the villi penetrate the myometrium &/or its blood vessels .This phenomenon which occur in 17% of all complete moles , it is an exaggerated expression of the capacity of normal trophoblast for invasion .
Invasive mole : hydropic villi within the myomatrium
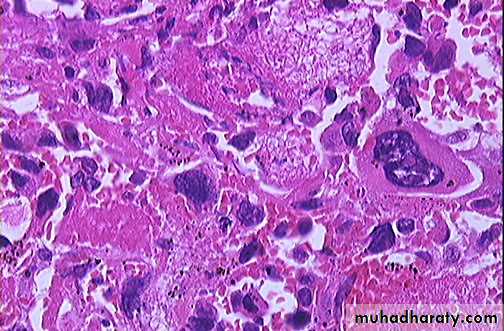
Choriocarcinoma
It is a malignant tumor of trophoblast & is formed of both cytotrophoblast & syncytiotrophoblast.It is a unique neoplasm in that being purely fetal origin .
It is neoplastic allograft in the mother .
The tumor follows H.mole in 50% of cases & unremarkable abortion in a further 25% ;the remainder develop often after a period of months or years ,as a sequel to an apparently normal pregnancy .
Choriocarcinoma & H.mole secrete placental HCG & assay of serum & urinary levels of this tumor marker are used in patient management .
There is increased risk of choriocarcinoma for women of group A married to men of the same group .
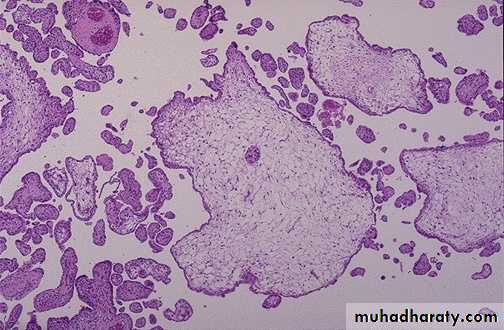
Microscopically :
The tumor is composed of cluster of cytotrophoblast separated by streaming masses of syncytiotrophoblast ,resulting in a characteristic dimorphic plexiform pattern .Villi are characteristically absent as a matter of fact ,their presence is said to rule out the diagnosis of choriocarcinoma .No matter how atypical the trophoblastic cells may be .
The natural history of untreated choriocarcinoma is characterized by the development of early hematogenous metastasis ,the most common sites being the lung, vagina, brain, liver, kidney &bowel & often present with massive hemorrhage .
Ovary
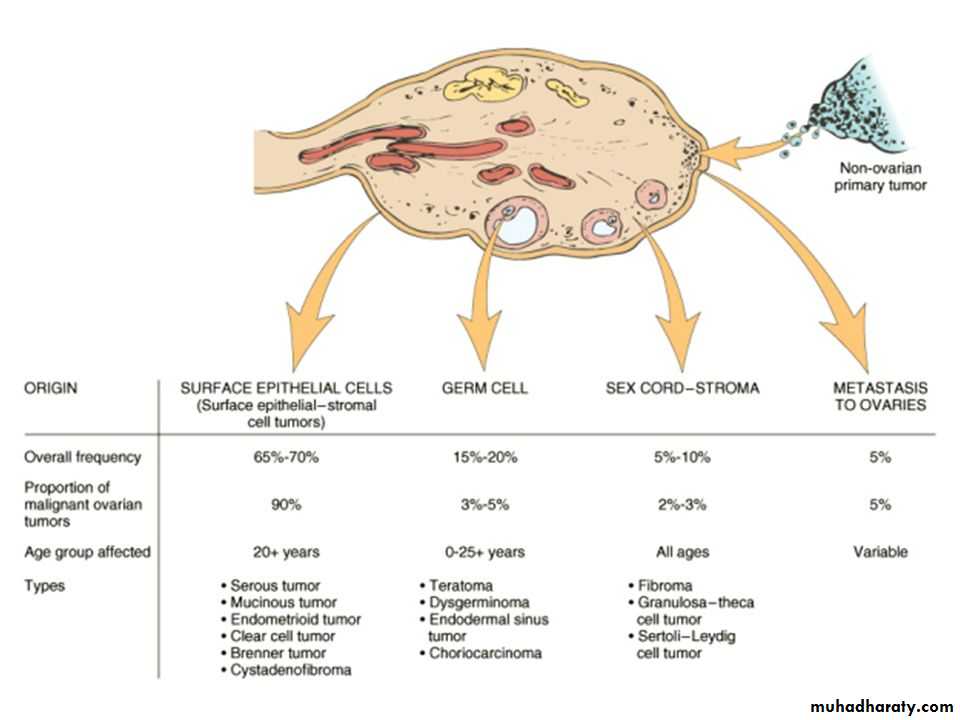
Classification of ovarian tumors
• A simplified form of the classification of ovarian tumors in to 5 groups :• I- Tumors derived from the surface epithelium(60% of all ovarian tumors):
• 1-Serous tumors ( benign ,border line ,malignant ).
• 2-Mucinous tumors (= , = , = ).
• 3-Endometriod tumors (= ,= , = ).
• 4-Clear cell tumors ( = , = , = ) .
• 5-Transitional cell tumors ( Brenner tumor of benign border line & malignant Brenner tumor).
• II-Tumors of sex cord & stromal origins
• 1-Granulosa –stromal cell tumors, leading to granulosa cell tumors ,tumors of the thecoma –fibroma group .
• 2-Sertoli-stromal cell tumors ; androblastoma.
• 3-Sex cord tumor with annular tubules .
• 4-Gynandroblastoma .
• 5-Steroid (lipid) cell tumors .
• III-Tumors derived from the germ cells
• 1-Teratoma• 2-Dysgerminoma identical to seminoma of testis .
• 3-Yolk sac tumor ( endodermal sinus tumor).
• 4-choriocarcinoma
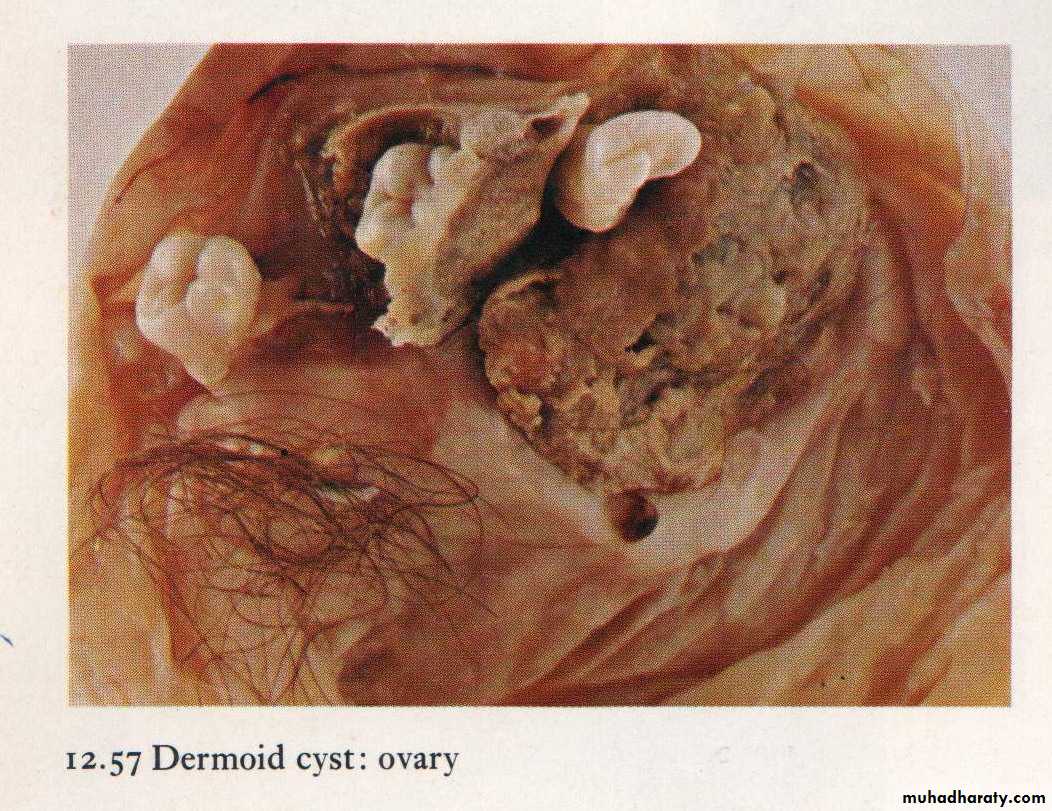
Teratoma containing tooth, cartilage & hair
• IV-Miscellaneous tumors
• Primary lymphoma of the ovary .
• V-Metastatic tumors
• The ovary is a common site of secondary tumors especially from the uterus ,breast & GIT.• Krukenberg tumor :
• it is secondary tumor in the ovaries which is due to transcoelomic spread of a gastric or colonic adenocarcinoma & is characterized by the presence of mucin –containing signet ring cells scattered in a fibrous stroma which is extremely cellular .