Ischemic and rheumatic heart
diseases
Dr. Ameer kadhim Hussein
M.B.Ch.B. FICMS

Ischemic heart diseases
In most western countries, 30% of all deaths in
men, 25% in women are caused by IHDs.
Case fatality rate = 25–28% within 28 days (and
55% within first hour). It eats about 3.4–9.4 years
of life expectancy of men, and even greater for
women.
IHDs are a 'modern epidemic', one spread not from
person to person but due to a lifetime of bad
habits. After sweeping the developed countries,
CHD is on the decline (although still very
prevalent) there, while affecting more the
developing countries.
Ischemic heart diseases
The ischemic heart diseases have a kind of
‘incubation period’ of 10 years, i.e.the lag period
between behavioral change and onset of disease.

Risk factors of IHD
Risk factors of IHD
• Smoking.
• Hypertension (BP > 140/90 or any body on
antihypertensive drugs) .
• HDL < 40 mg/dl.
• Diabetes mellitus.
• Family history of IHD.
• Age (men > 45 years, women > 55 years).
• Obesity (BMI > 30), physical inactivity.
• Alcohol > 75 g/day.

Risk factors of IHD
IHD
Risk factors of
• Male sex/ postmenopause/OCP intake.
• Type A personality.
• Lack of dietary fibers, high cholesterol diet, too
soft water, deficiency of polyunsaturated fatty
acids, too much salt.

Dyslipidemia
Of all lipids, LDL cholesterol is most directly
related to IHD. Current recommendation is to
screen for blood lipids in all adults over 20 years.
The screen
should include a fasting lipid profile (total
cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol and
HDL cholesterol) repeated every 5 years.
Apo B and Apo A are probably better indicators
than the lipoproteins themselves. Lipid goal. HDL
> 45 mg/dl; LDL < 160 mg/dl; total cholesterol /
HDL < 3.5.

Smoking
Smoking is an important, but reversible risk
factor.
Smoking cause atherogenesis by releasing
carbon monoxide and ↑ sympathetic tone.
Hypertension
Hypertension
Is the strongest risk factor for IHD. CVD risk doubles
for every 10 mm Hg increase in DP or 20 mm Hg
increase in SP.

DM
mellitus, insulin resistance and the metabolic
Diabetes
syndrome
Most patients of diabetes mellitus die from
atherosclerosis and its complications. The abnormal
lipoprotein profile associated with insulin resistance,
known as ‘diabetic dyslipidemia’, accounts for part of
elevated cardiovascular risk in patients with Type II
diabetes.

DM
While diabetic patients often have LDL
cholesterol near average, the LDL particles are
smaller, denser and more atherogenic. There are
also low HDL and high triglycerides.
Hypertension often accompanies diabetes and
indeed, this cluster of risk factors is now known
as the ‘metabolic syndrome’.
Diabetes mellitus may also cause ‘silent’ AMI.
The target is to keep sugar under 120 mg/dl at
all times and BP < 130/85.

Metabolic syndrome
The metabolic syndrome is any three risk
factors of the following:
• Abdominal obesity (waist circumference):
Men > 102 cm, women > 88 cm.
• BMI > 30.
• Triglycerides > 150 mg/dl.
• HDL cholesterol: Men < 40, women < 50.
• Blood pressure > 130 or > 85 mm.
• Fasting glucose > 110 mg/dl.

Others
Male sex/postmenopausal state
Decades of observational studies have verified
excess coronary risk in men compared with
premenopausal women.
After menopause, both become equal. In this
regard, estrogen has been found to increase
HDL and reduce LDL.
Dysregulated coagulation or fibrinolysis.


Prevention
•
prevention
Primordial
.1
Preserve traditional food habits, implement 'dietary
goals‘.
.2
Avoid initiation of smoking, fast foods, colas and
candies. Schools play the most important role in
primordial prevention.
•
in
every body
Primary prevention (for
population)
.1
Prudent diet (rich in fruits and vegetables)
.2
Abstinence from smoking and alcohol.
.3
Control of stress and hypertension.
Prevention
•
Secondary prevention (for those with risk
factors)
Screening for hypertension,
hypercholesterolemia, diabetes and medical
management of such diseases. Screening is
recommended each 5 years in all adults over 20
years.
•
Tertiary prevention
Include lifelong β blockers and Aspirin,
angioplasty.
RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE

Introduction
Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) is the ultimate, sequelae and
crippling stage of rheumatic (Rh) fever, which in turn is the
result of streptococcal pharyngitis.
Rheumatic fever is an acute febrile disease, affecting the
connective tissues particularly in the heart and joints, which
occurs following the infection of throat (pharynx) by group A
beta-hemolytic streptococci. Thus although Rh fever is a non
communicable disease, it results from communicable pharyngitis.
About 20 percent of all sore throats among children are due to
streptococcal infection and of these about 2 percent result in
rheumatic fever. Almost 80 percent of those who get Rh fever,
end up with Rh heart disease.

Introduction
RHD is the late sequel of Rh fever, which in turn is the
result of the infection of tonsils, pharynx, adenoids, etc.
caused by Group A, β-hemolytic streptococci (also
called S. pyogenes). Reservoir of infection include all
the cases and the carriers of streptococcal pharyngitis.
Among the carriers, both temporary and chronic carrier
state occurs.
Cases of strep. pharyngitis are at a greater risk of
developing Rh. fever than the carriers. Incidence is
maximum among school children, in the age group of 5
to 15.It is equal in both the sexes.

Immunity
There has been an immunological basis for the
development of Rh fever and RHD.
According to toxic immunological hypothesis,
the streptococci have certain toxic products
leading to immunological process, resulting in
Rh fever.
Another concept is that it requires repeated
exposure to precipitate the illness. Another
belief is that RHD is an autoimmune disease.

Predisposing factors
Rh fever and RHD is considered as ‘Social disease’, because
many social factors are responsible for the prevalence of this
disease such as poverty, poor housing, undernutrition, illiteracy,
ignorance, large families, over crowding, etc.
Prevalence declines sharply as the standard of living improves.

Recommendations of the American Heart Association
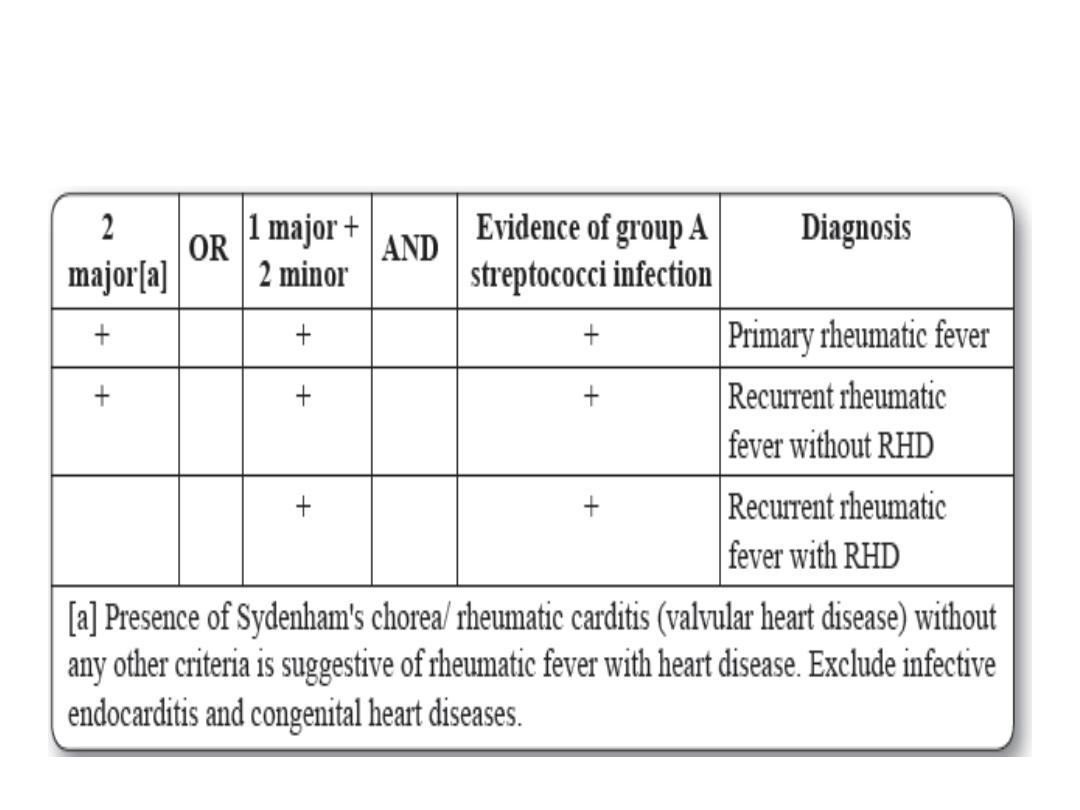
Diagnostic chart for rheumatic fever

Prevention of Rheumatic Fever and
Rheumatic Heart Disease

Health Promotion
Measures necessary for primordial prevention are:
• Improvement in the living conditions.
• Improvement of sanitation in and around the house.
• Prevention of overcrowding.
• Prevention of malnutrition among children.
• Improvement in the socioeconomic condition.
• Health education of the people regarding dangers of
sore throat.
• ‘Health-Fair’ should be conducted in the schools to
make the children health conscious.

Specific Protection
• No vaccine is available.
• Chemoprophylaxis of the contacts of a case of
pharyngitis or scarlet fever with Benzathine penicillin.
• ‘Secondary prophylaxis’ is given for all cases of Rh
fever to prevent RHD with 1.2 million units of
Benzathine Penicillin, once in 3 weeks, regularly for 5
years or until the age of 18 years. If they have
developed RHD, prophylaxis is continued for life.

Early Diagnosis and Treatment
• By conducting periodical ‘School health
survey’, to detect the cases of sore throat.
• By surveillance of ‘high-risk’ groups such as
slum dwellers.
• Detected cases of sore throat (or acute
pharyngitis) are treated by 1 dose of 1.2 million
units of Benzathine penicillin, a long acting
one. This essentially prevents the subsequent
development of Rh fever and RHD.

Disability Limitation and
Rehabilitation
This consists of limiting the development of disability in an
individual who has already developed RHD. This consists of
giving intensive treatment with Aspirin for joint pains and
prednisolone for carditis, life long Benzathine Penicillin, 1.2
million units, once in 3 weeks and Balloon valvotomy or valve
replacement. Rehabilitation by social, vocational and
psychological measures of those who are suffering from RHD.
