The Steps for dealing with completely edentulous patient in dental clinic.
Complete DentureDiagnosis & Treatment PlanningExamination: is the investigation carried out for the purpose of diagnosis.
Diagnosis :is the scientific evaluation of the existing condition.
Treatment plan:
The sequence of procedures planned for the treatment of a patient following diagnosis.
Prognosis:
denture prognosis is a judgment or opinion for success the fabrication and usefulness of the dentures.History and Examination
Personal dataPatient name
Age/ sex
Address/ phone number
Occupation
Dental History
History of tooth loss: cause, Time, Edentulous period
Reasons for loss of teeth:
Periodontal diseaseCaries of teeth
Other causes
• Previous denture experienceReasons why patient needs new dentureExamination of an Old Denture Wearer
• Esthetics, lip fullness, symmetry, amount of display during smiling, phonetics, teeth position, size, excessive wear
• Fracture, cracks, porosity, denture hygiene
• Occlusal vertical dimension (due to excessive occlusal wear, OVD may have reduced)
• Systemic Status
• Medical History• 1.Arthritis
• 2.Diabetes
• 3. Anaemia
• 4.Radiotherapy
• 5.Neuromuscular disorder
• 6. Cardiovascular Disease.
• Psychological Evaluation (House Classification of Denture Patients)
• Philosophical patient : well motivated, cooperative, calm ,has the best mental attitude for accepting the denture& accept treatment with denture without question.
• Exacting (critical):dissatisfied with past treatment
• and do not accept advice.
• They need to be explained about details of treatment procedures .because of his poor education the dentist must re-educate him with firm control.
Hysterical patients: these patient have a negative attitude , emotionally unsteady, apprehensive and excited and will show unnecessary fear for dental service . prognosis of denture is unfavorable so additional confidence is mandatory to such patient and need psychiatric treatment.
Indifferent patient: these patients show least concern with his dentist , not follow instructions , they often go without dentures for years. they have no desire to wear dentures. those patients have unfavorable prognosis.
• Extra-oral Examination
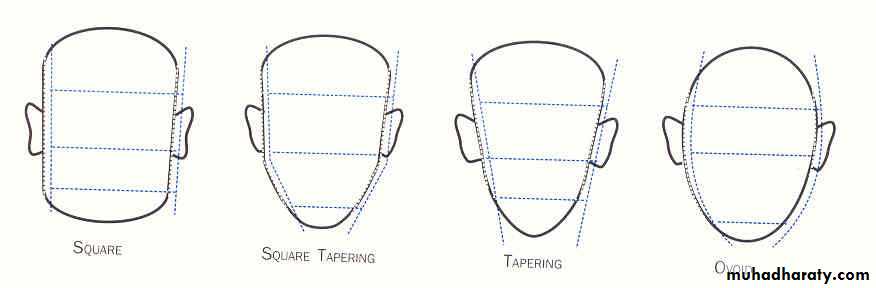
Face Form:Square
Tapering
Ovoid
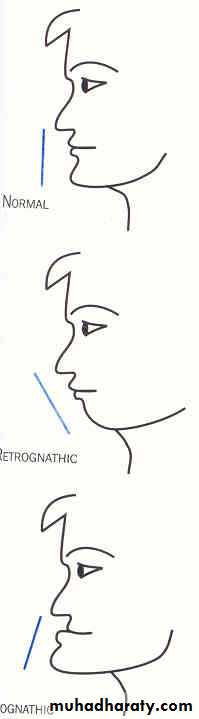
Face Profile
NormalRetrognathic
prognathic
Symmetry: Symmetrical/asymmetrical. Facial height: Decreased/normal/increased. Facial muscle tone: Normal/flabby/spastic. Color of hair: Black/brown/grey/white. Color of eyes: Black/brown/white/grey
• Lips
• Length : short /average/ long• Thickness: thin/average/ thick
• Smile line: Lip smile line
Normal smile line
High smile lineExtraoral Examination
TMJ examinationPalpation of the head & neck (lymph nodes & muscles)
• Intraoral Examination
Cheeks, tongue, floor of the mouth, maxillary tuberosity,
hard palate, soft palate, arch relationship, residual ridge form, saliva, undercutsArch Form: U - shaped/ V- shaped
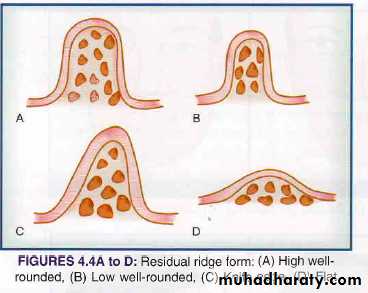
Residual Alveolar Ridge (Cross Sectional form)
High well roundedLow well rounded
Knife-edge
Flat
Depressed
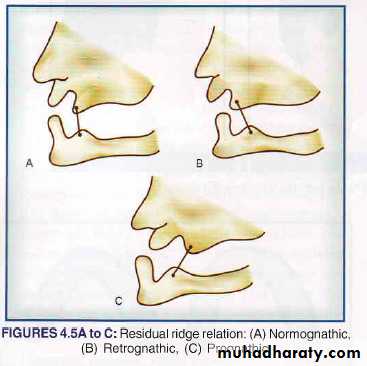
Residual ridge relation
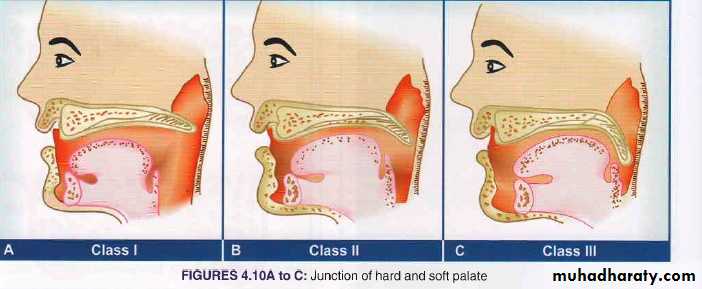
Normognathic : Class IRetrognathic : Class II
Prognathic: Class III
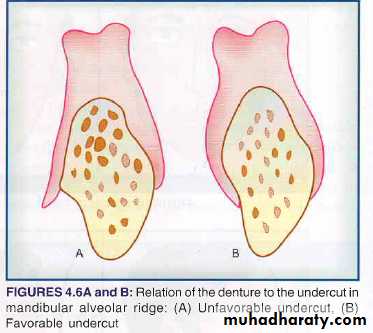
Undercut
The favorable undercuts should be detected that aid in retention and the unfavorable undercuts should be planned for block out or surgical correction.
Bony irregularities location: Radiographic examination will be aid in differentiating the irregularities caused by bone and any residual tooth structure.
Surgical correction should precede any prosthodontic treatment.
Retained root pieces: It can be confirmed byradiographic examination followed by surgical
removal.
Mucosa
attached / non-attachedColour
Resilien: Ideal requirement
. Hard : Unequilibrium of support
. Inflamed: Very fragile
. Hyperplastic/Displaceable: surgical treatment for elimination of hyperplastic tissue
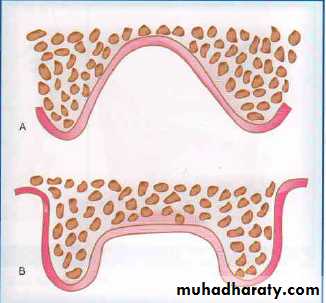
Vault of the palate
'V' shaped or 'U' shaped. It could be either high
vault or flat vault. The 'U' shaped palate is suitable in reference to retention and stabilitywhile the 'V'shaped palate causes deflective forces
Junction of hard and soft palate
Saliva
• Amount:• Normal: ideal for denture retention
• Excessive: make denture construction difficult
• Reduced: reduced retention and increased soreness; salivary substitutes may be prescribed
• Consistency:
• Thin serous: provides an insufficient film for denture retention.
• Thick mucus: thick ropy saliva tends to displace denture.
Tongue SizeNormalLarge
Frenal attachment: Maxillary/ mandibular1. Normal
2. Close to the crest
3. Broad
نهاية المحاضرة الأولى (الجزء الأول)
Anatomical Landmarks of the Maxillary arch
Mandibular archAnatomical Landmarks of the Maxillary arch
Alveolar processHard palate
Soft palate
Maxillary Tuberosity
Incisive papilla
Hamular notch
Rugae area
Midpalatine raphe
Labial Frenum
Buccal Frenum
Maxilla
Alveolar processThe alveolar process: is a process of the maxilla
Alveolar ridge :is the reminant of the alveolar process which originally contained sockets of natural teeth after the natural teeth are extracted , the alveolar ridge is expected to resorb.
Maxillary Tuberosity:It is the most distal posterior portion of the maxillary alveolar ridge.
Hamular notch: is a deep depression located posterior to the maxillary tuberosity.
Hamular notches
Over extension - extreme pain
Under extension - non-retentive
Must be captured in impression
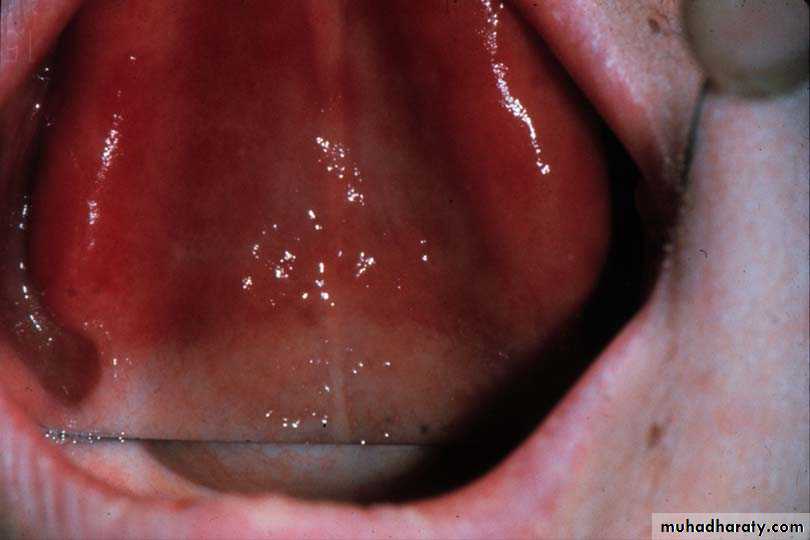
Incisive papilla
The incisive foramen is located in the midline of the hard palate immediately behind the central incisors. There is a definite prominence in the oral mucosa over the incisive foramen is called the incisive papilla.The papilla is a guide for determining the midline relationship of upper anterior teeth.
I P
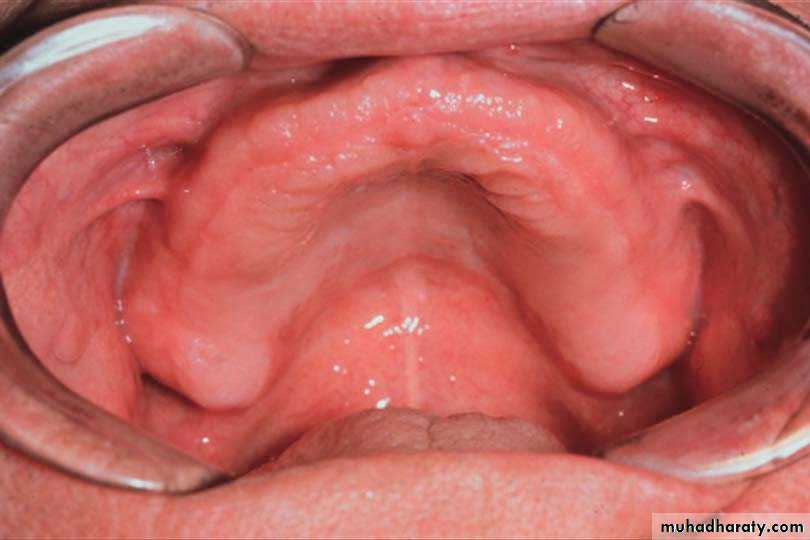
Rugae: are irregular ridges of fibrous tissue in the anterior one-third of the hard palate.
Significances
. It is concerned with phonetics.
. It increases the surface area of the foundation and
thus, supplements the values of retention.
. It is denture-stabilizing area in the maxillary
foundation
Vibrating line: an imaginary line conjunction between the hard and soft palate ,this line falls between the two hamular notches.
Fovea Palatinae: the two fovea are located on either side of the midline near the vibrating line.
V L
R A
V P
Midpalatine Raphe or Median Raphe
It is an area extending from the incisive papilla to the distal end of the hard palate along the sutural joint.This is a stress relief area in the maxillary
edentulous foundation and consideration is needed for stability of maxillary denture.
MPR
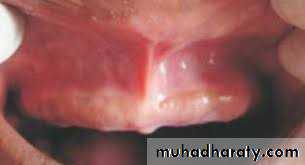
Maxillary Labial Frenum
' Appears as a fold of mucous membrane extending from the mucous lining of the lip to/ towards the crest of the residual alveolar ridge on the labial surface.Clinical considerations
Sufficient allowance should be created during final impression procedure and in the completed prosthesis because over riding the function of the frenum will cause pain and dislodgement of the denture.
L F
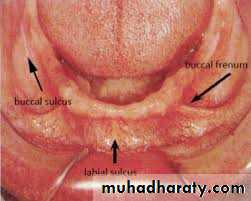
Maxillary Labial Vestibule
It extends on either side of the midline from labial frenum anteriorly to the buccal frenum posteriorly. It is bounded laterally by the labial mucosa and medially by the maxillary residual alveolar ridge. Reflection of the mucous membrane superiorly marks the heightClinical consideration: For effective border contact
between denture and tissue, the vestibule should be
suitably filled with impression material.
L V
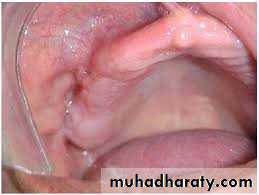
Maxillary Buccal Frenum
Appears as a single fold or multiple folds of mucous membrane reflection area to or towards the slope or crest of residual alveolar ridge.Clinical significance
. During final impression procedure and in the final
Prosthesis, sufficient allowance should be created for the movement of frenum because over riding the function of the frenum will cause pain and
dislodgement of the denture.
B F
Buccal Vestibule
It is bounded anteriorly by the buccal frenum, laterally by the buccal mucosa and medially by the residual alveolar ridge.CIinical consideartions
During the impression procedure the vestibule should be suitably filled with impression material for proper border contact between denture and the tissue.
B V
Anatomical Landmarks of Mandibular arch
The Residual Alveolar RidgeThe support for the lower denture is provided by the mandibular residual alveolar ridge and the soft tissue covering it.
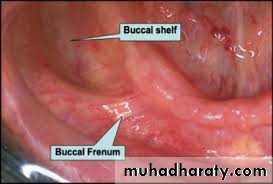
Buccal Shelf Area
Significance :It is the primary stress bearing area in the mandibular foundation
MandibularLabial Frenum
It is the fold of mucous membrane extending from the mucous lining of the mucous membrane of the lips towards the crest of the residual alveolar ridge on the labial surface.Clinical considerations
. During the impression procedure, the lip has to be
reflected anteriorly and horizontally.
. During impression procedure and in final prosthesis
allowance should be made in the form of a notch to
prevent over-riding of function, which may result in
laceration of the tissue
Mandibular Labial Vestibule
It is bounded anteriorly by the labial frenum, posteriorly by the buccal frenum, laterally by the labial mucosa and medially by residual alveolar ridge.Clinical considerations: For effective border contact between the denture and tissue, the vestibule should be suitably filled with impression material during the impression procedure.
MandibularBuccal Frenum
It is the fold of mucous membrane extending from the mucous membrane of the buccal mucosa to / towards the crest of the residual alveolar ridge on the buccal surface. It may be single or multiple.MandibularBuccal Vestibule
It is bounded anteriorly by the buccal frenum, posteriorly by the massetric notch area, medially by residual alveolar ridge and laterally by buccal mucosa.
Clinical consideration This space constitutes an area be suitably filled by impression material during impression procedure .
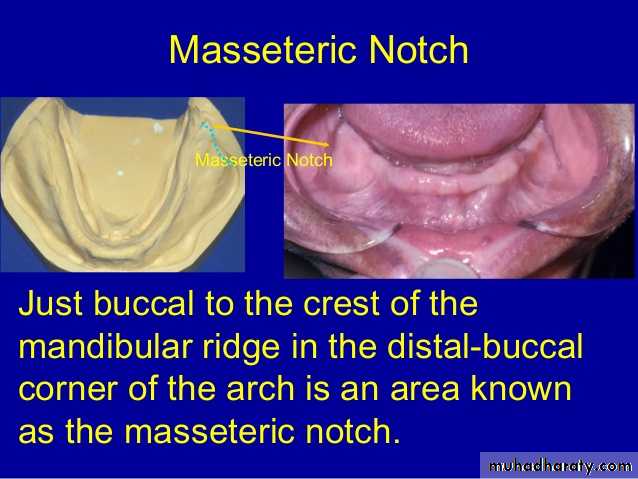
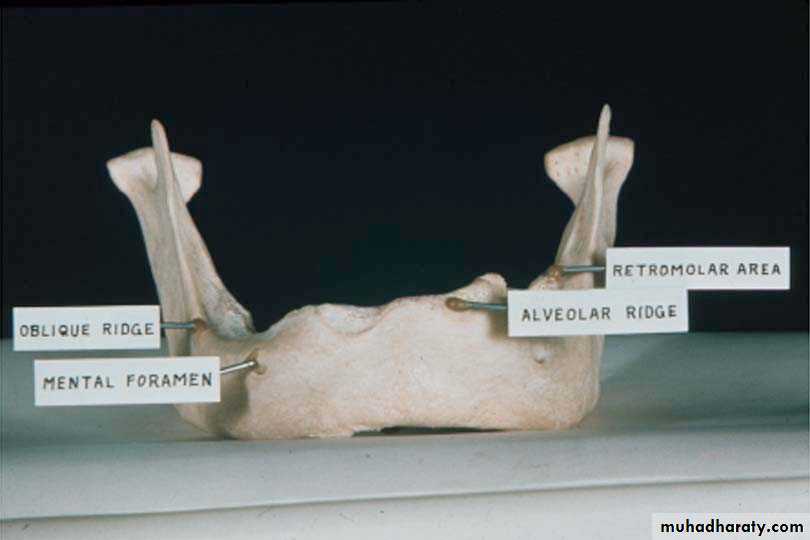
Masseteric Notch Area
Ii is immediately lateral to the retromolar pad andcontinues anteriorly to buccal vestibular sulcus.
Significance: It is an area where the masseter muscle in
function (anterior fibers) may push against the distal part
of the buccinator muscle
Clinical consideration
. It is due to the contraction of the masseter that a
depression is formed at the distobuccal corner of the
retromolar area.
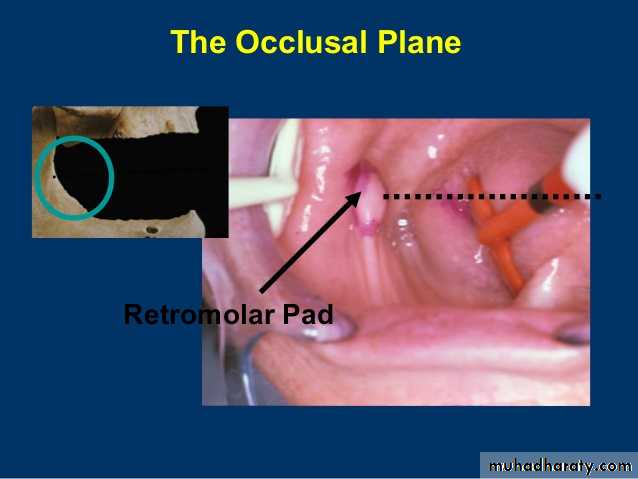
MandibleRetromolar Pad
It is a pear shaped body at the distal end of the residual alveolar ridge. It is also known as the retromolar triangle.
Significance
. Represents distal limit of the mandibular denture.
Retromolar Pad
CIinical considerations. Helps in maintaining the occlusal plane.
. Divide the retromolar pad into anterior 2l3rd and posterior 1/3rd
. Posterior height of occlusal rims should not cross the anterior 2l3rd
Teeth should not be placed on the retromolar pad because of its inclined plane, which will act as a dislodging factor with the forces being inclined anteriorly.
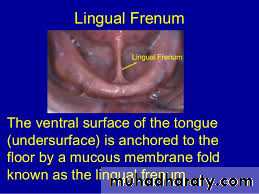
MandibularLingual Frenum
CIinical consideration. Sufficient allowance should be given in the impression and the final denture to prevent over-riding of function of the frenum.
. During impression procedure, the patient should touch the tip of the tongue to the incisive papilla region
Mandible
External Oblique RidgeDo not extend dentures to this ridge
Mandible
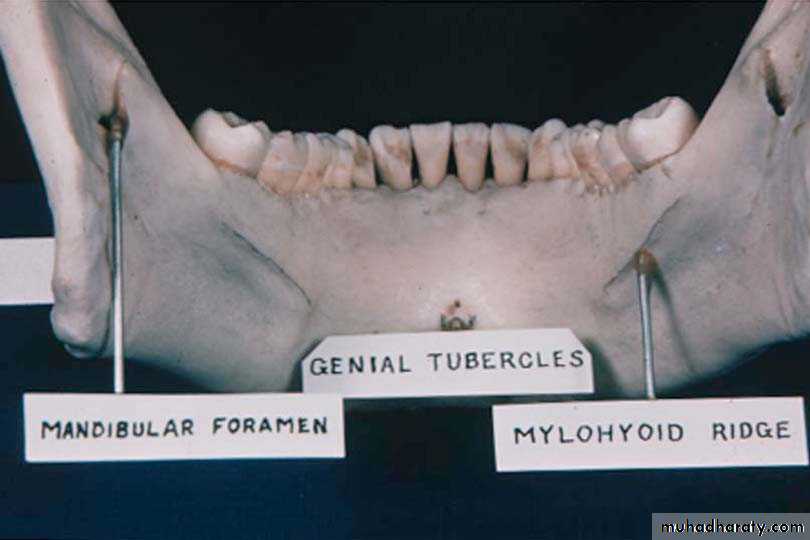
Mylohyoid RidgeOrigin of mylohyoid muscle which influences length of lingual flange
Can be prominent, and/or sharp, requiring relief
• Lingual Tori
• Raised bony structures• May require relief when covered by a denture
• Thin mucosa can ulcerate easily