
GIT 1
Third Year Class
By Dr.Riyadh A. Ali
Department of Pathology
TUCOM
Titles
• Salivary gland
– Pleomorphic adenoma
– Warthin's tumor
• Esophagus
– Esophageal carcinoma
• Squamous cell carcinoma
• Adenocarcinoma

Salivary gland
Pleomorphic adenoma
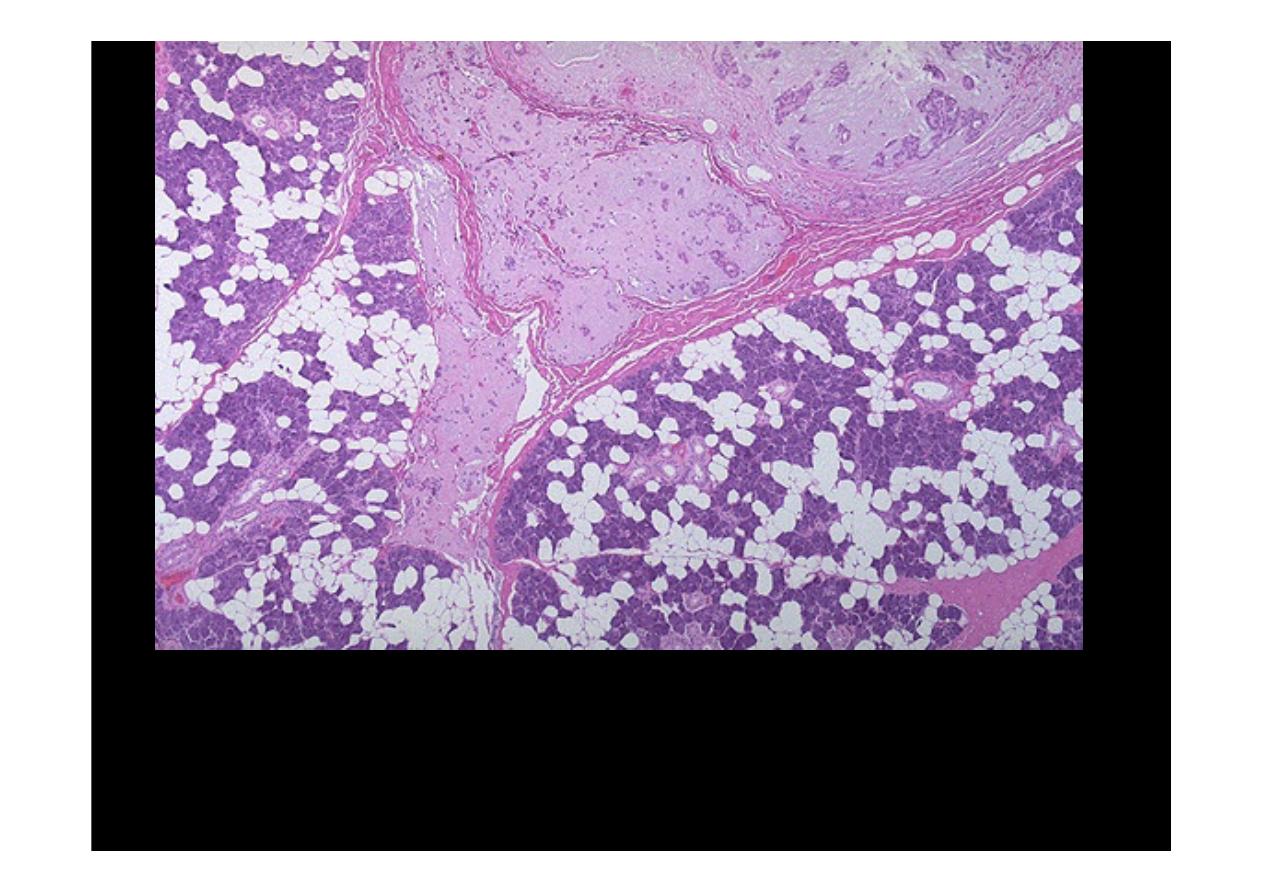
The low power microscopic appearance of a
pleomorphic adenoma (mixed
tumor) of salivary gland
is shown here at the top and center extending into
surrounding normal
parotid gland
. Such pleomorphic adenomas are the most
common salivary gland tumor, and the most common location for them is in the
parotid gland. These lesions are usually slow-growing, but can recur following
incomplete resection.
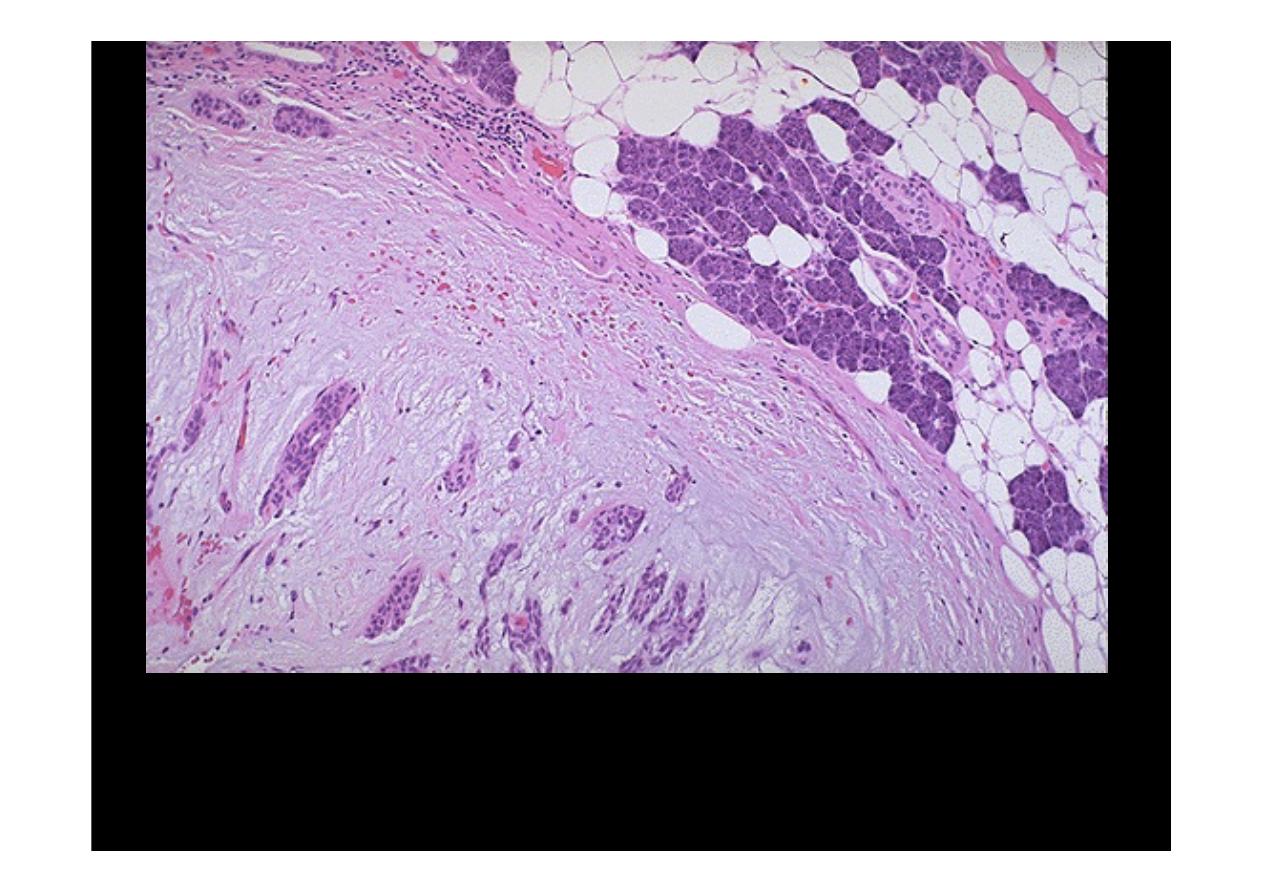
A
pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland
is seen here at high magnification next
to a portion of adjacent normal parenchyma at the upper right. The neoplasm is a
mixed proliferation of both ductal epithelium and a chondroid / myxomatous stroma.
Infrequently, a carcinoma can arise in a pleomorphic adenoma.
Salivary gland
Warthin's tumor
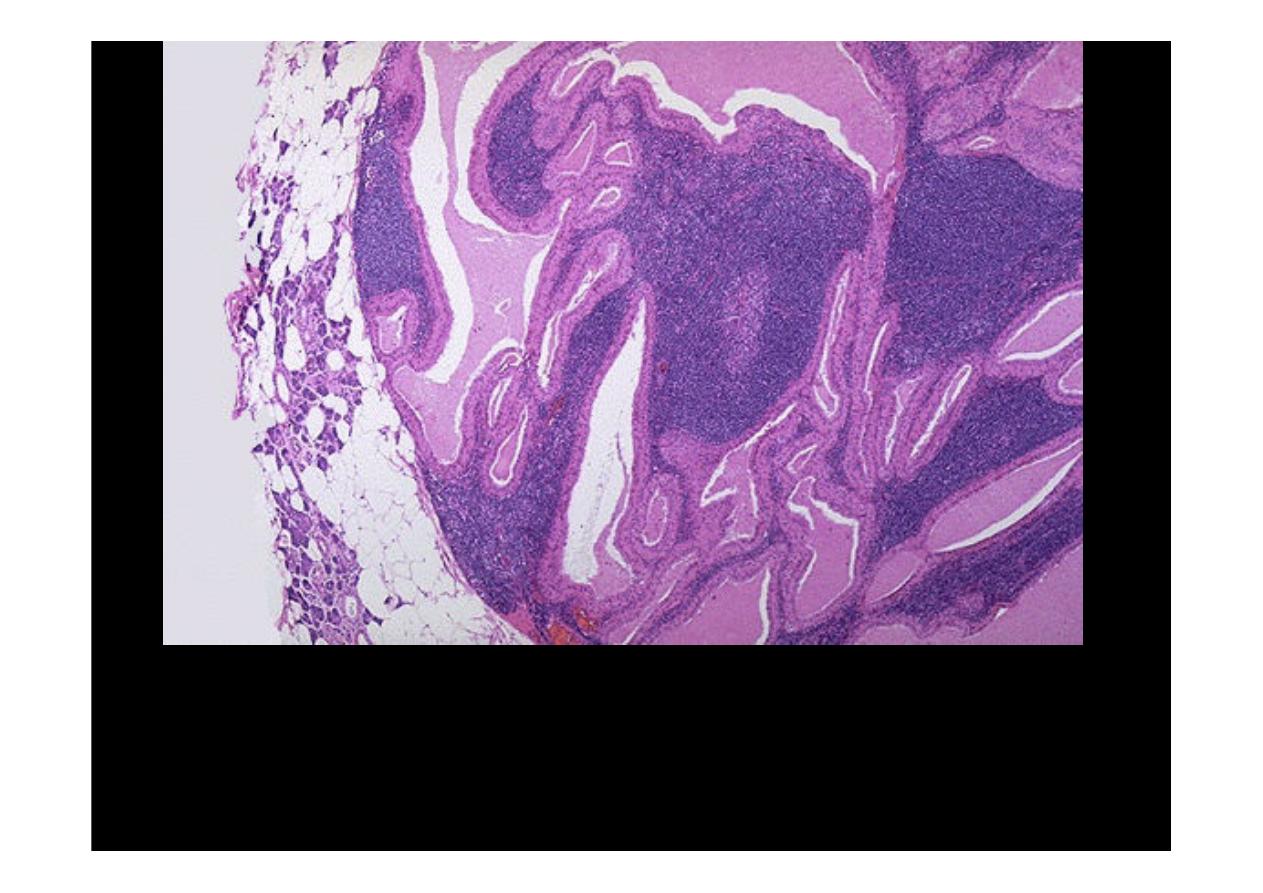
Here is a "purple cow" or a lesion with a very distinctive histologic appearance. This
is the low power microscopic pattern of a benign papillary cystadenoma
lymphomatosum, or
Warthin's tumor, of salivary gland
. A rim of compressed
normal parenchyma is seen at the left. This is the second most common salivary
gland tumor. It is almost always found in the parotid gland, is much more common
in males, and in some cases can be multifocal or bilateral.
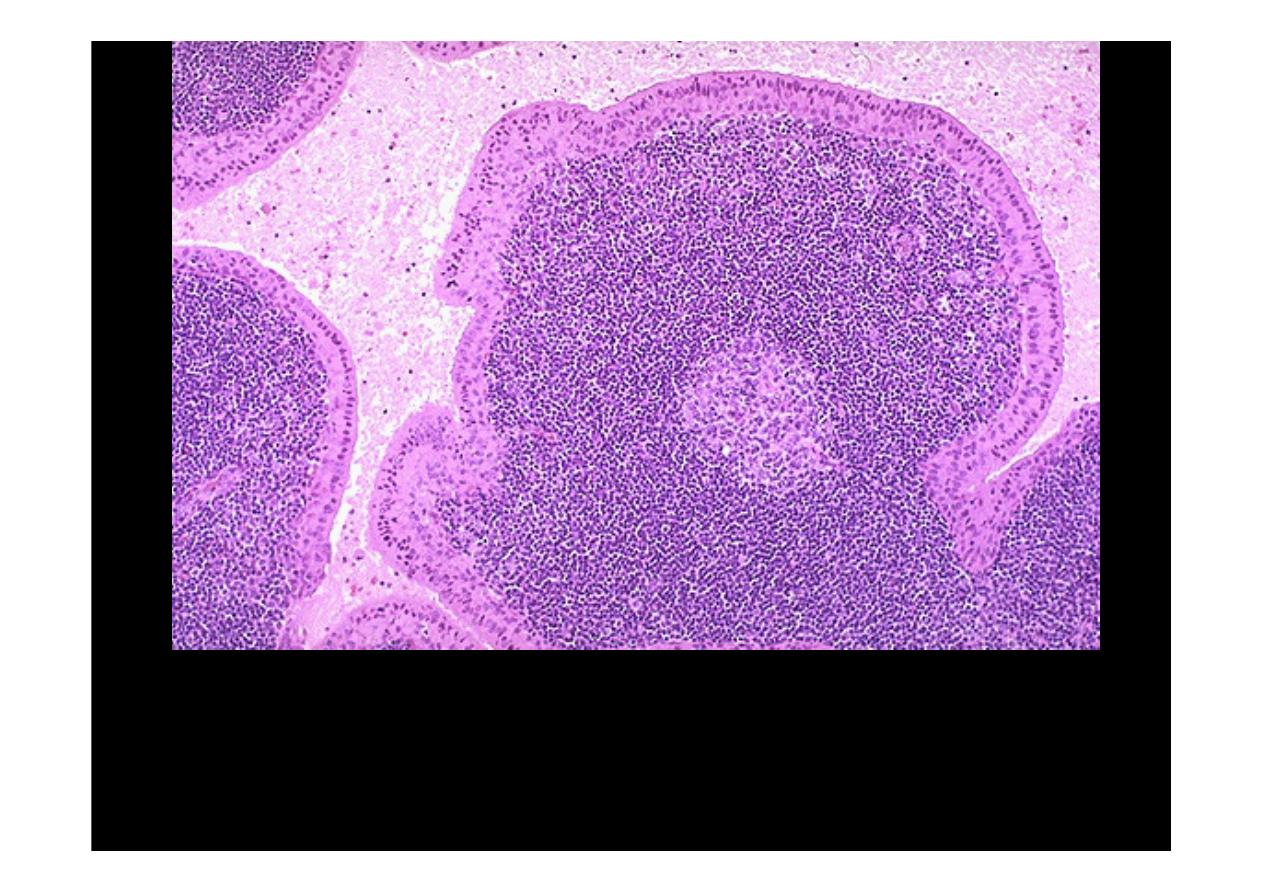
The microscopic pattern of a
Warthin's tumor
is shown here. There are cystic to cleft-
like spaces filled with pale pink mucinous to serous secretions. The spaces are lined
by a double layer of pink (oncocytic) cuboidal to columnar epithelial cells over papillary
fronds. The fronds beneath the epithelium are filled with lymphocytes, sometimes with
germinal centers.

Esophagus
Esophageal carcinoma
• Squamous cell carcinoma
• Adenocarcinoma
Esophageal carcinoma
• Squamous cell carcinoma
• Adenocarcinoma
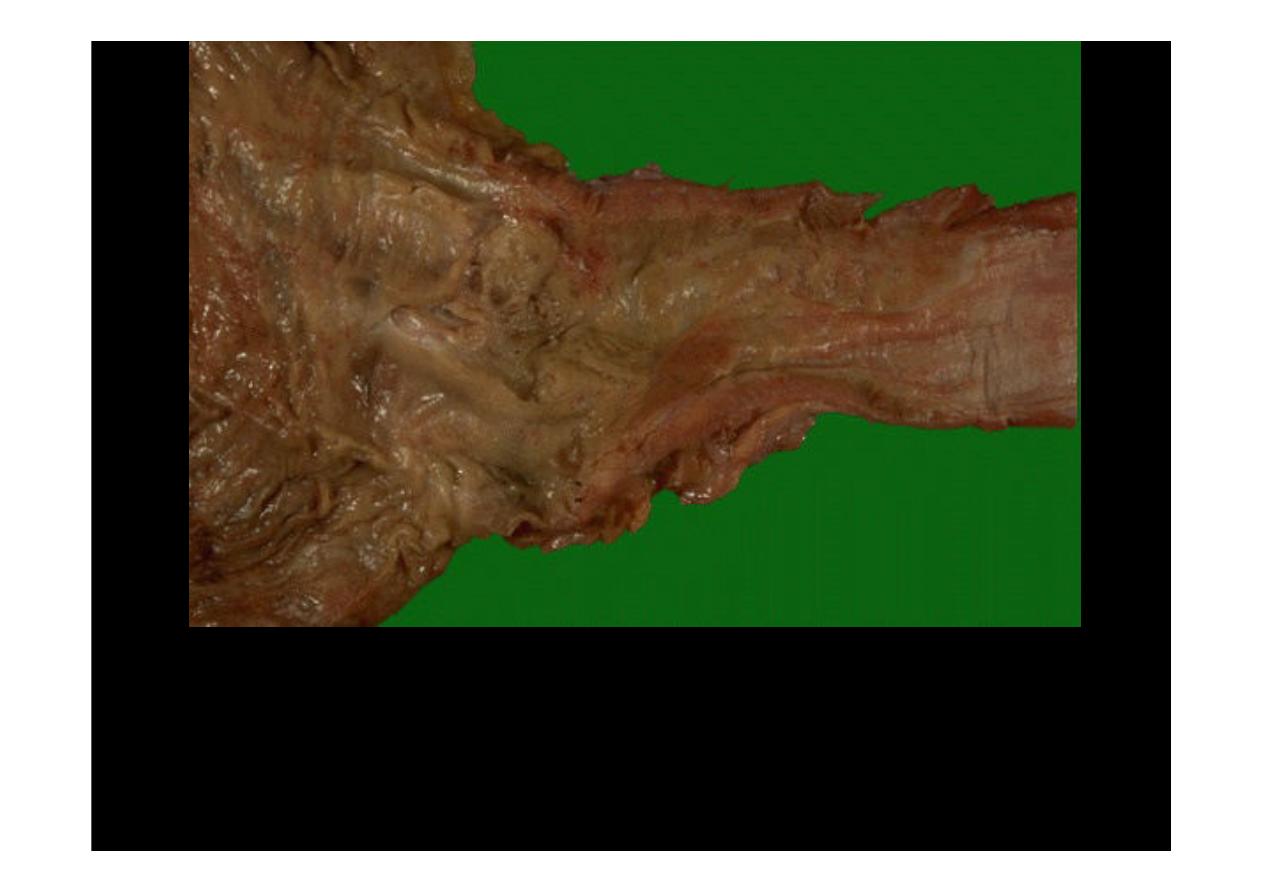
A history of smoking and/or alcoholism is often present in patients with
esophageal squamous carcinoma
, while a history of Barrett's esophagus
precedes development of esophageal adenocarcinoma in many cases. Here,
an ill-defined mass at the gastroesophageal junction produces mucosal
ulceration and irregularity, which led to the clinical symptoms of pain and
difficulty swallowing.
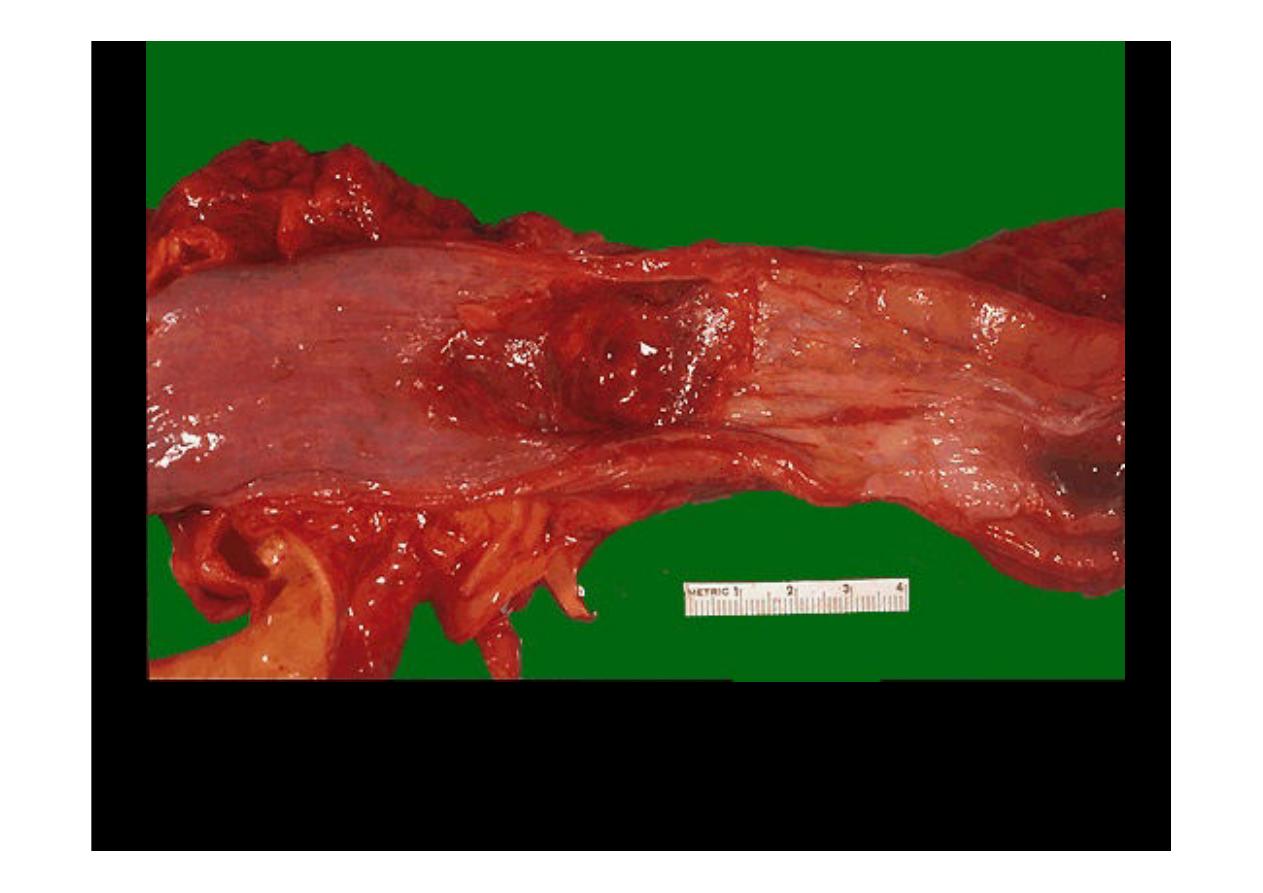
This irregular reddish, ulcerated exophytic mid-esophageal mass as
seen on the mucosal surface is a
squamous cell carcinoma
. Risk
factors for
esophageal squamous carcinoma
include mainly
smoking and alcoholism in the U.S.fs
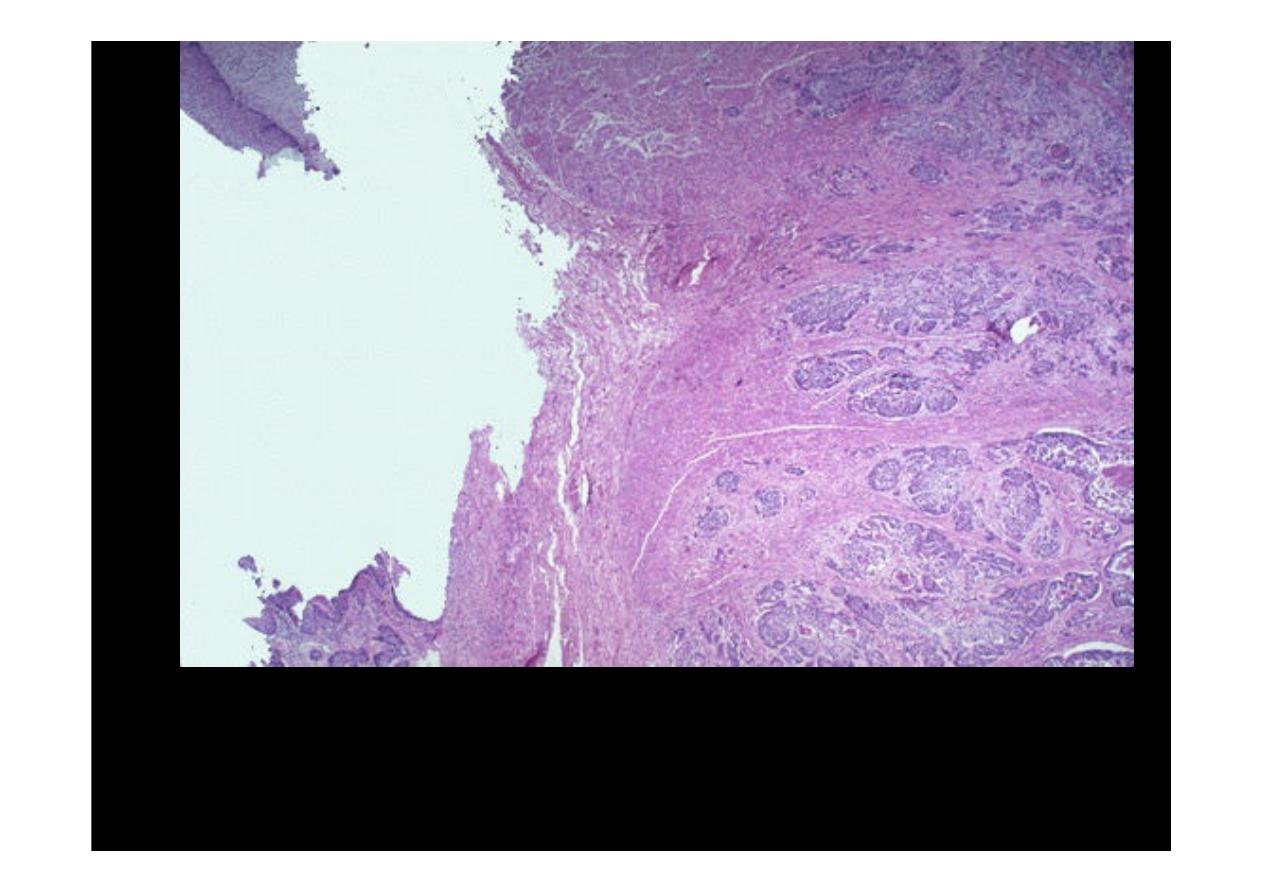
At the upper left is a remnant of squamous
esophageal
mucosa that has
been undermined by an infiltrating
adenocarcinoma
. Nests of
neoplastic glands are infiltrating through the submucosa at the right.
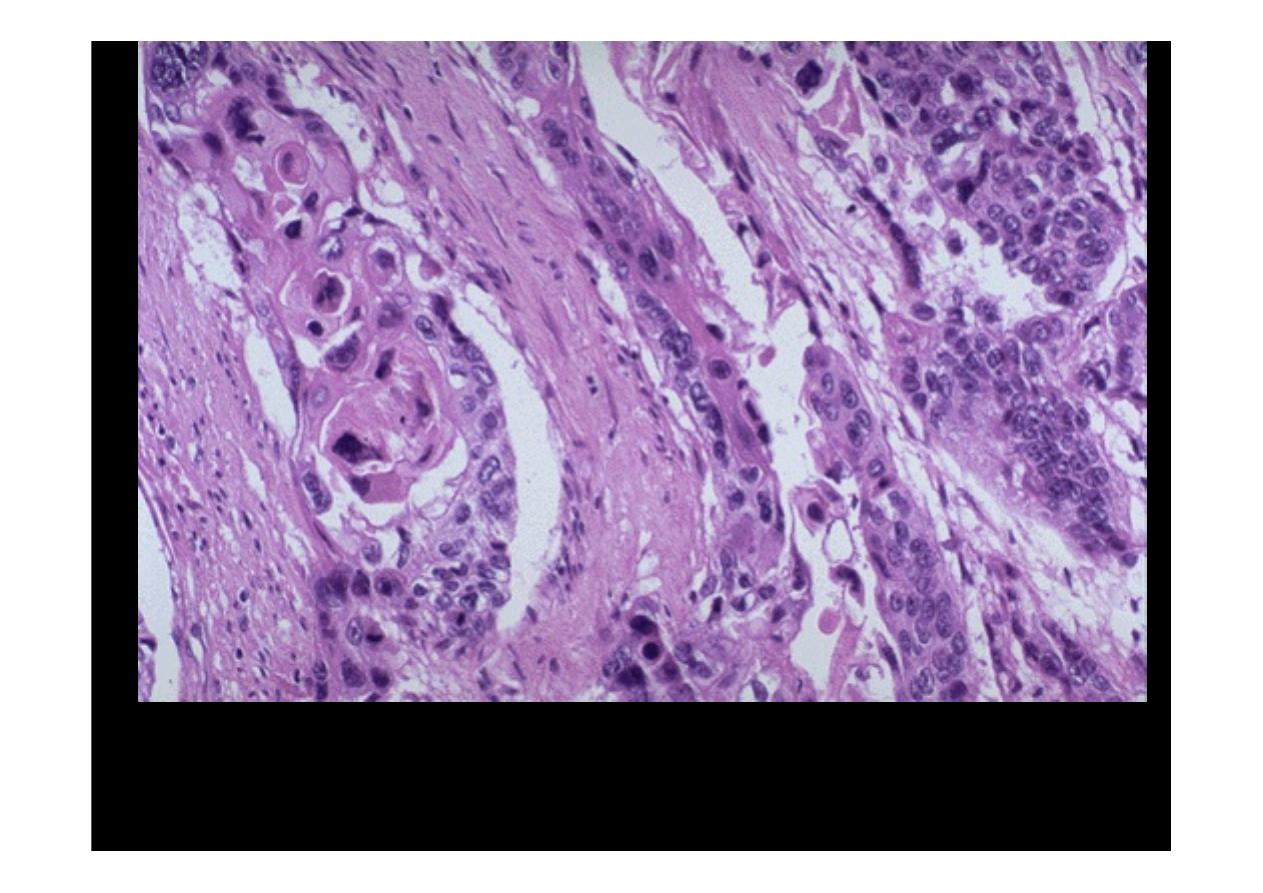
At high power, these infiltrating nests of neoplastic cells have abundant pink
cytoplasm and distinct cell borders typical for
squamous cell carcinoma
.
Esophageal carcinomas are not usually detected early and, therefore, have a
very poor prognosis.
