Active
Orthodontic appliancesOrthodontic appliances can be defined as devices, which create or transmit forces to individual teeth and/or maxillofacial skeletal units.
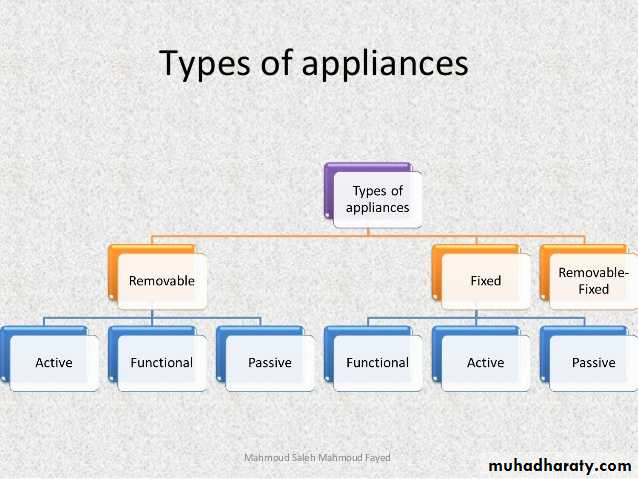
CLASSIFICATION OF ORTHODONTIC APPLIANCES
The simplest classification is probably based on the patient's ability to remove the orthodontic appliance. Based on this premise the appliances can be classified as-removable, semi-fixed or fixed.
Removable Appliances
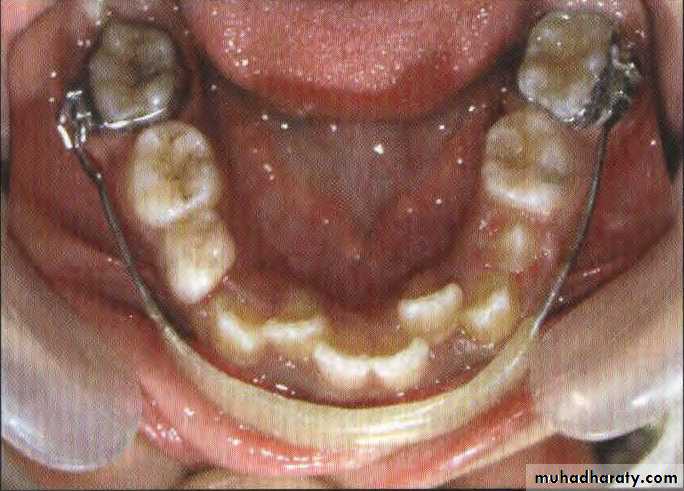
As the name suggests, these appliances can be removed from the mouth by the patient. The patient can insert and remove these appliances without the intervention of a clinician. They may be active or passive, depending upon their capability to generate forces.Active (functional app.- frankle) , removable app.
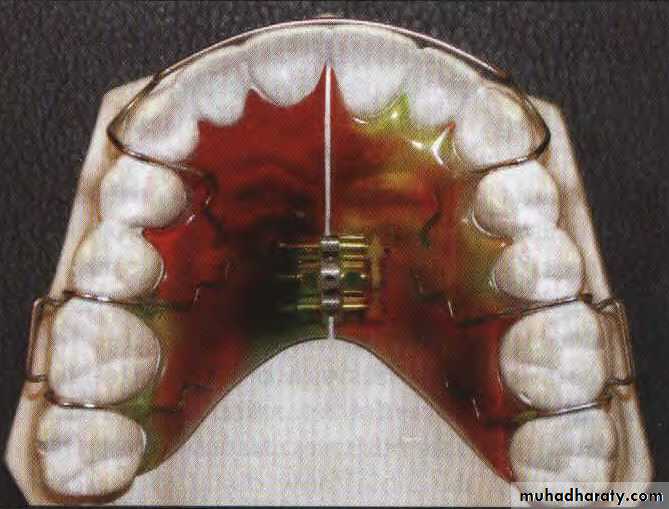
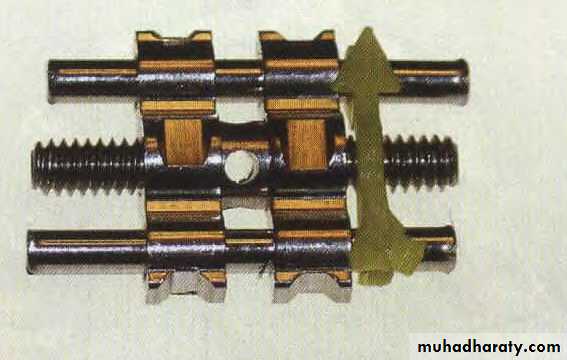
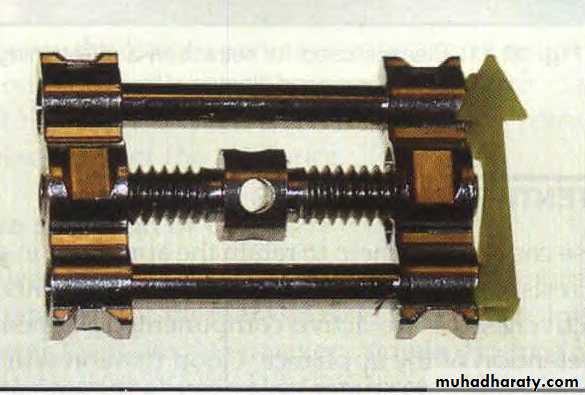
Removable appliances with screw for arch expansion
Screw before activation
Screw after activationFixed appliance
Lip bumper semi fixed
Passive removable appliances
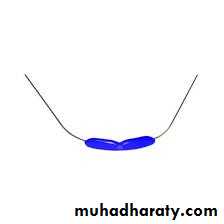
Passive removable appliances are designed to maintain teeth in their designated or present position, e.g. space maintainers, retainers.Retainer
Advantages Of Removable Appliances
• The patient can continue with routine oral hygiene procedures. The oral cavity as well as the appliance can be kept clean.• All restorative procedures can also be carried out during such an orthodontic appliance therapy.
• Most forms of tipping movement can be carried out successfully.
• These appliances, generally are more acceptable to the patients than fixed appliances.
• Since these are relatively simple appliances they can be delivered and monitored by the general dentist.
6. Appliance fabrication is done in specialized labs and hence the chair side time for appliance delivery is considerably less as compared to the fixed appliances.
7. The patient can remove a broken impinging appliance. Thus, a broken appliance is never an emergency for the clinician.
8. These appliances are relatively cheap as compared to the fixed appliances.
Disadvantages Of Removable Appliances
1. Patient cooperation is the key word in removable appliance therapy. The duration for which the appliance is worn is the duration for which the appliance is able to act. So, the treatment can become prolonged depending on patient cooperation.2. These appliances are capable of only certain types of movements, they do not give three-dimensional control over the teeth to be moved.
3. Multiple movements are difficult, Since all corrections cannot be carried out simultaneously the treatment time may be increased.
4. The patient has to have a certain amount of skill to be able to remove and replace the appliance for successful treatment to be possible.
5. The chance of appliance loss or breakage is more.
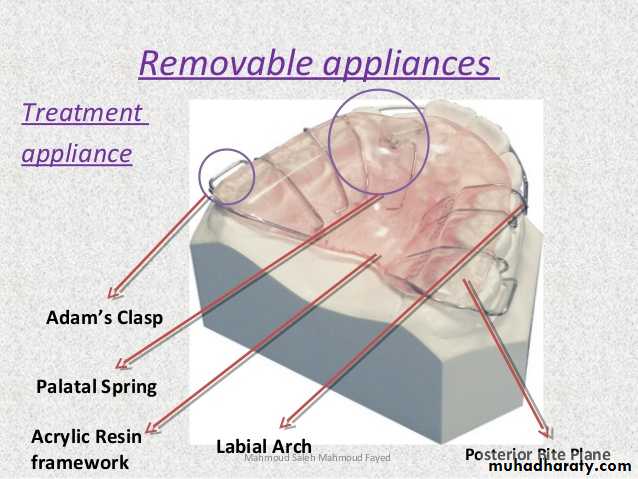
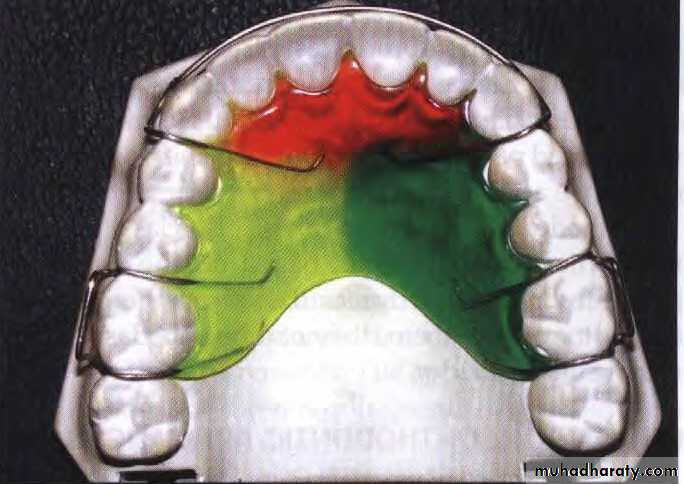
Components of Removable Appliances
1. Active components-:comprises of springs, screws or elastics.2. Retentive components-usually include clasps.
3. Base plate or framework-s-can be made of cold cure or heat cure acrylic.
ACTIVE COMPONENTS
These constitute the components of the removable appliance, which apply forces to the teeth to bring about the desired tooth movement. The activecomponents include:
a. Springs-made up of 0.5, 0.6 or 0.7 mm diameter stainless steel wire.
b. Screws
c. Elastics
elastics
SPRINGS
A wide variety of springs are available for incorporating in the removable appliance. Springs can be broadly classified into:Based on the presence of helices
• Simple spring : no helix present
Compound spring : helix incorporated
• Helical springs : helix is present
•Looped spring : no helix, but a loop is included in the design
Simple spring Spring with helix
Spring with 'U' loop
Based on the mode of support provided to maintain the integrity of the spring
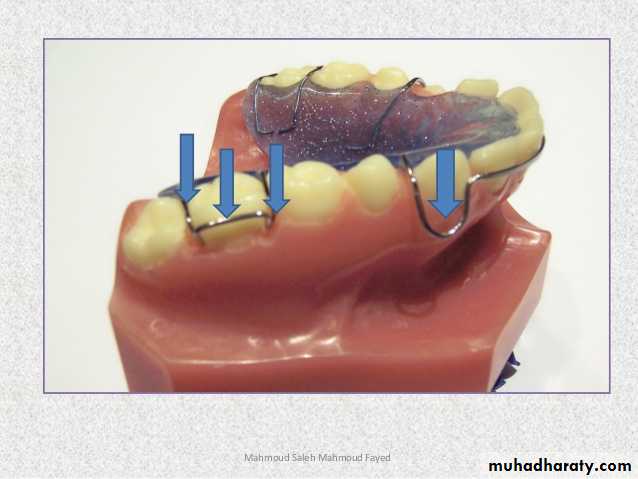
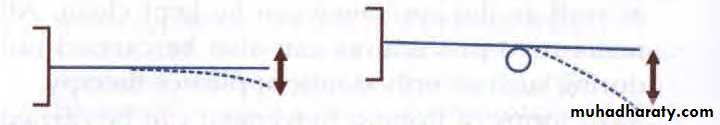
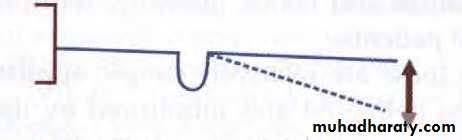
• Self-supported springs-these springs are made up of thicker wire to avoid distortion by the patient.• Supported springs-these springs are made up of thinner wire and therefore to protect these delicate springs, a guide wire may be provided. Alternately they may be supported by an additional sleeve or 'boxed' by acrylic to ensure adequate stability.
guide wire
Designing a Spring
The most suitable material for orthodontic springs is stainless steel (ss) wire, there is a relationship between the length, diameter and amount of deflection of a spring which is expressed as:D=