DENTAL X-RAY FILM
PROCESSINGFilm Processing: Refers to a series of steps that collectively produce a visible permanent image on a dental radiograph.
The Purpose of Film Processing
1-To convert the latent image on film to visible image2- To preserve the visible image so that it permanent and dose not disappear from dental radiograph.
Introduction
Silver halide crystals absorb x-radiation during x-ray exposure and store the energy from the radiation, depending on the density of the object in the exposed area, the stored energy within the silver halide crystals forms a pattern and creates an invisible image within the emulsions on exposed film. This pattern cannot be seen an is referred to as latent image, it is remain invisible until it undergoes chemical processing procedure and resulted in visible image.
Latent Image Formation
Development
The film is placed in a chemical developing solution for a specific amount of time and temperature, the developer distinguish between the exposed and unexposed halide crystals by the presence of silver part in the exposed crystals which is act as catalyzed or window for developing action. The developer soften the emulsion layer and reduce the exposed crystals to the metallic silver where the unexposed crystals are remain an affect by developer.Processing Procedure
Processing Procedure
RinsingRinsing the developing solution of the film and stop the developing process and the developer chemicals are removed from emulsion.
Fixing
During fixing the unexposed undeveloped crystals are removed from the emulsion leaving a clear area on the film through which light can easily pass. The undeveloped crystals are converted to the soluble silver salts by fixing chemicals in addition the fixing solution hardens the emulsion layer.
Processing Procedure
WashingThorough washing of the film after fixing is critical so that all the excess chemicals are removed. Inadequate washing which leaves chemicals behind allow discoloration of the film over time. The fixing chemicals and the metallic silver on the film oxidize to a brown silver sulfide this effect the diagnostic quality of the film.
Drying
The film may be air dried at room temperature in dust free area or placed in heated drying cabinet.
Processing Procedure
Black Area
The black areas are created by deposit of black metallic silver the degree of blackness depends on the amount of tissues exposed.Structure that permit the passage of x-ray beam and allow more x-ray to reach the film its appearing black or radiolucent.
If more x-ray reach the film more silver halide crystals exposed resulting in increased deposited of black metallic silver that appear black .
Visible Image
White Area
White area resulted from the removal of unexposed and underdeveloped silver halide crystals.Structures that resist the passage of x-ray beam and restrict the amount of x-ray that reaches the film.
A radiograph with area of unexposed crystals that have been removed during processing no metallic silver deposit appears white or radiopaque.
Visible Image
A- Manual Processing:
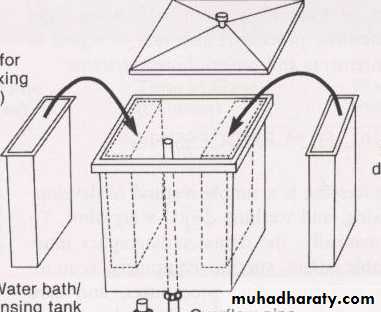
• 1- Processing Tank
• Is a container divided into compartments to hold the developer solution, water, and fixer solution .
• Processing tank has two insert tank and one master tank.
• The processing tank should be constructed of stainless steel which dose not react with processing solutions and easy to clean.
• The processing tank should be equipped with tight light cover to protect the solution from the oxidation, evaporation and during the processing to protect the film from exposure to visible light.
Processing Techniques
Processing Techniques
Processing Techniques
2-Thermometre
Is used to determine the temperature of the developing solutions, it should be placed directly in the developer and not in the water bath.
The optimum temperature of developer is 68F, should be check before the processing if the developer temperature is below the 60 F the chemical work too slow and result in under development, where if it over the 80 F lead too rapidly work developing and resulted in film fog.
• 3-Timer
• X-ray film is processed in the manual processing for specific time intervals indicated by the manufacturer of processing solutions.4- Film Holder
Is a device equipped with clips used to hold films during processing. Film hanger is made of stainless steel
Processing Techniques
Processing Techniques
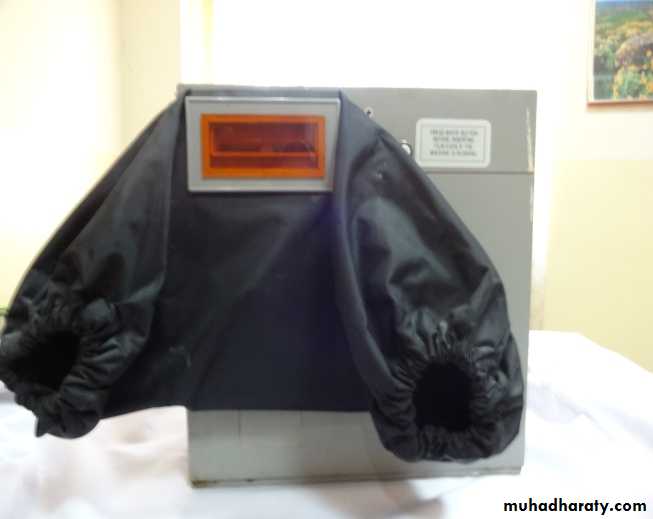
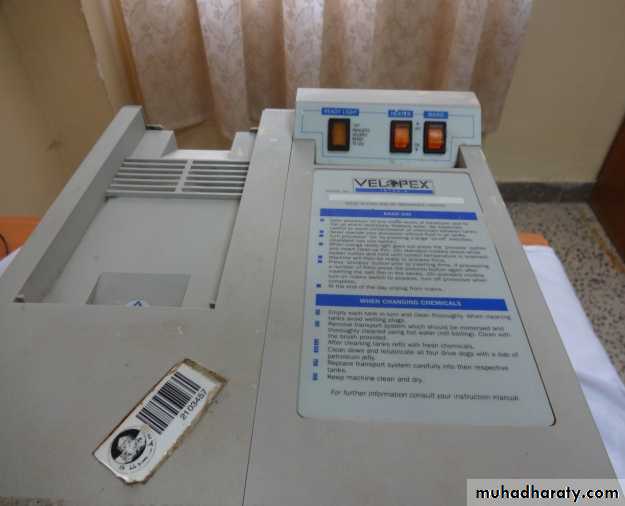
B- Automatic Film ProcessingAdvantages
Less processing time is required.
Time and temperature are automatically controlled.
Less equipment is used.
Less space is required.
Disadvantages
Regular cleaning is essential, dirty roller produce marked films.
Equipment is relatively expensive.
Smaller machines cannot process large extra oral film.
Processor Housing: enclose all the component parts of the processor.
Film Feed Slot: Is an opening in the outside of the processor housing that is used to insert unwrapped film into the processor .Roller Film Transporter: Is a system of rollers used to move the film rapidly through the developer fixer water and drying component and to produce squeegee action to removes the excess solution from the emulsion .
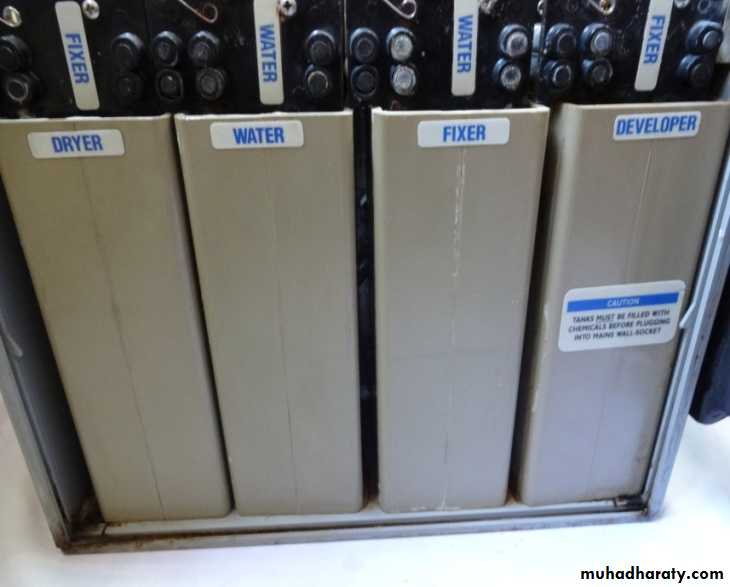
Developer Compartment: Is used to hold the developer solution, the developer solution used in an automatic processor is highly concentrated solution to react at temperature between 80-90F.
Components Parts Of Automatic Processor
Fixer Compartment: Hold the fixer solution, the fixer solution is highly concentrated that contain additional hardening agents.
Water Compartment: Hold circulating water, water is used to wash the film following fixation.
Drying Chamber: Hold heated air and is used to dry the wet film.
Film Recovery Slot: Is an opening on the outside of the processor housing where the dry, processed radiograph emerges from the automatic processor.
Components Parts Of Automatic Processor
Processing chemicals are become exhausted or loss their effectiveness with use or by exposure to air or by contamination with water or other processing chemicals or other compounds from the tank or environment, replenishing solution restore the capacity of solution to perform their function without having to replace the entire volume.
Replenishment
• Dark Room: Environment where x-ray film can be handled and processed and its used to provide a completely darkened to produce a diagnostic radiograph.
• Room Requirement
• Conveniently located
• Adequate size
• Equipped with correct lighting
• Arranged with enough work space with a adequate storage.
• Temperature and humidity control.
• DARK ROOM
• DARK ROOM
Location and SizeIt should be located near the area where x-ray unit are installed.
Must be large enough to accommodate film processing equipment.
Allow enough working space .
Should be measure at least 16-20 square feet.
Provide enough space for one person to work comfortably.
Lighting
The dark room must completely dark and must exclude all visible white light.In the dark room when all the light are tuned off and the door is closed, no white light should be seen.
Any white light coming around the door, through keyhole or through the wall is light leak.
White Room Lighting:
Is required for procedures not associated with the act of processing film.
White light is necessary to perform tasks such as cleaning, stocking materials and mixing chemicals.
• DARK ROOM
Lighting
Safe Lighting:It is a low intensity light composed of long wavelengths in the red–orange portion of visible light spectrum.
Safe light provide sufficient illumination in dark room to carry out processing activities safely with out exposing or dose not affect unwrapped film dose not cause film fog.
• DARK ROOM
• DARK ROOM
Dark Room Work Space:Must be include Adequate counter area for unwrapped film prior processing.
It should clean, dry and free of processing chemicals, water, dust and debris.
Dark Room Storage Space:
Must include enough room for chemical processing solutions and film cassettes.
Boxes of opened extra oral film must be stored in the dark room in a tight light drawer.
• DARK ROOM
Temperature and HumidityMust be controlled to prevent the film damage, a room temperature of 70 F is recommended if the temperature is higher than 90 F lead to the film fog .
A relative humidity level between 50-70% should be maintained, when the humidity level is too high the film emulsion dose not dry and when the humidity is too low the static electricity become a problem and cause film artifact.
Film Mounting: Is the placement of radiograph in a supporting structure or holder
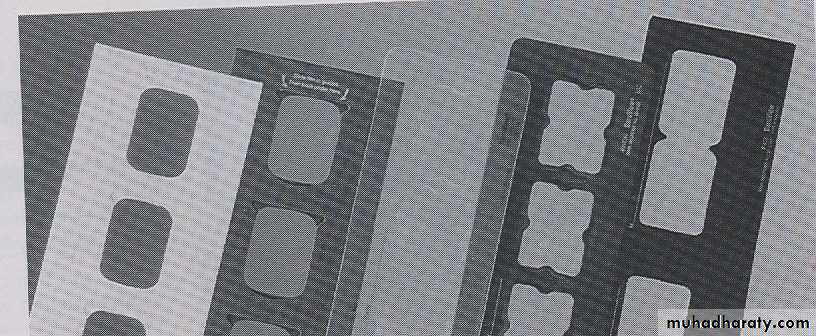
Film Mount:Is a cardboard, plastic or vinyl holder that is used to support and arrange dental radiograph in a anatomic order.
Each film mount has a number of windows or framers in which the radiograph are placed or mount .
Film Mounting
Film Mounting
A film mount may be opaque or clear, opaque film mount is preferred because it masks the light around each radiograph.Film mounts are commercially available in may size and configurations.
Film mounts are accommodate any numbers of films, mount available for single film, bitewing, a complete mouth series and combinations of film.
Labial Mounting:
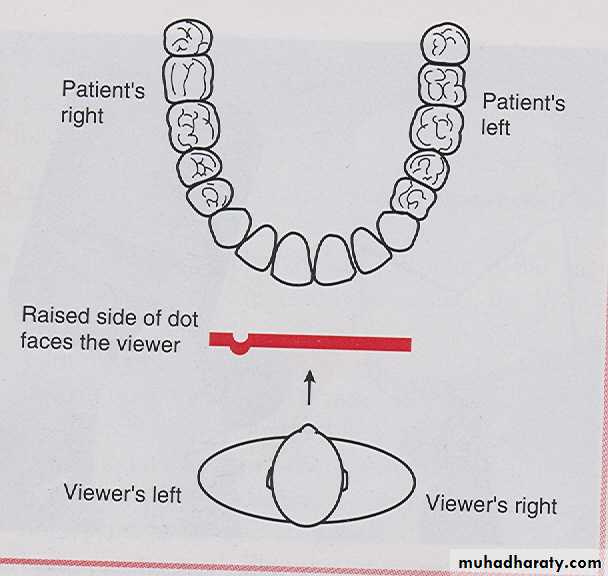
Labial mounting is preferred method of mounting dental radiographs and recommended by American Dental Association. In labial mounting method the radiographs are placed in the film mount with the raised (convex) side of identification dot facing the viewer, the radiograph are then viewed as if the viewer is looking directly at the patient, the patients left side is on the viewer right side and the patients right side on the viewer left side.Film Mounting Methods
Lingual Mounting:
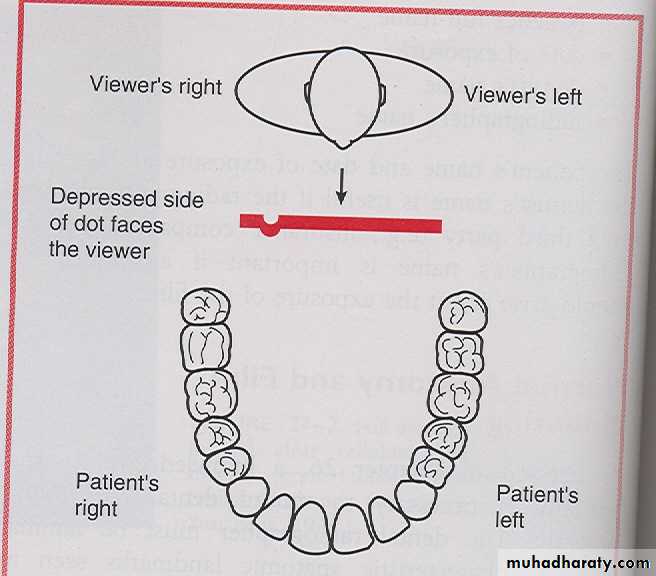
Lingual mounting can be used as an alternative method. In the lingual mounting, the radiograph are placed in the film mount with the depressed dot of the identification dot facing the viewer. The dental radiographer then views the radiographs from lingual aspect, with this methods the radiograph are viewed as if the dental radiographer is inside patient mouth and looking out, the patients left side on the viewer left side and patients right side on the viewer right side .Film Mounting Methods
Film Viewing
Is examination of dental radiographs and its essential in the interpretation of dental radiographs.Equipment Required for Film Viewing:
An adequate light source and magnification are required for optimal film viewing, both a view box and magnifying glass are necessary.
Film Viewing
Light Source
A light source known as a view box or illumator is required to view dental radiographs accurately and assist in the interpretation of image the viewing area should be larger enough to accommodate a variety of mounted film as well as unmounted extra oral films. The light from view box should be of uniform intensity.Magnifying Glass
The use of magnifying glass is useful in interpretation, magnifying aids the viewer in evaluation of slight changes in density and contrast in radiographic image.
Film Viewing
Film Viewing
Step–By–Step ProcedureThe dental radiograph must use this recommended viewer sequence to examine film for each of the following.
Unerpted , missing and impacted teeth
Dental caries and the size and the shape of pulp cavities.
Bony changes , the level of alveolar bone and calculus.
Root and periapical areas
Remaining area of the jaw, sinus and so on.