
Strabismus
!
Misalignment of visual axis
!
Binocular single vision compenent
•
Simultaneous perception
•
Fusion
•
Perception of depth
!
Strabismus leads to loss of BSV
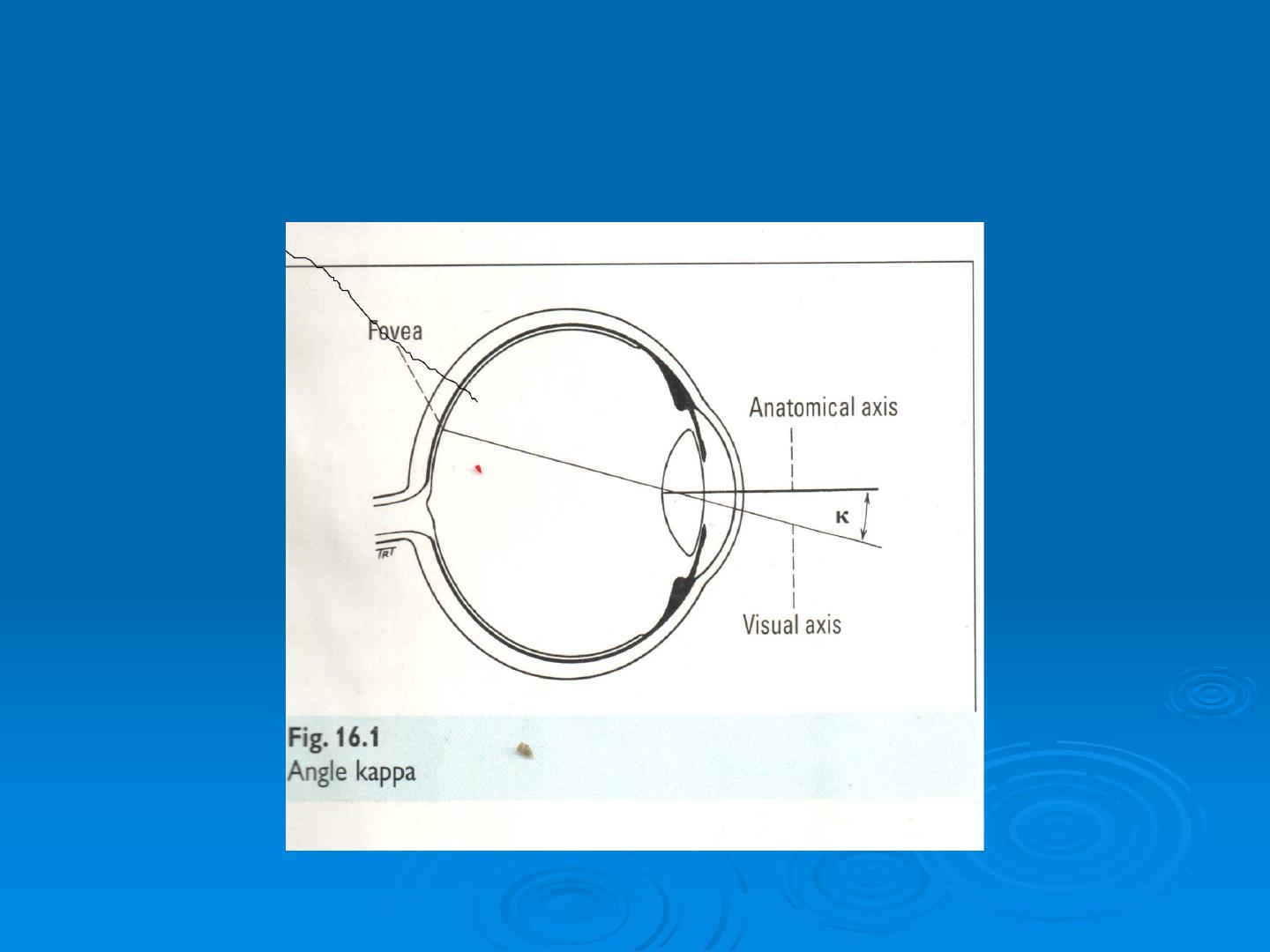

Approach to strabismus
!
Observation
!
VA
!
Visual function check for RAPD
!
Corneal reflexes
!
Cover test
!
Deviation
!
Motility
!
Accommodation
!
Fixation
!
Binocularity check for SP with worth 4-dot te
st or bagolini glasses

Classification
Apparent strabismus
Epicantus , IPD, Ptosis ,Refractive
True strabismus
o
Latent strabismus (Phoria)
o
Manifest strabismus (Tropia)
Comitant
o
angle of the deviation is the same in all positi
ons of gaze.
o
Extraocular movement are full.

Non-comitant (paralytic or restrictive)
angle of deviation is different in different po
sitions of gaze
Extraocular movement is not full
Accomodative
Fully accomdative
Partially accomodative
Non accomodative

Accommodative esotreopia
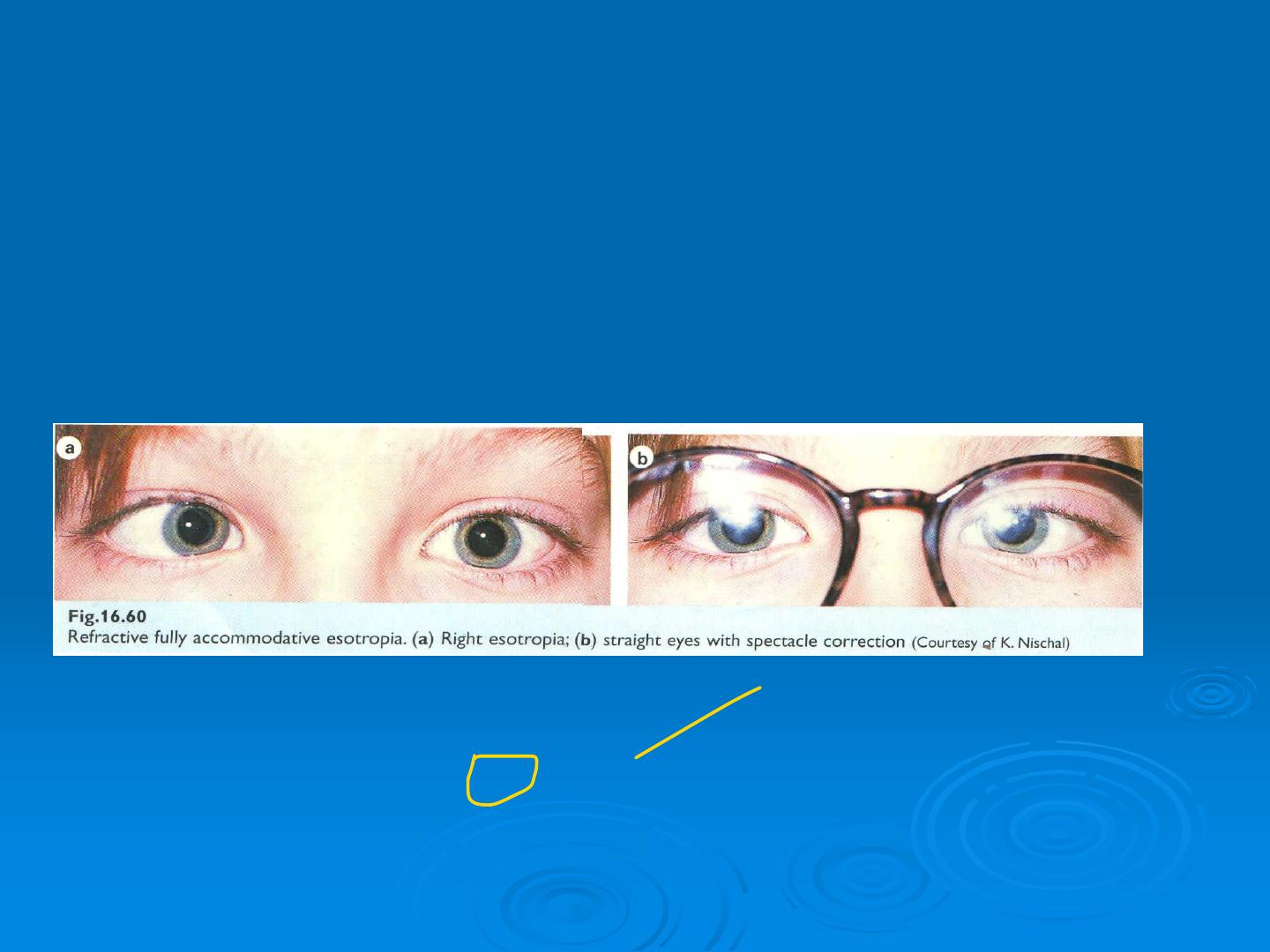

Fully accommodative esotropia
Esotropia fully corrected for distance and near by hypermetropic correct
ion (usually +2 to +7D)
AC:A ratio
Normal BSV if corrected
Intermittent initially and appear with fatigue and illness
Treatment by full hypermetropic correction ; treat any associated ambly
opia.
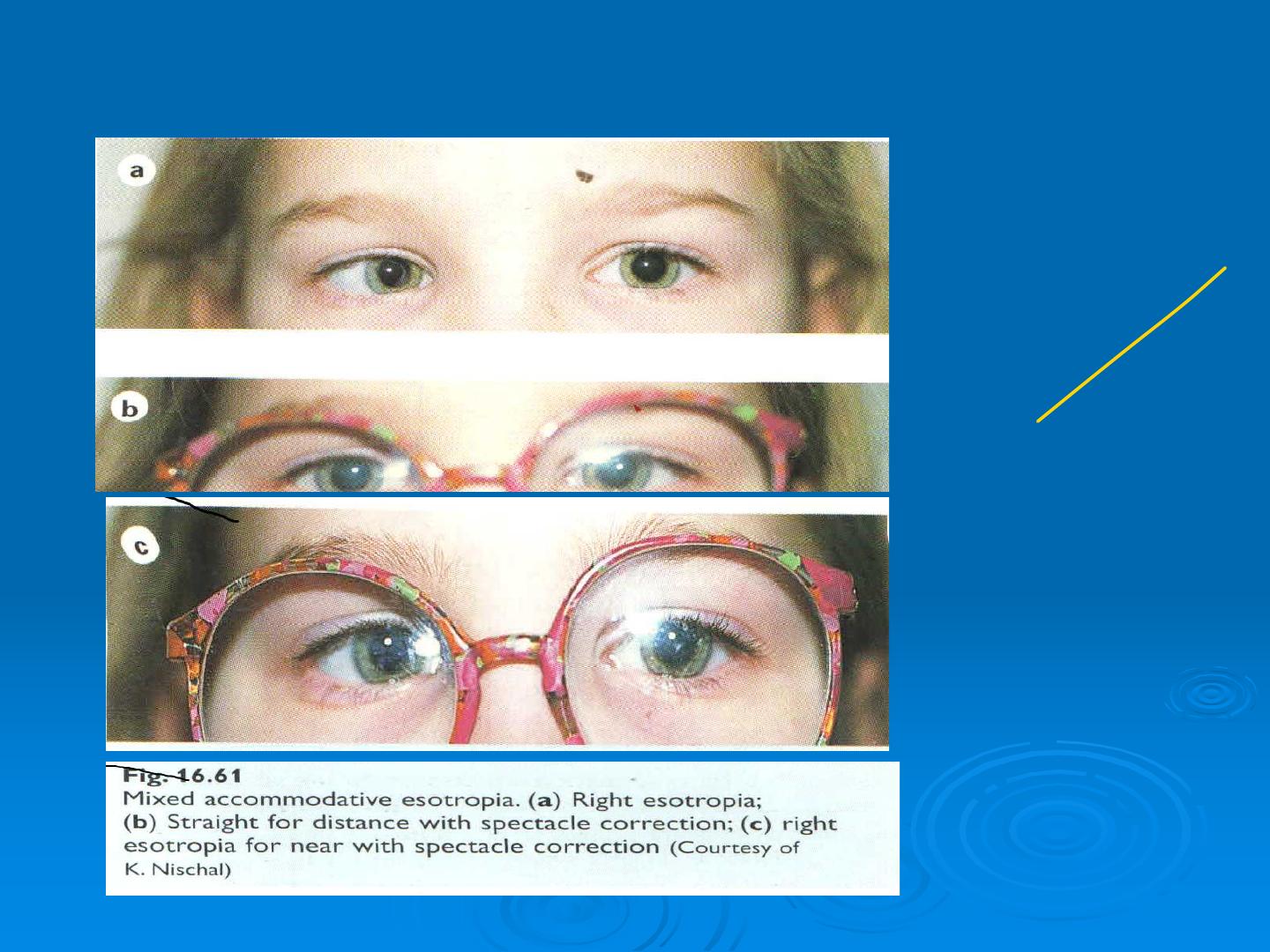
Partially accommodative esotropia
Esotropia partially corrected by full hypermetropic correction
BSV absent or limited with ARC
may be associated with bilateral IO overaction
Treatment
Full hypermetropic correction , treat amblyopia ; consider surgery if pot
ential for BSV or for cosmesis

Causes
1.
Convergence excess
2.
Hpoacommodative convergence excess
this is diagnosis by near point of accommodation( NPA)
Characterized by esotropia at near and the eye straight at distance
Treatment
"
Bifocal consecutive type
"
Pilocarbine cause peripheral accommodation
3- Mixed type : refractive and non refractive
Esotropia at near more than distance
Bifocal glasses
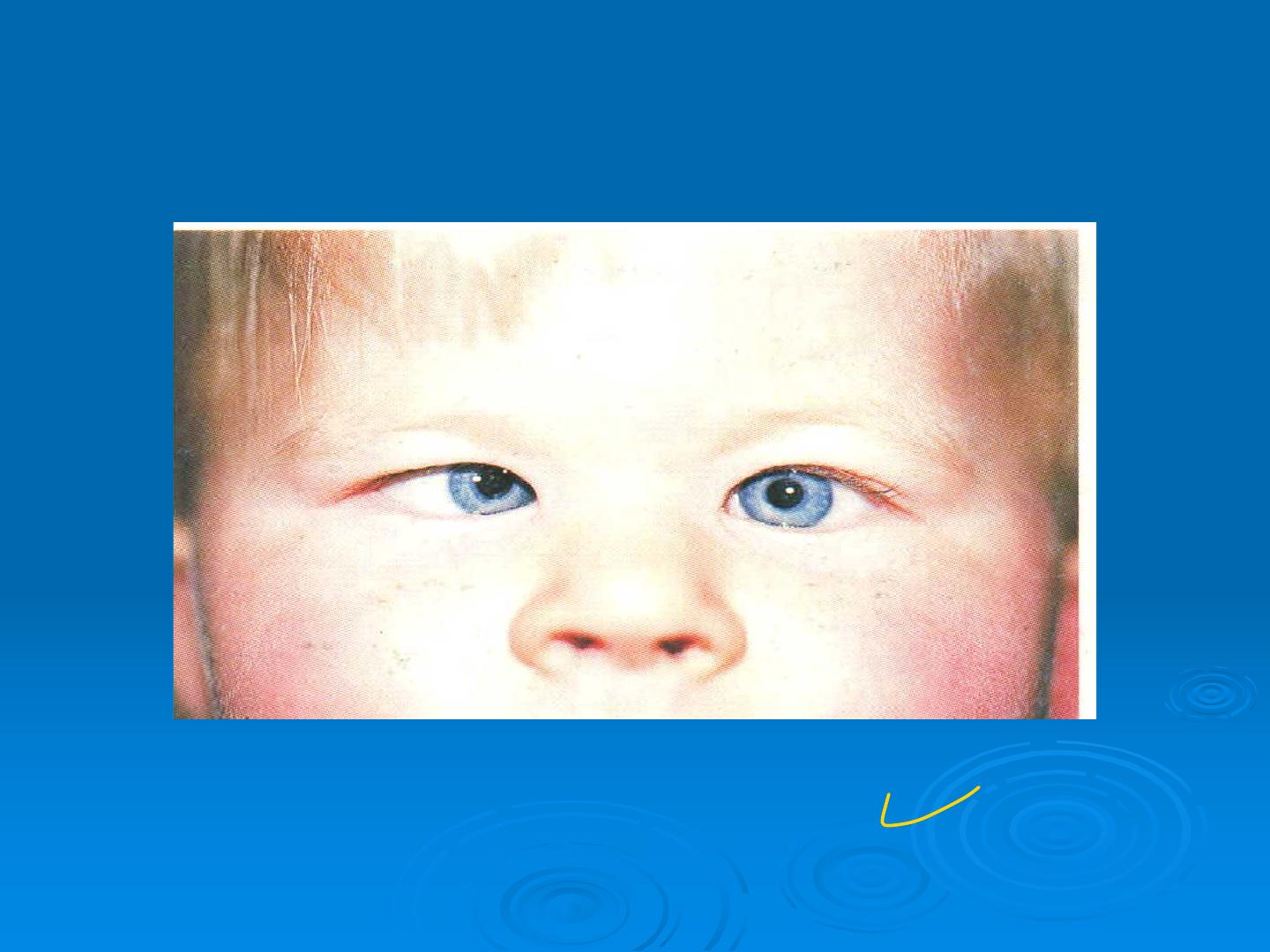
Essential infantile esotropia
convergent esotropia

“infantile esotropia”
- the commonest non-accommodative type
-presenting before 6 months
-large angle more than 30-45 prism diopter
-poor BSV potential
-often emmetropia/mild hypertropia
-alterating
-
cross fixation
-
Refraction normally or slight hypermetropia
- May be associated with IO overaction and DVD
(slow upward deviation on dissociation i.e covering one eye
with recovery on removal of cover and no movement of oth
er eye
-
May be associated with manifest latent nystagmus

Treatment
!
Treat any associated amblyopia ( e.g occlusion of better eye if not f
reely alternating )
!
Correct hypermetropia if ˃ 2D
!
Surgery aims for ocular alignment by 18 months
!
Additional surgery for significant IO overaction may be required
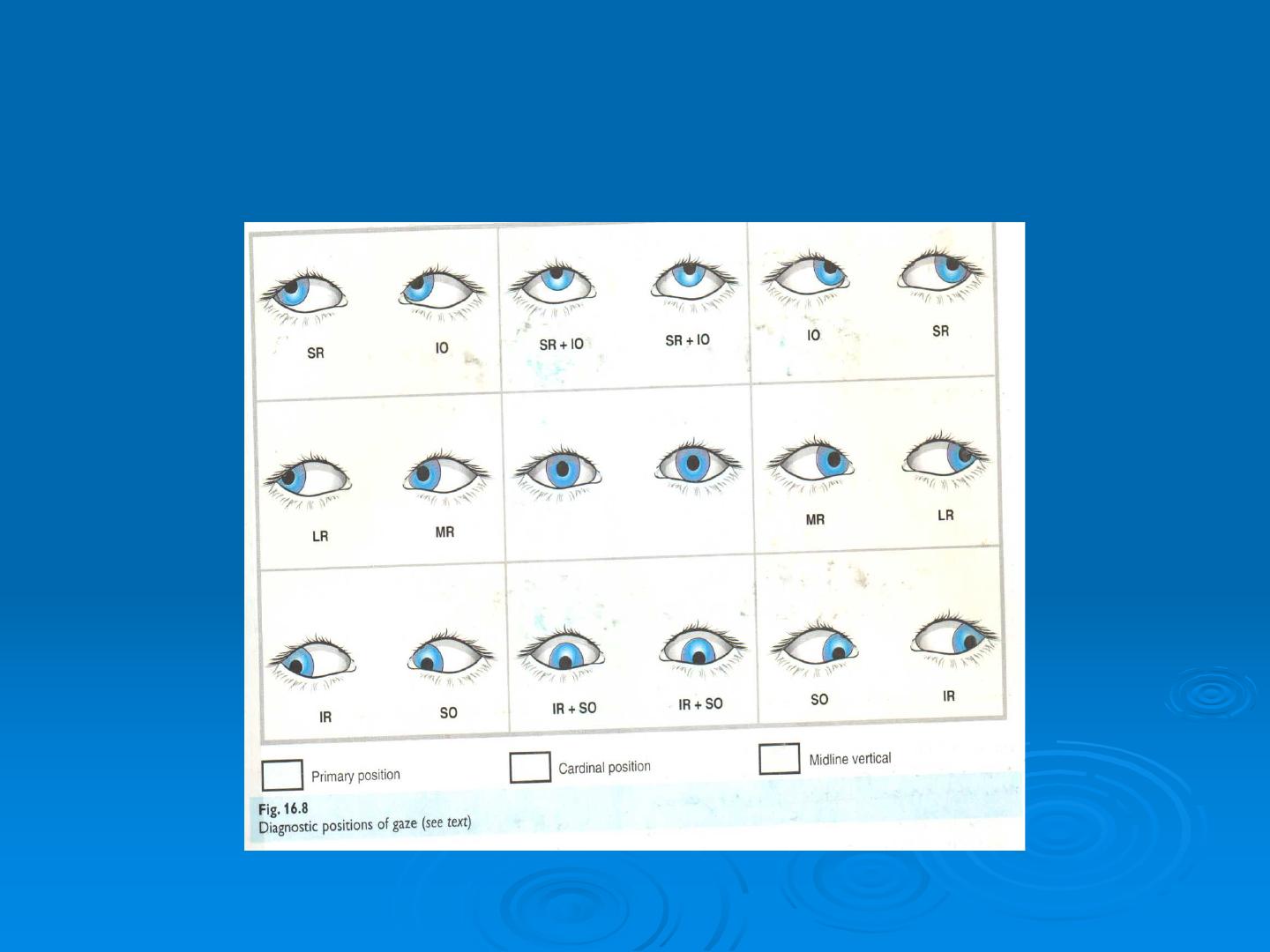
Ocular movement
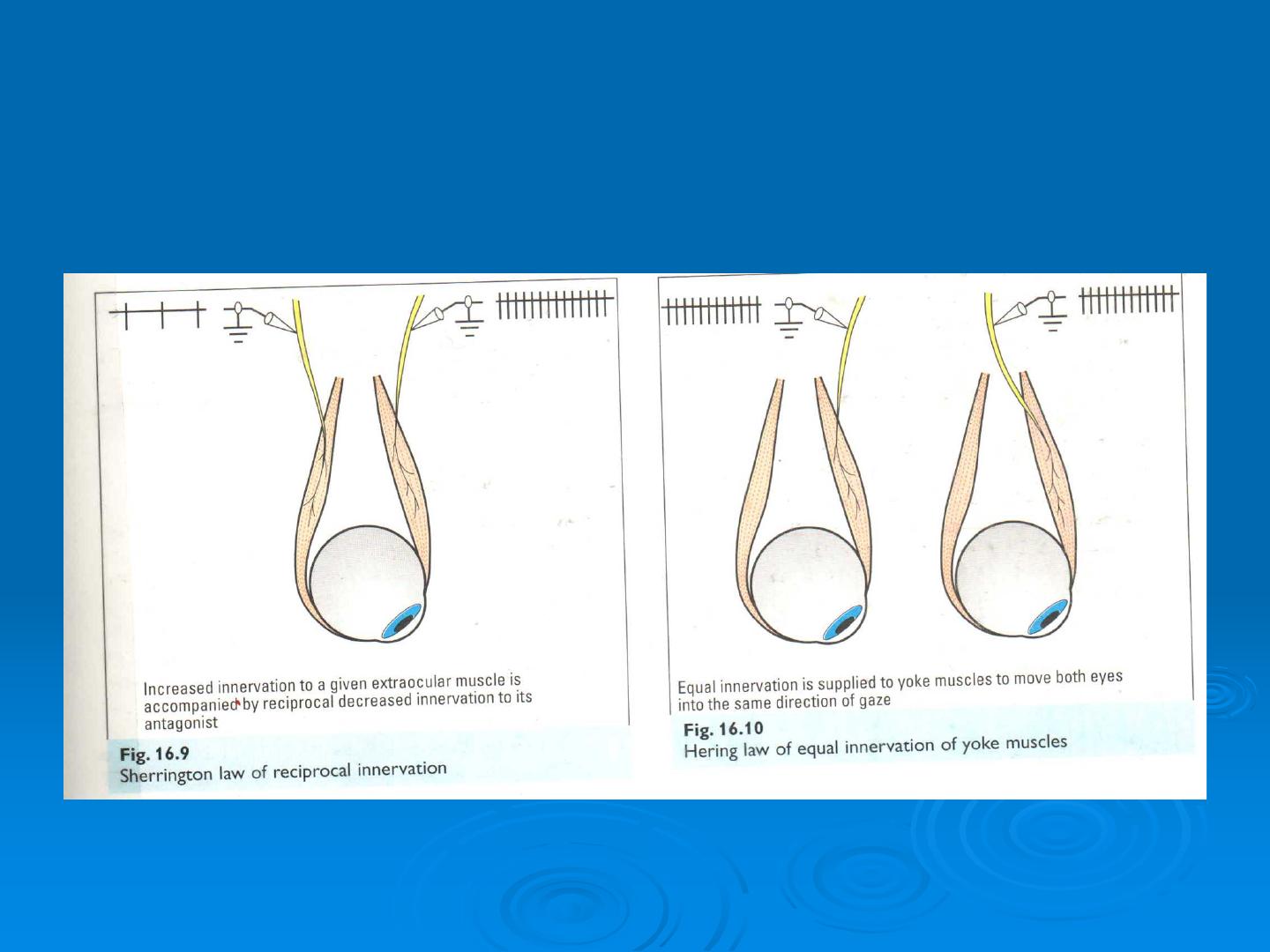
Sherrington and Hering law
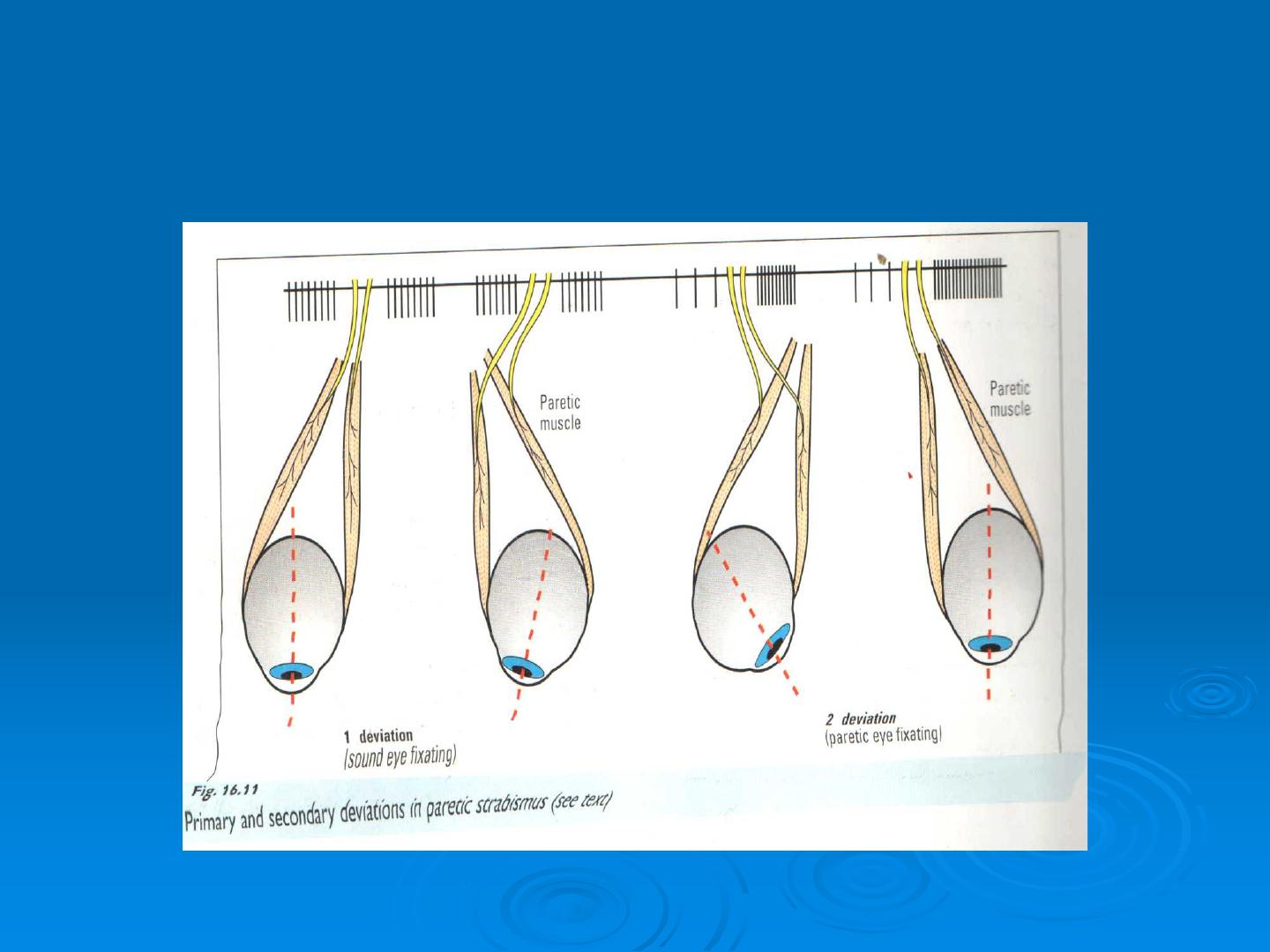
Primary and secondary deviation in paretic str
abismus
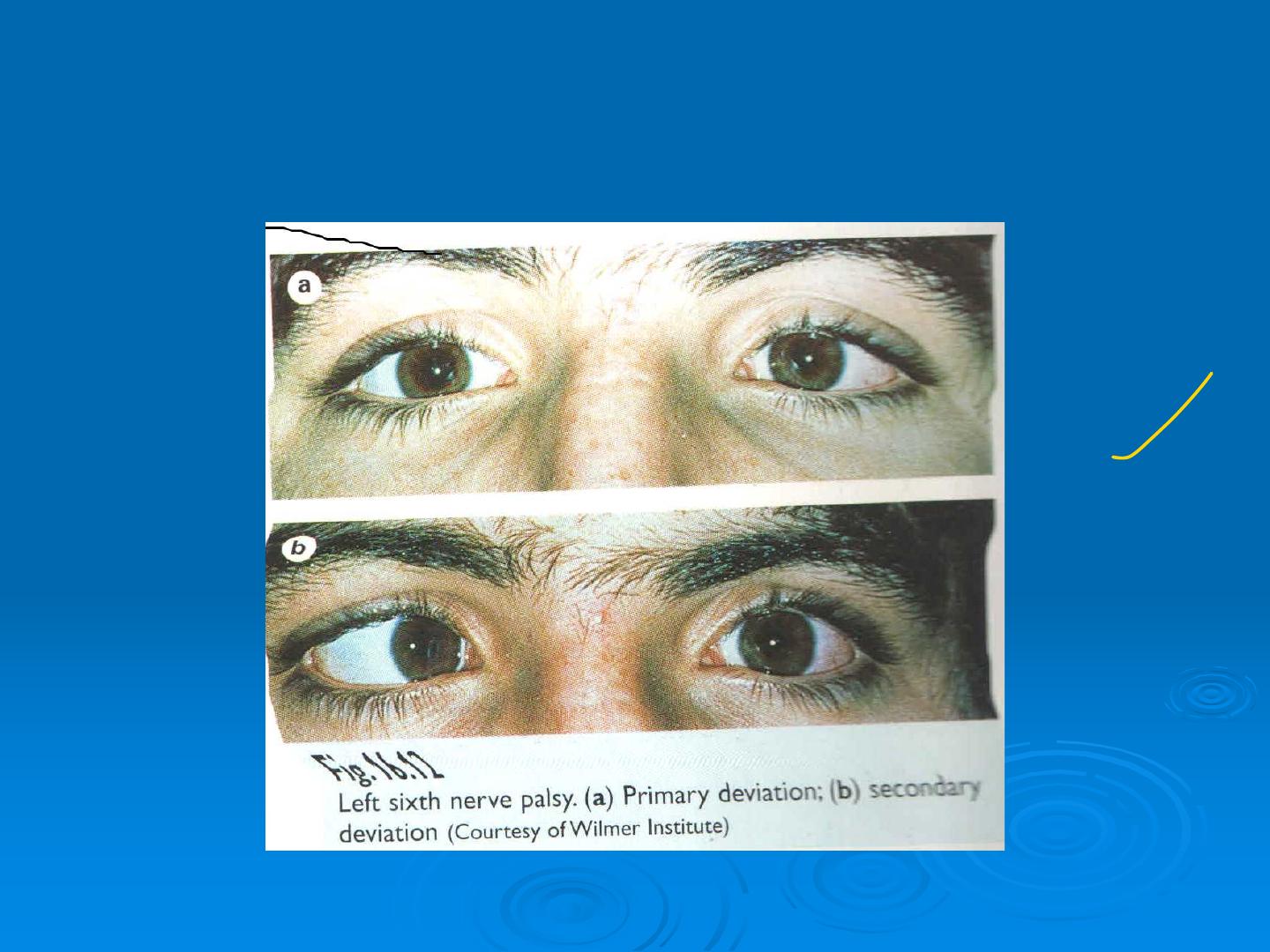
Primary and secondary deviation in paretic s
trabismus
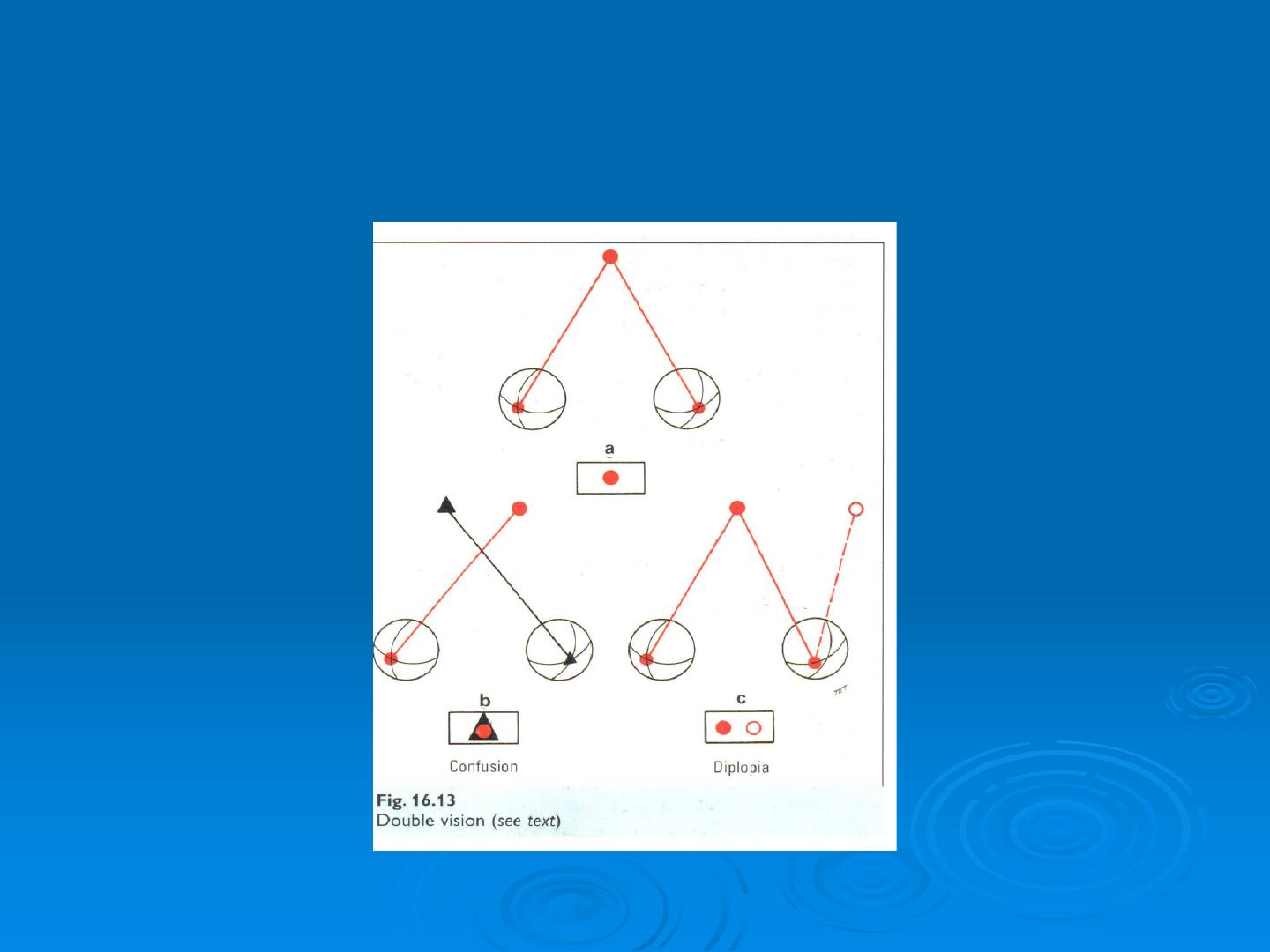
Diplopia and confusion
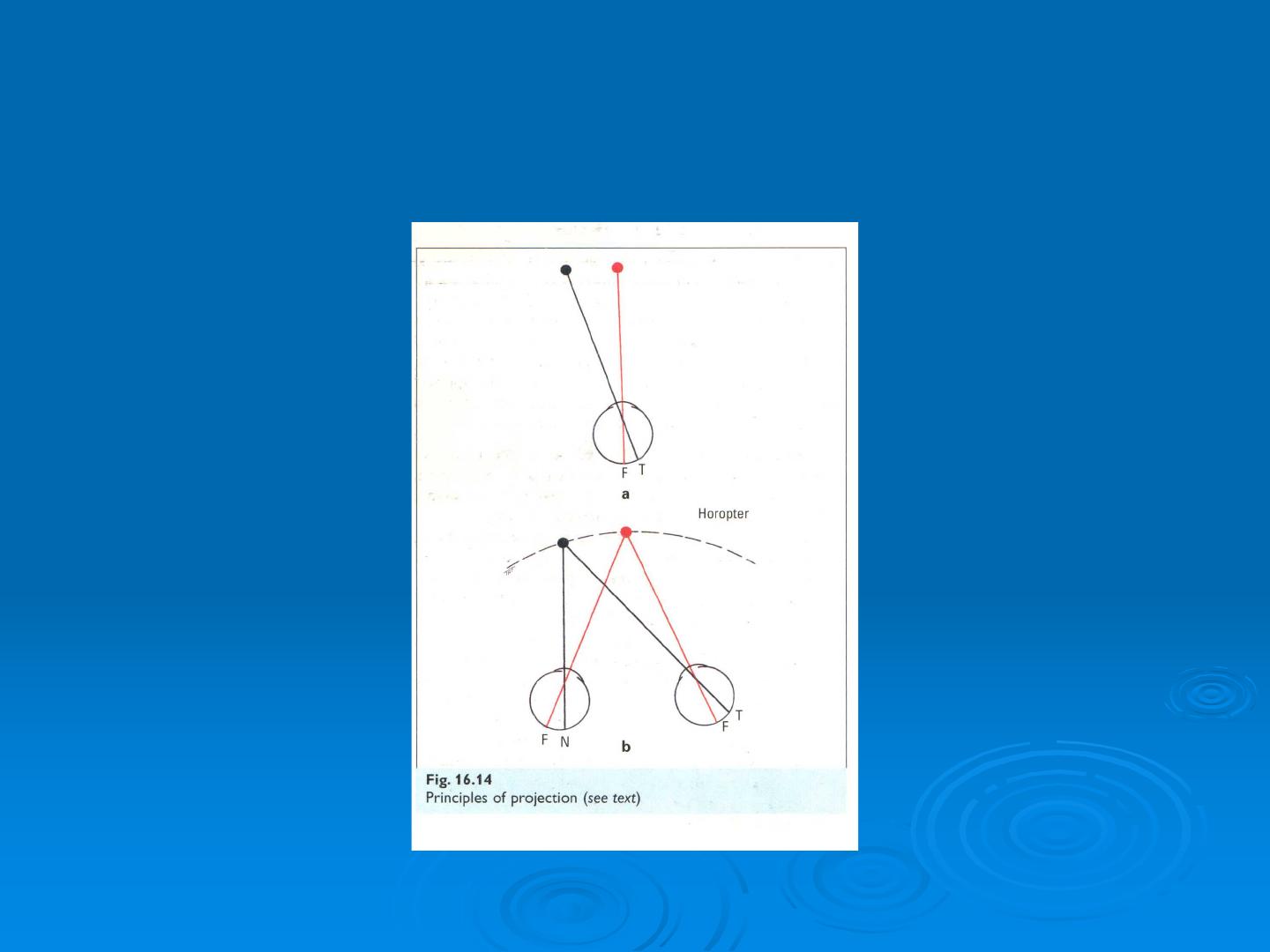
Principle of projection

Titmus test for perception depth

Visual acuity test in children

Synaptophore test for binocular single visi
on
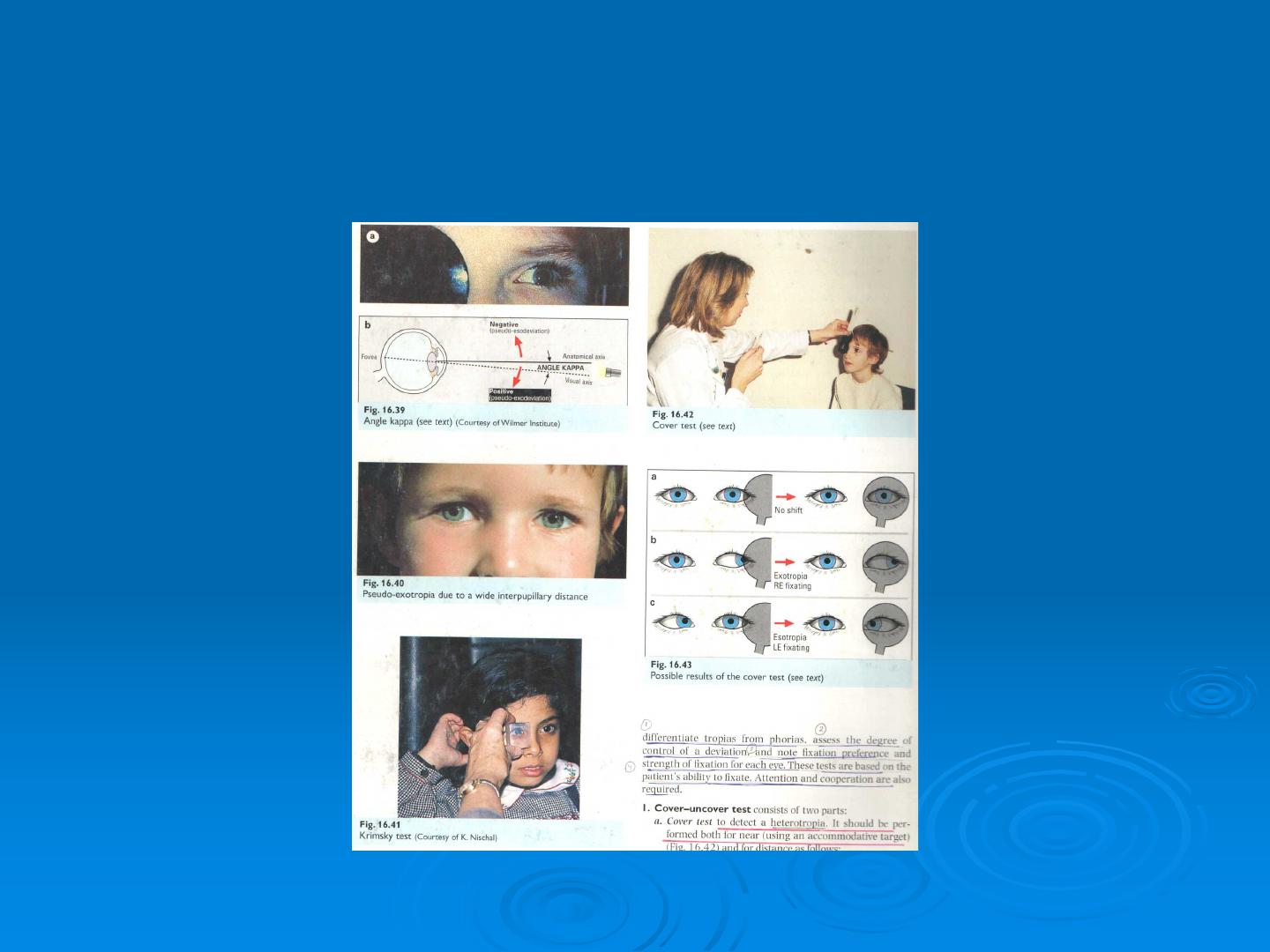
Cover /uncover test
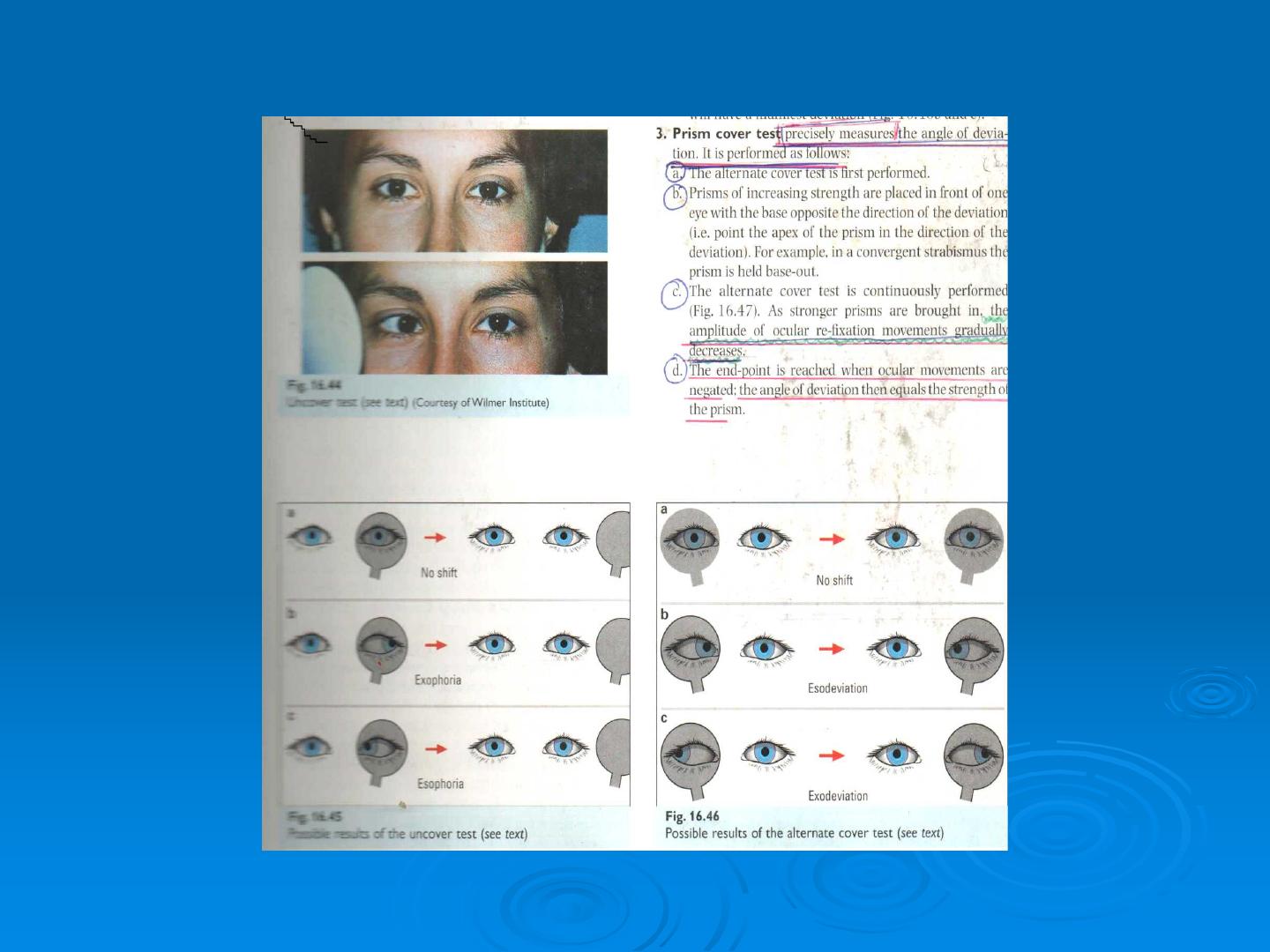

Prism cover test (krimsky test )

Hess chart of recent right lateral rectus palsy
Test shows underaction of right lateral rectus and overaction of left medial rect
us ( six crainal nerve palsy )
