
Tumors of oropharynx and
hypopharynx
Definition
an abnormal growth of tissue that possesses no
physiological function and arises from
uncontrolled usually rapid cellular proliferation


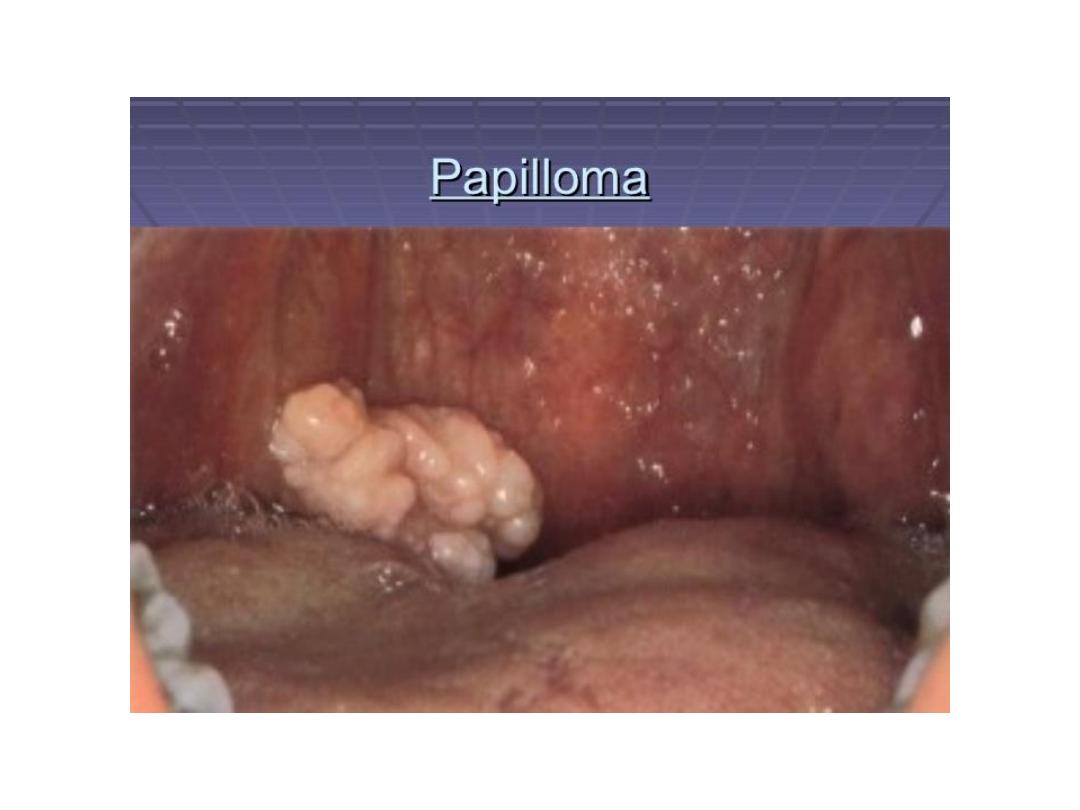
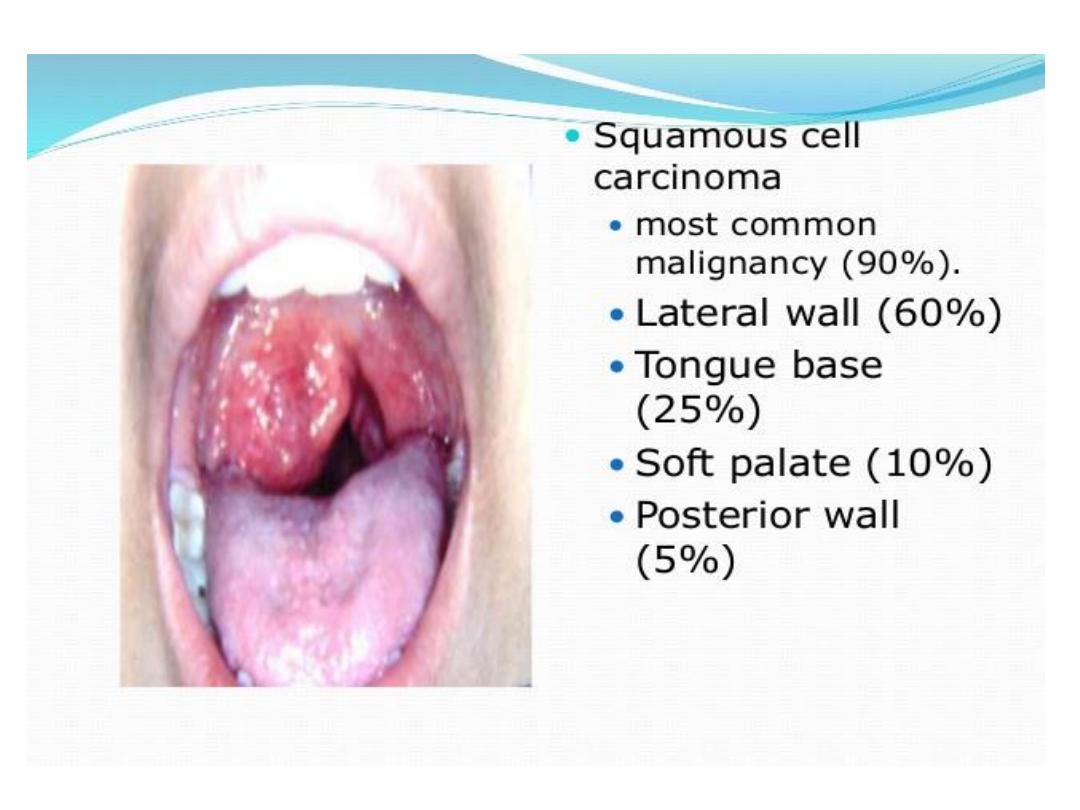
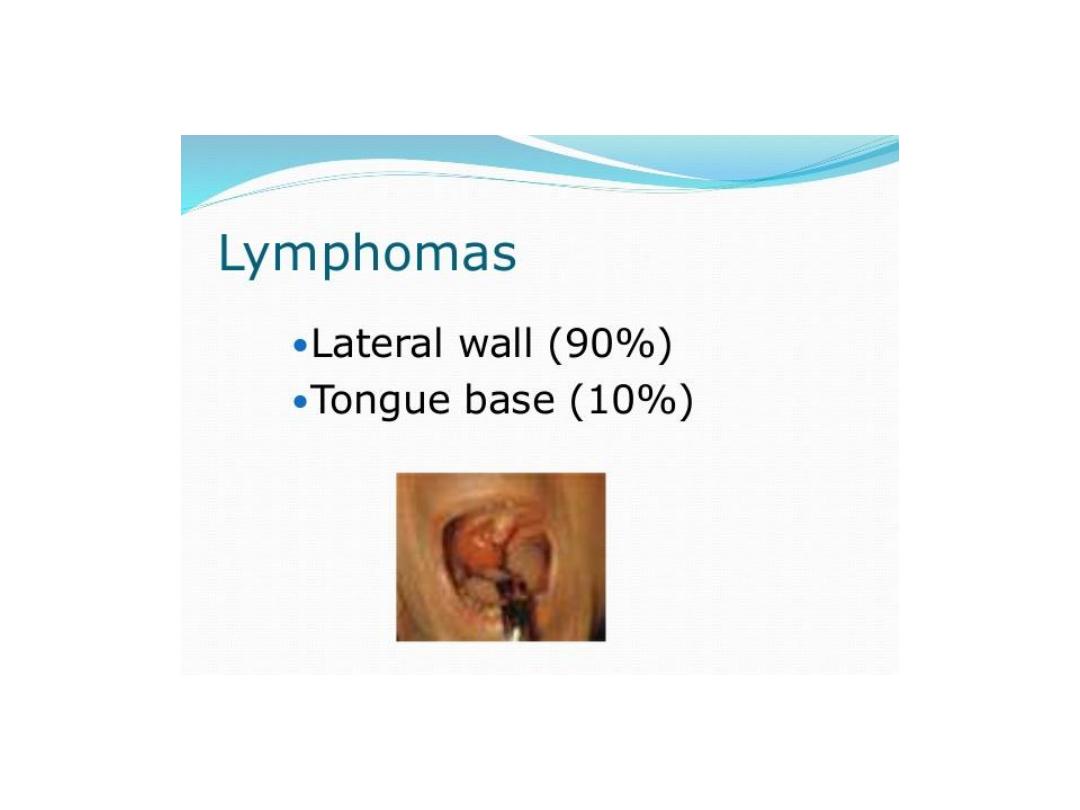




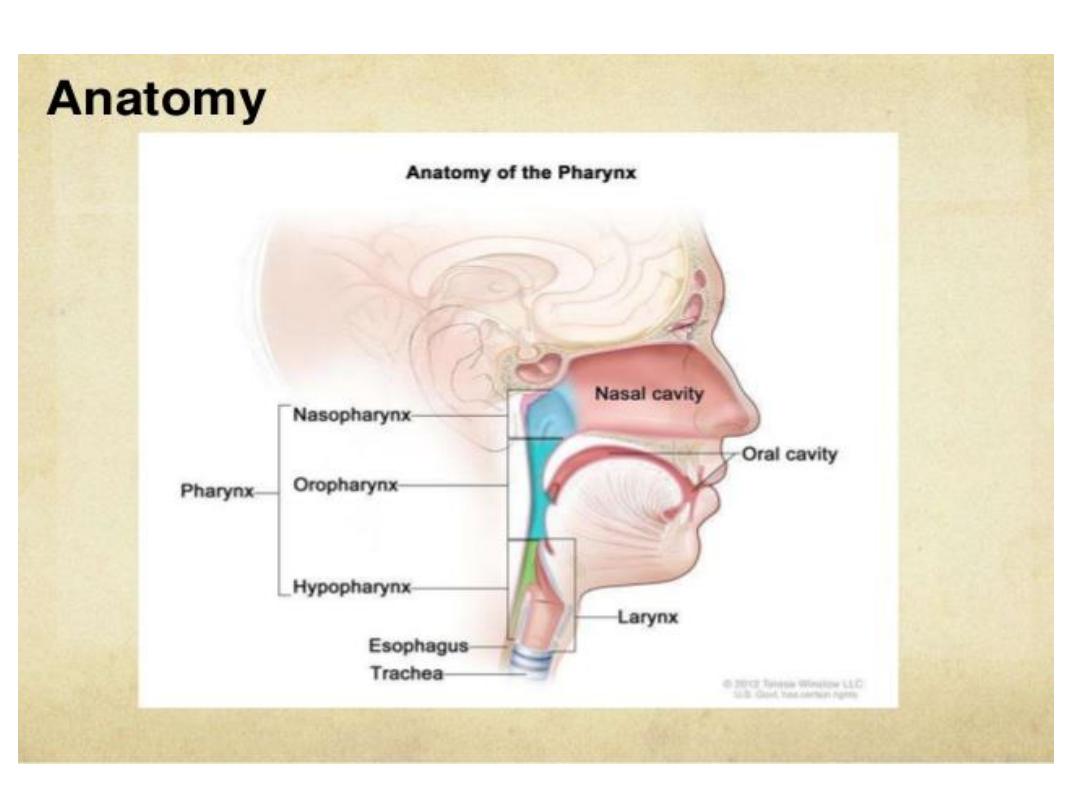
Tumor hypopharynx
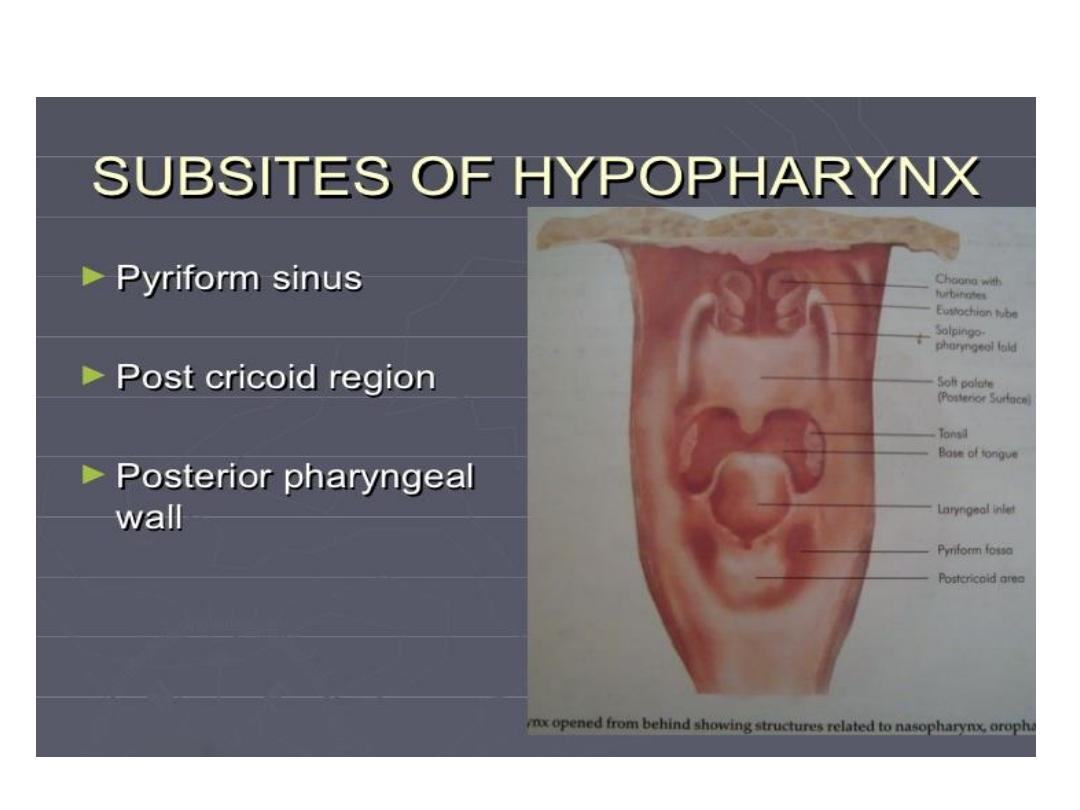
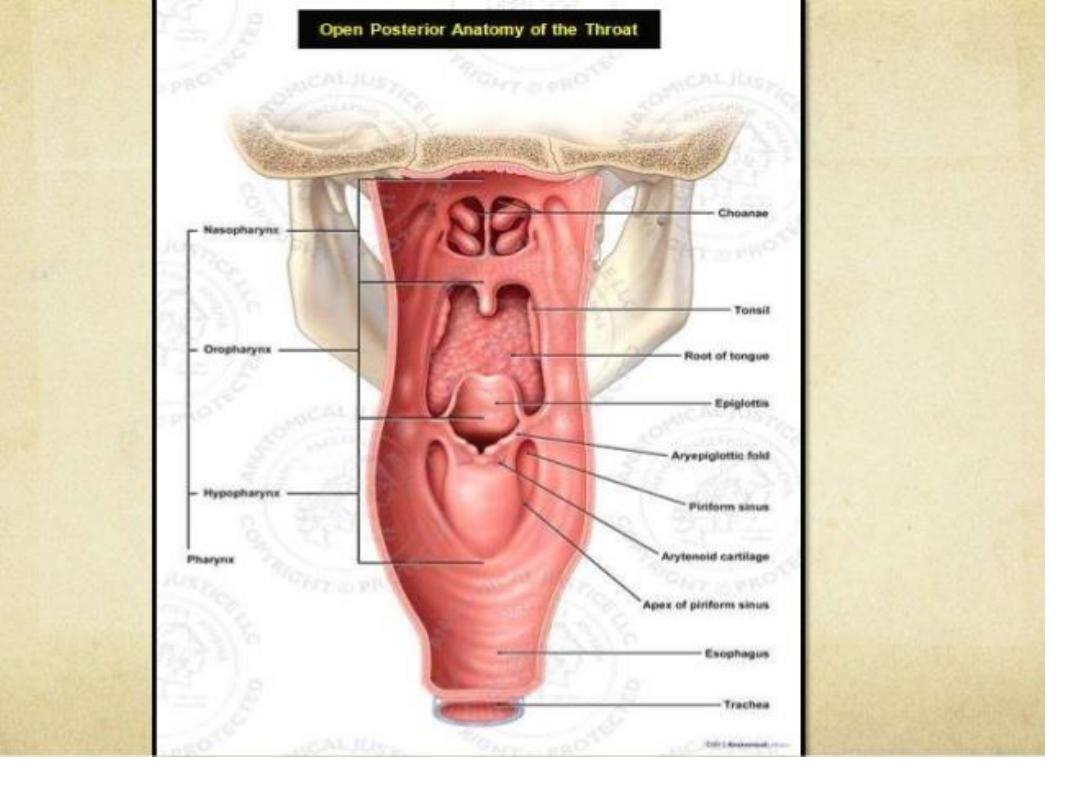



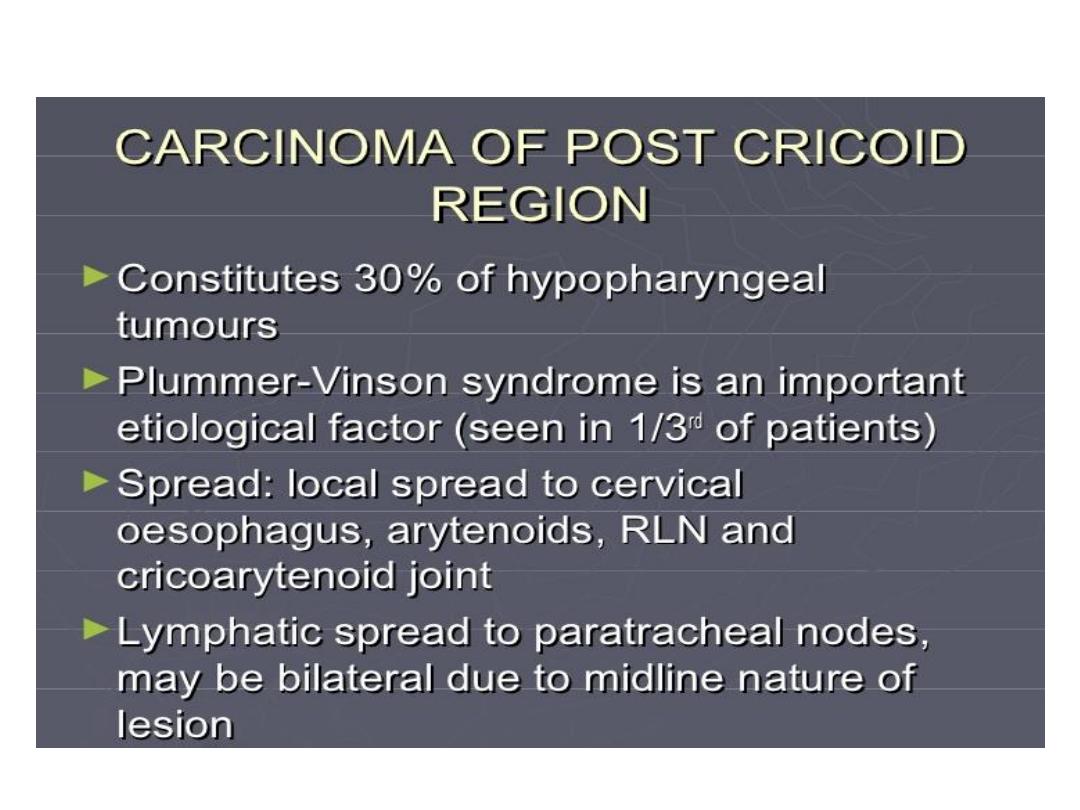
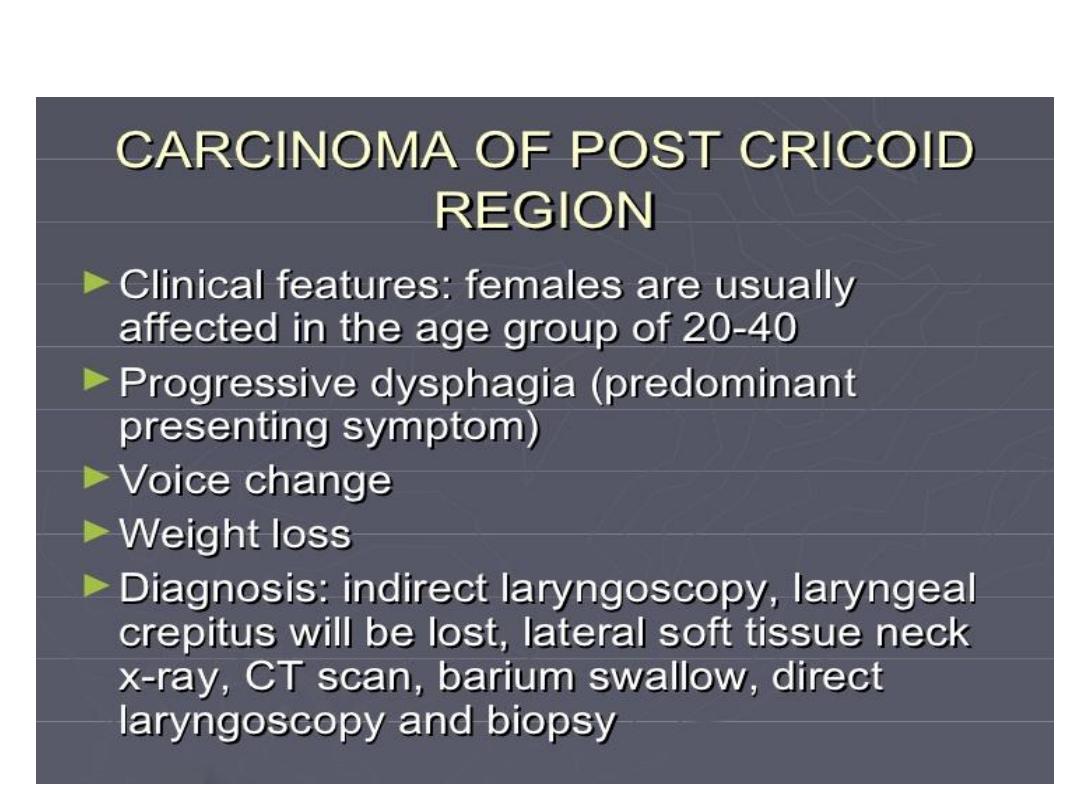


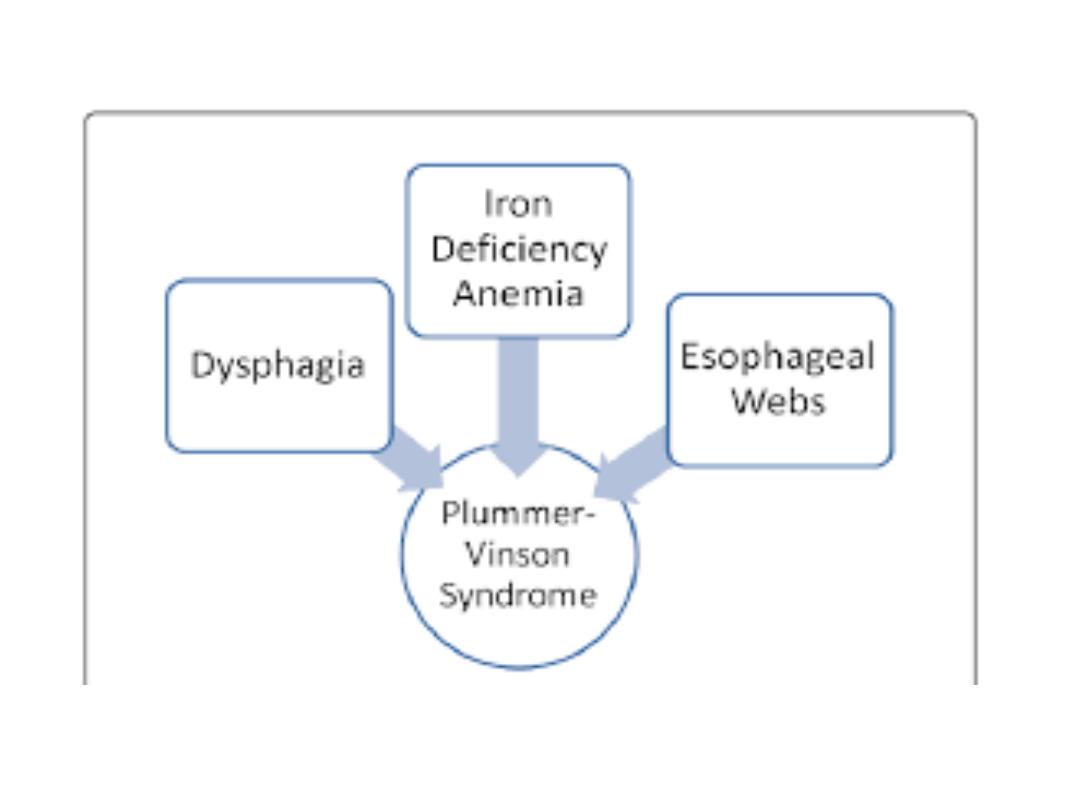
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
Definition
Plummer-Vinson syndrome (PVS) is a classical
triad of postcricoid
dysphagia, upper esophageal webs, and iron
deficiency anemia.
Identification and follow-up is relevant due to
increased risk of
squamous cell carcinomas of the esophagus
and pharynx

Clinical features
Symptoms:
• Dysphagia, is typically intermittent and
limited to solids.
• Odynophagia (painful swallowing, also called
algiaphagia)
• Choking spells and aspiration may occur
because of the proximal location of the web.
• Weakness, fatigue and dyspnea are
secondary to iron deficiency anemia.
• Weight loss is uncommon.

• Signs:
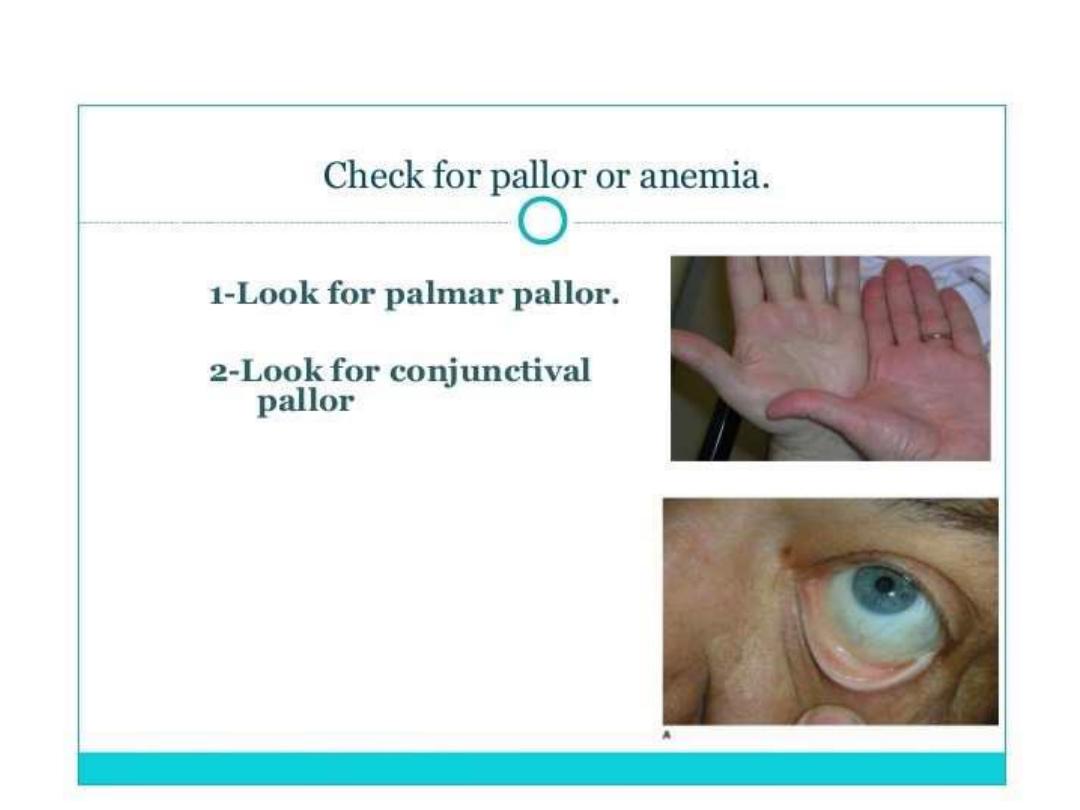
• Manifestations of iron deficiency (with or without anemia) include:
• • Angular stomatitis
• • Glossitis
• • Koilonychia (spoon nails)
• • Pallor
• Others include:
• • Splenomegaly
• • Edentia (loss of teeth) - due to esophagial relux
• • Enlarged nodular thyroid glands
• • Gastritis with Acholorhydia
• • Post cricoid webs
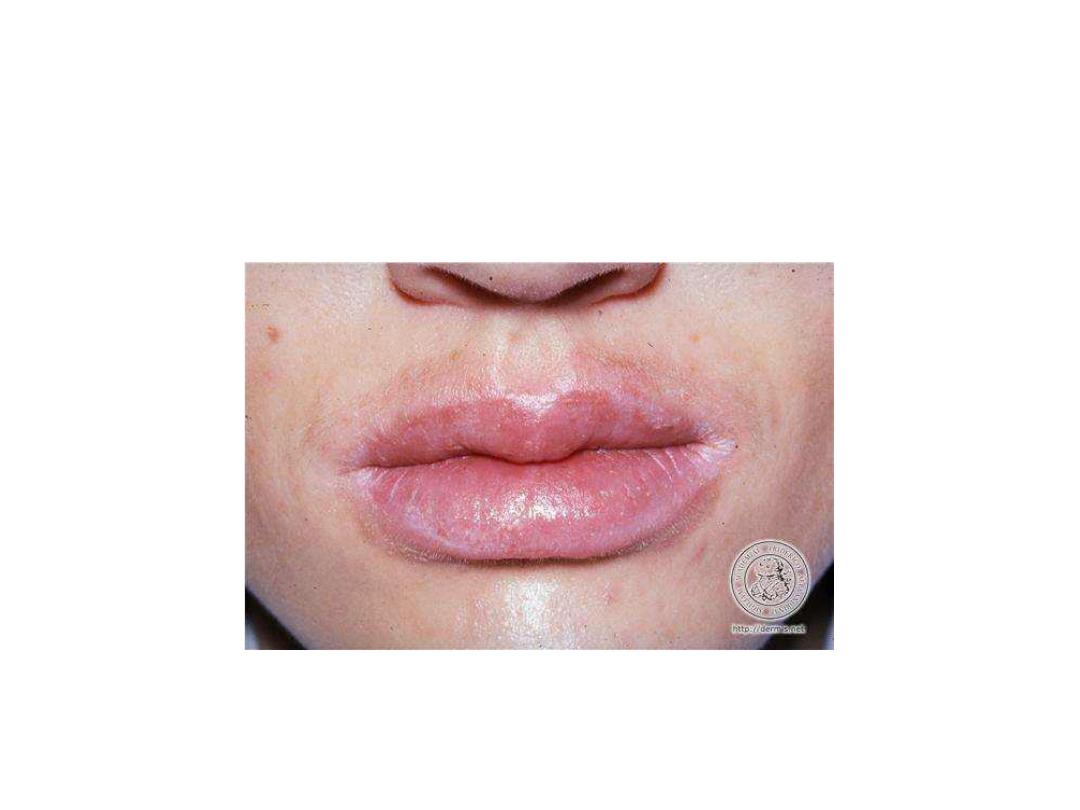
Cheilitis (angular stomatitis)
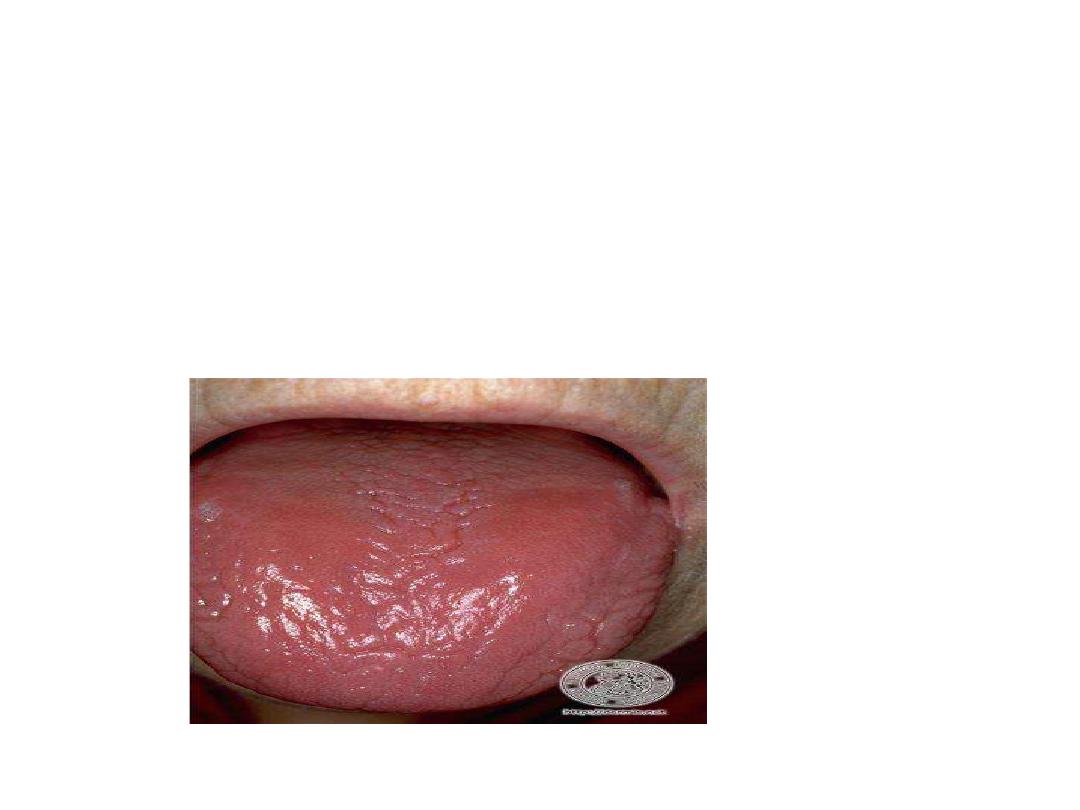
Atrophic Glossitis
burning sensation of the tongue, and
atrophy of lingual papillae produces a
smooth, shiny red tongue dorsum
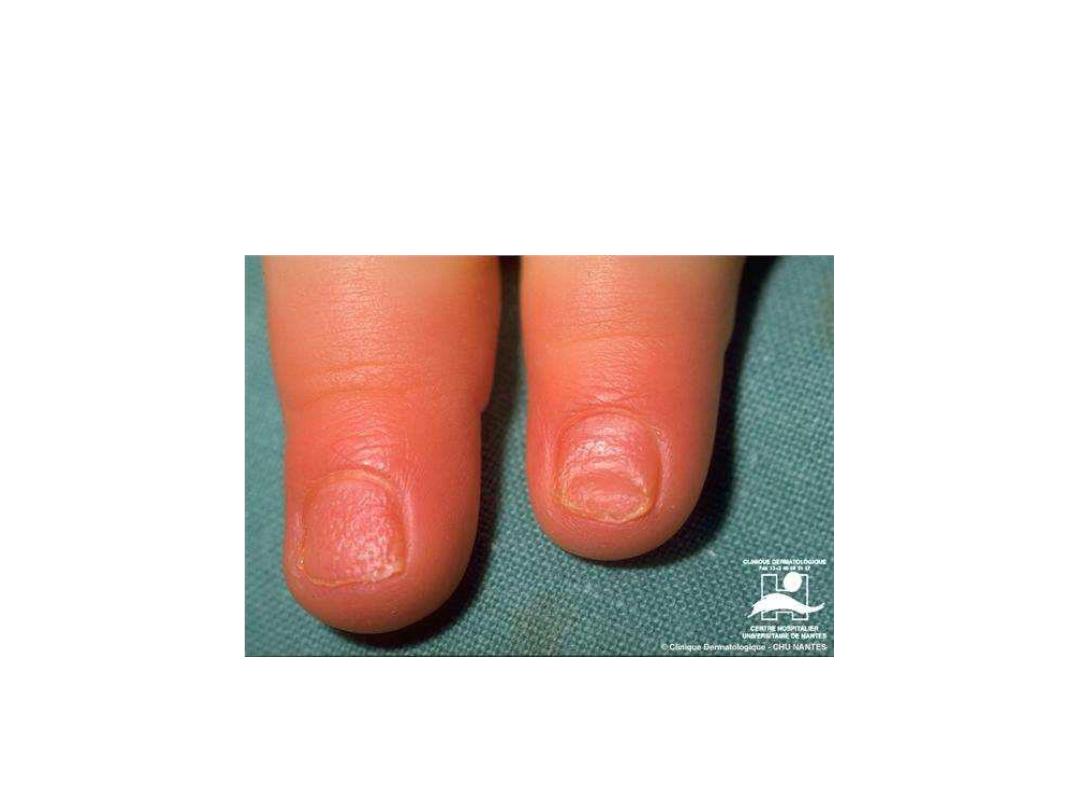
Koilonychia
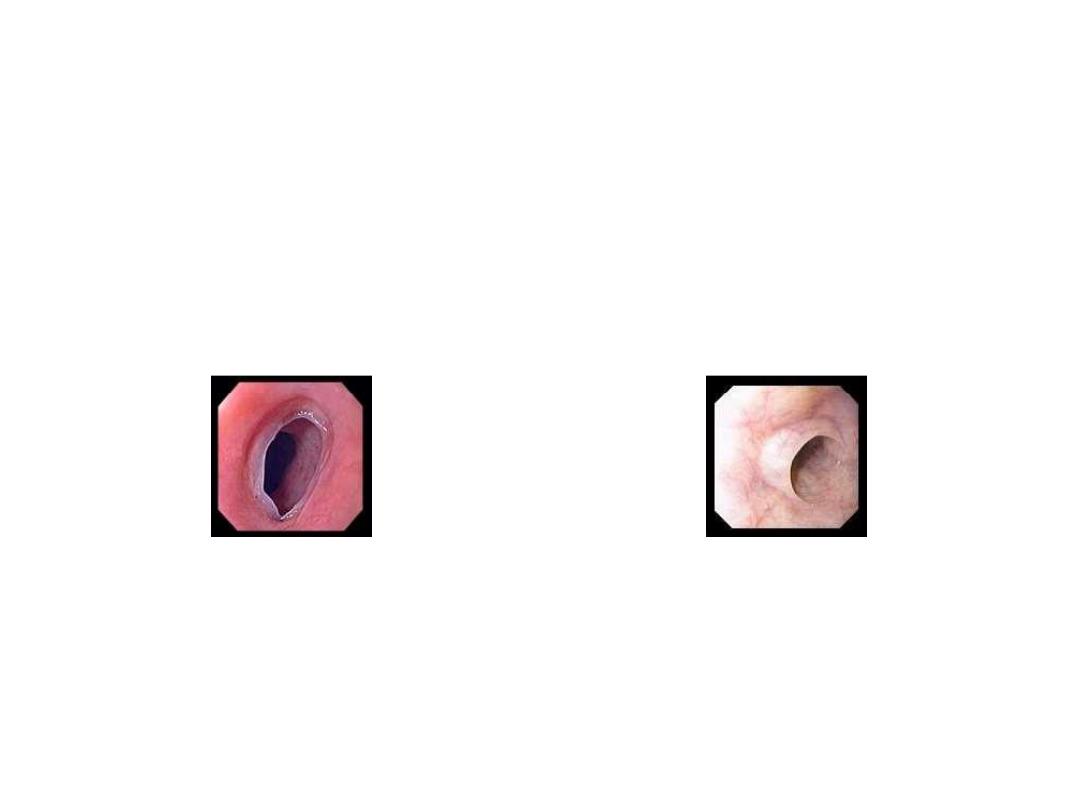
Post cricoid webs on endoscopy
(Pathognomonic)

investigations
• 1- haematology
• 2-radiology
• 3-endoscopy
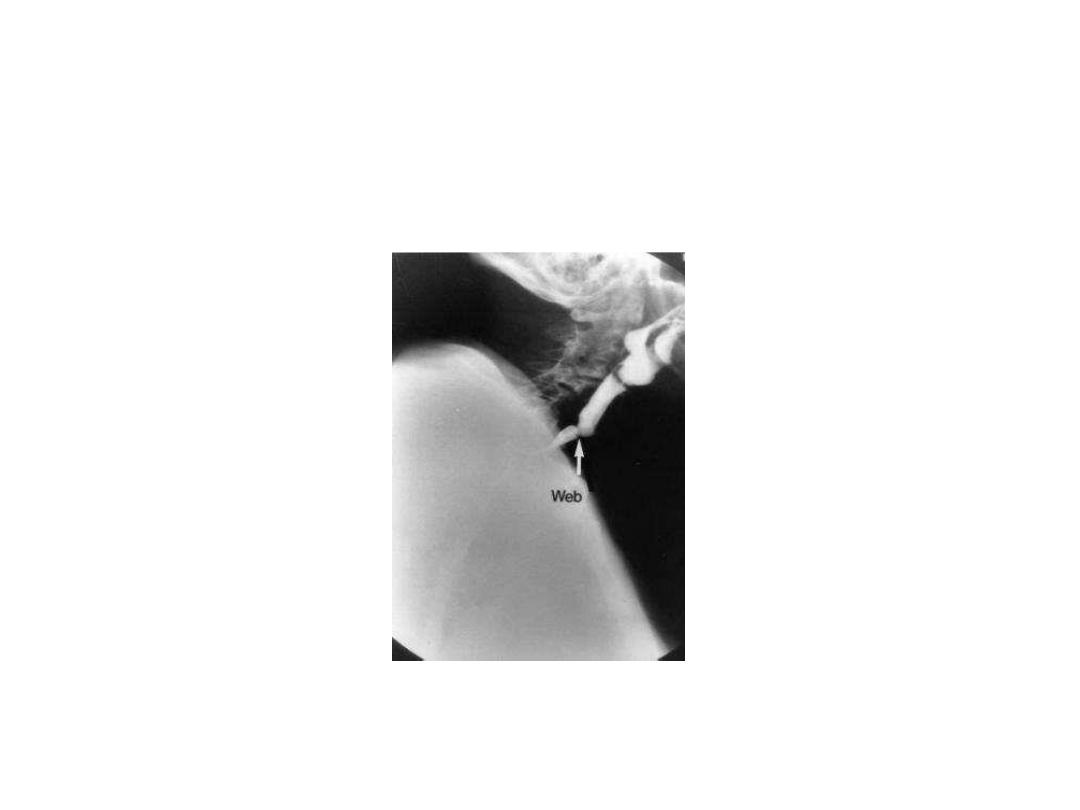

Barium swallow x-ray on lateral view

treatment
• Treat iron deficiency and its underlying cause
• • Iron replacement (Ferrous Sulphate)
• • Address the cause of iron deficiency (celiac sprue,
bleeding, malignancy)
• Treat dysphagia and the web
• • Mechanical dilation by upper endoscopy
• • Bougie (eg, Savary dilator)
• • ND:YAG laser therapy
• • Needle-knife electroincision
• Diet
• • Eat slowly and chew thoroughly.
• • Solid foods cut in small pieces, especially meats.

Long-term monitoring
• • Due to increased risk of squamous cell
carcinoma of the pharynx and the esophagus,
• the patients should be followed closely. A
surveillance upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
• is recommended every year.
• • Follow-up complete blood cell counts (CBCs)
and iron studies in 3 months, after
• initiation of iron replacement, to document
resolution of sideropenia and anemia.

Prognosis
• Prognosis of the Plummer-Vinson syndrome is
excellent.
• • Dysphagia and anemia can be treated
effectively.
• • Complications: In case of an associated
squamous cell
• carcinoma of the hypopharynx or upper
esophagus the prognosis
• worsens dramatically
