
BY
Dr. Amer salih

Pharynx
It is a muscular tube
Lies behind and communicates with the nasal, oral,
and laryngeal cavities
Lies in front of the prevetebral fascia
About (12 cm) in adult

Pharyngeal subdivisions
Nasopharynx
Oropharynx
Hypopharynx
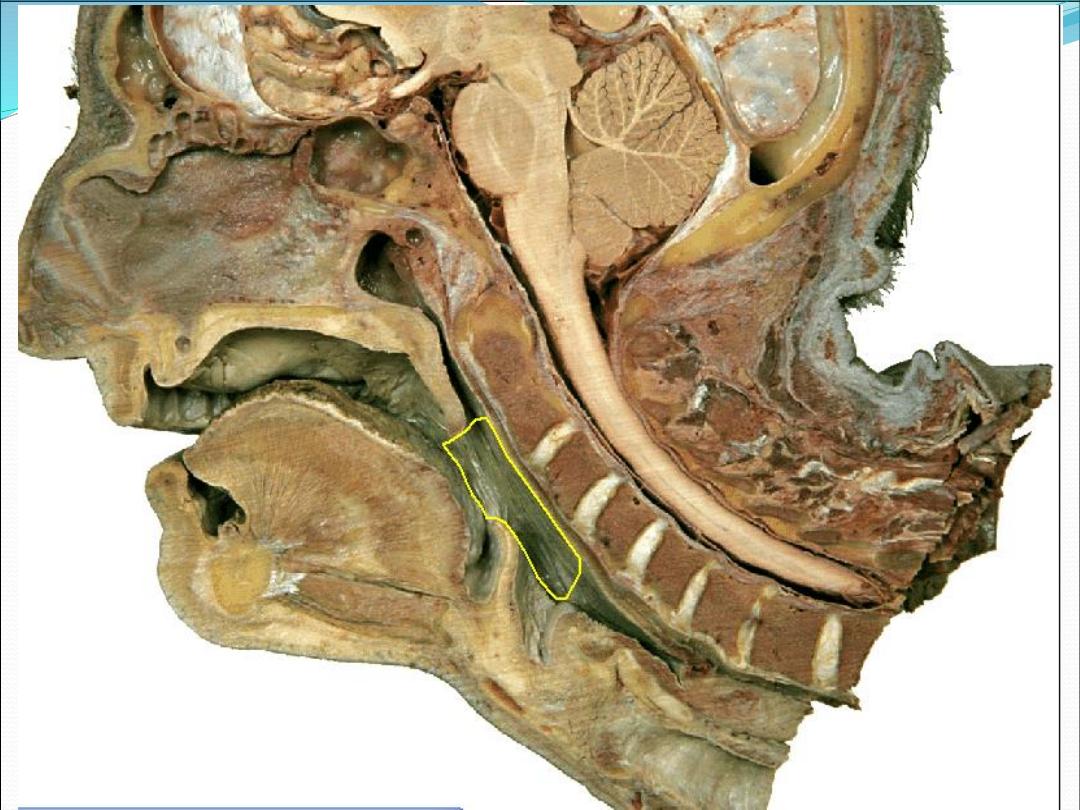
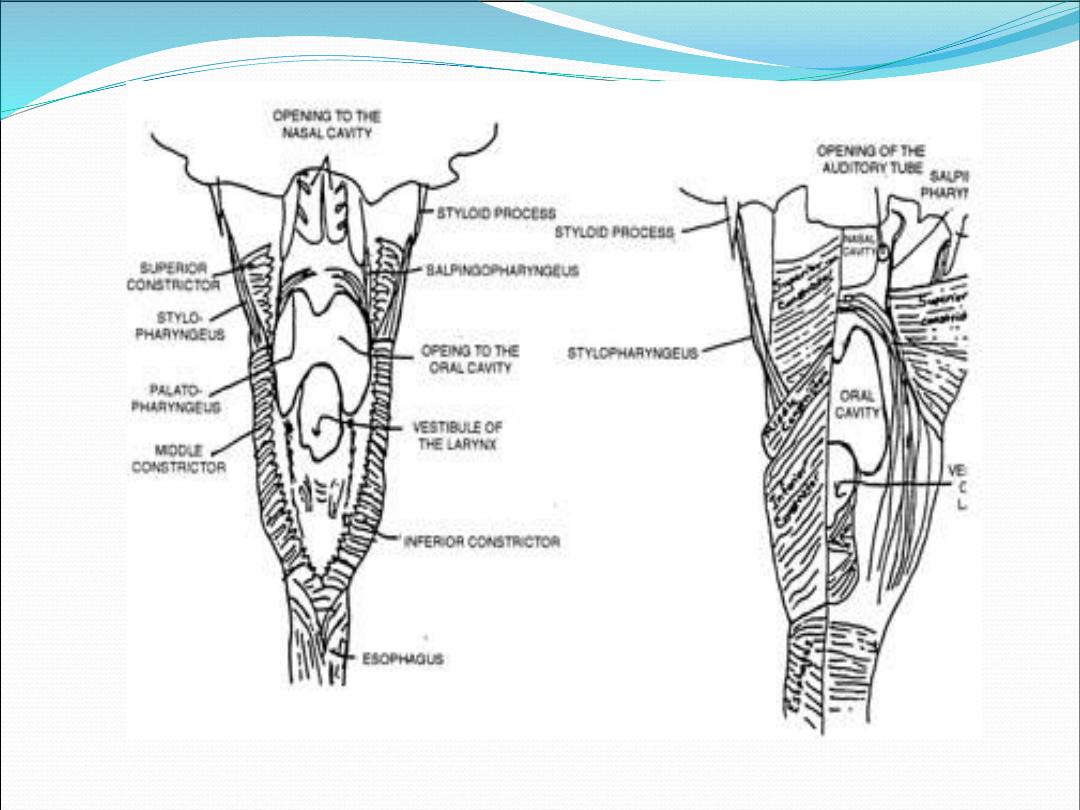

layers
Mucosa: non-keratinized stratified squamus
epithelium & ciliated columnar epithelium
Pharyngobasilar fascia: fibrous layer
Muscles : longitudinal and circular
Buccopharyngeal fascia: loose areolar tissue that
separate pharynx from prevertebral fascia

Inner layer
Salpingopharyngeus
Stylopharyngeus
Stylohyoid
Palatopharyngeus (posterior pillar)

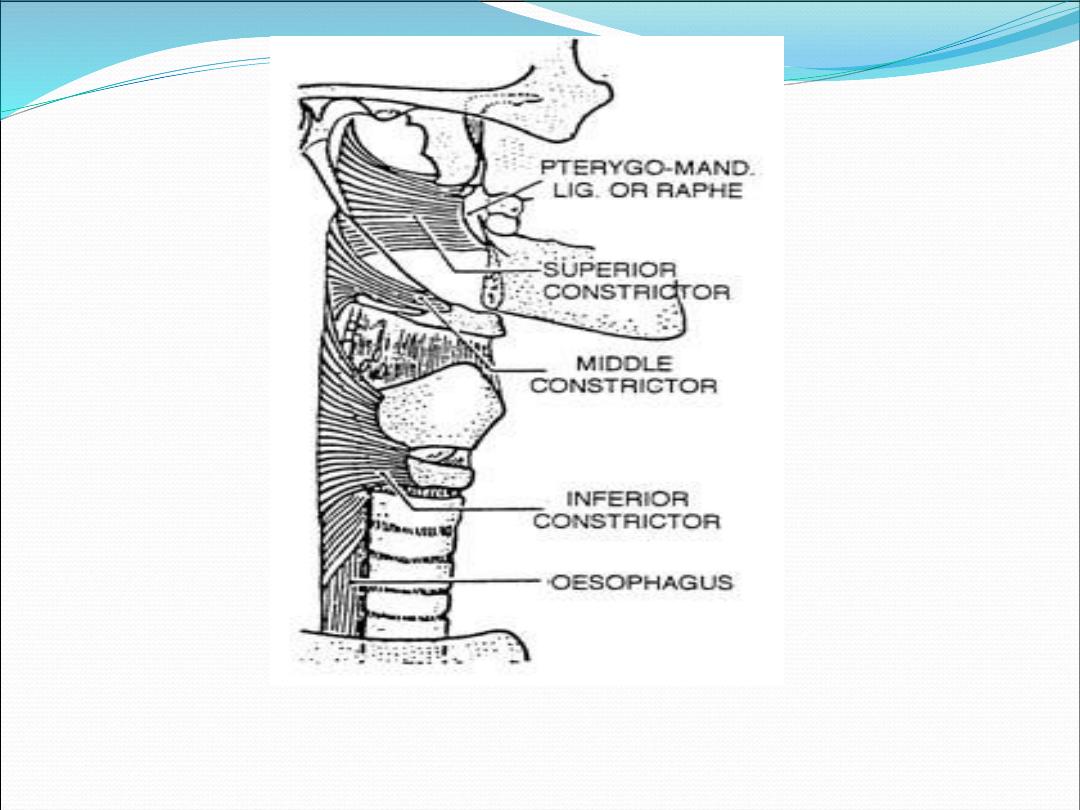
Outer layer (constrictors)
Superior constrictor
Middle constrictor
Inferior constrictor

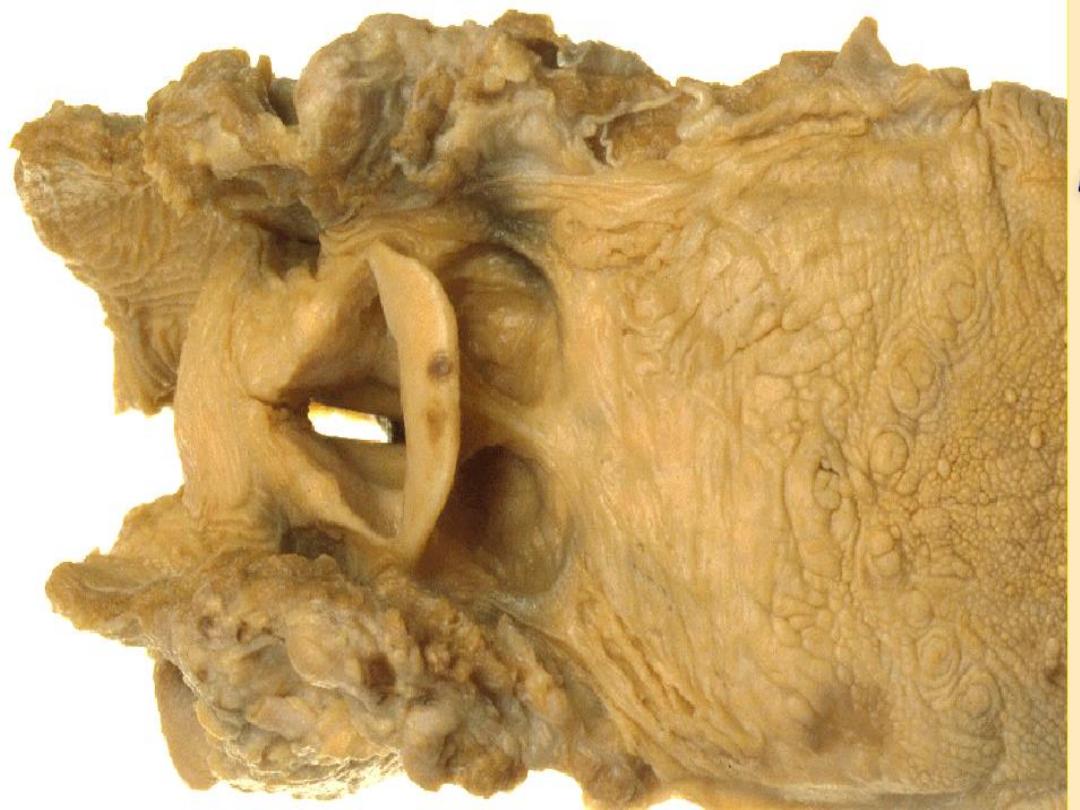
Nasopharynx
Extend from the base of the skull to the level of soft
palate
Continuous with the nasal cavity througth the
choanae
Eustachian tube in the lateral wall
Above and behind ET. There is a depression which
called fossa of rosenmullar
Adenoid :collection of lymphoid tissue lies in the
posterior superior wall

Oropharynx
Extend from the junction of soft and hard palate to the
floor of the valleculae (level of hyoid bone)
Subuints:
1-soft palate 2- base of tongue
3-median and lateral glossogoepglottic folds
4-valleculae 5-posterior pharyngeal wall
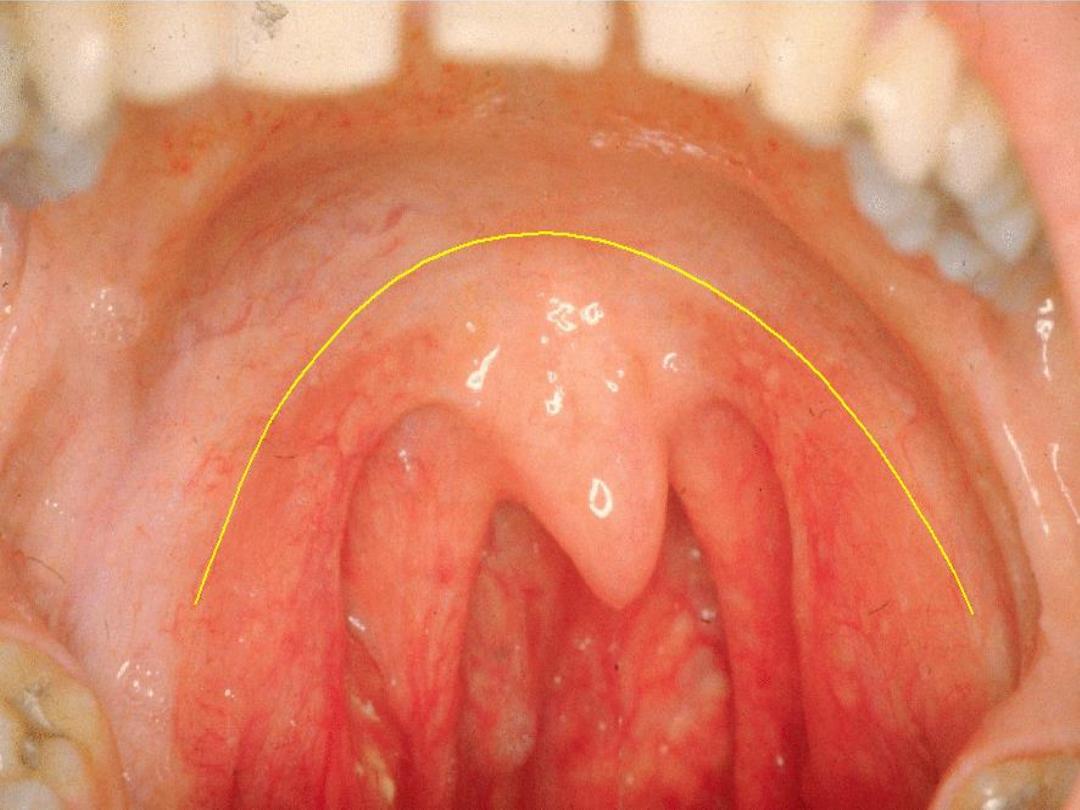
Palatine Tonsil
lies in tonsillar fossa between
palatoglossal and palatopharyngel folds and coresponding
muscles, it compose of lymphoid tissue with germinal
center containing 6—20 epithelium-lined crypts. Tonsillar
capsule (thin areolar tissue) separate it from the under
lying superior constrictor

Lingual tonsil
collection of lymphoid
tissue in the base of tongue
•
B-lymphocytes proliferates in germinal center
•
Immunoglobulines(IgG, A, M ,D) complements,
and cytokines accumulate in the tonsil
•
The role of tonsil remain cotraversal and to date
there is no proven immunologic effect from
tonsillectomy

Hypopharynx
Extend from the level of hyoid to the lower edge of the
cricoid
Subunits :1-pyriform fossi, 2-posterior and lateral
walls, and 3-postcricoid region

Airway
Swallowing
Sound resonate

Swallowing
Oral phase
(voluntary): 1-mastication 2-adation
and mixing of saliva 3-control of bolus 4-selection of
bolus (volume, taste, fish bone, etc.)
Pharyngeal phase
(involuntary), quick, and
including:-
1.
Nasopharyngeal closure
2.
Cessation of respiration
3.
Glottic closure
4.
Bolus propulsion
5.
Laryngeal elevation & pharyngeal shortening

Esophageal phase
(involuntary): peristaltic
movement from superior part downward associated
with relaxation of lower esophageal sphincter


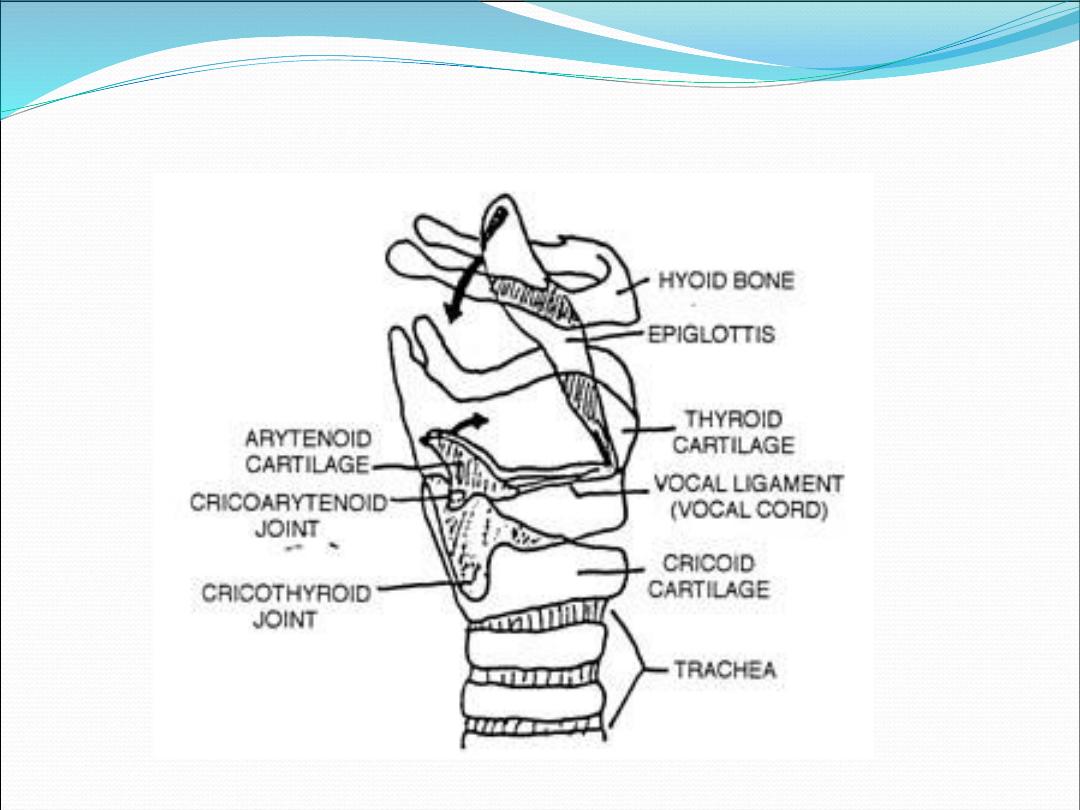
Cartilages of the larynx
1.
Thyroid cartilage (single)
2.
Cricoid cartilage (single)
3.
Epiglottis (single)
4.
Arytenoid cartilages (paired)
5.
Corniculate cartilages (paired)
6.
Cuneiform cartilage (paired
)
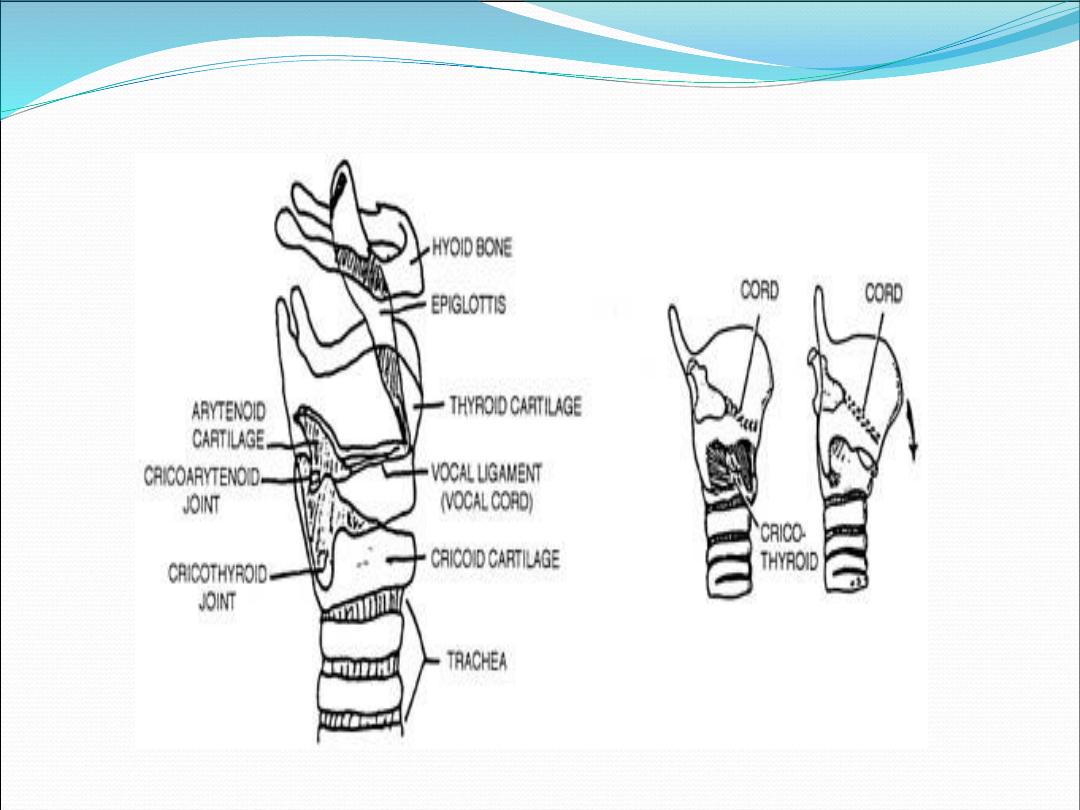

It is commonly described as part of the
laryngeal framework, because it is an
important point of attachment for
extrinsic muscle of the larynx

1.
Thyrohyoid membrane
2.
Cricothyroid membrane
3.
Cricotracheal ligament
4.
Vocal ligament

•
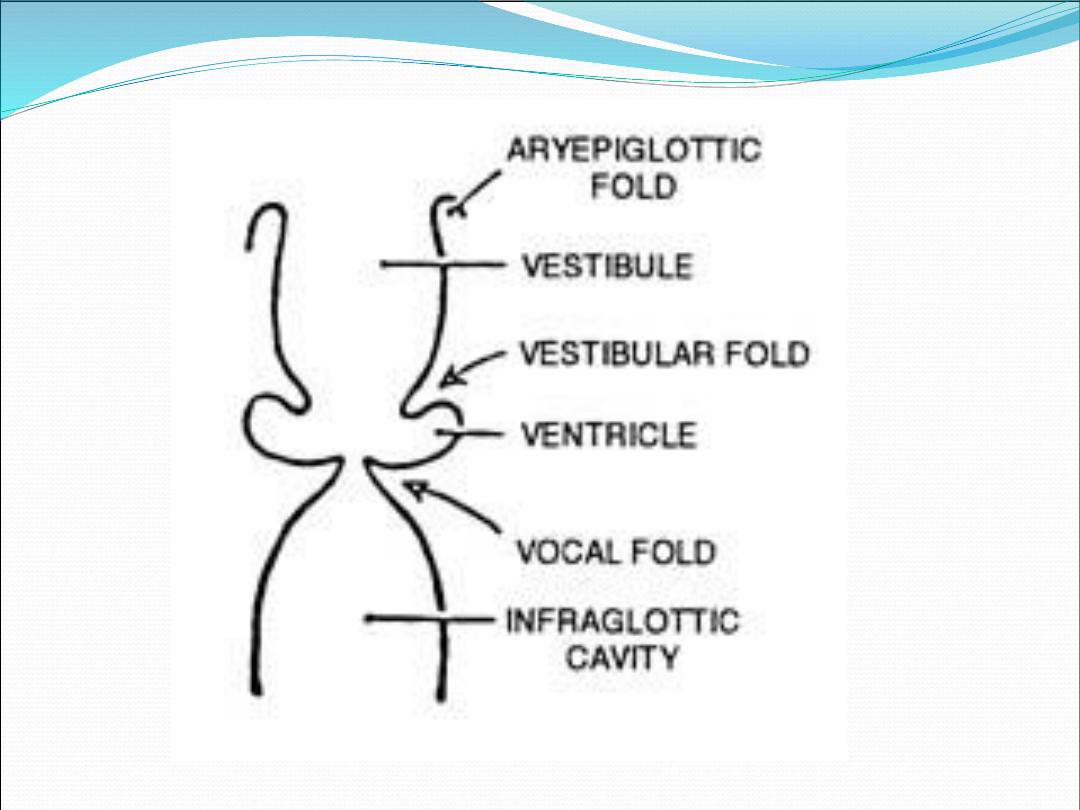
Supraglottis
1.
Epiglottis
2.
Aryepiglottic folds
3.
Arytenoid
4.
Ventricle

1.
Anterior and posterior commissures
2.
True vocal cords
Subglottis
Extend from the under surface of the vocal cords
to the inferior edge of cricoid cartilage

Extrinsic m.
•
Sternohyoid muscle
•
Thyrohyoid m.
•
Geniohyoid m.
•
Stylohyoid m.
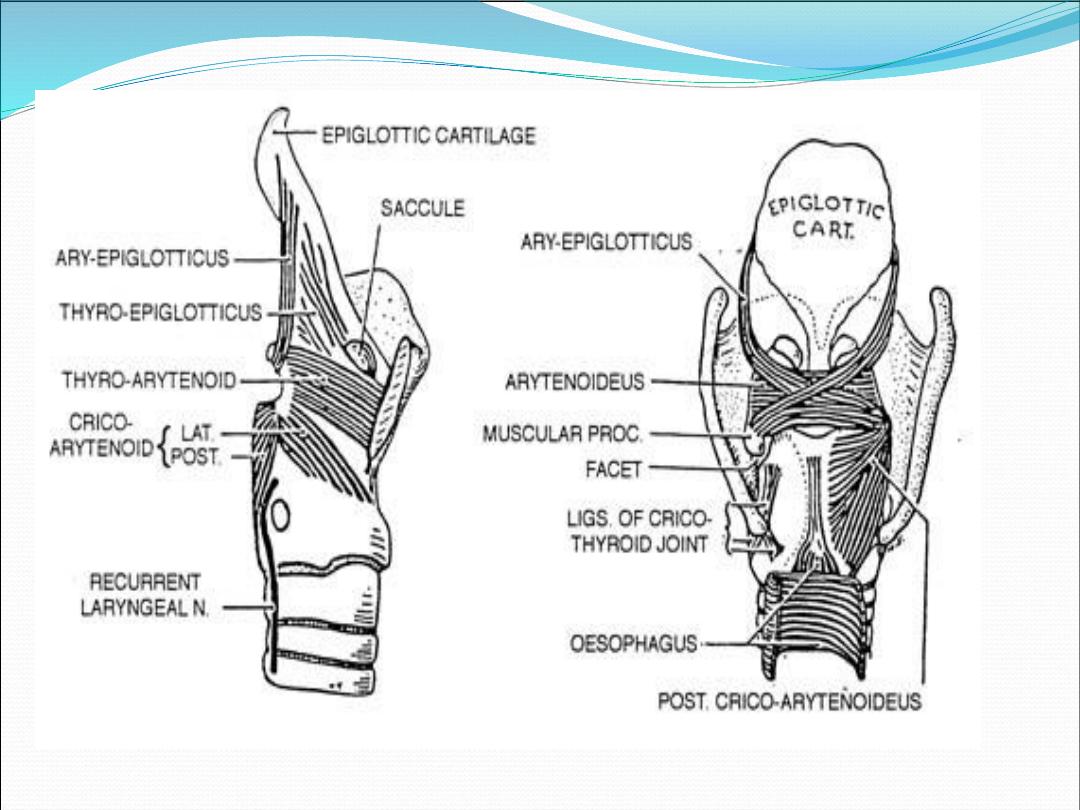
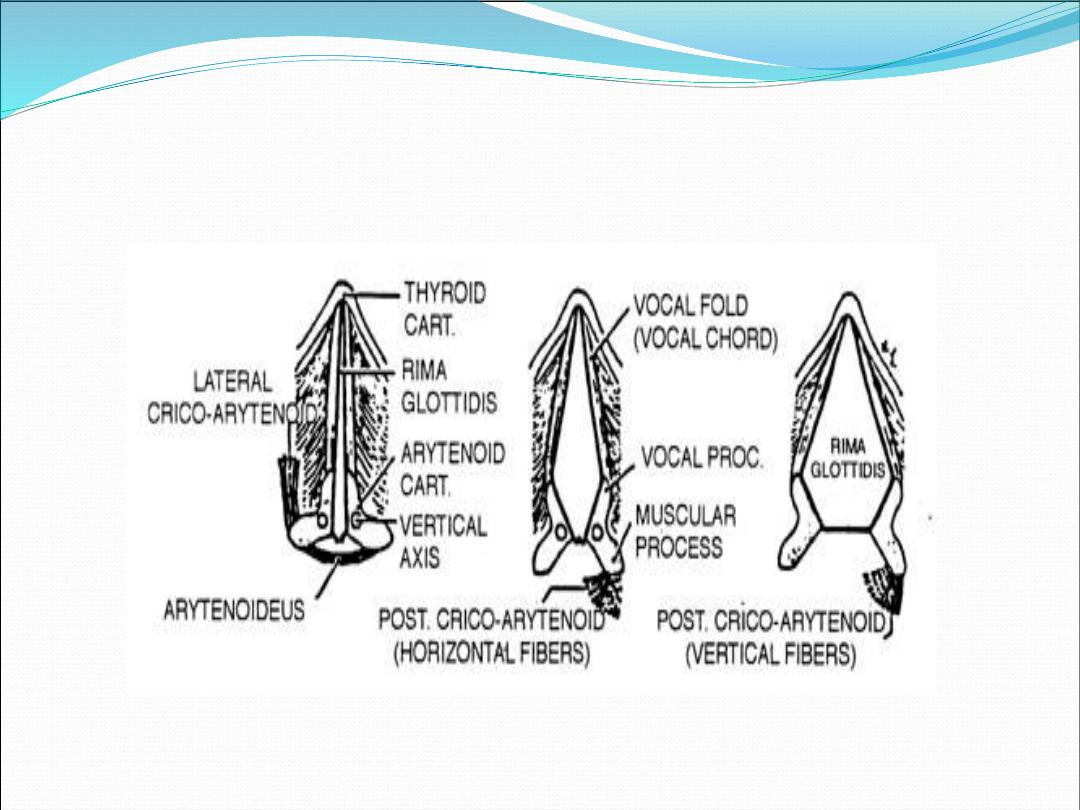
Intrinsic muscle
•
Thyroarytenoid m.
•
Interarytenoid m.
•
Posterior cricoarytenoid m.
•
Lateral cricoarytenoid m.
•
Cricothyroid m.

•
St . Sq. epithelium is found over true vocal cords
•
Ciliated columnar epithelium in other regions


Airway protection
Respiration
Phonation
Others
(Fixation of the chest)

Phonation
Speech result from the production of
fundamental tone at the level of the true
vocal cords, this then modified by the
resonating chambers of the upper
aerodigestive tract.

Vocal tract components
1.
Activator : (lung and respiratory muscles)
2.
Sound source generator (vocal cords)
3.
Resonator (supraglottis, hypopharynx,
oropharynx and nasopharynx
4.
Articulator (palate, tongue, teeth, and lips
are used to modulate the sound signal)
