Dr.Amer Salih aljibori

Atopy
is a tendency to develop an exaggerated IgE
antibody response
Allergy
is the clinical presentation of atopic disease in
the presence of allergen
Aetiology
G
enetic and family history
E
nvironmental factors like exposure to allergen ,air
pollution and irritant, occupational allergen like flour,
wood dust, latex in surgical gloves,tobacco,detergents
and bleach.

F
ood occasionally provoke IgE allergic rhinitis, it may be due
to sensitivity to preservatives, some type of food contain
histamine like cheese and wine
D
rugs like penicilline, asprin, antihypertensive, B-blocker,
ACE inhibitor

The allergic responses can be divided into two
phases. The first is an
that occurs
immediately after exposure to an allergen. This
phase can either subside or progress into a "
late
phase reaction
" which can substantially prolong the
symptoms of a response, and result in tissue damage

Pathogenesis
IgE has a property of binding to high affinity receptor on the
mast cell and basophil .the interaction of allergen with IgE
initiate secretion of active mediators that cause clinical
manifestation,thes mediators either
preformed
mediators
(histamine, proteases, chemokines, heparine);
or
newly
formed
mediators (prostaglandins, leukotrienes,
thromboxanes)
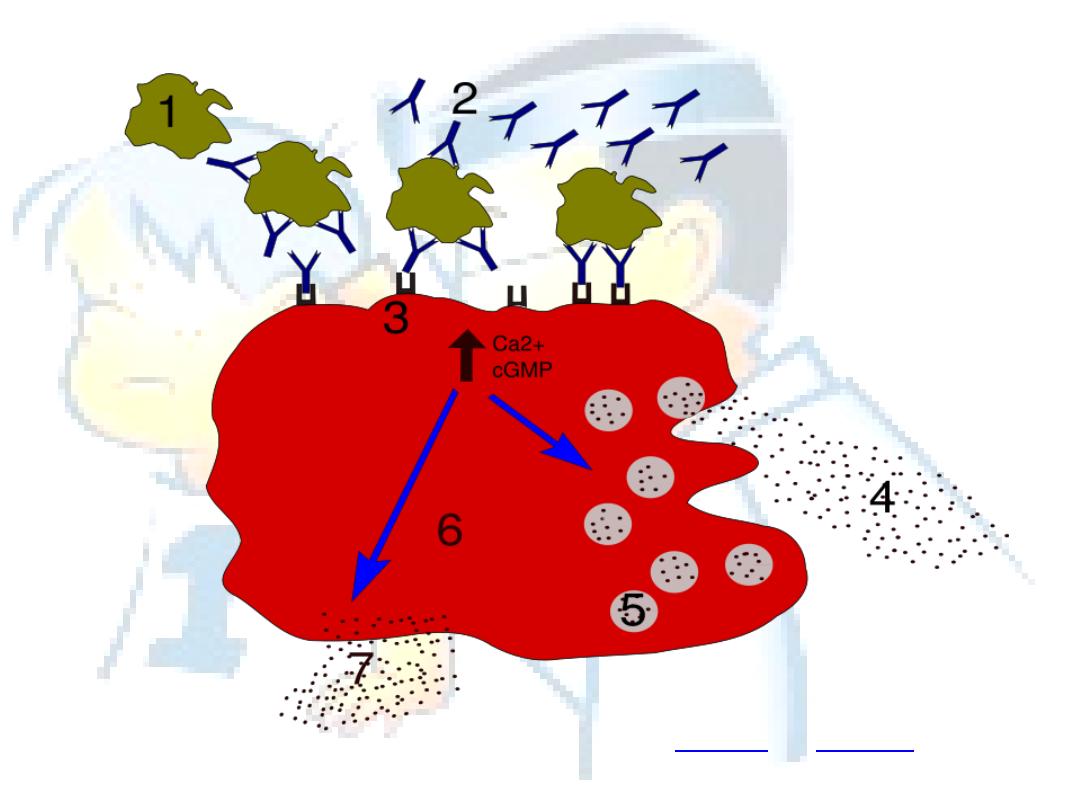
Degranulation process in allergy.1 - antigen; 2 - IgE antibody; 3 - FcεRI receptor; 4 -
preformed
mediators
(histamine, proteases, chemokines, heparine); 5 -
; 6 -
; 7 -
newly
formed mediators
(prostaglandins, leukotrienes, thromboxanes)



Allergic rhinitis
Rhinitis if defined clinically by a combination of two
or more nasal symptoms
Nasal obstruction…….blocking
Rhinorrhea…………...running
Itching and sneezing
Allergic rhinitis occur when these symptoms are the
result of IgE mediated inflammation following
exposure to allergen
Classification
Seasonal
Perennial
occupational
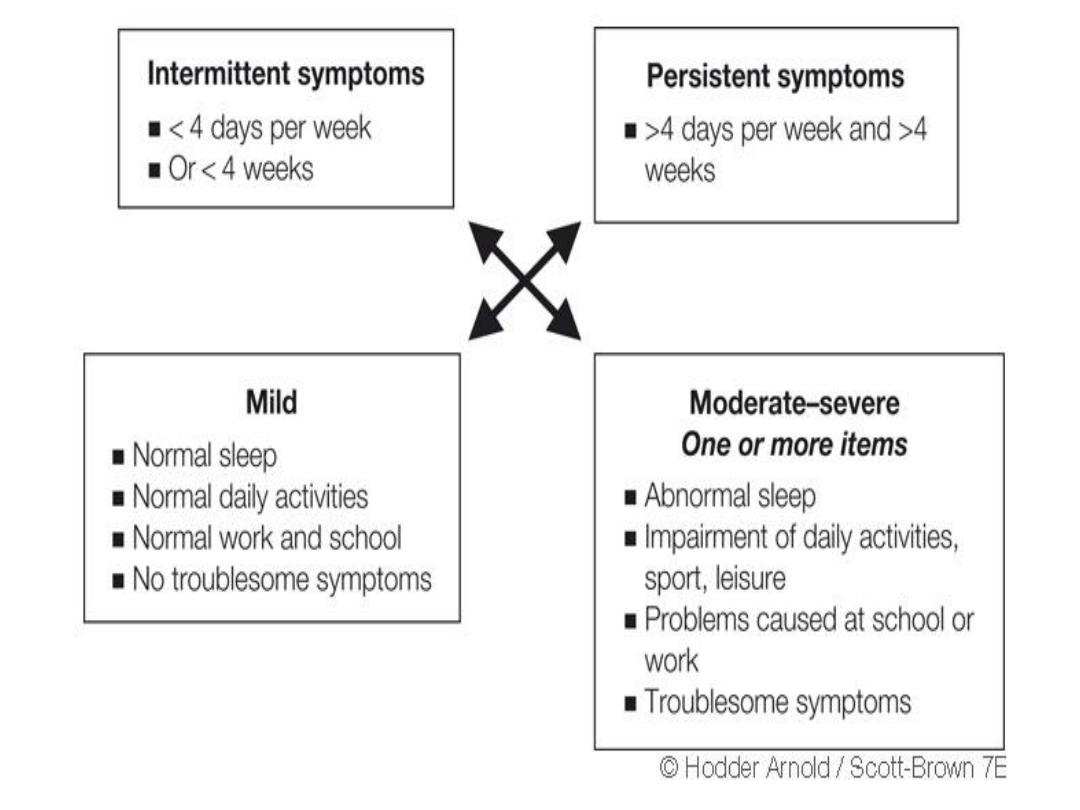

New classification by ARIA guideline (allergic rhinitis and its
impact on asthma)
Mild
Normal sleep
Normal daily activities
Normal work and school
No troublesome symptoms
Moderate or severe
Abnormal sleep
Impairment of daily activities
Problems caused at school and work
Troublesome symptoms

Intermittent symptoms
Less than 4 days/week
Or less than 4 weeks
Persistent symptoms
More than 4 days/week and more than 4 weeks

Co-morbidities
Other conditions associated with allergic rhinitis are
asthma,sinusitis,otitis media,sleep disorder,lower
respiratory tract infection
Rhinitis and asthma are linked by
epidemiological,pathophysiological characteristics and by
common therapeutic approach.
█
Rhinitis is a risk factor for the development of subsequent
asthma ,
█
is a frequent cause of asthma exacerbations ,and
█
effective rhinitis treatment reduce asthma
So patient with persistent allergic rhinitis should be
evaluated for asthma and the converse is true

Clinical presentation
Seasonal
type allergic symptoms of sneezing ,rhihinorrhea
and itching are easily recognized
Perennial
allergic inflammation is mainly expressed as nasal
obstruction,hyperreactivity and poor sense of smell,the
sinus lining is also usually involved so that the picture is of
one of a chronic inflammatory rhinosinusutus,in those
patient immediate symptom not present and may undergo
unnecessary operations for septal deviation or turbinate
befor the true nature of the problem is diagnosed
properly
!!!!

Examination
The mucosa appear pale, or
bluish,boggy,swollen,NSD,polyp,inferior turbinate
hypertrophy

Lab tests
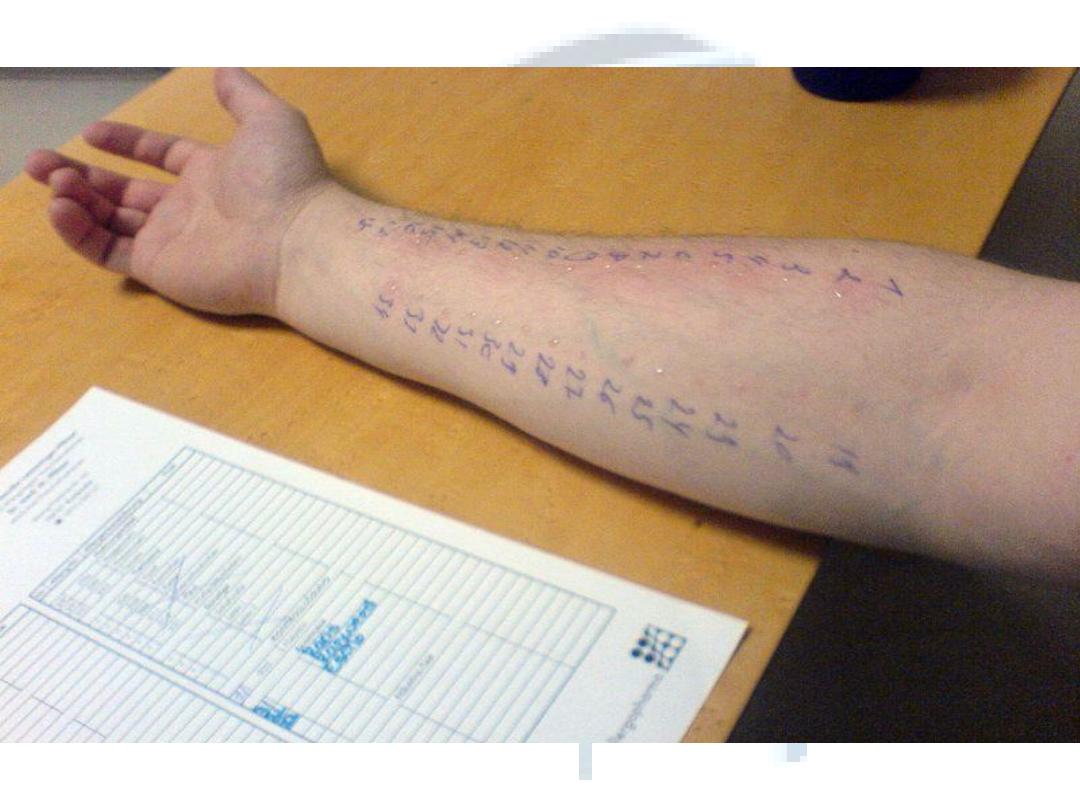
1
skin prick test
2
serum IgE measurement either
RAST
radioallergosorbant test
ELISA
enzyme linked immunosorbant test
3
nasal cytology for eosinophil
4
nasal swab for bacterial and viral studies
5
nasal allergen challenge

Treatment
◙
identification and avoidance
◙
pharmacotherapy
Antihistamine
It relieve running,itching,and sneezing but have little or no
effect on blockage
First generation like chlorpheneramine,diphenhydramines
should be avoided because of sedation,psychomotor
retardation and learning impairment because it cross the
BBB and interact with histamine receptors
Second generation antihistamine act with an hour topical
ones within 15 minutes

Terfenadine,astemazole
block potassium channel and
cause cardiac arrhythmia, QT prolongation,so care taken
not overdose and nor to combine with
erythromycin,ketokanazole,grapefruit juice,antiarrythmia .
Citrizine,fexofenadine,and desloratidine
not block
potassium channels even at supranormal dose
Desloratidine is exception that affect on nasal blockage

Topical corticosteroid
Are the most effective treatment of rhinitis especially if
started prior to allergen exposure it reduce the relative risk
of asthma exacerbation by 50%
Side effects
are minor include epistaxis and nasal irritation
Beclomethasone-------- Beconase
Budenoside--------------Rhinocort
Fluticasone -------------Floxanase
Sodium cromoglicate
It is weakly effective against all rhinitis but safe means it is
useful for small children less than four years for whom a
topical corticosteroid is not available
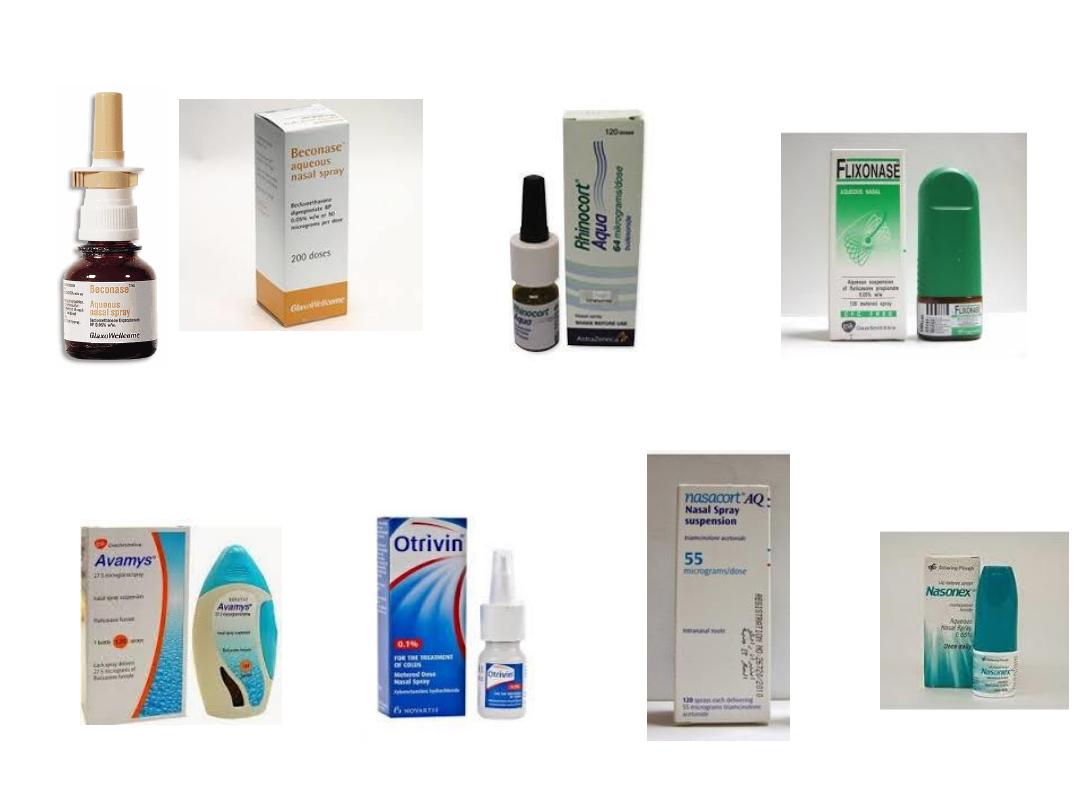

Fluticasone
Beclomethasone
Budenoside
Fluticasone
Triamcinolon Acetonide
Mometasone Furoate
?

Decongestants
Used topically reduce nasal obstruction but increase
rhinorrhea,regular use for more than few days result in
rhinitis medicamentosa
Systemic decongestant are relatively ineffective with side
effects like hyperactivity,insomnia in children and
hypertension in adult

Ipratropium bromide
Response in patients who do not response to topical
corticosteroid alone
Systemic corticosteroid
Used to unlock the nose at start of treatment or for sever
symptoms,used for few days Depot injection not
recommended because they are not stopped if side effects
occur
Antileukotriens LRA
Recently been licensed in rhinitis it can also be helpful in
polyposis
Nasal douching

◙
Immunotherapy
It is alter the course of allergic disease and prevent the
progression of allergic rhinitis to asthma .session long
As more as 2-3 years and should be given by trained
personnel and only under medical observation
◙
Surgery
May play role especially when the main symptom is nasal
obstruction.
Correction of NSD ,reduction of IT,surgery to improve nasal
patency.