
DISEASES OF THE TONSIL
Dr. Amer salih aljibori

Acute Tonsillitis: acute inflammatory condition of
the faucial tonsil which may involve the mucosa,
crypts,follicles and /or tonsillor parenchyma.
Causatve agents;
-Viral:Initially starts with viral infection then
followed by secondary bacterial infection.Common
viruses are influenza,parainfluenza.adenovirus and
rhinovirus.
-Bacterial:Streptococcus hemolyticus,Hemophilus
influenza,pneumococcus,M.catarrahalis.

Pathology and pathogenesis:
Usually it starts in the childhood when
there is low immune status.Depending on the progress of the disease,this
can be classified further into the following types.
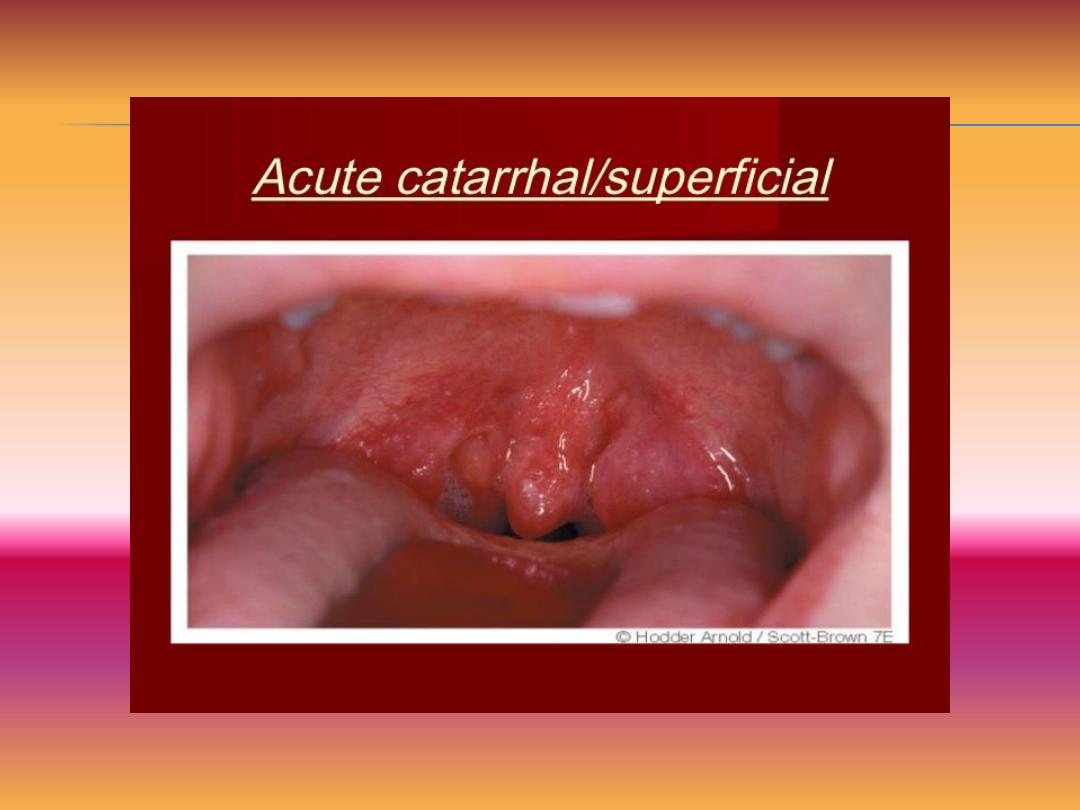
•Catarrhal tonsillitis:It occurs due to viral infection of the upper
respiratory tract involving the mucosa of the tonsil
•Cryptic tonsillitis: Following viral infection ,secondary bacterial infection
supervenes and gets entrapped within the crypts leading to localized form
of infection
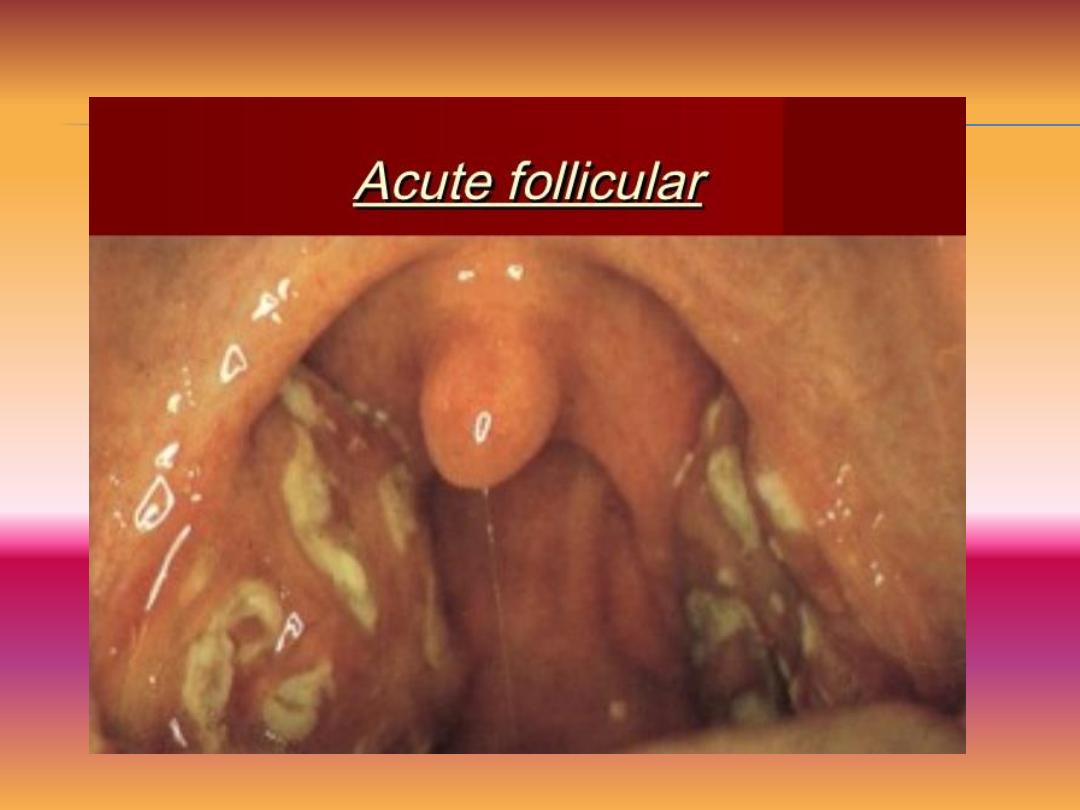
•Acute follicular tonsillitis. It is sever form of tonsillitis caused by virulent
organisms like streptococcus hemolyticus and Hemophilus. It causes
spread of inflammation from tonsillar crypts to the surrounding tosillar
follicles.
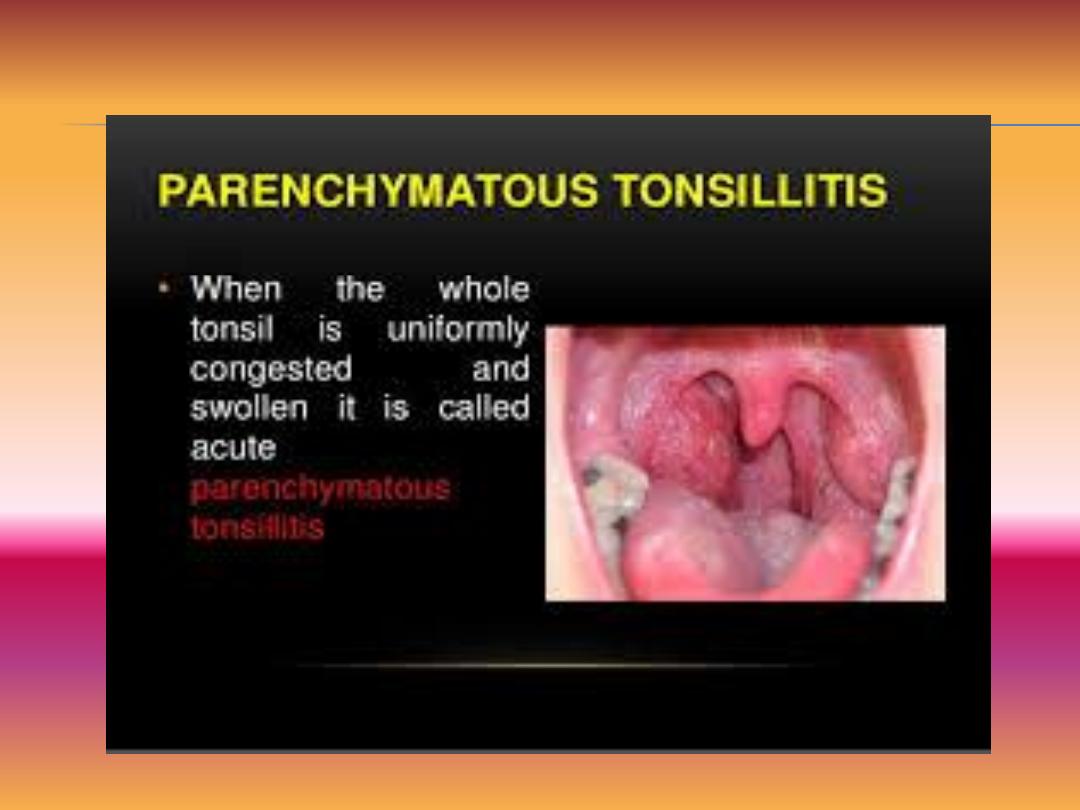
Acute parenchymal tonsillitis: The secondary bacterial infection will
invade to the crypts and it is rapidly spreads into the tonsillar
parenchyma..
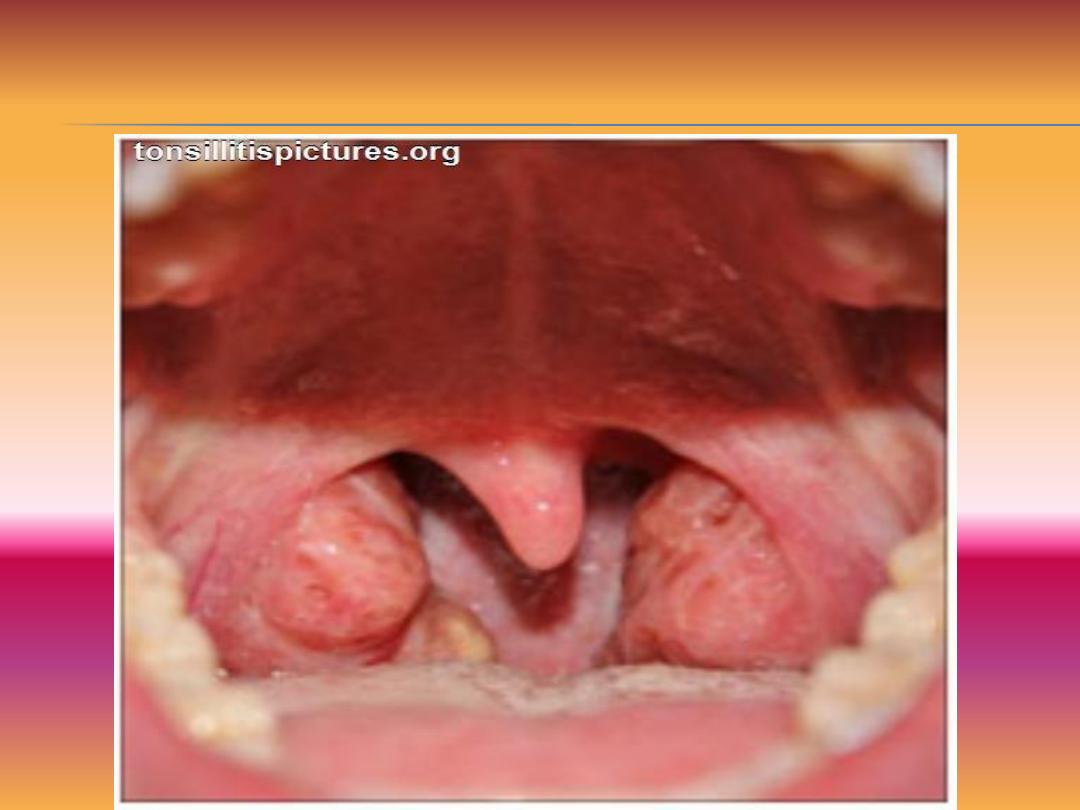
Cryptic tonsillitis
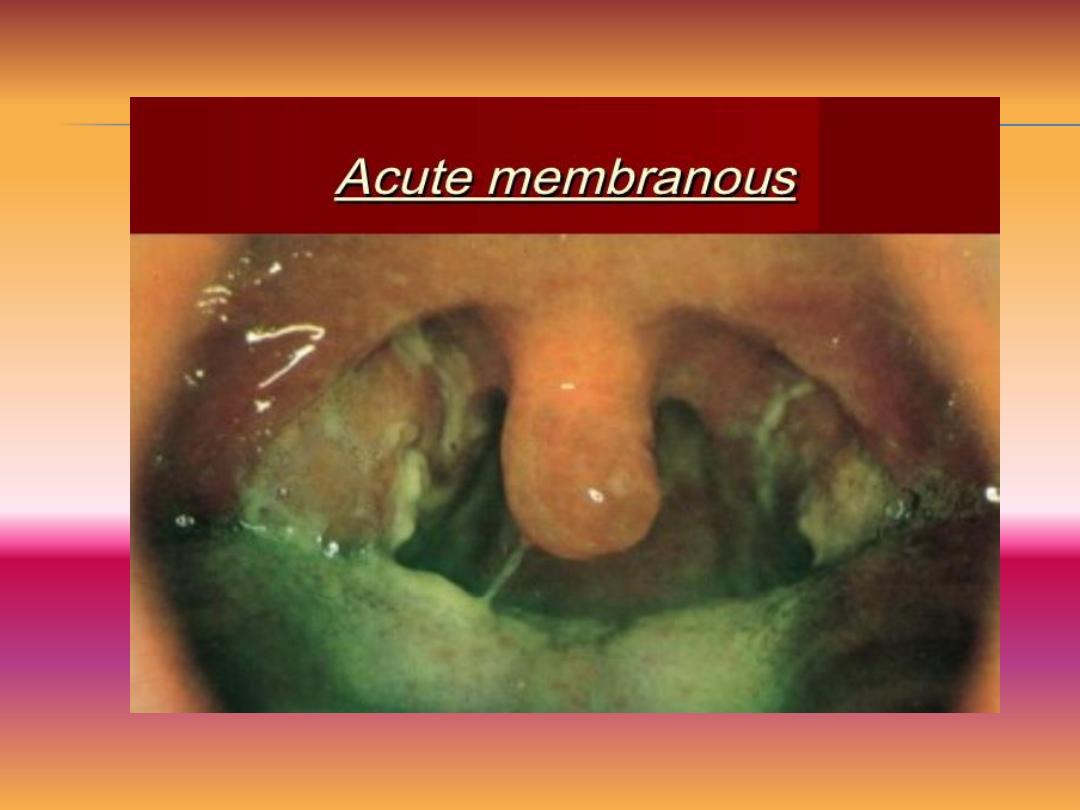

1- Symptoms
-Fever
-Generalized malaise and bodyache.
-Odynophagia.
-Dry cough.
-Sorethroat.
2- Signs
-Congested and oedematous tonsils
-Tonsils may be diffusely swollen in parenchymatous
tonsillitis.
-Crypts filled with pus in follicular tonsillitis.
-Membrane cover the tonsil and termed as membranous
tonsillitis.
-Tender enlarged jugulodigastric lymph nodes.
-Signs of upper respiratory tract infection and adenoiditis.

Investigations.
-Throat swab for culture and sensitivity.
-Blood smear to rule out hemopoeitic disorders like
leukemia,agranulocytosis.
-Paul-Bunnel test may be required if membrane seen
to rulr out infectious mononucleosis.
-X-ray of paranasal sinus to rule out nasosinus
septic foci.
-X-ray of the soft tissue of the nasopharynx to rule
out adenoid hypertrophy.

Treatment
-Pencillin is the drug of choice especially for
streptococcus.B-Lactamase producing
hemolytic streptococci should be treated with
amoxicillin+clavunalic acid
combinations.Erythromycin should be preferred
in patients sensitive to penicillin.
-Antiseptic gargles and throat lozenges may be
given.
-Paracetamol for pain and fever.

Differential diagnosis.
-Scarlet fever.
-Diphtheria.
-Vincents angina.
-Agranulocytosis.
-Other causes of membrane over the tonsil like
leukemia

COMPLICATIONS.
1-Local.
-Acute otitis media.
-Retropharyngeal ,parapharyngeal abscess.
-Peritonsillor abcess.
-Respiratory obstruction.
2-General.
-Acute rheumatic fever.
-Septicemia.
-Glomerulonephritis.

Chronic Tonsillitis: It is the chronic
inflammation of the palatine tonsil which occurs
as a result of repeated attacks of acute tonsillitis
or due to inadequately resolved acute tonsilittis.
Etiopathological.
-b-hemolytic streptococcus.
-As complication of acute tonsillitis.
-Mostly affects children and young adults.
-Predisposing factors may be due to chronic
infection in sinuses or teeth.
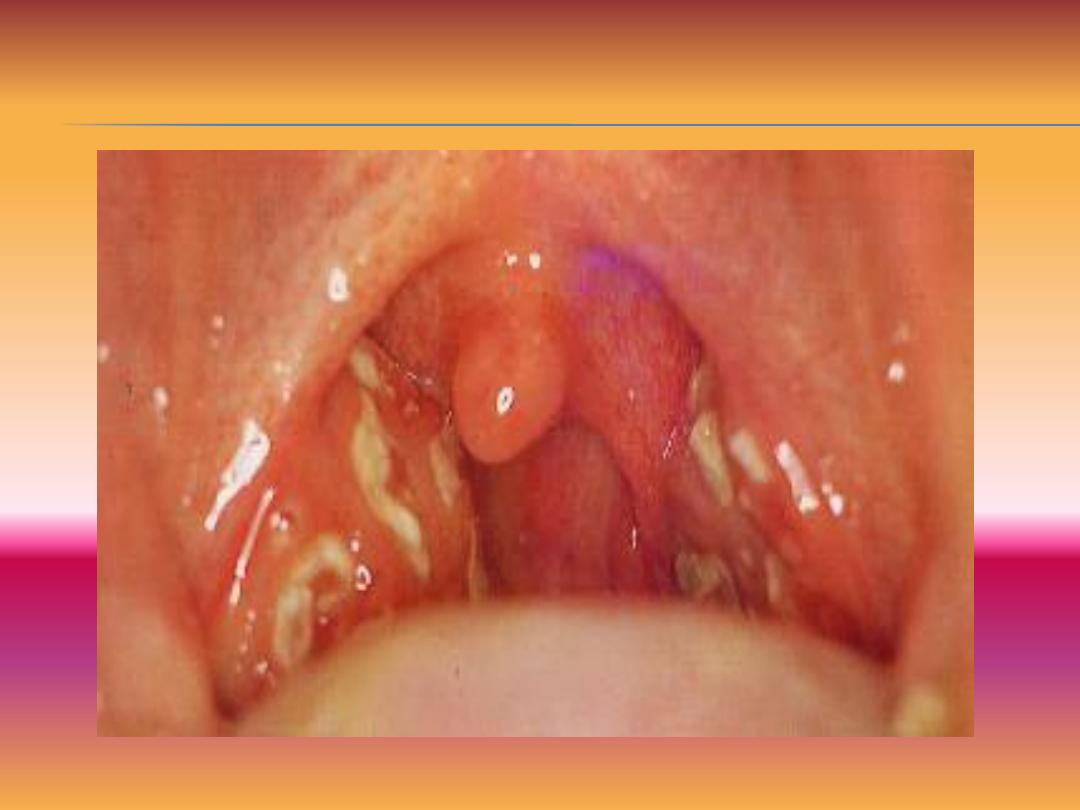
Chronic follicular

Types
A-Chronic follicular tonsillitis.Tonsillor crypts are
full of cheesy material that appear as yellowish
spots.
B-Chronic parenchymatous tonsillitis.following
repeated attack of acute tonsillitis the lymphoid
follicles of tonsillar parenchyma under
hyperplasia..
C-Chronic fibrotic tonsillitis.Here the tonsillis are
small due to atrophy.

Clinical features
1- Symptoms.
-Sore throat.
-Cough.
-Halitosis.
-Bad taste of the mouth.
-Thick speech.
-Difficulty in swallowing.
-Sleep apnea.

2- Cardinal signs
-Persistent congestion of anterior pillor.
-Positive tonsillor sequeeze.
-Enlarged jugulodigastric lymph node.
-Enlarged tonsils
Treatment
1-Conservative
-diet.
-Good oral hygen.
-Treatment of tooth and sinus infection.

2-Surgical.
Tonsillectomy
Indications
a- Absolute indications
-Biopsy if there is suspicion of malignancy.
-Sleep apnea syndrome.
-peritonsillor abscess:Second attack.
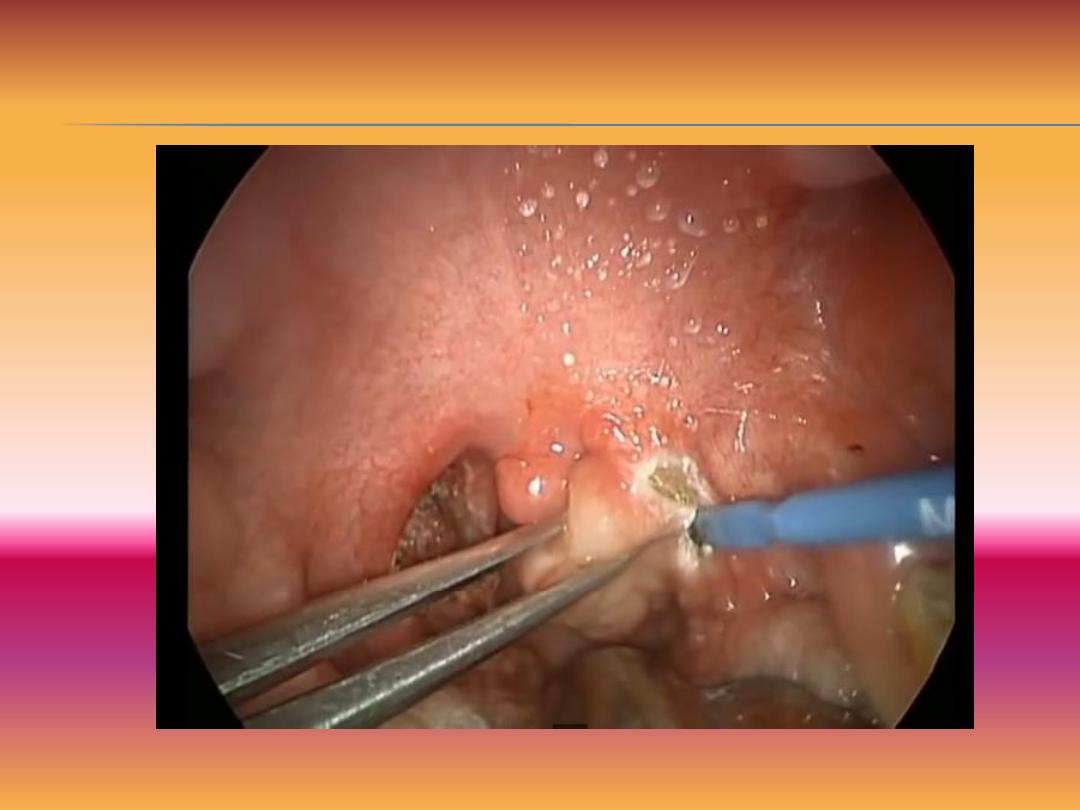

b-Relative indications.
--Repeated episodes(6 attack/year for 2 years)
-Access in glossopharyngeal neuroctomy. And
resection of ossified styloid process.
-As Part of Uvulo-palato-pharyngo-plasty).
-Tonsillar cyst,tonsillolith.
-IF the tonsil acting as septic foci for rheumatic
heart diseases ,arthritis and glomerulonephritis.
-Failure to thrive.

Contraindications
-Active infections
-Bleeding disorders.
-Cervical spine pathology.
-Endemic of polio.
-Failure to control hypertension and
diabetes.

Complications
1-Immediate.
-Primary and reactionary hemorrhage.
-Injury to structures-Teeth,lips,gums,tongue and palate.
-pain throat and referred otalgia.
-Fever.
-Airway obstruction may occur due to uvular oedema,hematoma
and aspiration of material.
-Secondary hemorrhage occurs usually in the 6
th
-10
th
days.
2-Delayed.
1-Lingual tonsillitis.
2-Nasopharyngeal stenosis.
3-Velopharyngeal insufficiency.
4-Residual tonsillitis.

Types of posttonsillectomy hemorrhage.
1-Primary hemorrhage.This occur during surgery due
to paratonsillar veins.due to
-Poor selections of cases.
-Improper technique.
Treatment
-Packing the tonsillar fossa with wet guaze and wait for
5 minute.
-If bleeding persists so ligat or cauterize the bleeding
vessel.

2-Reactionary hemorrhage. This occurs in the postoperative
period within 24 hours,due to
-Slipping of the ligature.
-Failure to ligate all vessels.
-Hypotensive anesthesia.
-Clot in the fossa.
-Injured muscle.
Treatment.
1-Vital signs should maintained. treat hypovolumia and blood
loss.
2-Remove the clot and apply pressure with simple pack.
3-Hyderogen peroxide gargle is helpful in removing the clot and
mild cauterizing agent.
4-If bleeding persist, so admit the patient to the theater and ligate
or cauterize the bleeding vessel.

Secondary hemorrhage.This is due t o sepsis of the tonsillar
fossa and usually occurs in the 6
th
to 10
th
days
Treatment
1-Vital signs and treat blood loss.
2-Start parentral broad spectrum antibiotic including
metronidazole.
3-Cold liquid diet.packing for five minutes and application of
hyderogen peroxide.
4-IF bleeding persist so should enter the patient to the theature
and interpillor suturing is done.
Peritonsillar abscess(Quinzy)
It is acute inflammatory process associated with pus collection in
the peritonsillar space which lies between the tonsillar capsule
and superior constrictor muscle

Clinical features
-symptoms
-Fever,chills,malaise,body ache and toxic features.
-Acute sever unilateral odynophagia.
-Refered otalgia.
-Neck pain.
-Trismus.
-Muffled voice
-Dribbling of the saliva.
Signs
-Tonsil is usually pushed medially and downward .
-Congested tonsil/membrane may covered the tonsil.
-Uvula is edematous ,congested and deviated to opposite side.

Treatment
-IV antibiotic and analgesia.
-If dysphagia is sever :Hospitalization and IV
fluid.
-Wide bore needle aspiration.
-Incision and drainage.
-Hot tonsillectomy

Tonsillolith
This is calculus created by deposition of the salt in the
crypt forming hard mass.
Clinical features
-Halitosis.
-Discomfort.
-Sore throat.
-Fever.
Treatment
-Removal of the tonsillar stone.
-Recurrent stones is treated by tonsillectomy.
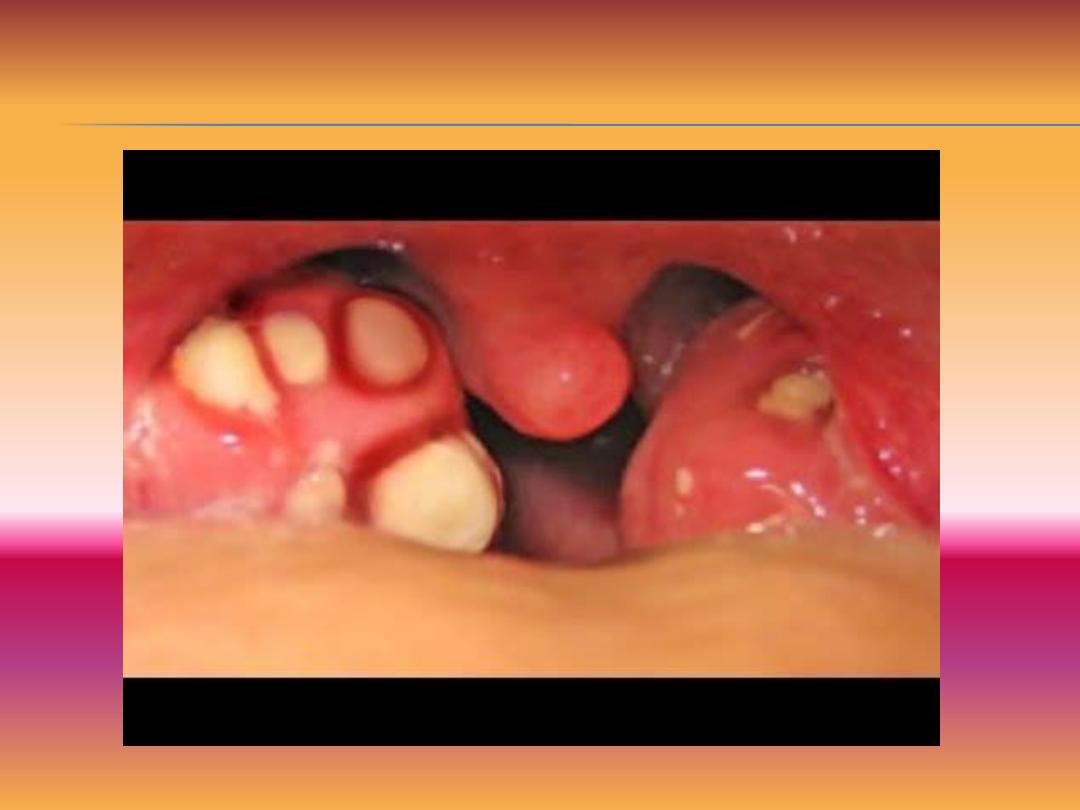
Tonsil stones

Ulceration of the tonsil
-Infections(acute and chronic)
-Neoplastic(lymphoma,sq.cell carcinoma)
-Blood diseases(leukemia,Agranulocytosis)
-Miscellaneous(Aphthus ulcer,Behcet).
DDX of unilateral tonsillar enlargement.
-peritonsillar abcess
-parapharyngeal mass.
-Lymphoma or squamous cell carcinoma.

