MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI )

MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
is noninvasive method of mapping the internal
structure and certain aspects of function within
the body.
It uses nonionizing electromagnetic radiation and
appears to be without exposure-related hazard .

HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE
Name of MRI previously is nuclear magnetic
resonance (NMR),first described by Bloch and
Purcell in 1946 .
NMR has been used extensively as a laboratory
method for studying the properties of matter at
the molecular level (NMR spectroscopy

MRI
In applications to medicine, it is now commonly
referred to as magnetic resonance (MR).

Application for human study between
1973-1977

MRI
MR describes the phenomenon whereby the
nuclei of certain atoms, when placed in a
magnetic field, absorb and emit energy of a
specific or resonant frequency.

..
Mean that the nuclei of certain elements align
with the magnetic force when placed in
astrong magnetic field .

…
At the field strengths currently used in medical
imaging ,hydrogen nuclei (protons ) in water
molecules and lipids are responsible for
producing anatomical imaging .
MRI
which each contain two
. When a person goes inside
the powerful
of the scanner,
of these protons align
with the direction of the field.

BASIC PRINCIPLE OF MRI
• The hydrogen (1^H) atom inside body possess “spin”
• • In the absence of external magnetic field, the spin
directions of all
• atoms are random and cancel each other.
• • When placed in an external magnetic field, the spins
align with the
• external field.
• • By applying an rotating magnetic field in the
direction orthogonal to
• the static field, the spins can be pulled away from the
z-axis with an
• angle \alpha

MRI
• •
The rapidly rotating transverse magnetization
(M_xy)
• creates a radio frequency excitation within the
sample.
• • If we put a coil of wire outside the sample, the RF
• excitation will induce a voltage signal.
• • In MRI, we measure this voltage signal.
• • Voltage produced is (Faraday’s Law of Induction)

MRI
If radiofrequency of hydrogen is applied
,aproportion of the protons change alignment
,flipping through apreset angle , rotate in phase
with one another.fallowing this radiofrequency
pulse,the protons return (realign )to their original
postion .










MRI
Advantage :
Provide high resolution anatomic structure (as
with X-ray CT)
• Provide high contrast between different soft
tissues (X-ray CT cannot)
• No exposure to radiation and hence safe
• More complicated instrumentation •
Disadvantage :
Takes longer to acquire a scan than CT, more
susceptible to patient motion

MRI
The hydrogen (1
^H) atom inside body possess “spin”
• In the absence of external magnetic field, the spin
directions of all
atoms are random and cancel each other.
• When placed in an external magnetic field, the spins
align with the
external field.
• By applying an rotating magnetic field in the direction
orthogonal to
the static field, the spins can be pulled away from the z-
axis with an angle \alpha

..
As the protons realign(relax )they induce aradio
signal which ,although very weak,can be
detected and localize by coils placed around
the patient .
An image represent the distribution of the
hydrogen protons can be built up .

MRI
The strength of signal depends not only on
proton density but also on tow relaxation
times .T1 and T2

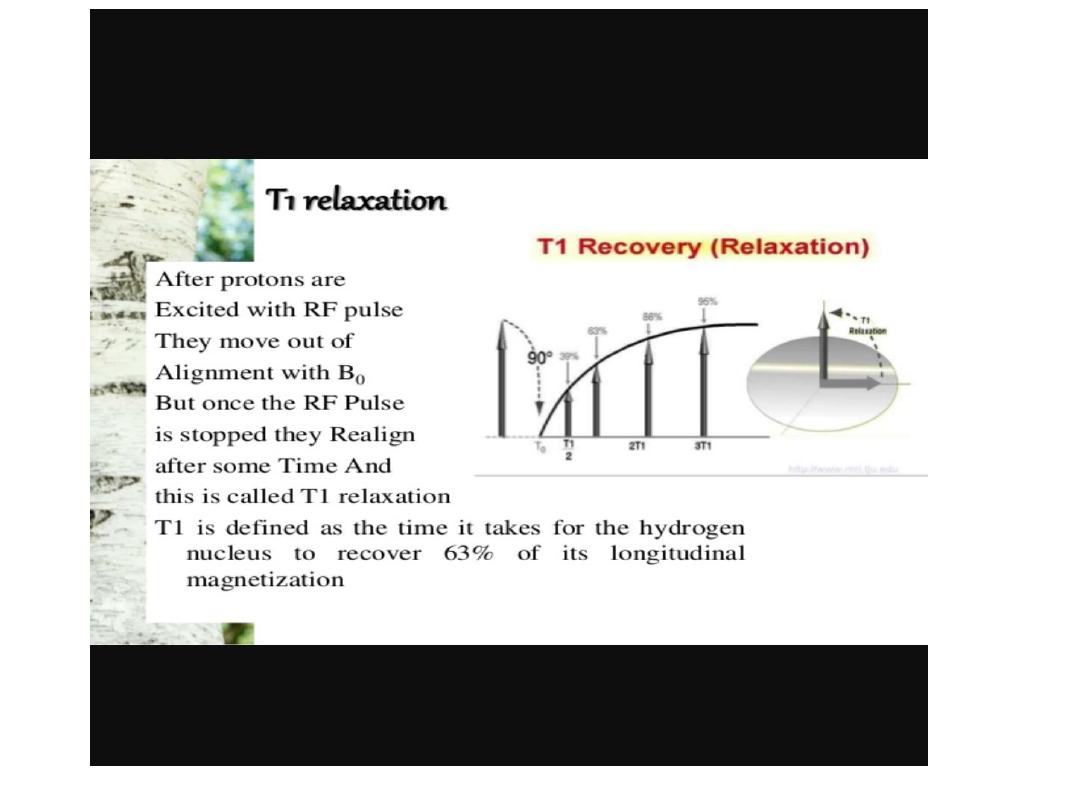
MRI
T1-depend on the time the protons takes to
return to the axis of magnetic fields.

T1 WEIGHTING
• • Short TR:
• – Maximizes T1 contrast due to different
degrees of saturation
• – If TR too long, tissues with different T1
all return equilibrium already
• • Short TE:
• – Minimizes T2 influence, maximizes
signal

SPIN DENSITY
• Signal at equilibrium proportional to
PD
• • Long TR:
• – Minimizes effects of different degrees of
saturation (T1 contrast)
• – Maximizes signal (all return to
equilibrium)
• • Short TE:
• – Minimizes T2 contrast -Maximizes signal

T2 WEGHTING
• Long TR:
• – Minimizes influence of different T1
• • Long TE:
• – Maximizes T2 contrast
• – Relatively poor SNR

MRI
Mean transfer of energy from the
protons to the tissue .

MRI
T2- depend on the time the protons take to
dephase .

MRI
T1 of tissue is longer than T2 of
tissue

MRI
• T2 is called transverse relaxation time, which
is the time for M_xy
• to decrease by 1/e.
• • Also called spin-spin relaxation time
• • T2 is much smaller than T1
• – For tissue in body, T2: 25-250ms, T1: 250-2500 ms

MRI
-Body fluid T1 is long compared to soft while
those of fatty structures are short
.
-Fluids have long T2 values than of soft tissues
and fat.

MRI
AT1-weighted images is one in which the
contrast between tissues due mainly to their
T1 relaxation propereties ,while in a T2-
weighted image the contrast between tissues
due mainly to their T2 relaxation
propereties .

MRI
Most pathological processes show increase T1 and
T2 relaxation times and these processes
therefore appear lower in signal (blacker )on a T1
–weighted scan and higher in signal (whiter ) on a
T2 –weighted scan than the normal surrounding
tissue

MRI
.
the T1 and T2 weighting of an image can be
selected by approperiatly altering the timing and
sequences of radiofrequency pulses .

MRI
T1 weighted images used for anatomical details
(normal stracture )and T2 weighted images used
for pathological processes

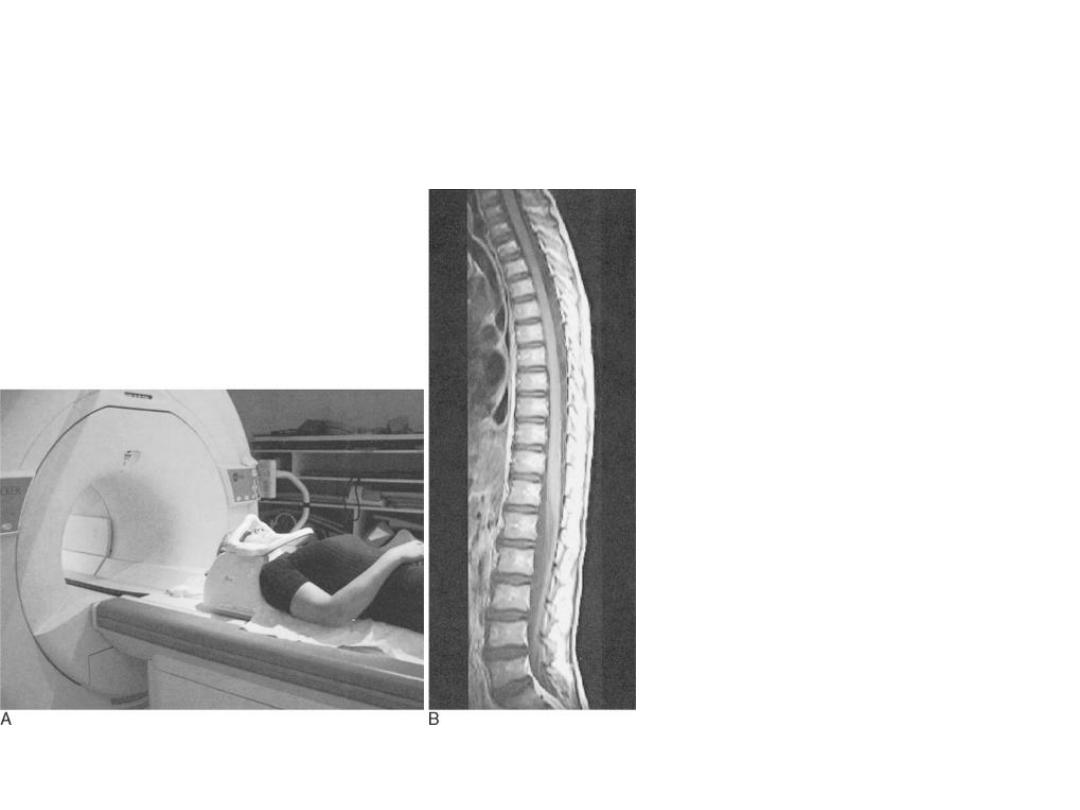
MRI SCANNER
Atypical MRI scanner consist of large circular
magnet.Inside the magnet are the
radiofrequency transmitter and receiver coils as
well as gradient coils to allow spatial
localization of the MRI signal .

MRI
Ancillary equipment converts the radiosignal
into adigital form which the computer can
manipulate to create image.

MRI
MRI scanner available now from 0.2 -8 Tesla
In our hospitals is 1.5 Tesla
MRI
MRI
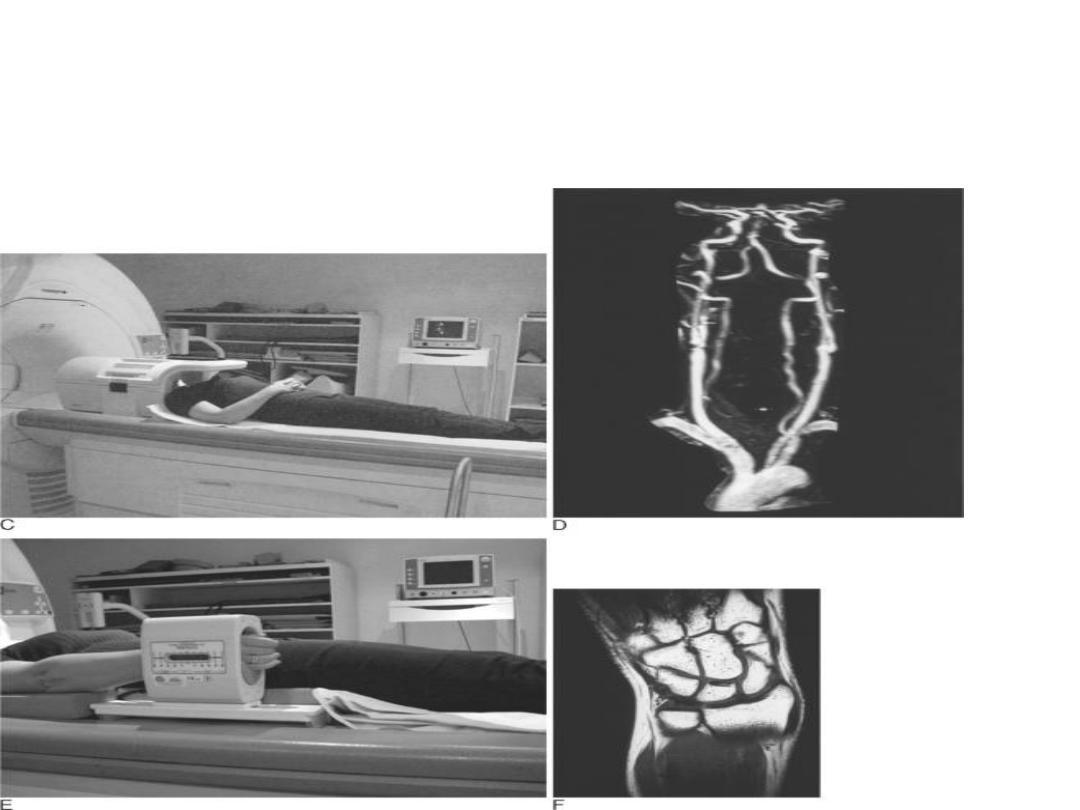
MRI

ADVANTAGES OF MRI
1-Information can directly imaged in any
plane .
2-No ionizaing radiation .
3-Bone and air do not produce artifact
4-Soft tissue contrast is high
5- Non invasive
6-No adverse biological effects .

DISADVANTAGE
1-Require longer scaning time comperd to CT scan ,so
the patient keep still during scaning procedure .
2-An avoidable movement from breathing cardiac
pulsation and perestalsis often degrade the image .

MRI
3-Strong magnetic field used mean that it is at
present contraindicated in patient with cardiac
pacemakers,intraocular metallic forign bodies and
certain types of aneurysm clip .
4-Acoustic noise .

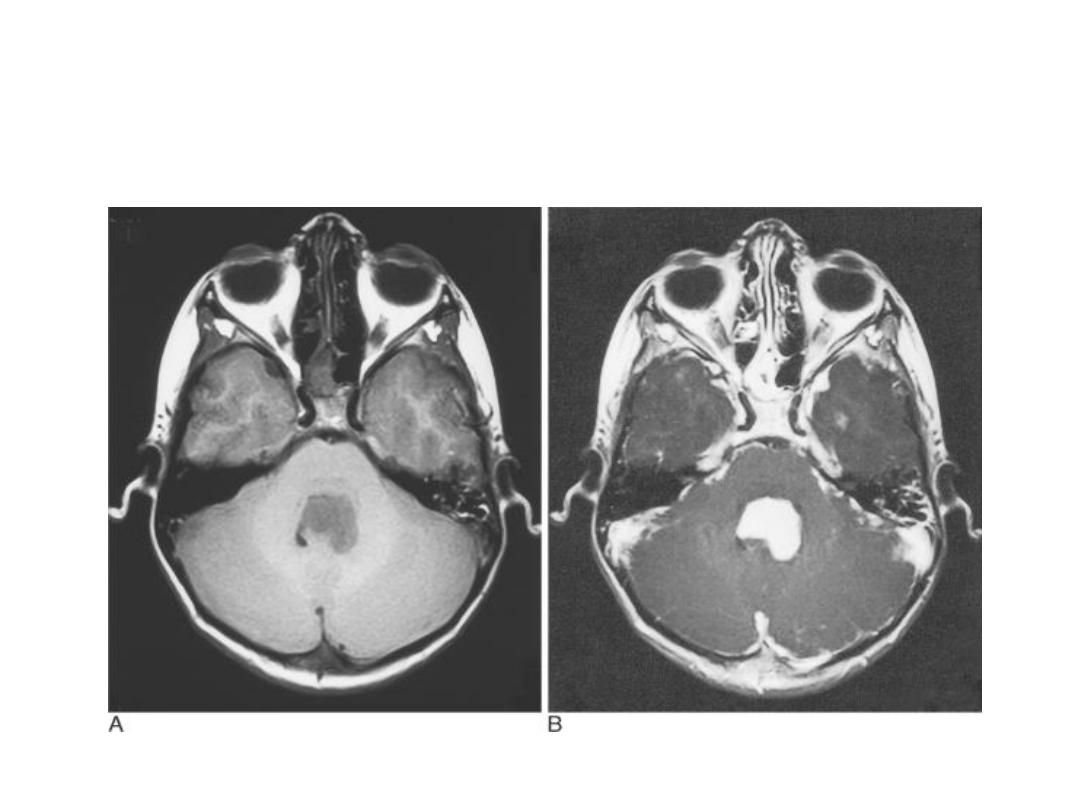
CONTRAST AGENT FOR MRI
Contrast agent providing useful diagnostic information
with MRI .
The most widly used agents are gadolinium compounds
which only cross the B.B.B. when it is damaged by
disease and which concentrate in tissue and diseases
processes with high blood supply .

MRI
Tissue which concentrate the agent show very
high intensity ( they appear white ) on T1 –
images .
Tissue specific media ,such as iron oxide agents for
reticuloendothelial cells imaging .
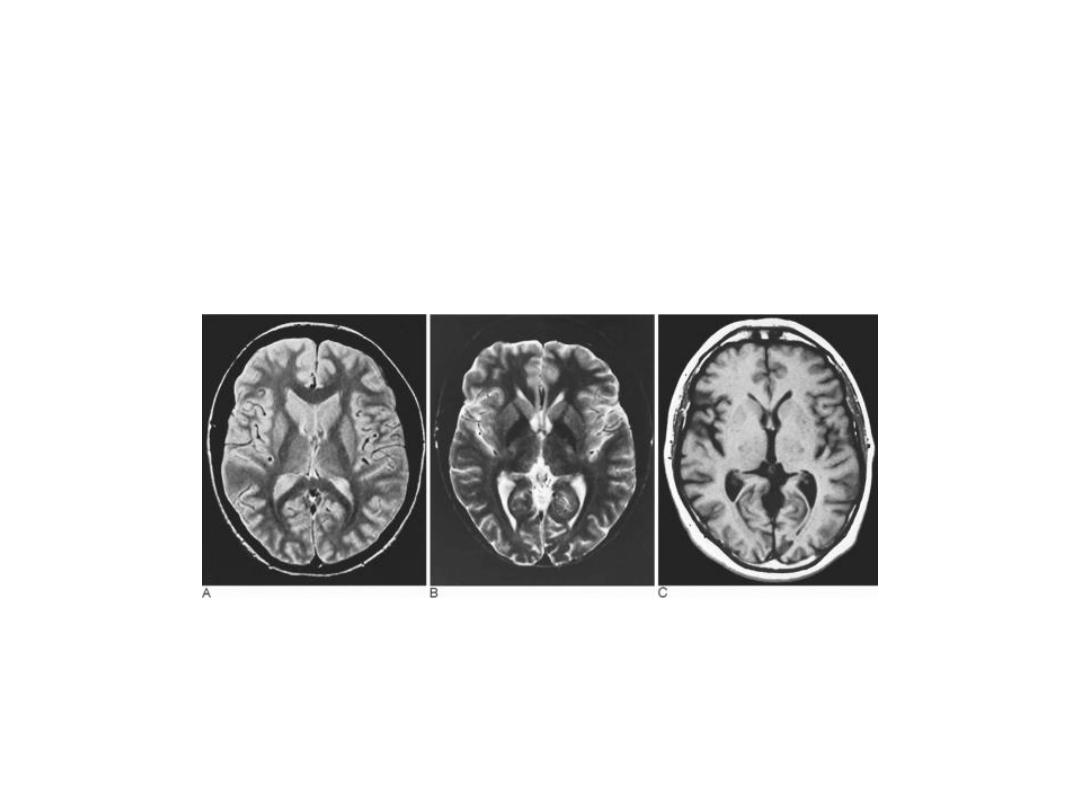
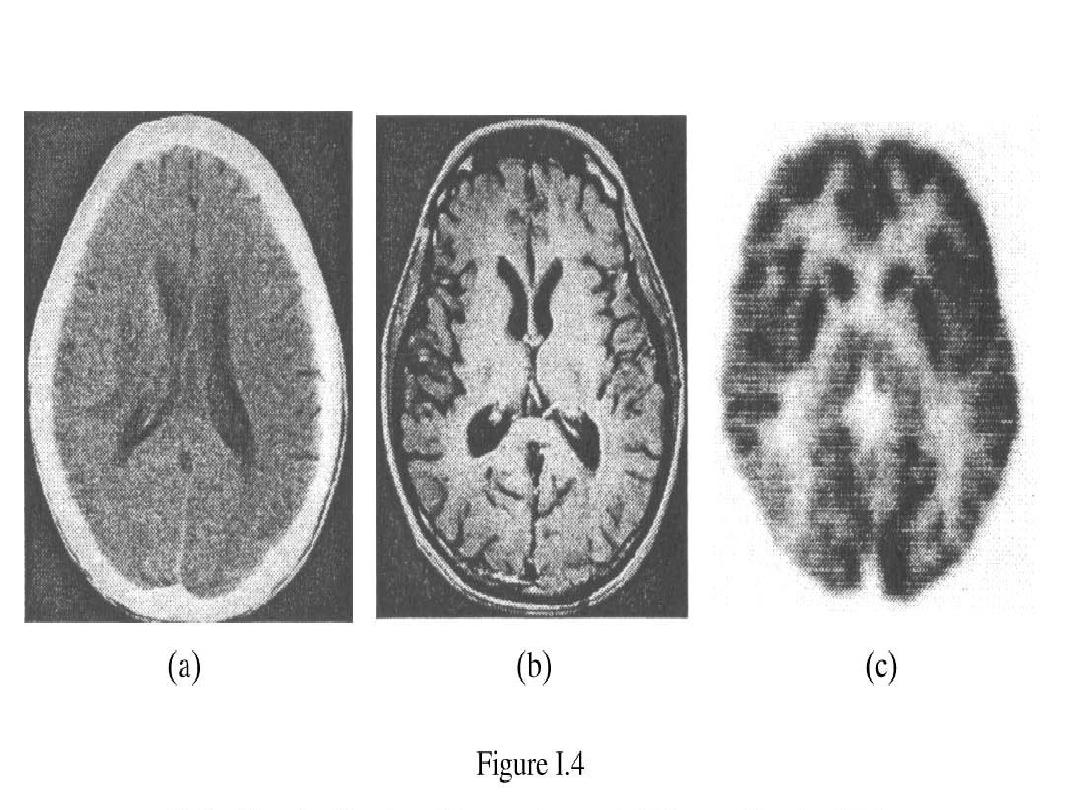
PD T2 T1
CT SCAN
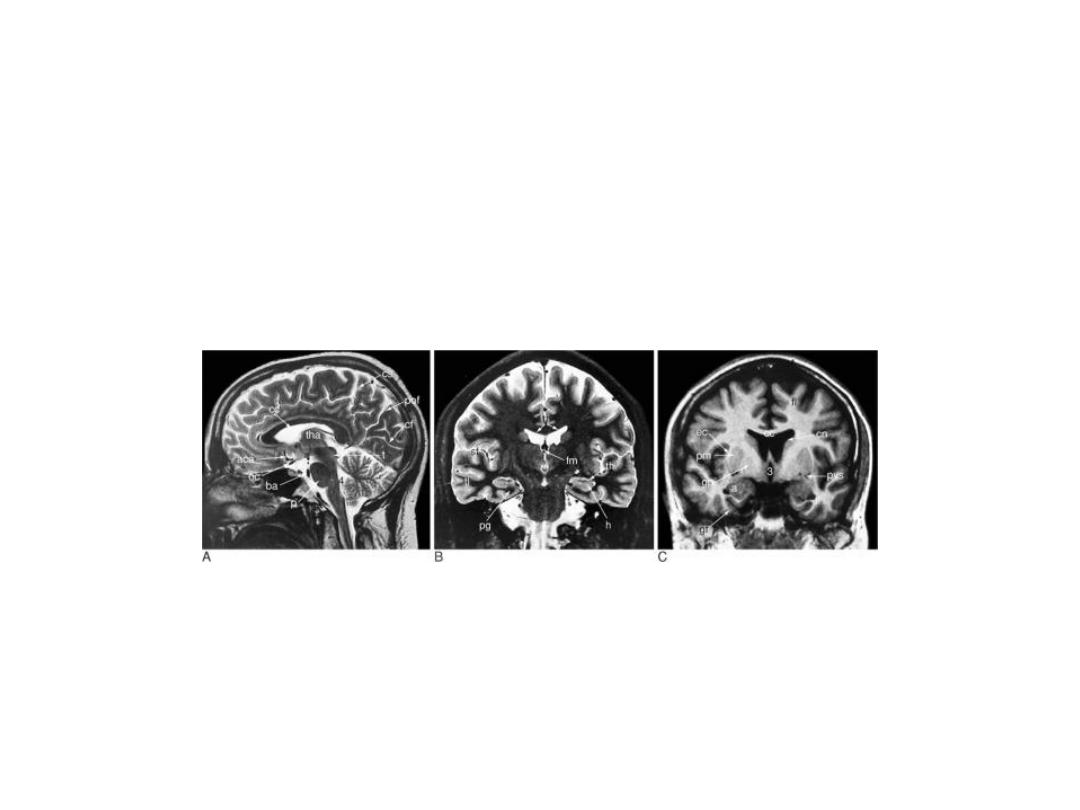
Sagittal coronal
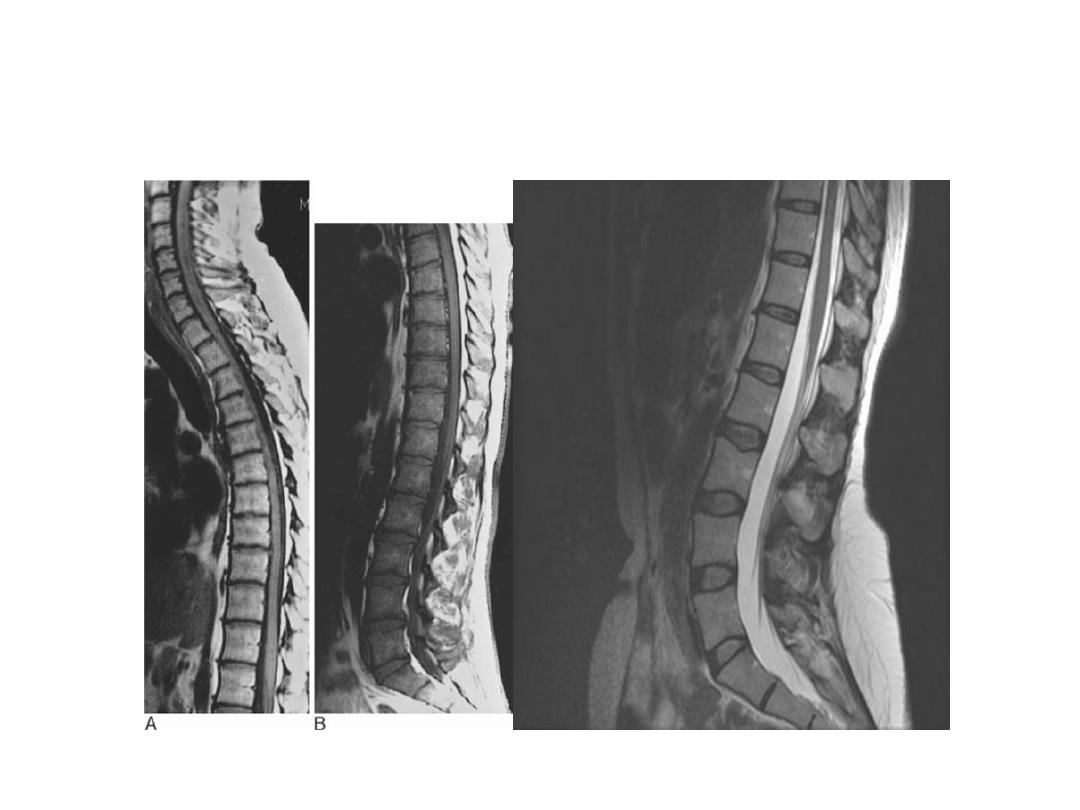
MRI
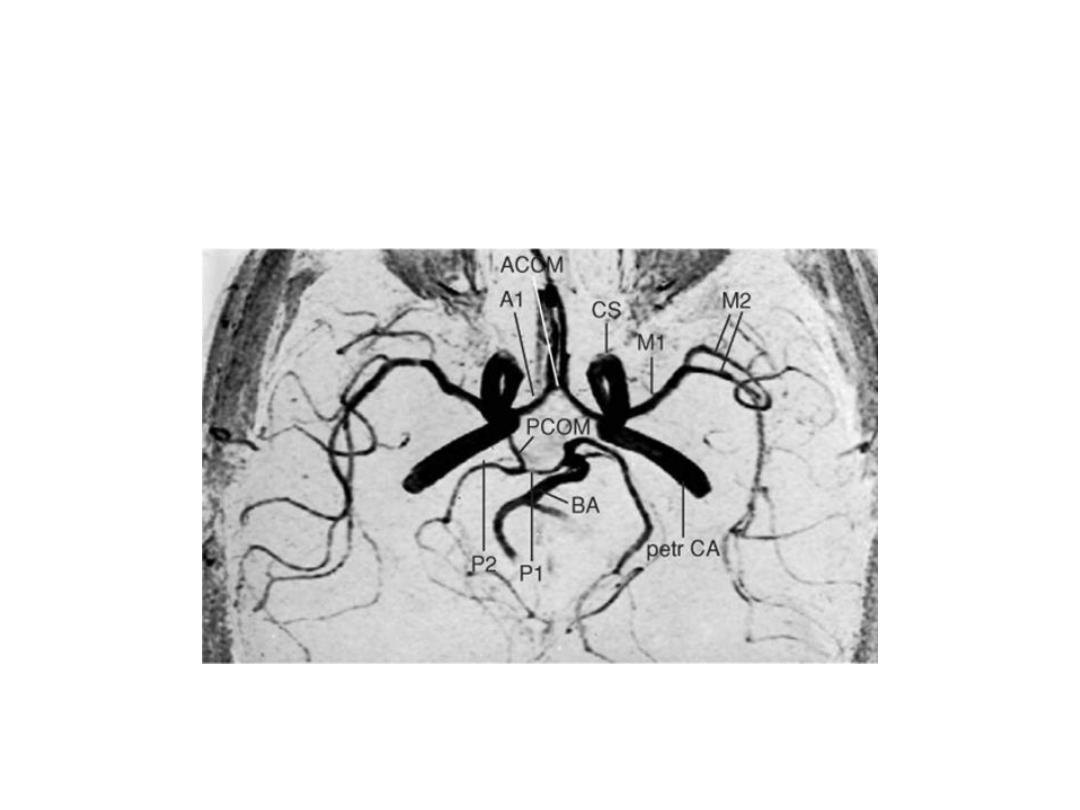
MRA
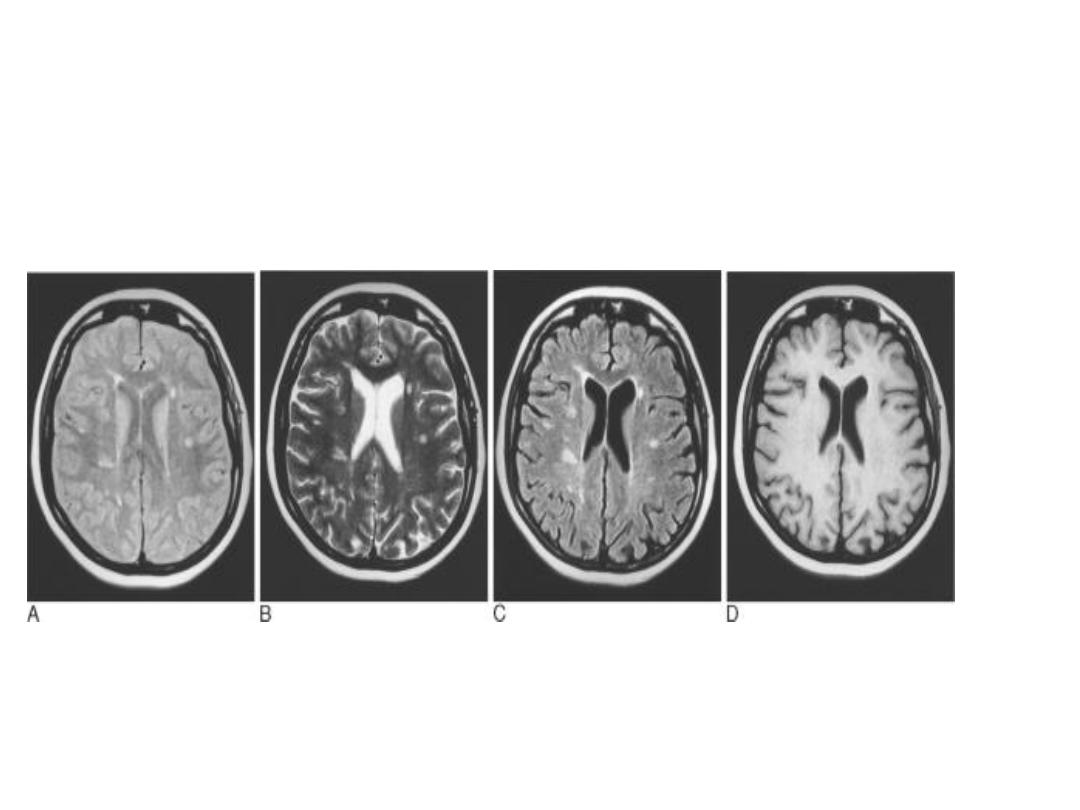
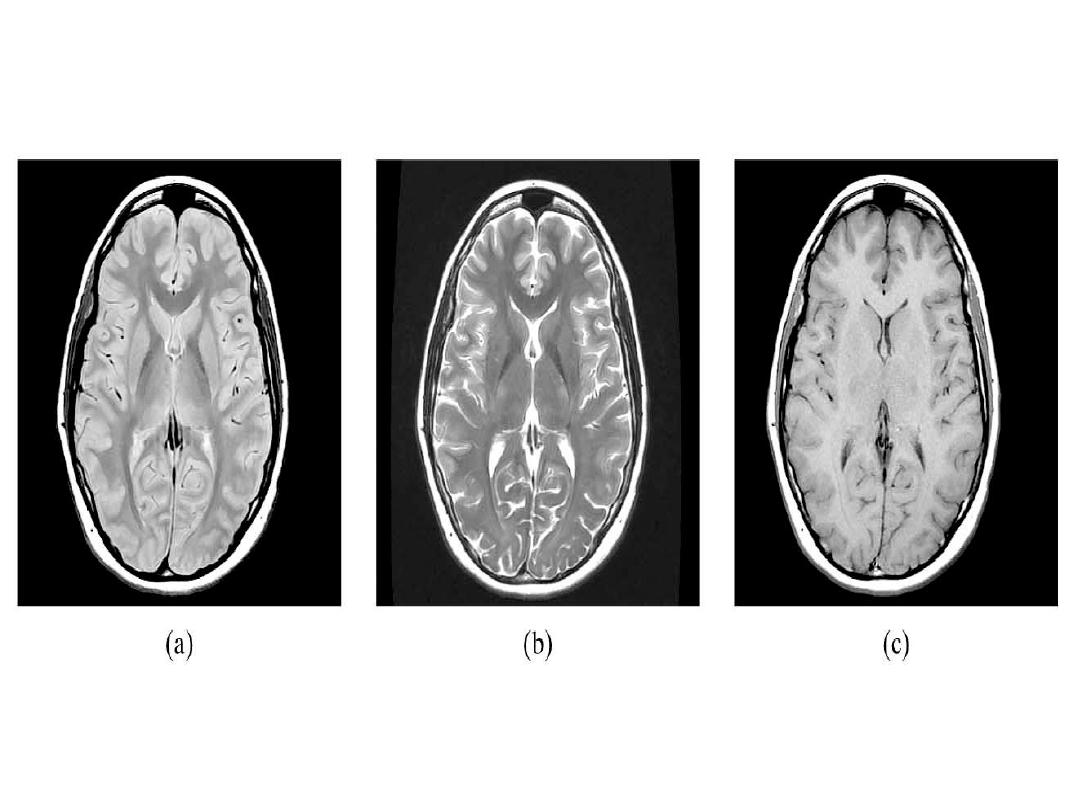
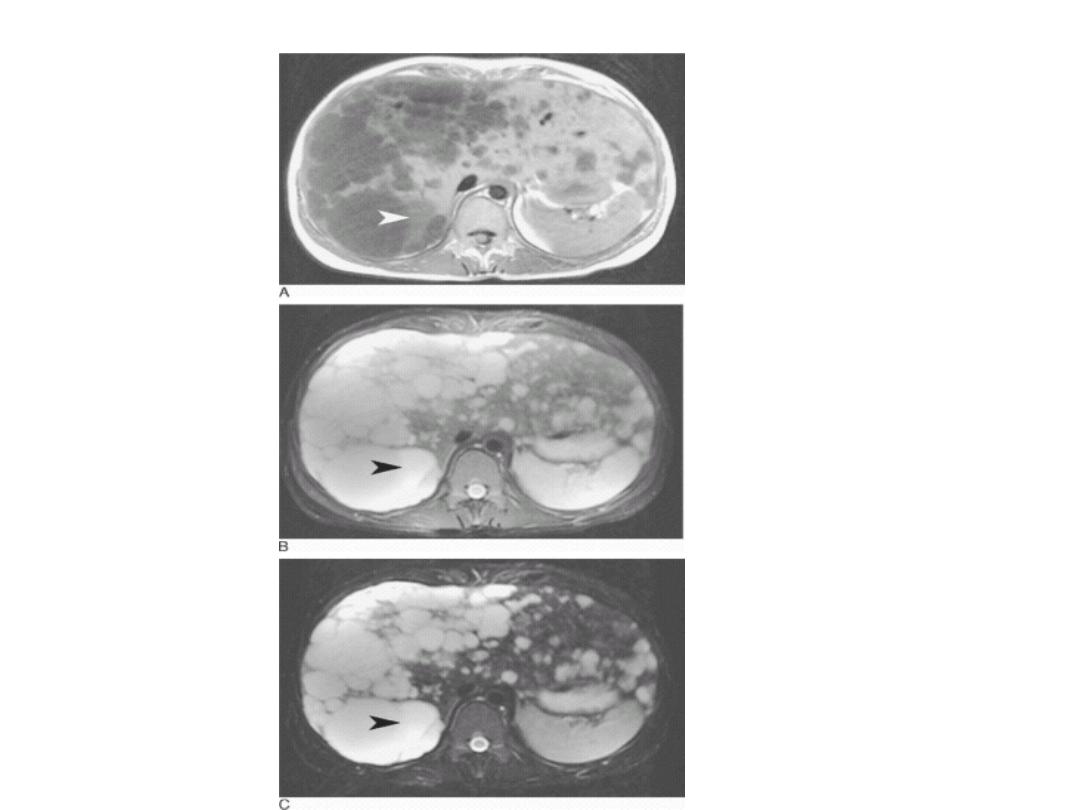
Patient with multiple sclerosis with plaques of demyelination
shown on (A) fast spin-echo (FSE) proton density; (B) FSE T2;
and (C) FSE FLAIR. There is no discernible abnormality on T1-
weighted images without contrast
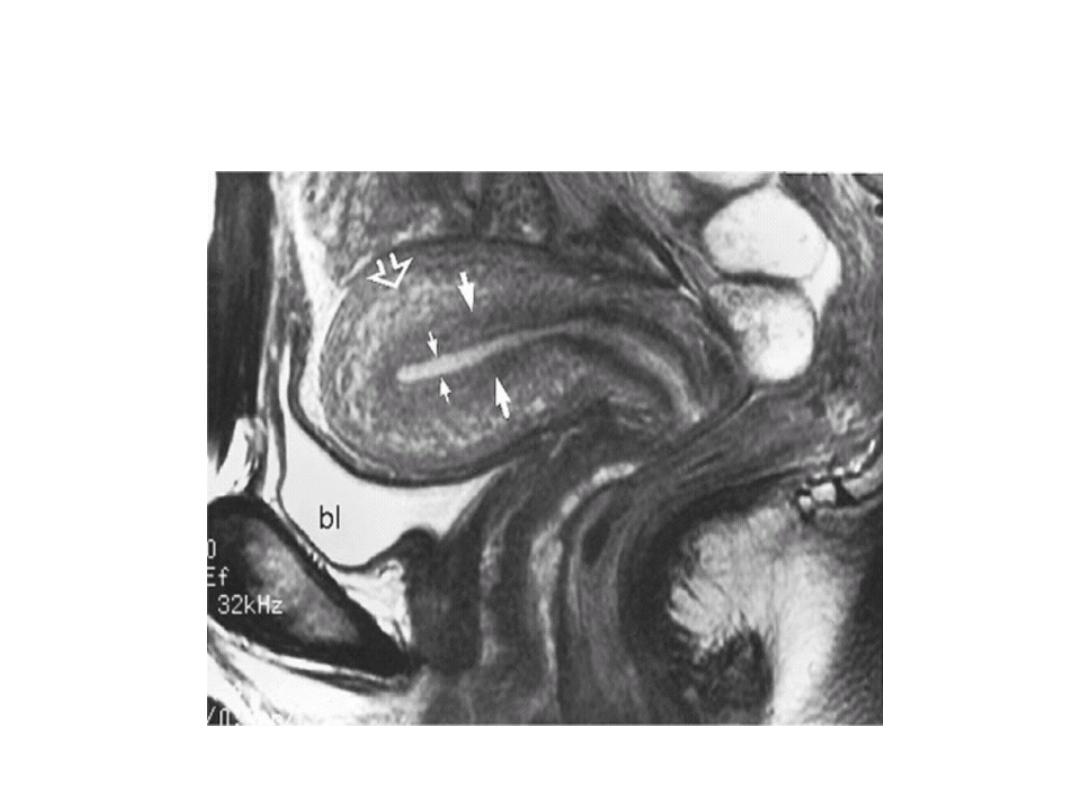
MRI
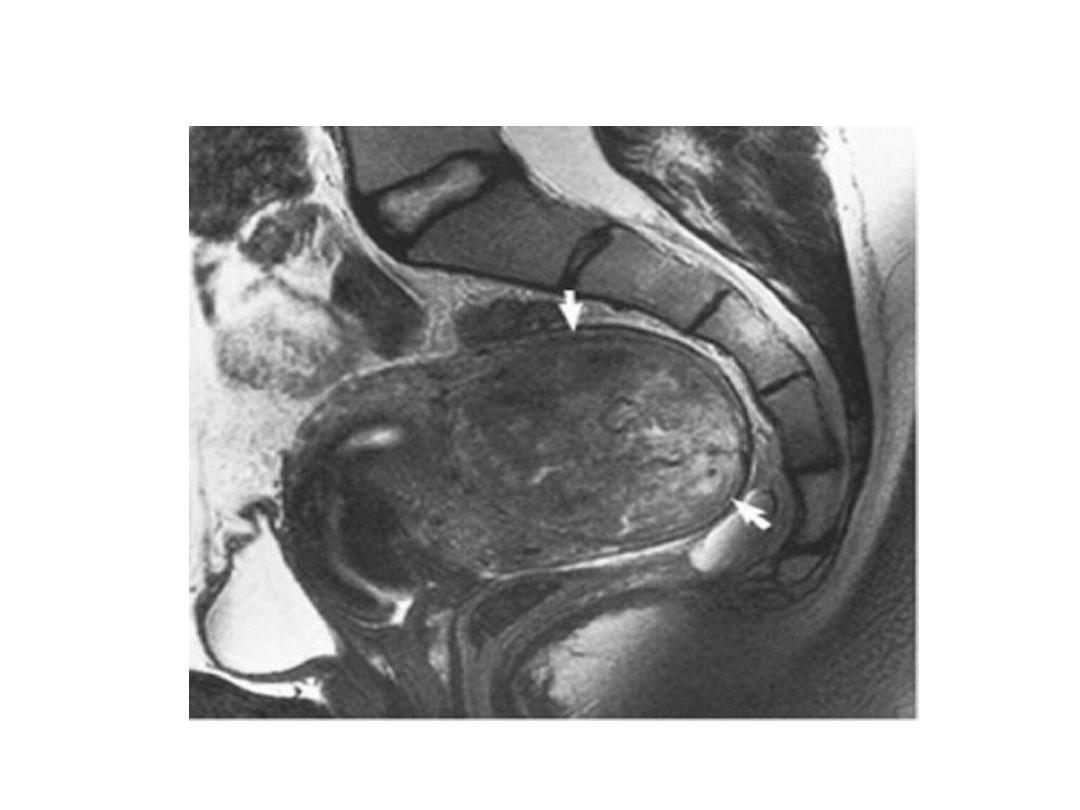
MRI
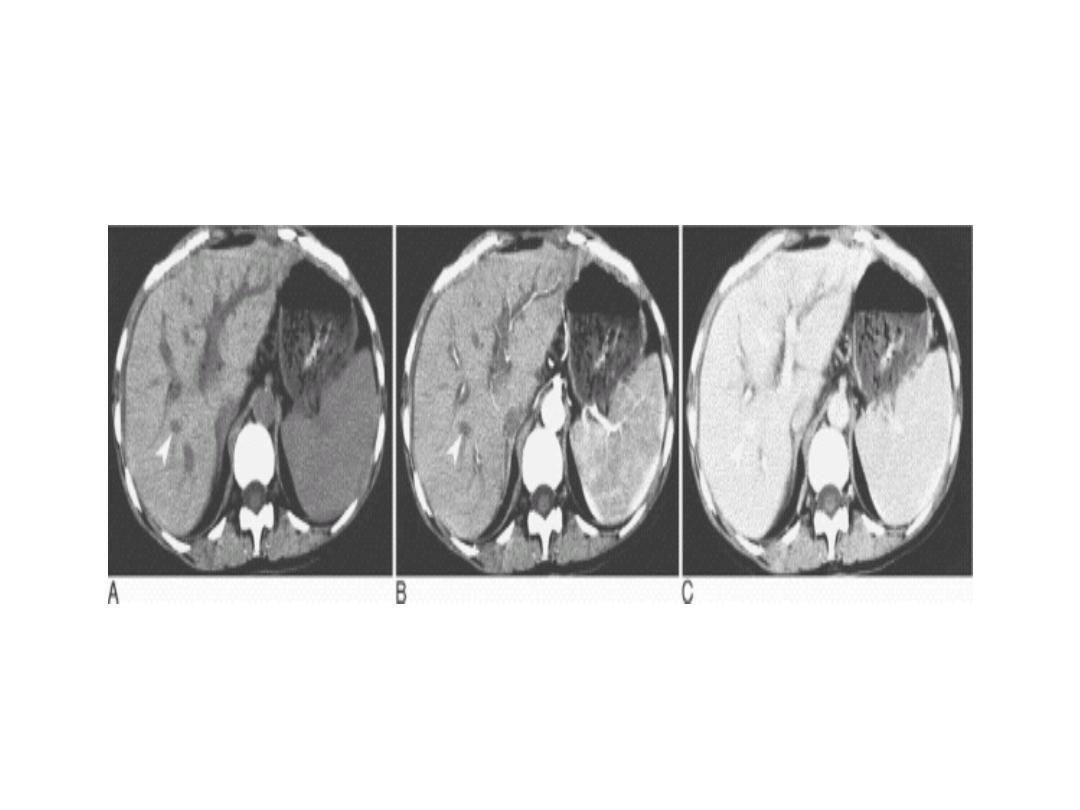
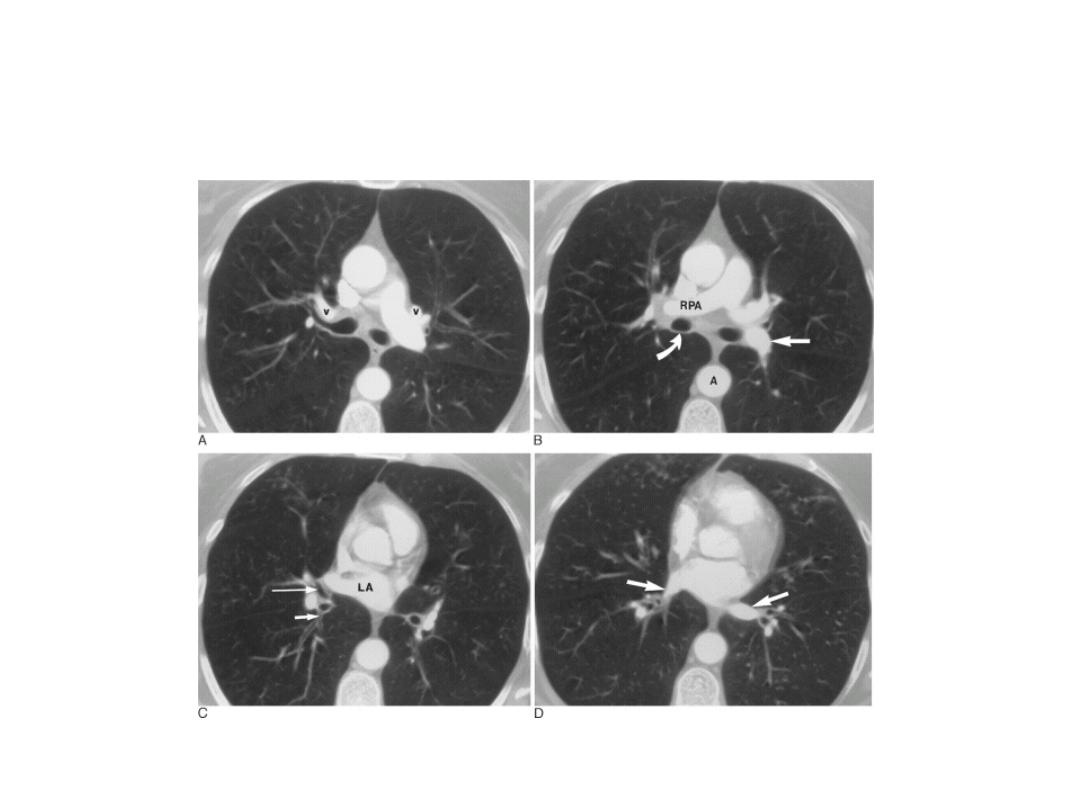
CT SCAN
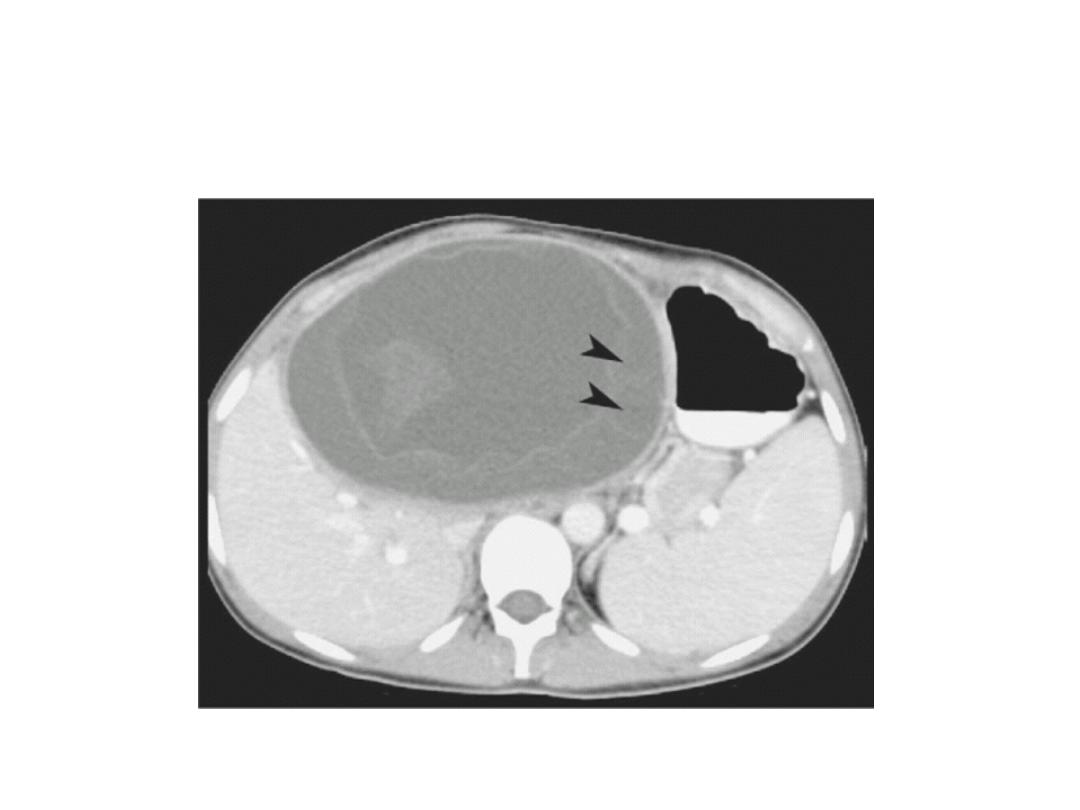
CT SCAN
MRI
CT SCAN
MRI
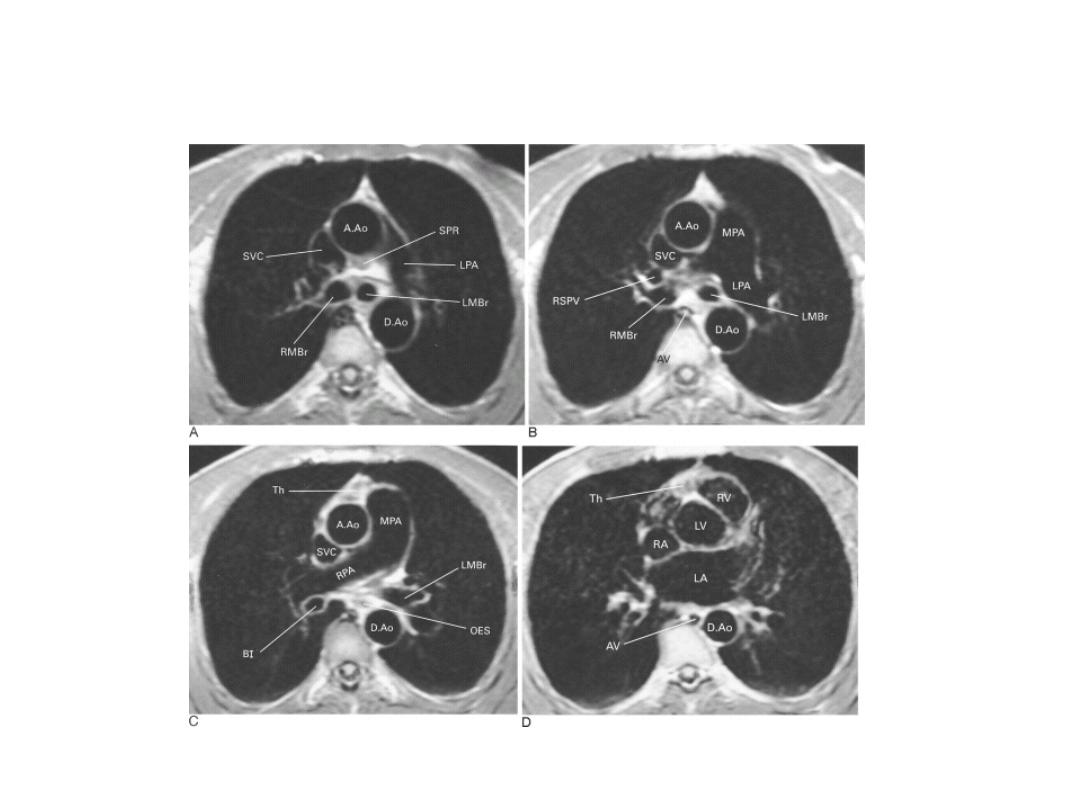
MRI
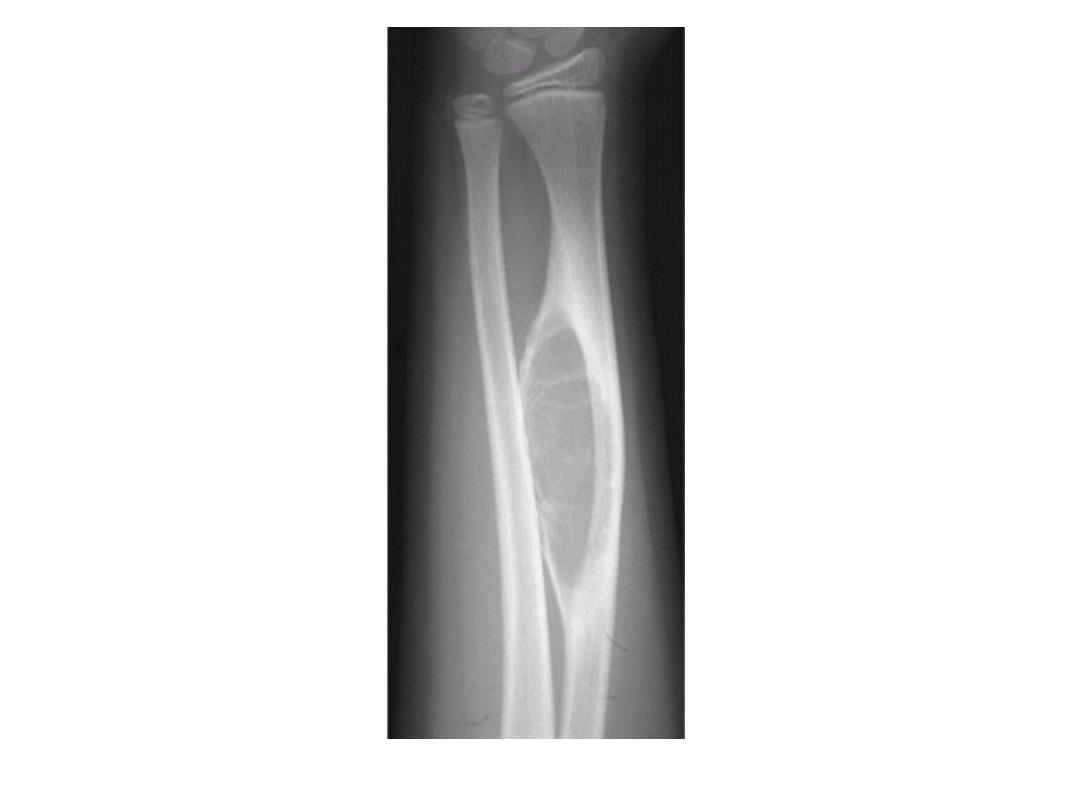
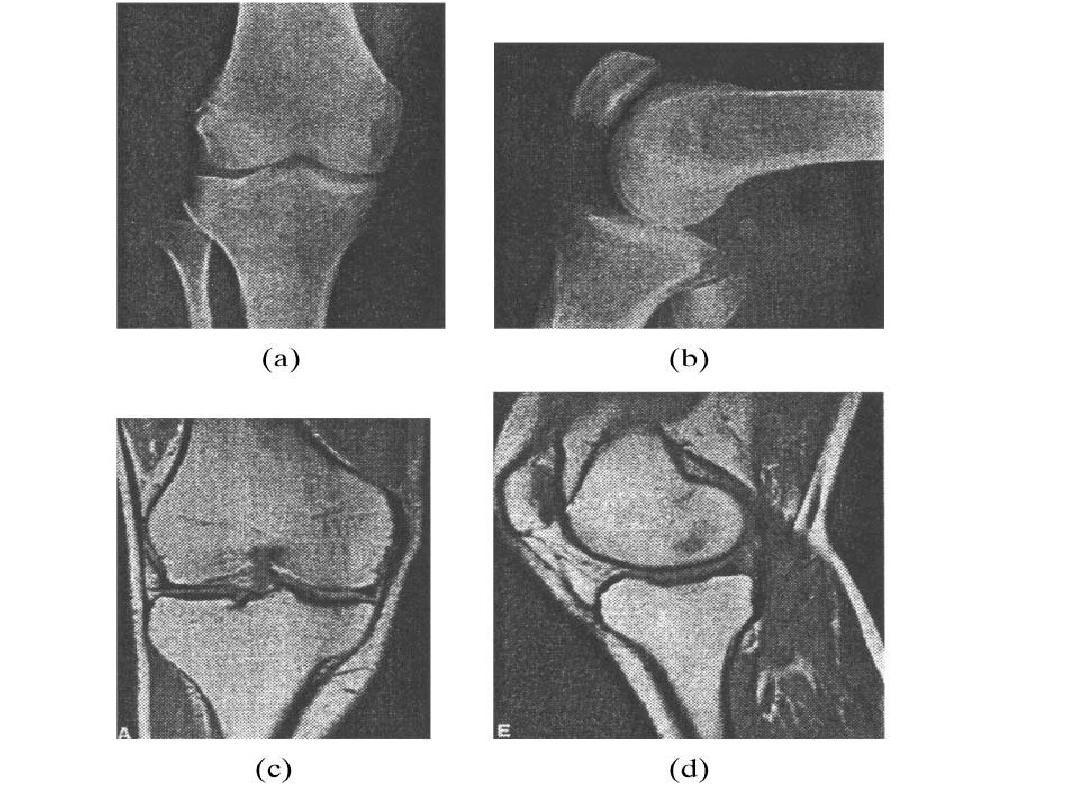
PLANI X-RAY
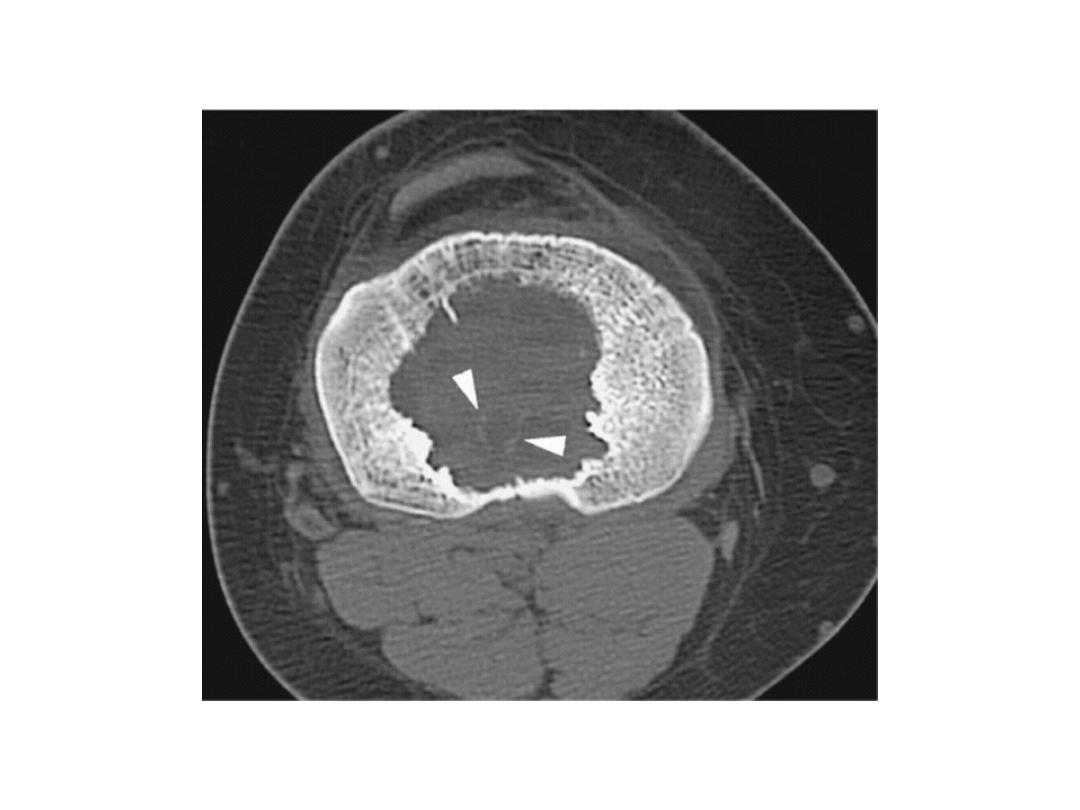
MRI
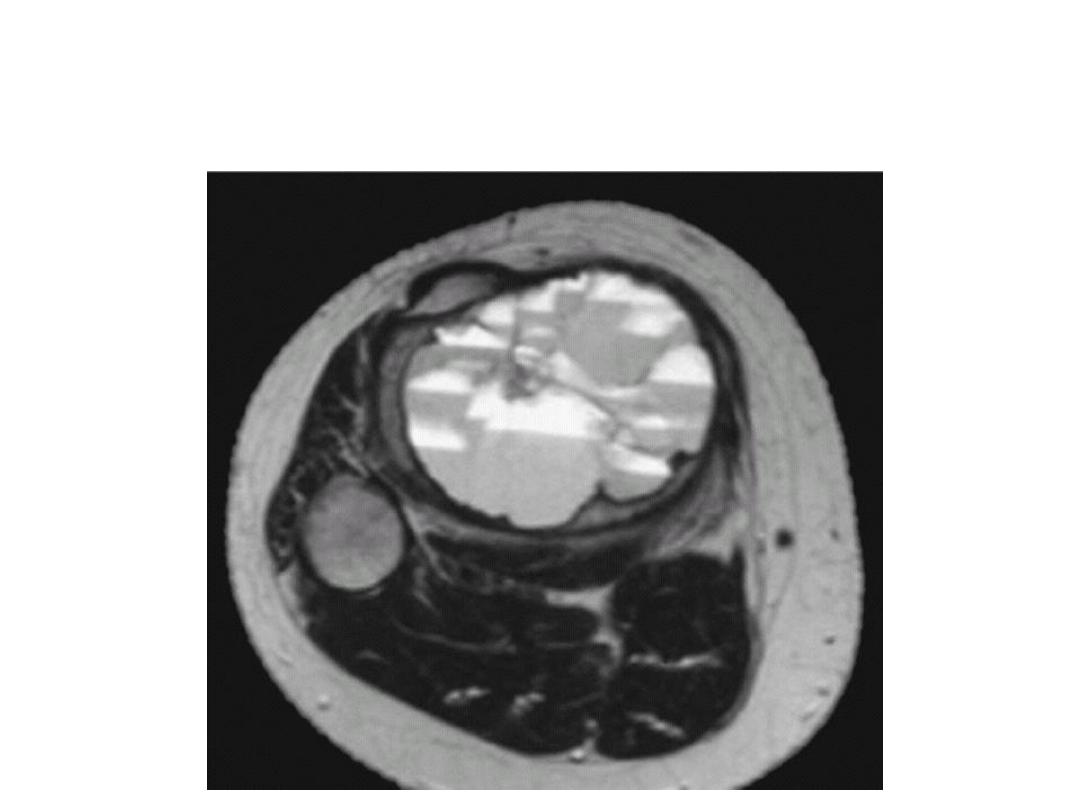
MRI
