
Urinary system
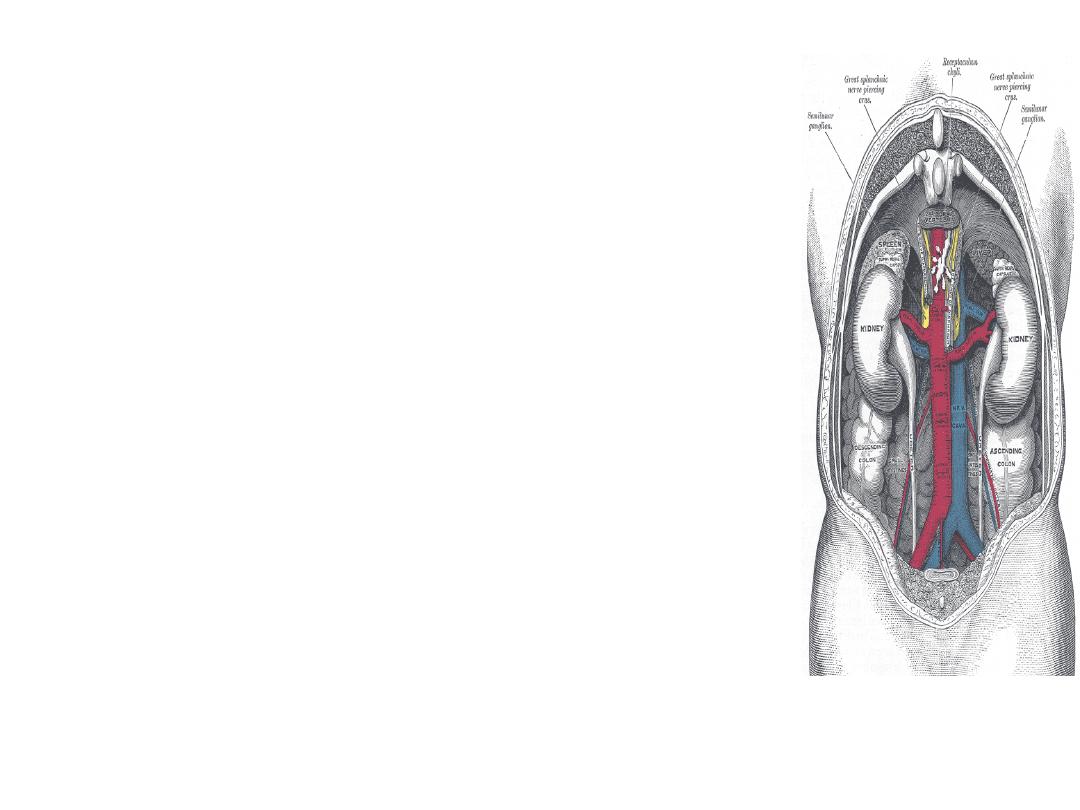
Anatomy
• Kidneys are retroperitoneal,
– T 12 – L 4
• Left
– inferior-medial to the spleen
– Abuts pancreas, stomach and bowel
• Right
– posterio-inferior to liver and
gallbladder
• Adrenal glands
– superior, anterior, medial to each
kidney
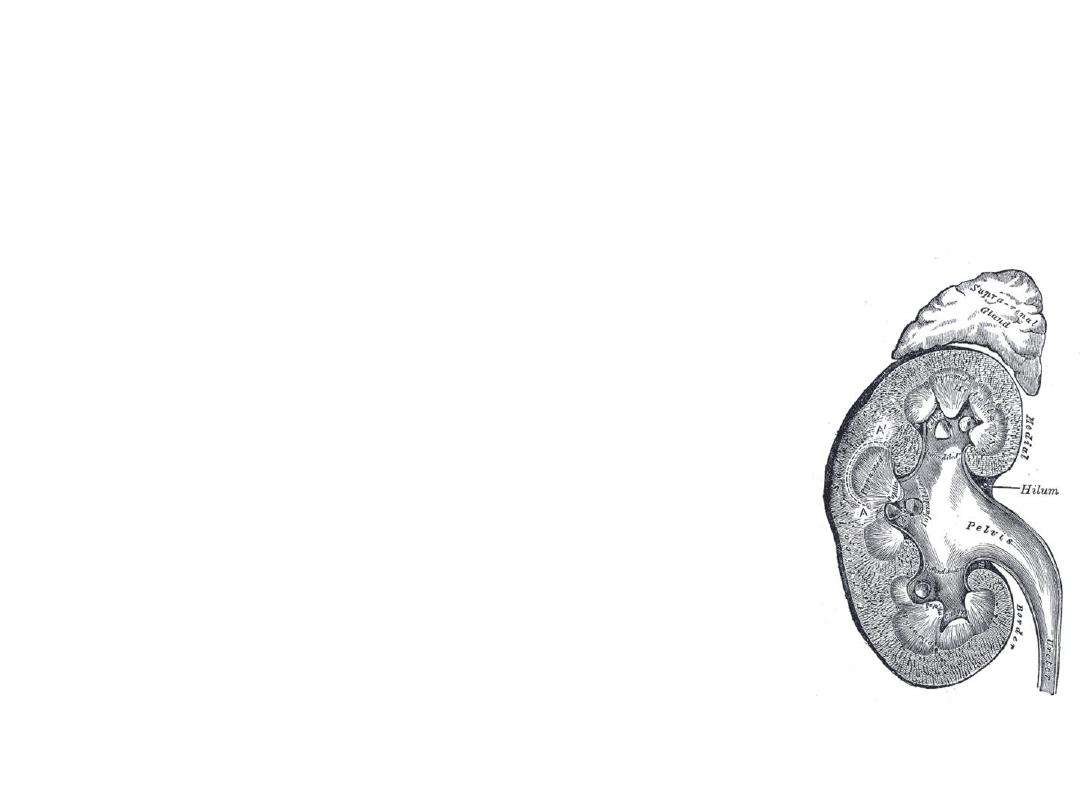
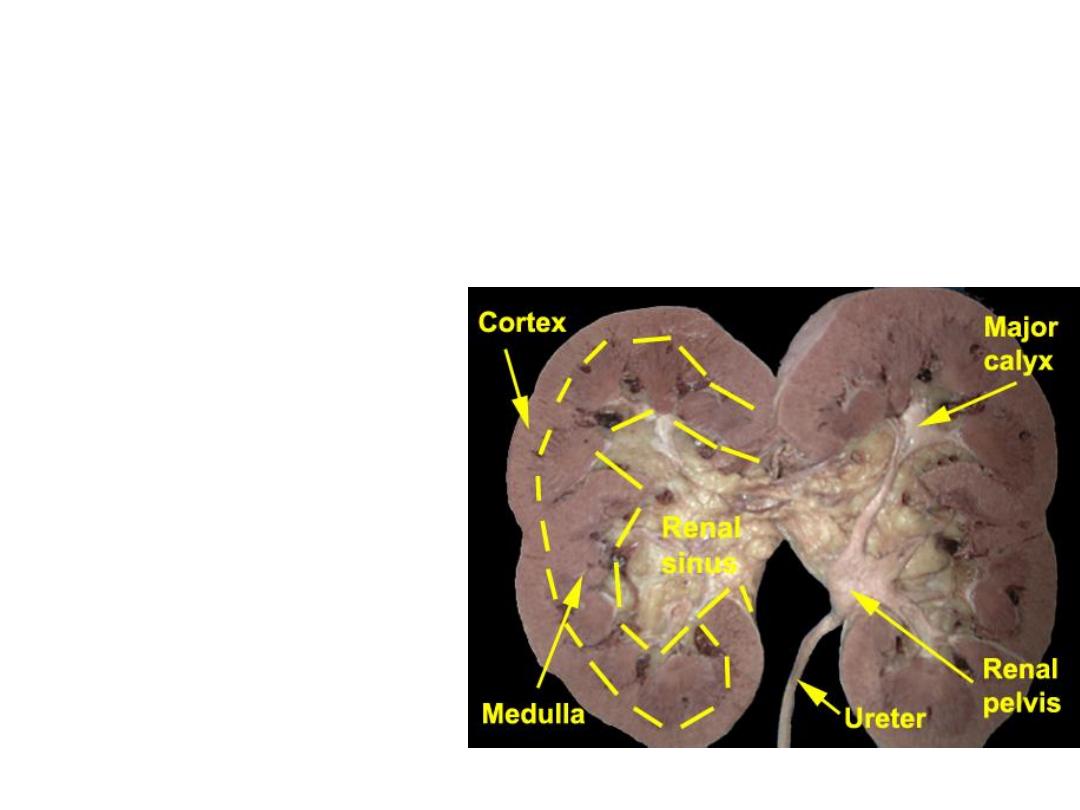
Anatomy
• Typical renal
– 9-12 cm long, 4-5 cm wide, 3-4 cm thick
• Sinus
– Hilum: vessels, nerves, lymphatic, ureter
– Pelvis: major and minor calyces
• Parenchyma surrounds sinus
– Cortex: nephrons
– Medulla: pyramids formed from collecting
ducts, separated by Columns of Bertin
• Capsule surrounds parenchyma
•
Gerota’s fascia encloses all + fat
Normal Ultrasound
• Cortex – + echo<liver
• Medulla
– Pyramids -
hypoecho
• Sinus - + echo
• Pelvis - black
• Capsule - + echo
• Ureter - ?

Pathological Findings
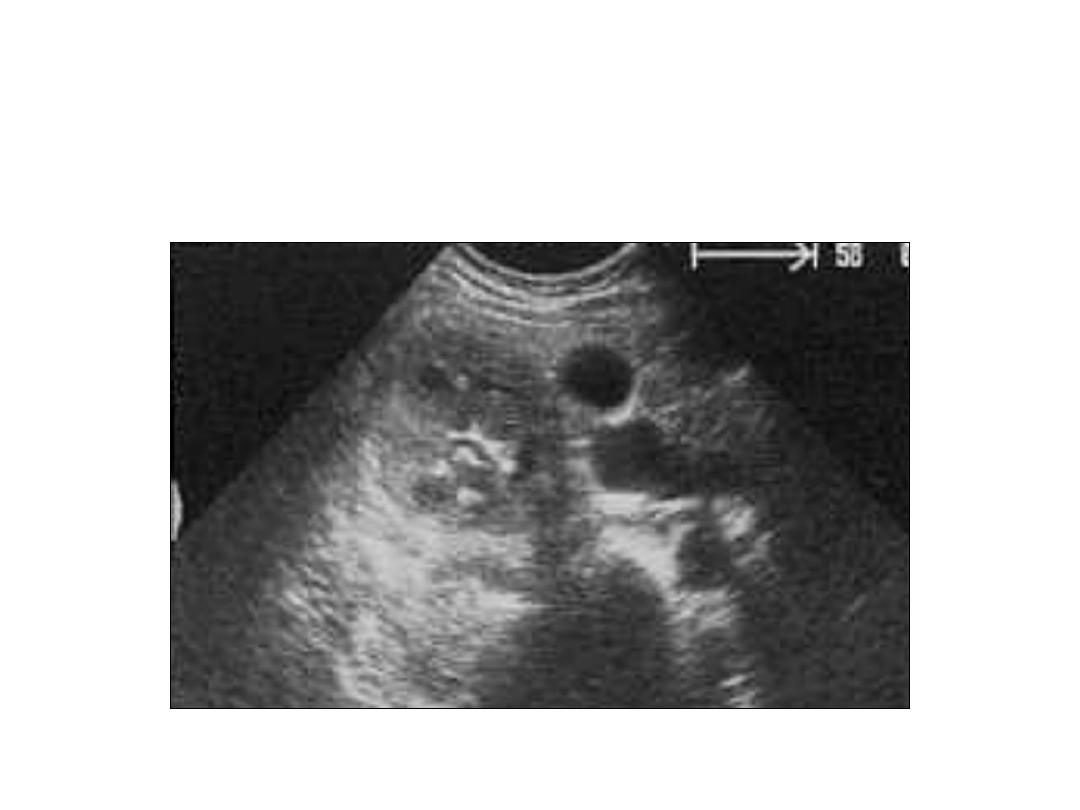
• Renal Cysts
– single, oval, sharp, anechoic
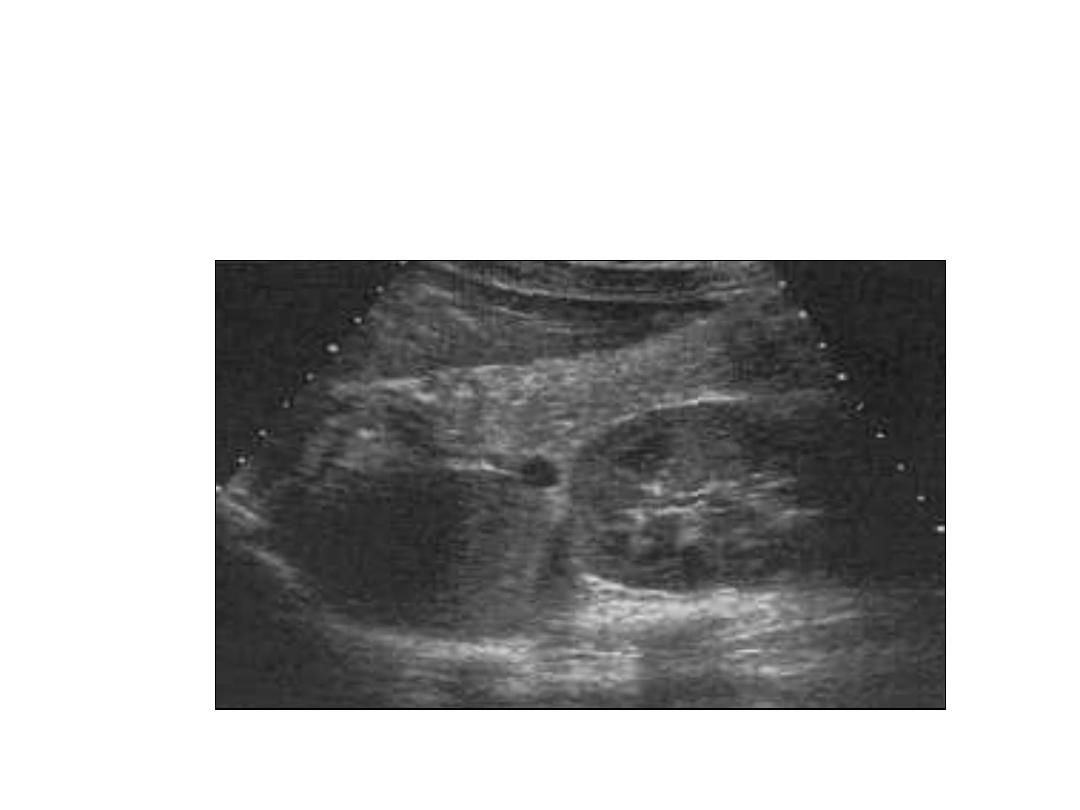
• Multiple cysts
– PKD
• Masses
– Irregular borders and ill-defined – RCC?
• Adrenal Mass
• Renal Trauma
– Hematomas Subcapsular /Perinephric
• Renal Abscess
– Hypoechoic with septations or granulation
• Pyelonephritis
– Usually normal appearing
– May see faint hyperechoic extension of sinus into cortex

Renal masse
•
Single mass:
include:-Tumors renal cell ca.
-Renal cyst.
-Hypernephrorna.
-In children: WiIm’s tumor
that could be (unilateral or bilateral).
Multiple:
-polycystic kidney disease
-multiple renal cortical cyst.
-multiple hydatid cyst
-multiple renal abscesses.
-multiple metastasis.
-lymphoma (lymphocytic infiltration -
diffuse
investigation of Renal masse
• 1-U/S - simple non invasive (displays the kidney and
outline) By U/S:
-the cyst appears echolucent (echofree), through
transmission of the sound (known as acoustic enhancement
) very thin wall well defined mass.
-a cyst shows clear echoes from the front and back wall
with no intervening echoes and enhanced echoes behind
the cyst.
• A solid lesion also shows echoes from front and back wall
but there are also numerous echoes arising within the mass
,little or no acoustic enhancement,may be irregular outline
and contain calcification.

:
IV U
-
2
-Basic sign of renal mass:
• 1. Bulging of the renal outline .sometimes the
outline is indistinct so that
the bulge can not be appreciated I.
2. Displacement of major and minor calyces.
3.
Increase in renal size: particularly if the mass is at
the upper or lower pole where it is bulk adds to the
renal length.
-having Dx the presence of a mass an attempt may
be to Dx its nature.
• 4-round lucency in the nephrogram

Sign suggesting a cyst: (or benign lesion)
• 1. No opacification of the mass.
2. Clear cut border between the mass and the
adjacent parenchyma.
3.
A claw of parenchyrna pulled out by the
mass.

*
Sings suggesting a malignant tumor:
• 1.
Opacification of any part of the mass.
2. Indistinct border between the mass and adjacent
nephrogrm.
3. Any solitary mass in a young child.
4.
Calcification in the mass --

Infection of kidney
acute pylonepheritis :
• Non specific radiological sign
• Mainly increase renal size
• IVU is normal
• Decrease echogencity of kidney because of
oedema

Infection of kidney
acute pylonepheritis :
• Non specific radiological sign
• Mainly increase renal size
• IVU is normal
• Decrease echogencity of kidney because of oedema

Chronic pyelonepheritis :
• Decrease renal size
• IVU is abnormal
• Dilatation of pcs due to reflux
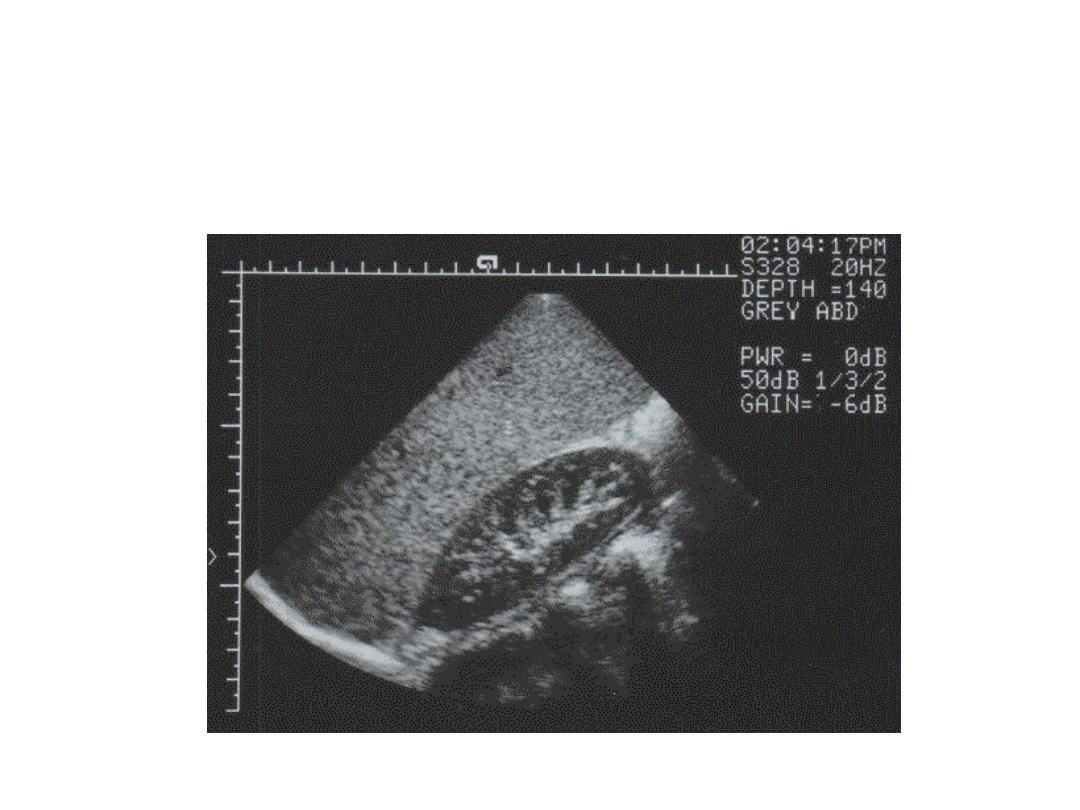
Right Kidney - Longitudinal
Right Kidney - Transverse
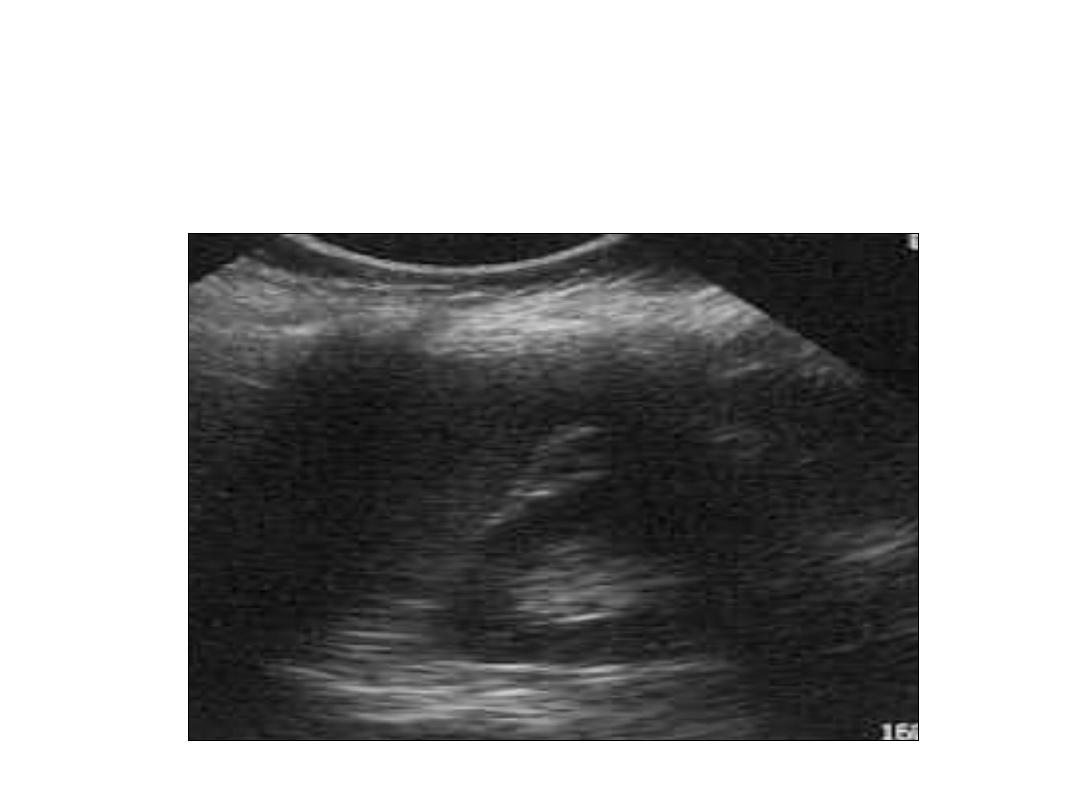
Left Kidney - Longitudinal
Left Kidney - Transverse

Renal Colic Evaluation
• Incidence 3% & 50% recurrence
• Affects 12% of US population
• Plain films sensitivity only 62%
• CT scan gold standard for stone visualization
• U/S for structure to see signs of obstruction

Renal Colic
• Rate of spontaneous stone passage by location
– 22% for proximal ureteral stones
– 46% for midureteral stones
– 71% for distal ureteral stones
• Rate of spontaneous stone passage by size
– 100 % for 1mm
– 80 % for 4 mm
– 55% for 5 mm
– 25 % for 7 mm

Hydronephrosis
• Many intrinsic and extrinsic causes
– Bladder retention
• Highly predictive of stone if found
– Sensitivity 87-90%
– Specificity 90-93%
– PPV 90-92%
• Graded along spectrum of mild to severe
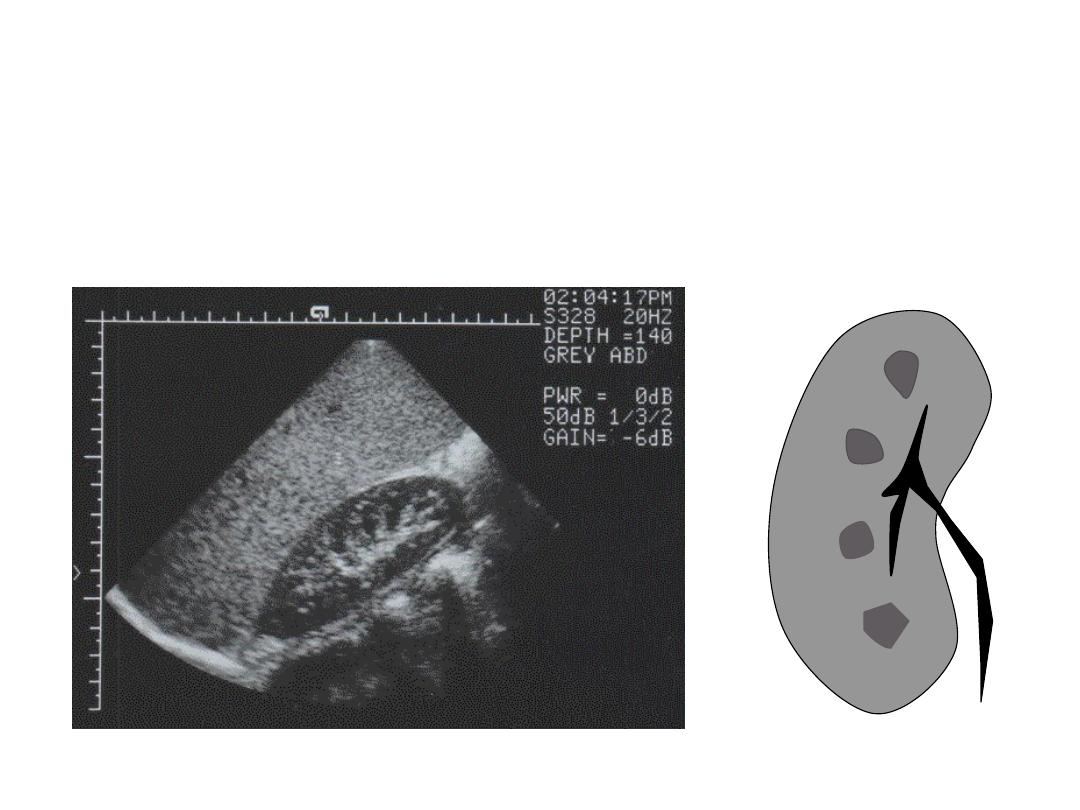
Range of Hydronephrosis
Normal
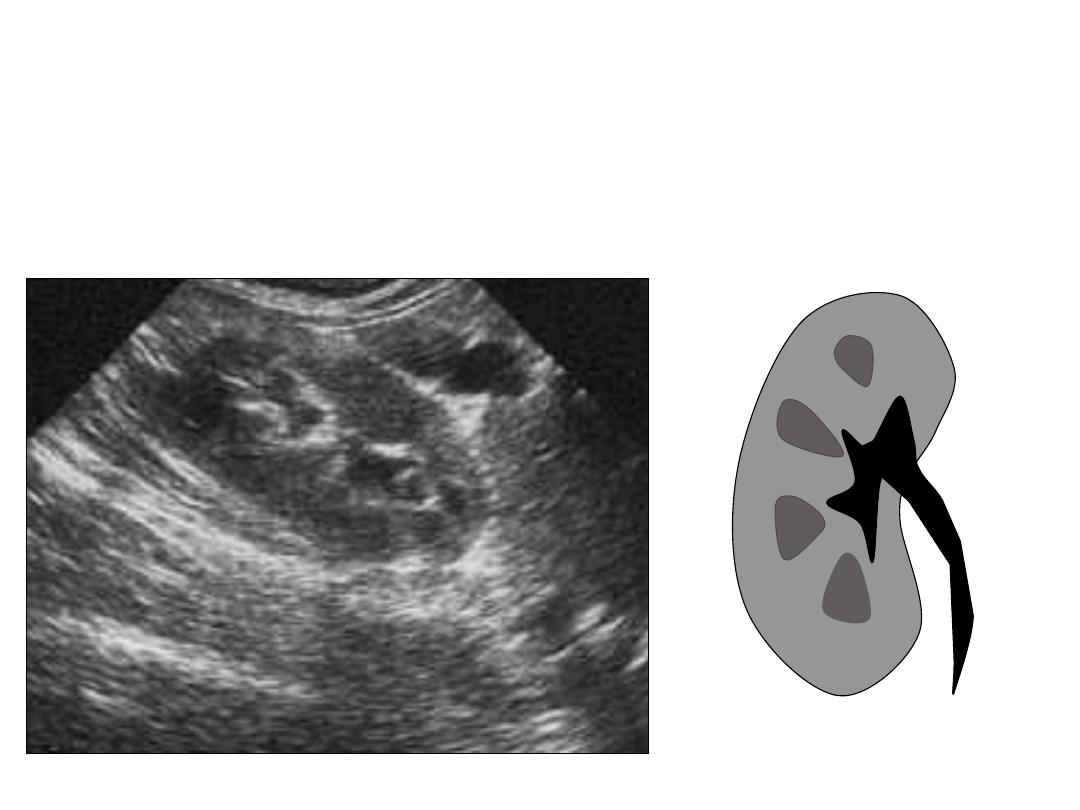
Mild Hydronephrosis
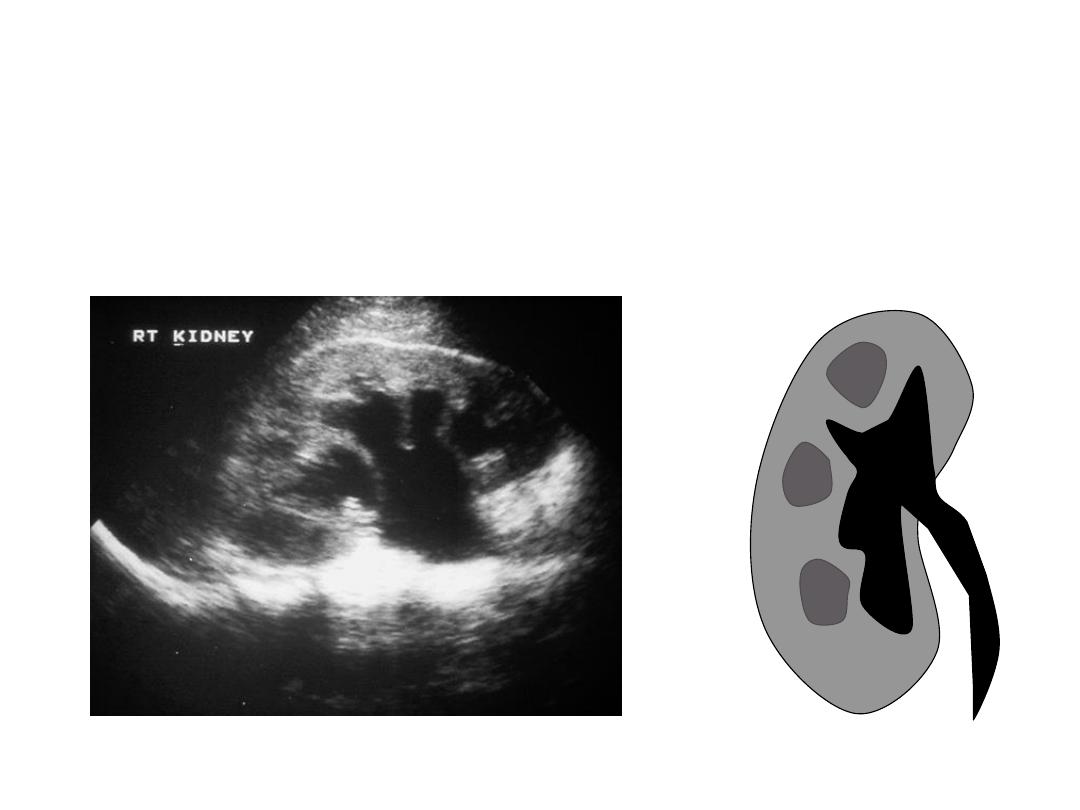
Moderate Hydronephrosis
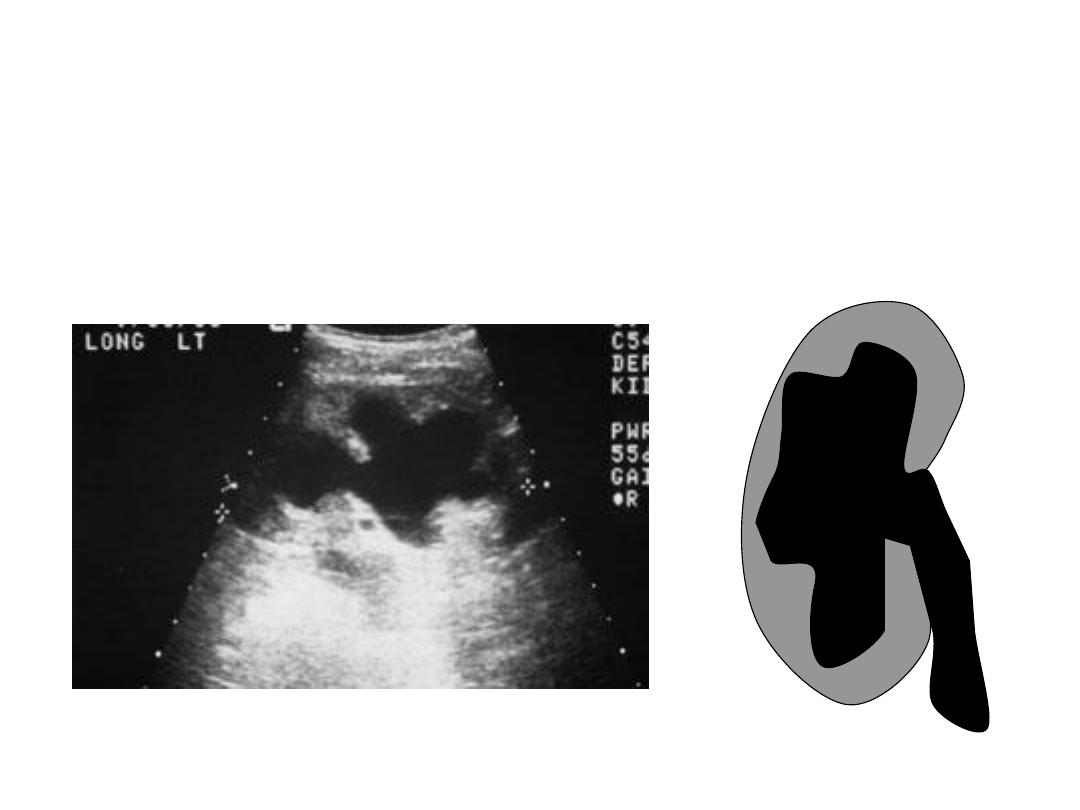
Severe Hydronephrosis
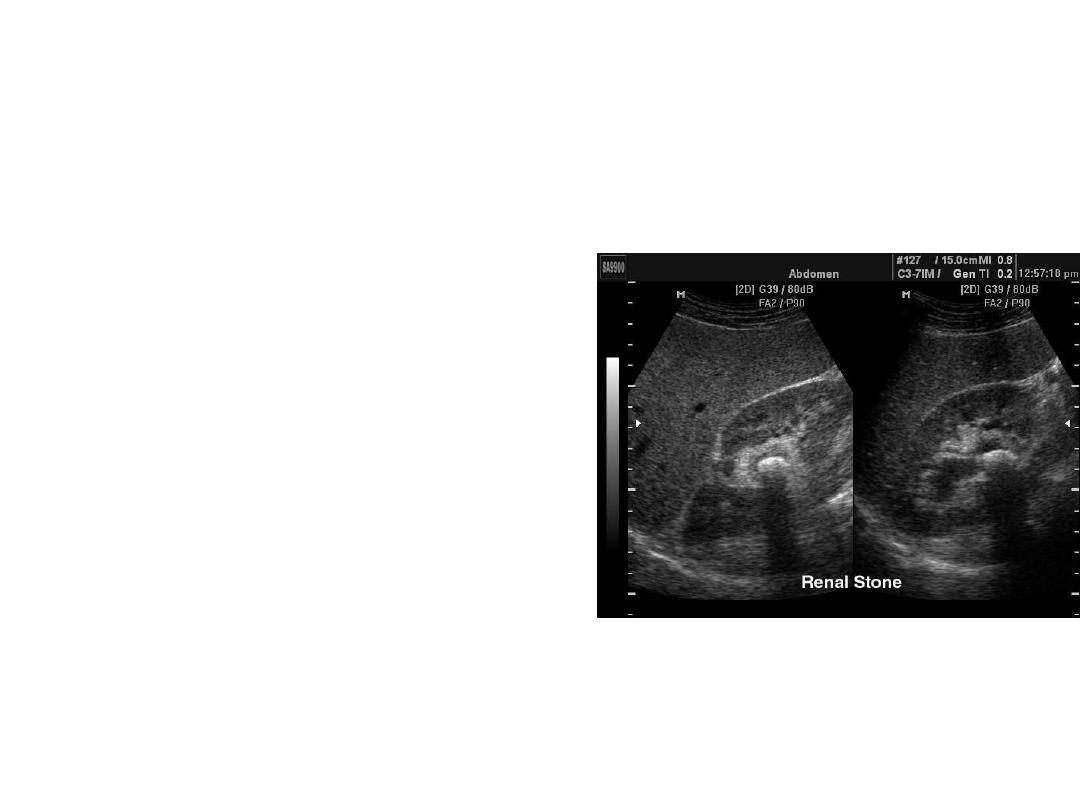
Nephrolithiasis
• Stones most commonly
found within kidney
– Rare to visualize in
ureter
– May be seen in bladder
or at UVJ
Nephrolithiasis
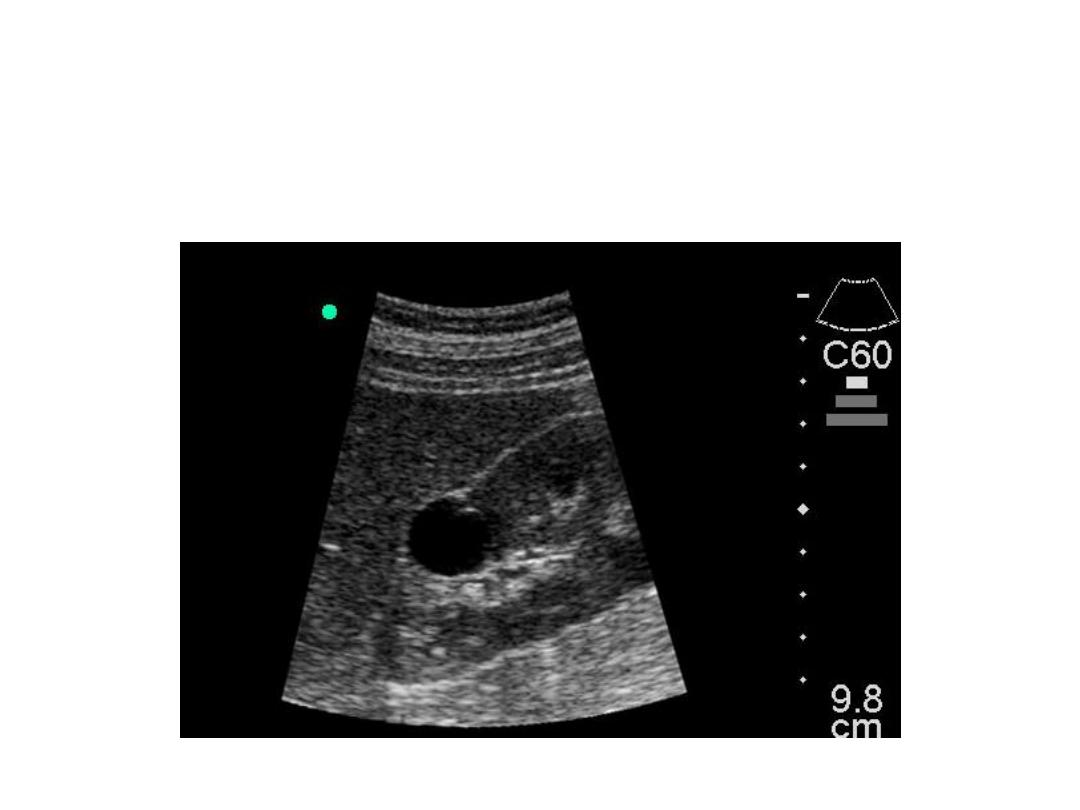
Simple Renal Cyst
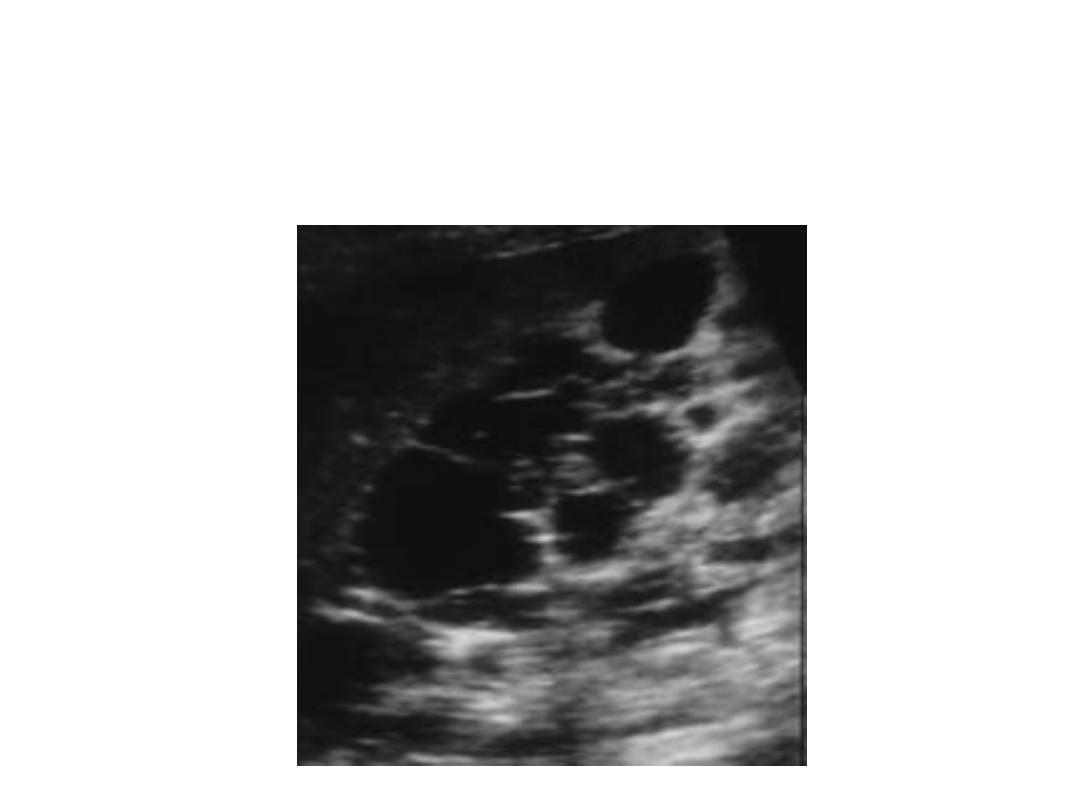
Polycystic Kidney Disease
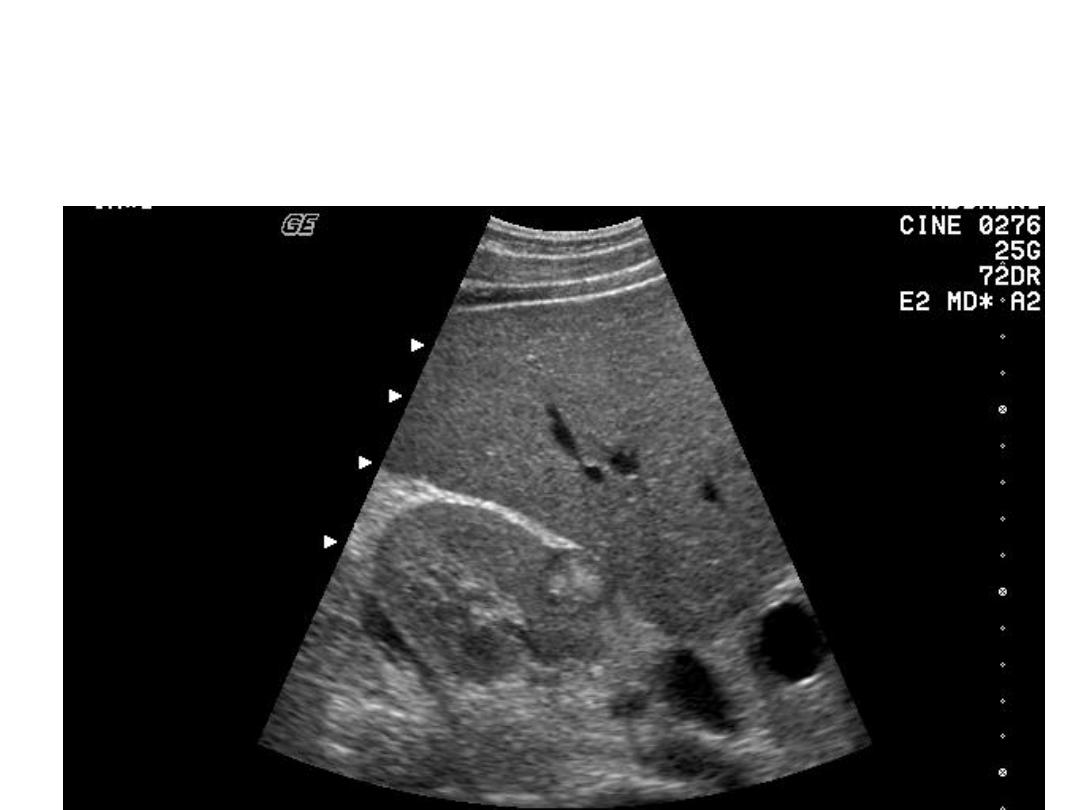
Renal Mass
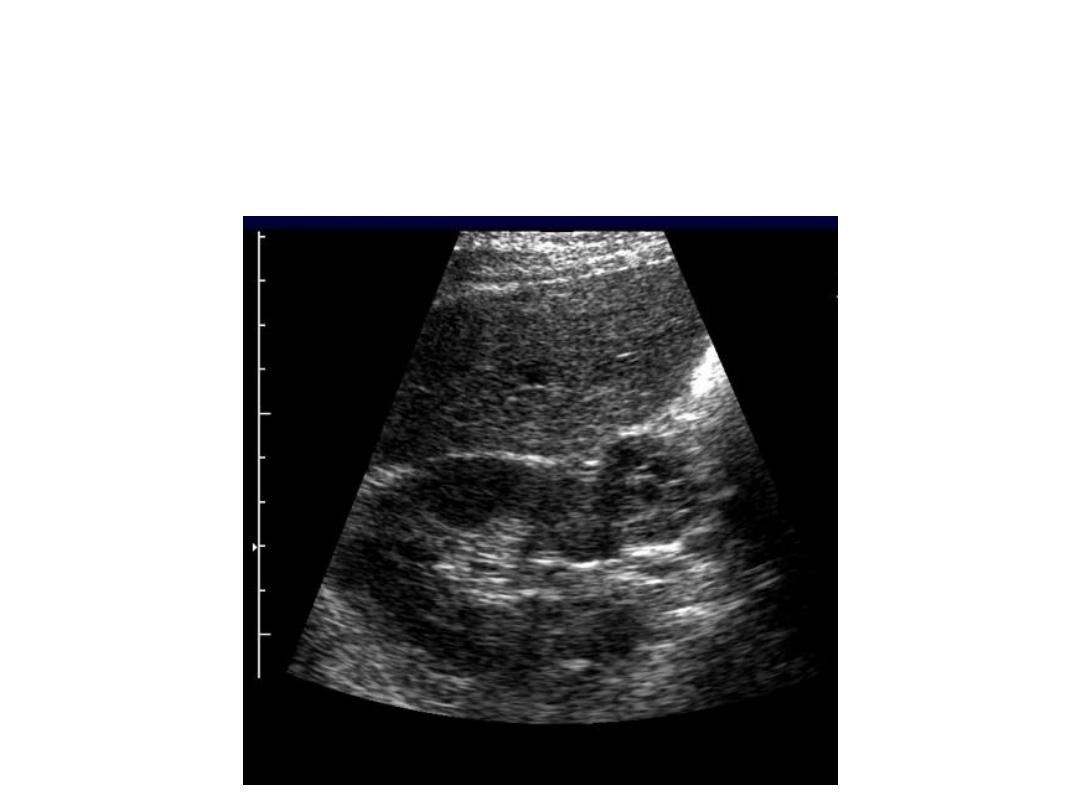
Adrenal Mass
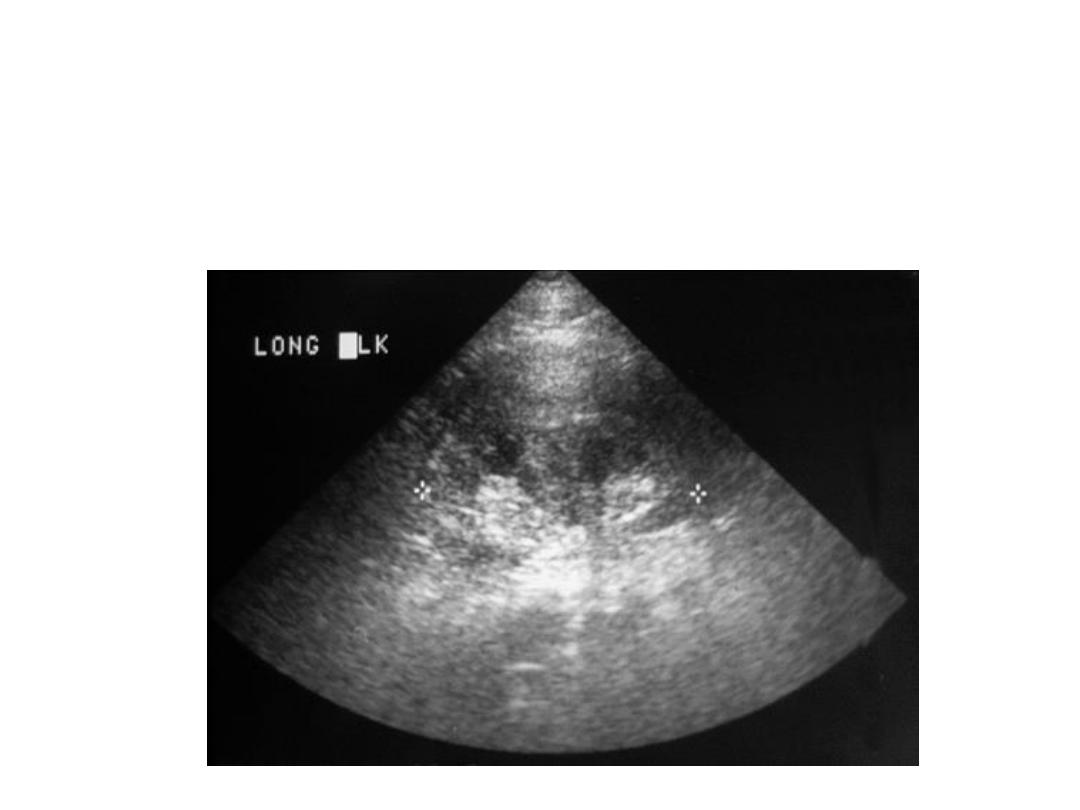
Renal Trauma
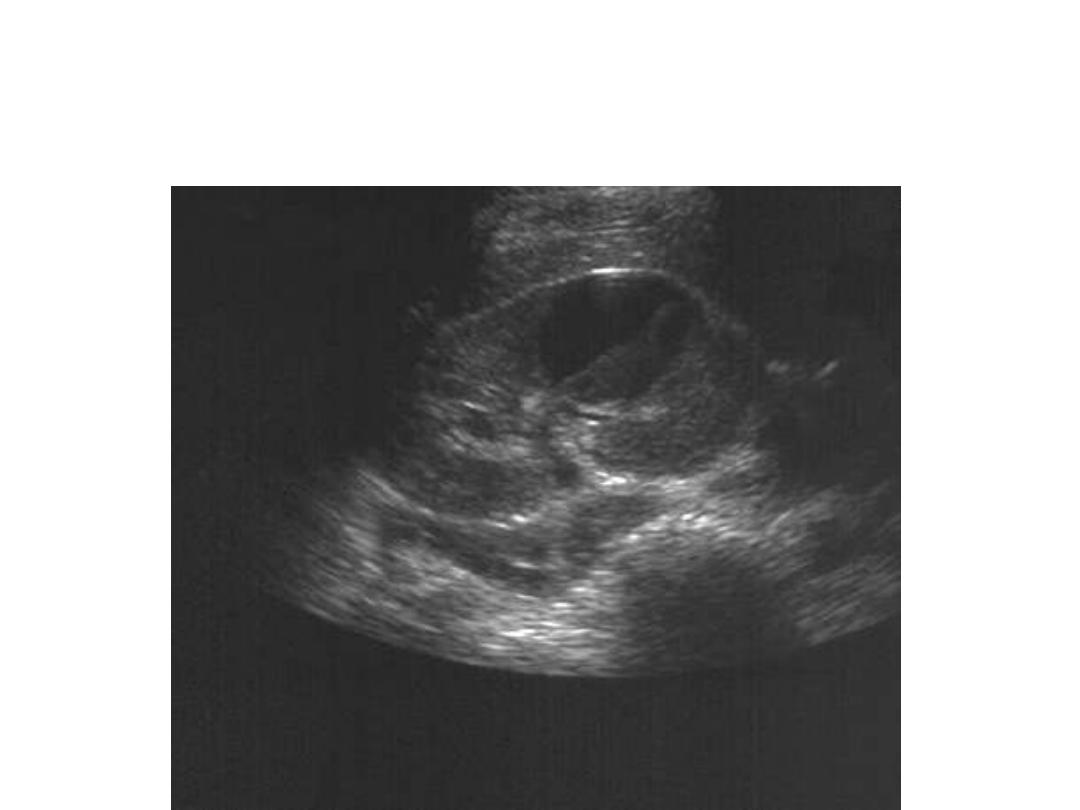
Renal Abscess
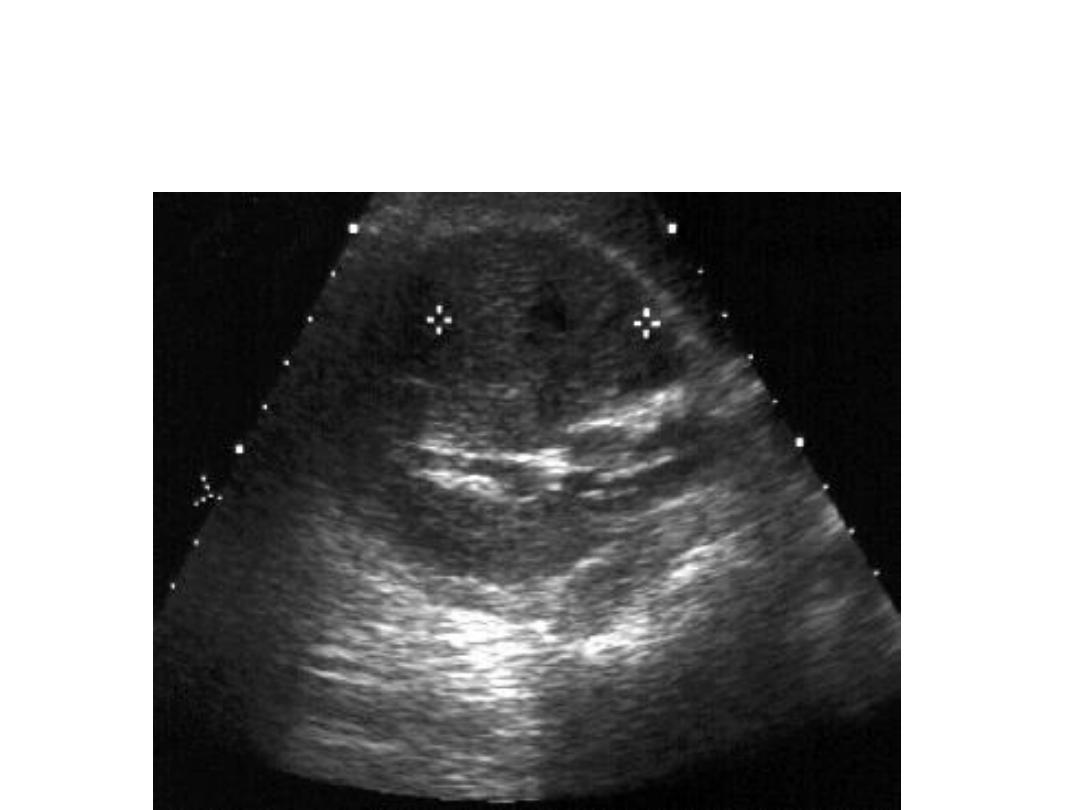
Pyelonephritis

Conginital disease of kidney
• Ureterocele
• Rotated kidney
• Medullary sponge kidney
• Hypertrophied column of Bertin
• Double collecting system
– Normal cortex and split system
• Horseshoe kidney
– Lower than normal with isthmus
• Renal ectopia
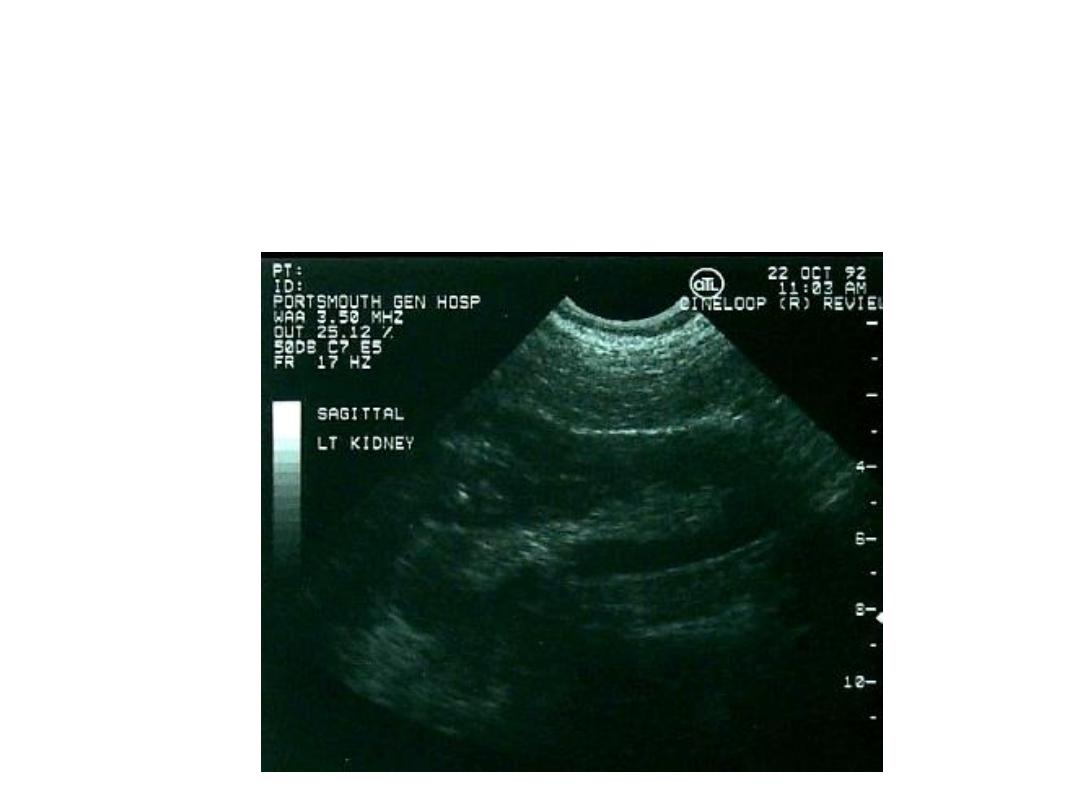
Dromedary Hump
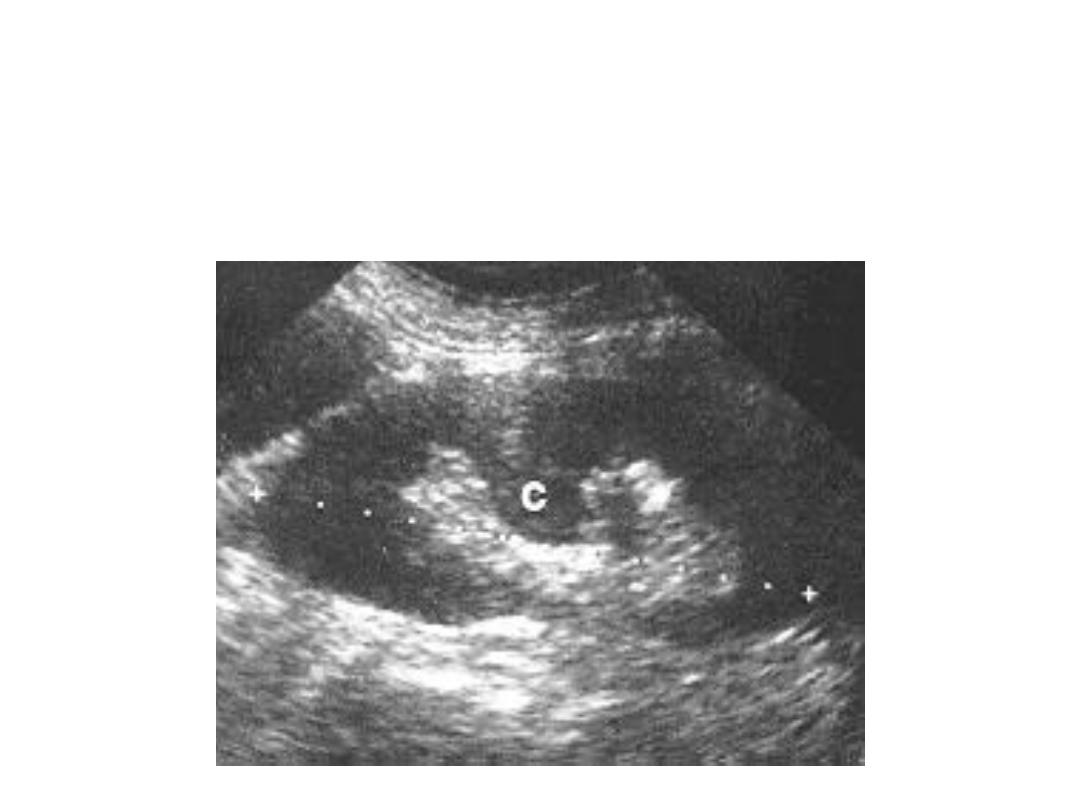
Hypertrophied Column of
B
ertin
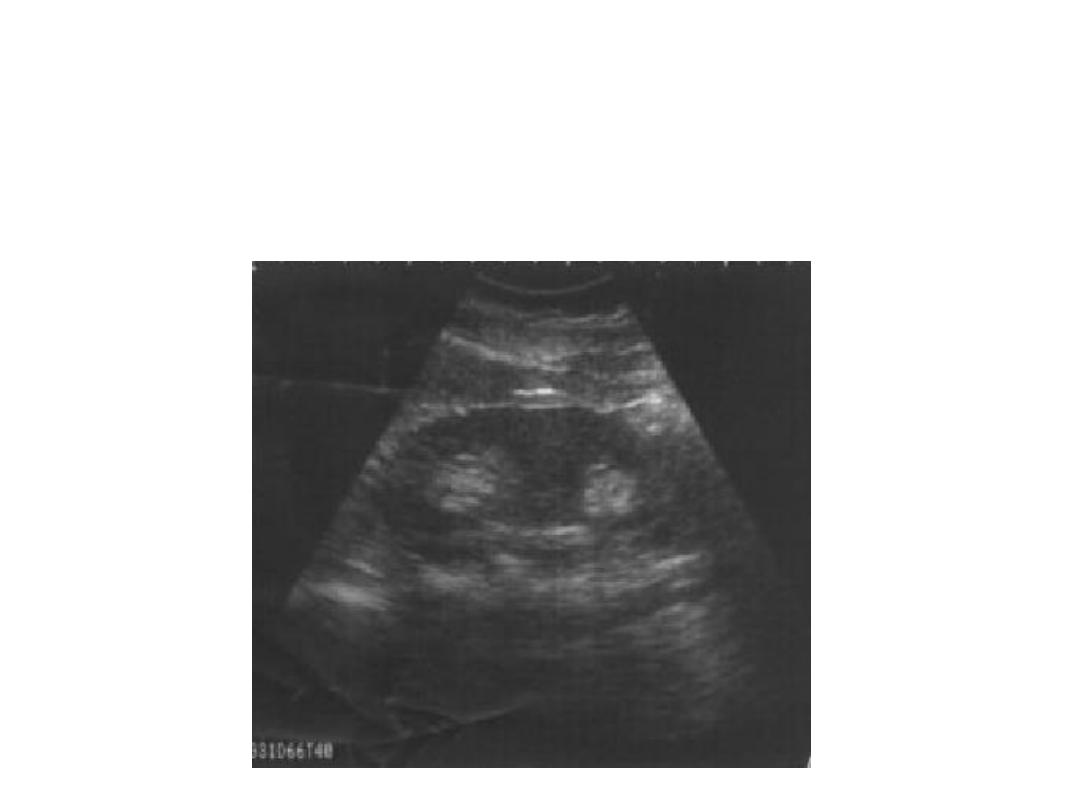
Double Collecting
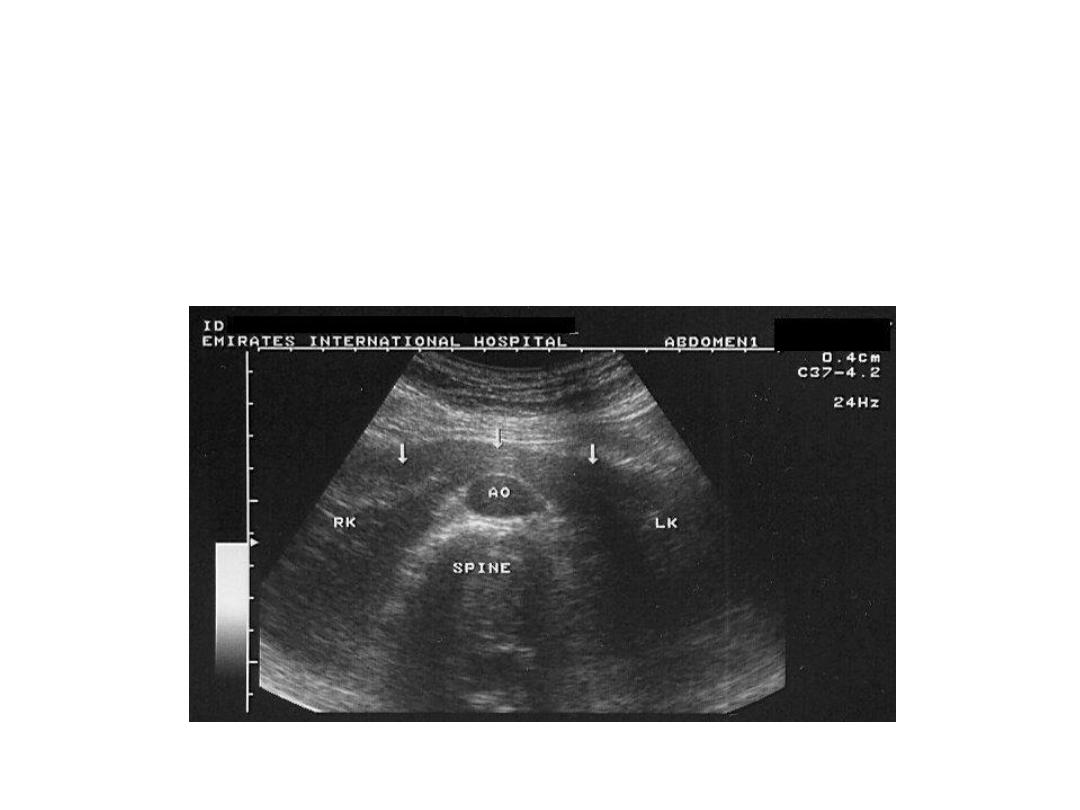
Horseshoe
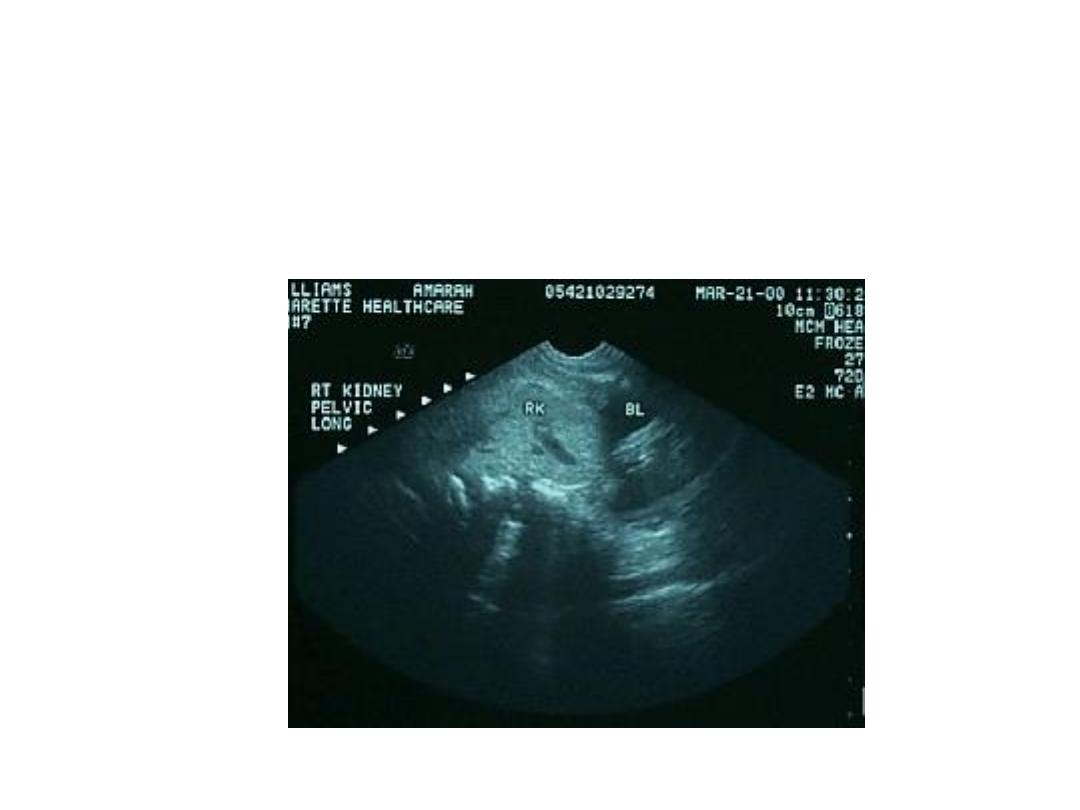
Renal Ectopia

Normal Sonographic Appearance
• Ureters are normally not seen
• Renal pelvis is black when visible
• Renal sinus is echogenic due to fat
• Medullary pyramids are hypoechoic
• Cortex is mid-gray, less echogenic than liver or
spleen.
• Capsule is smooth and echogenic
