
Neck
• The thyroid gland
* shape & texture: consist of 2 lobes with interconnecting isthmus .
& has homogenous intermediate echogenicity
* size : the isthmus is less than (1 cm) in AP diameter
each lobe is less than (2 cm) in AP diameter, (3 cm) in width &
(4 – 5 cm) in length.
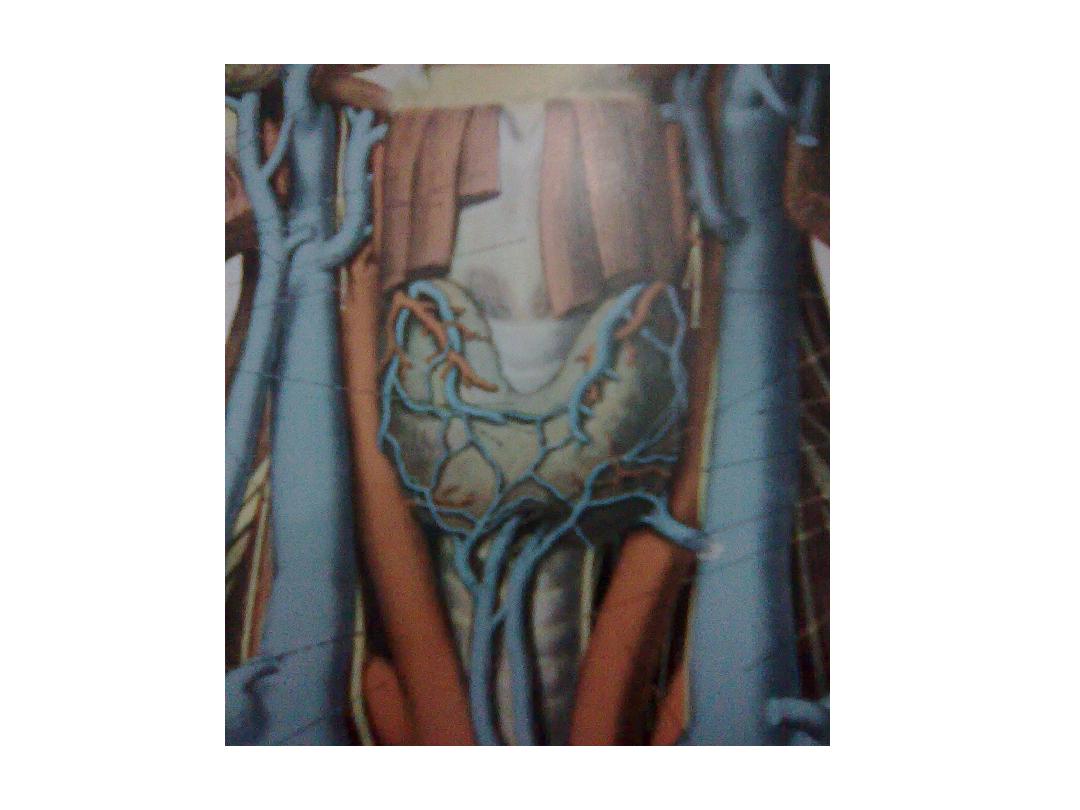
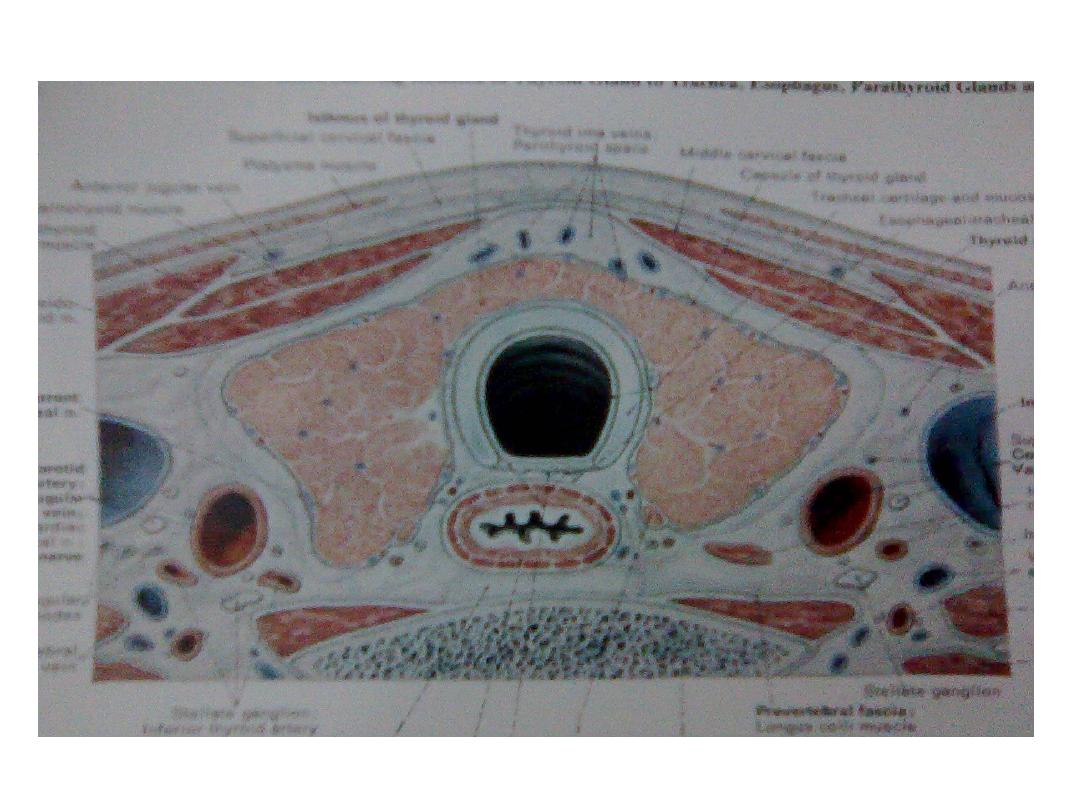
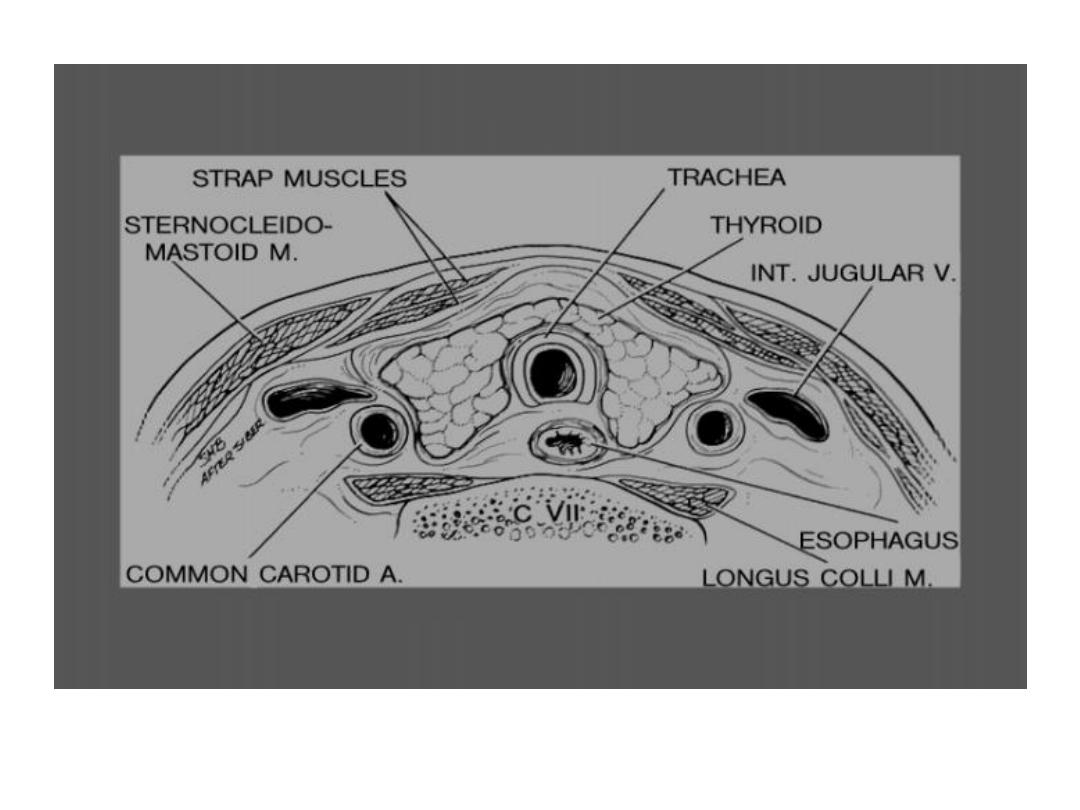
* site : the lobes situated on either side of the larynx & trachea & are
joined across the midline by the isthmus
• posteriorly : the larynx & trachea produce acoustic shadow &
oesophagus
may be seen posterio – laterally usually to the Lt side .
• laterally : the carotid aa. & internal jugular vv.
• anteriorly : the strap muscles , subcutaneous tissue & the skin .
• superiorly : the sublingual salivary gland in the floor of the mouth ,
laterally are the submandibular glands ,& more laterally &
superiorly are the parotid glands against the angle of mandible
& all have homogenous texture similar to that of the thyroid. .

How to do the examination
1. The patient lies supine with the neck extended.
2. Transverse scan at the mid cervical region to detect any
asymmetry .
3. Transverse scan at the lower cervical region to exclude
retrosternal extension .
4. Transverse scan at the upper cervical region to exclude
thyroglossal cyst or any other pathology & to
demonstrate the salivary gland .
5. Longitudinal scan starting from the midline & moving
laterally , to see each lobe separately , the carotid aa &
internal jugular vv. & to exclude any pathology or LAP.

Normal cervical U/S
• Thyroid gland : normal size & texture , no focal
lesion.
• Salivary glands : normal size & texture , no focal
lesion.
• Normal cervical vessels .
• No cervical mass or LAP.

Abnormal cervical U/S
• Thyroid
* size & texture :
1. enlarged & homogenous :
- physiological goiter due to increased demand at puberty , pregnancy ,
…
- iodine deficiency in endemic areas
in both cases there is high TSH level , normal or low T3, T4.
- Graves disease : there is thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin resulting
in
high T3 , T4 & low TSH.
2. enlarged , heterogeneous , multiple nodules of variable size & texture :
- Multinodular goiter : no symptoms apart from cervical swelling .
- sub acute thyroiditis (De Quervain ) : tender swelling , may progress to
- Hashimotas thyroiditis : tender swelling , may progress to :
- diffuse lymphoma : with cervical LAP

Continued abnormal cervical U/S
* Focal lesion
1. cyst :
- true simple cyst is not common
- more commonly are cystic degeneration of benign or
malignant nodule, abscess , haematoma & there for it
usually has thick irregular wall & internal echos.
2. benign adenoma : well defined heterogeneous with solid
& cystic components, calcifications & may have
surrounding hypoechoic halo.
3. malignant tumor : papillary , medullary , follicular ,
anaplastic CA & focal lymphoma. : usually less well defined
, other wise can not differentiated from benign nodule
unless ther is associated cervical LAP or vascular invasion .
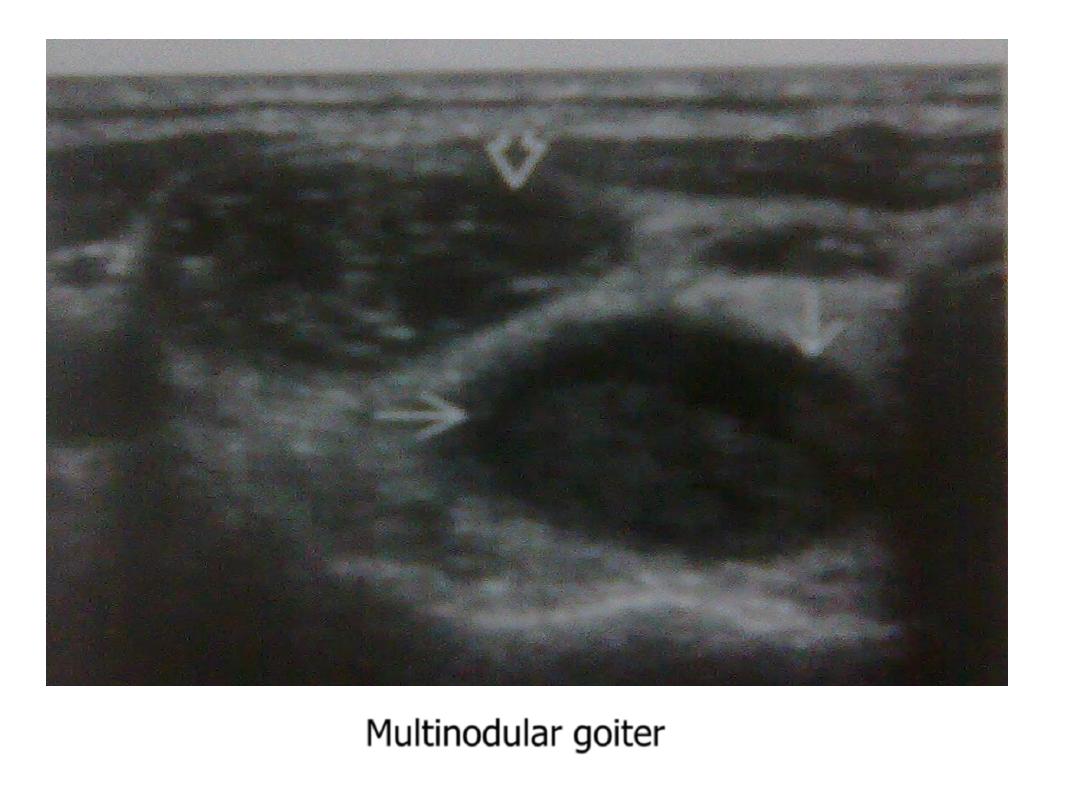
Multinodular goiter
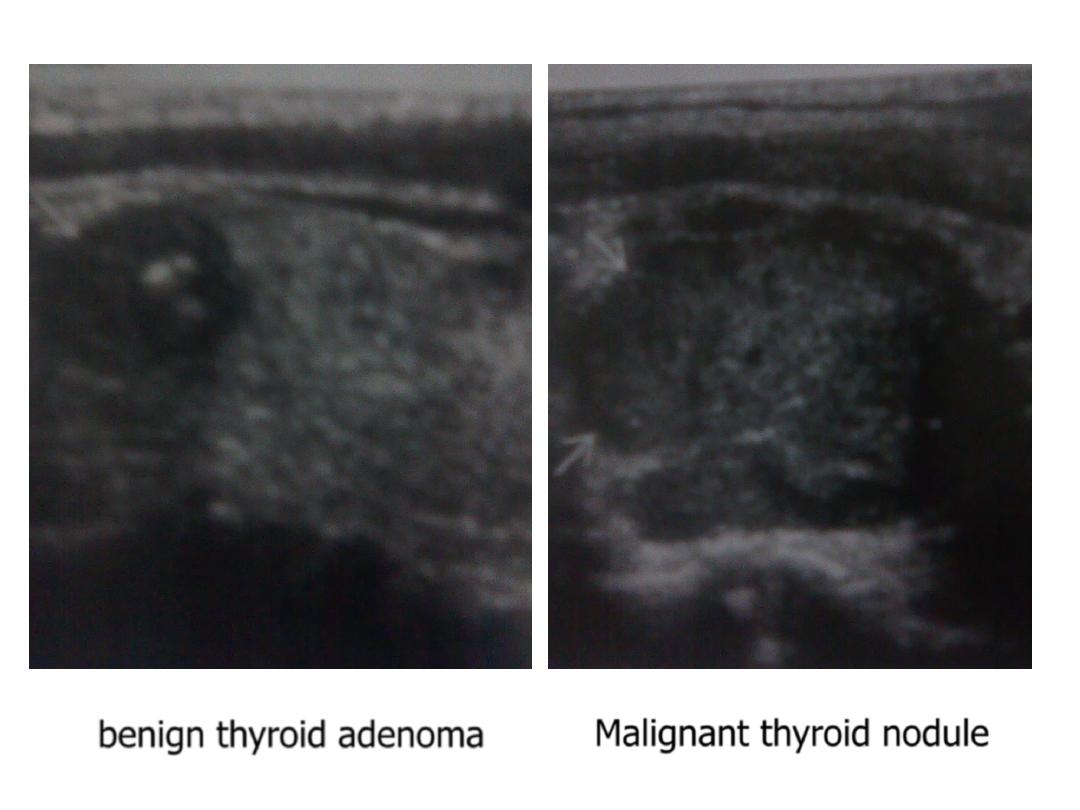
benign thyroid adenoma
Malignant thyroid nodule

Continued abnormal cervical U/S
• Salivary gland
* enlarged & hypoechoic: due to inflammation .
* focal lesion :
1. benign : more common in the parotid .
- Pleomorphic adenoma : well defined , homogenously hypoechoic.
- adenolymphoma (Warthin tumor ) : well defined , heterogeneous
with solid & cystic components ,may have multiseptated appearance .
- lipoma : well defined , homogenously hyperechoic , may be
hypoechoic & have hyperechoic lines .
2. malignant : more common in the smaller glands
usually ill defined , heterogeneous , hypoechoic , associated LAP .
• Cervical vessels :
- displaced or compressed by a mass
- abnormal narrowing or dilatation compared with the other side
- invaded by malignant tumor .
Continued abnormal cervical U/S
• Other masses :
- thyroglossal cyst : midline cyst above the thyroid isthmus
to which it may has a visible connected duct.
- abscess or haematoma : thick irregular wall , internal
debris .
• LAP :
1. benign : infection , sarcoidosis,….
2. malignant : leukemia ,lymphoma , metastasis
Malignant
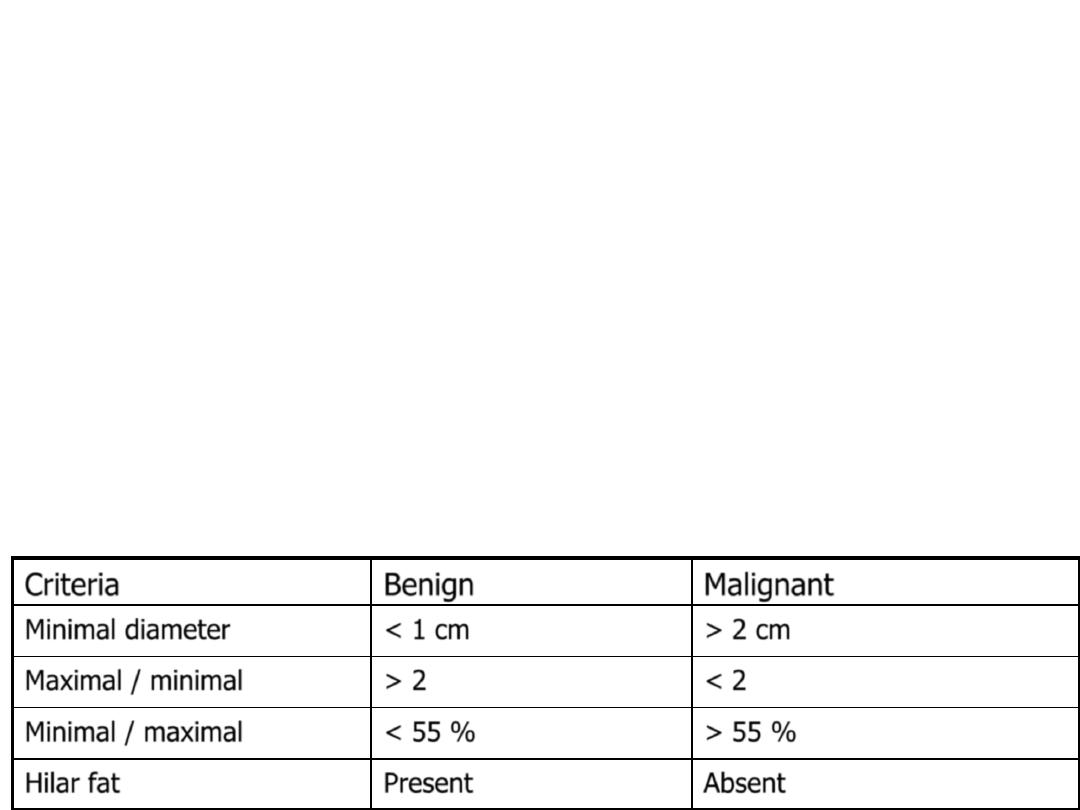
Benign
Criteria
> 2 cm
< 1 cm
Minimal diameter
< 2
> 2
Maximal / minimal
> 55 %
< 55 %
Minimal / maximal
Absent
Present
Hilar fat
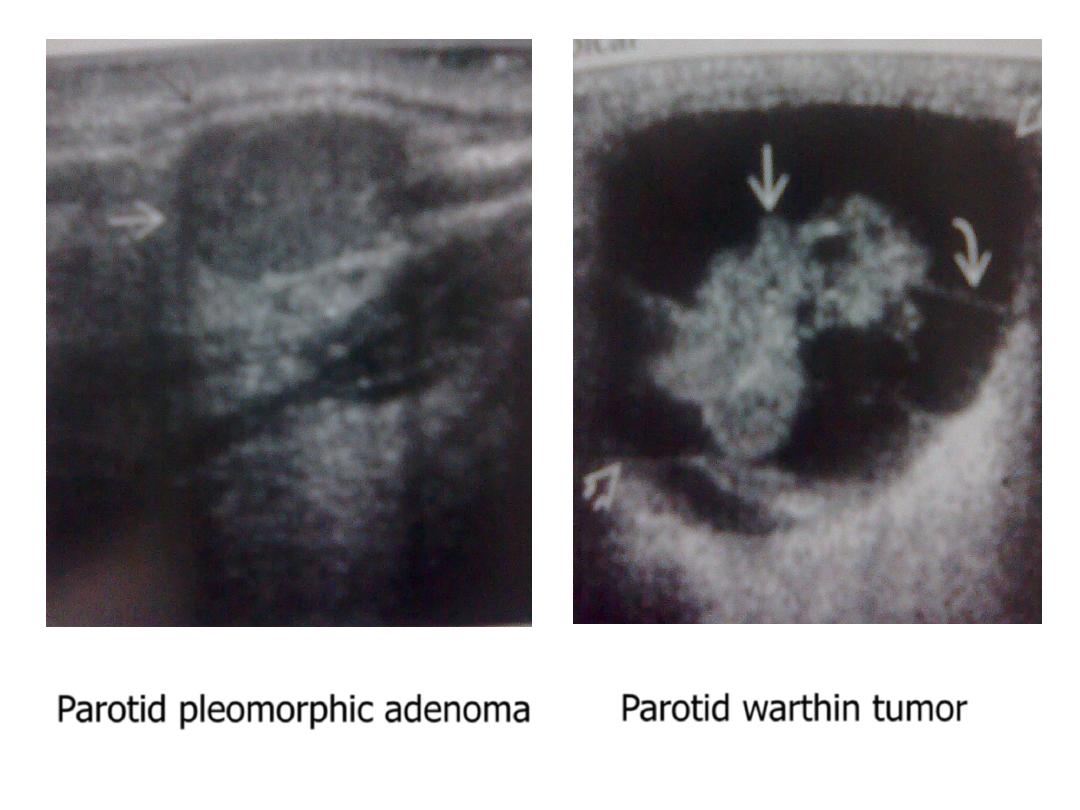
Parotid pleomorphic adenoma
Parotid warthin tumor
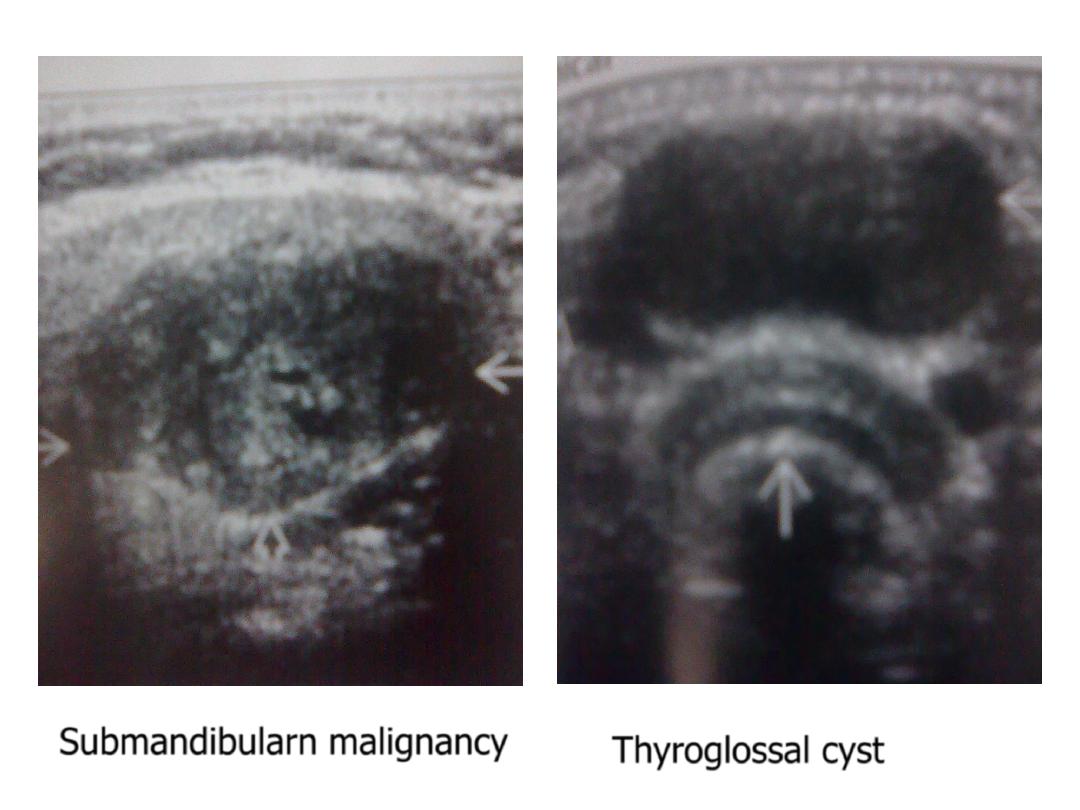
Submandibularn malignancy
Thyroglossal cyst

breast
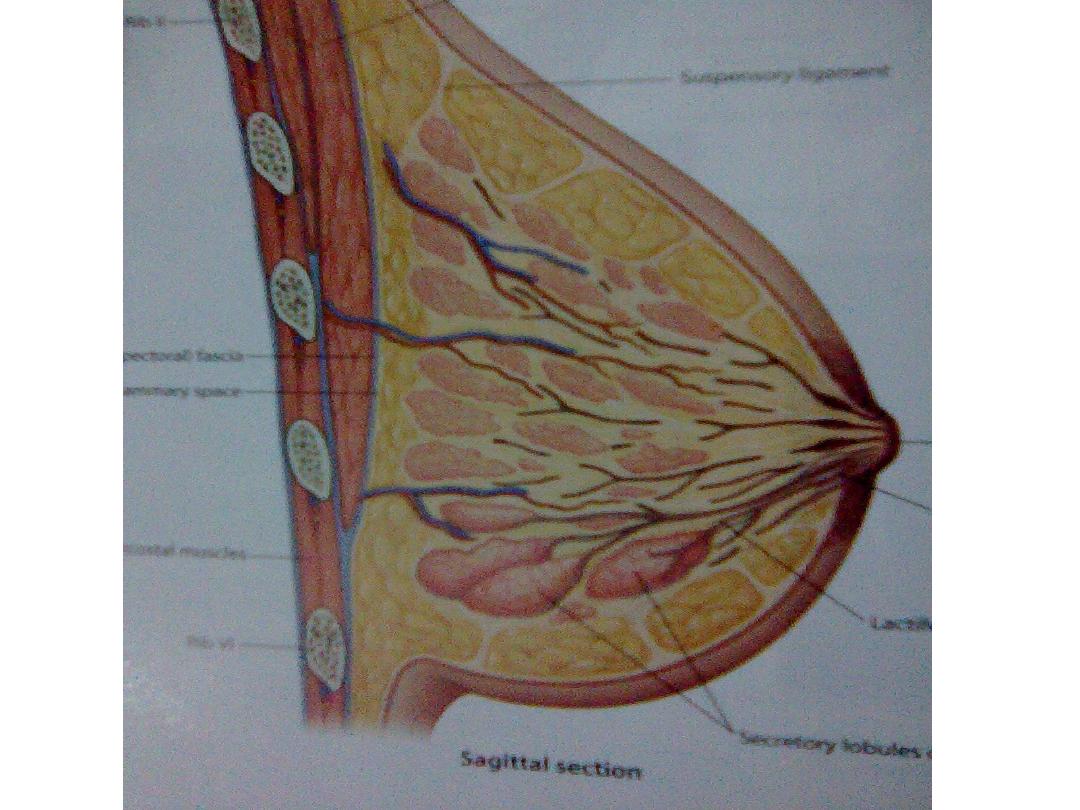
• The superficial chest wall fascia split into anterior ( superficial) &
posterior
( deep ) layers investing the breast tissue & form septa ( Coopers
ligament )
to attach it to the fascia of pectoralis muscle posteriorly & to the skin
& subcutaneous tissue anteriorly .
• The breast tissue consist of :
1. hyperechoic fibrous network
2. hypoechoic fat lobules
3. hyperechoic foci of glandular tissue
4. anechoic tubular lactiferous ducts
• The consistency is dependent on hormonal effect :
* more hyperechoic glandular tissue after menarche , pregnancy &
lactation
* less glandular tissue & more hypoechoic fat after menopause

How to do the examination
1. The patient lies supine with the arm of the same
side elevated above the head.
2. Perform transverse scans in anti radial direction
from the periphery of the breast toward the
nipple .
3. The patient turned to the opposite side to
examine the axillary tail & the axilla .
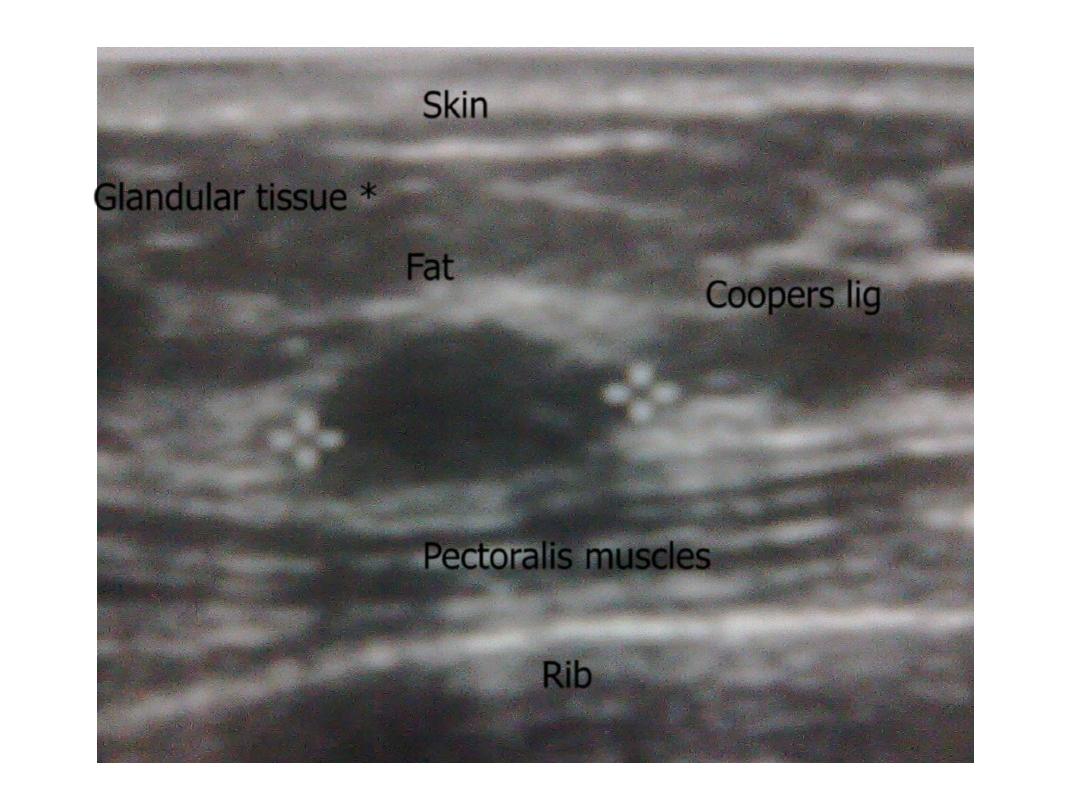
Skin
Rib
Pectoralis muscles
Coopers lig
Fat
Glandular tissue *

Normal breast U/S
• Normal texture of glandular , fatty & fibrous tissue
, no focal
lesion , normal non – dilated subareolar
lactiferous ducts ,
normal overlying skin & subcutaneous tissue .
• No axillary LAP

Abnormal breast U/S
• Edematous breast :
causes :
advanced or inflammatory CA
inflammation , abscess
part of generalized edema (HF , RF, …)
features :
thick skin
diffusely increased echogenicity
thick fibrous septa
• fibroadenosis (hormonal mastitis ) :
young patient , bilateral breast pain , tenderness & tenseness
especially
premenstrual .
features :
diffusely increased echogenicity
thick lace like fibrous septa
some times small cysts seen

Continued abnormal breast U/S
• Focal lesion :
1. Cyst :
Well defined, smooth outline , thin wall , echofree :
* simple cyst : common above the age of 40 y.
* oil cyst at the site of previous scar .
Ill defined, irregular outline , thick wall , internal echo,
solid components :
* galactocele in lactating breast.
* abscess with other features of infection .
* haematoma with history of trauma
* intracystic CA .
Continued abnormal breast U/S
2. Solid nodule :
* benign : fat necrosis, lipoma, fibroadenoma, papilloma,
phyloides tumor
* malignant : ductal, medullary, mucinous, papillary,
lobular …
Malignant
Benign
Criteria
> 40 Y
< 40 y
Age
Variable , deeper than wide
Ovoid , wider than deep
shape
Ill defined , irregular outline,
speculated
Well defined , smooth outline , 2 - 3
gentle lobulations
Margin
Heterogeneously hypoechoic
Homogenously hypo, iso, hyperechoic
Echotexture
Attenuation , posterior shadowing
Minimal attenuation , enhancement
Posterior effect
Microcalcification
Coarse
calcification
Non compressible
Compressible
Compressibility
Continued abnormal breast U/S
• dilated subareolar lactiferous ducts :
1. normal : pregnancy & lactation
2. pathological : due to obstructing ductal CA
• Enlarged axillary L.N. :
1. benign : infection , sarcoidosis ….
2. malignant : leukemia ,lymphoma ,metastasis from breast CA,
or rarely other primaries like ovarian CA.
Malignant
Benign
Criteria
> 2 cm
< 1 cm
Minimal diameter
< 2
> 2
Maximal / minimal
> 55 %
< 55 %
Minimal / maximal
Absent
Present
Hilar fat
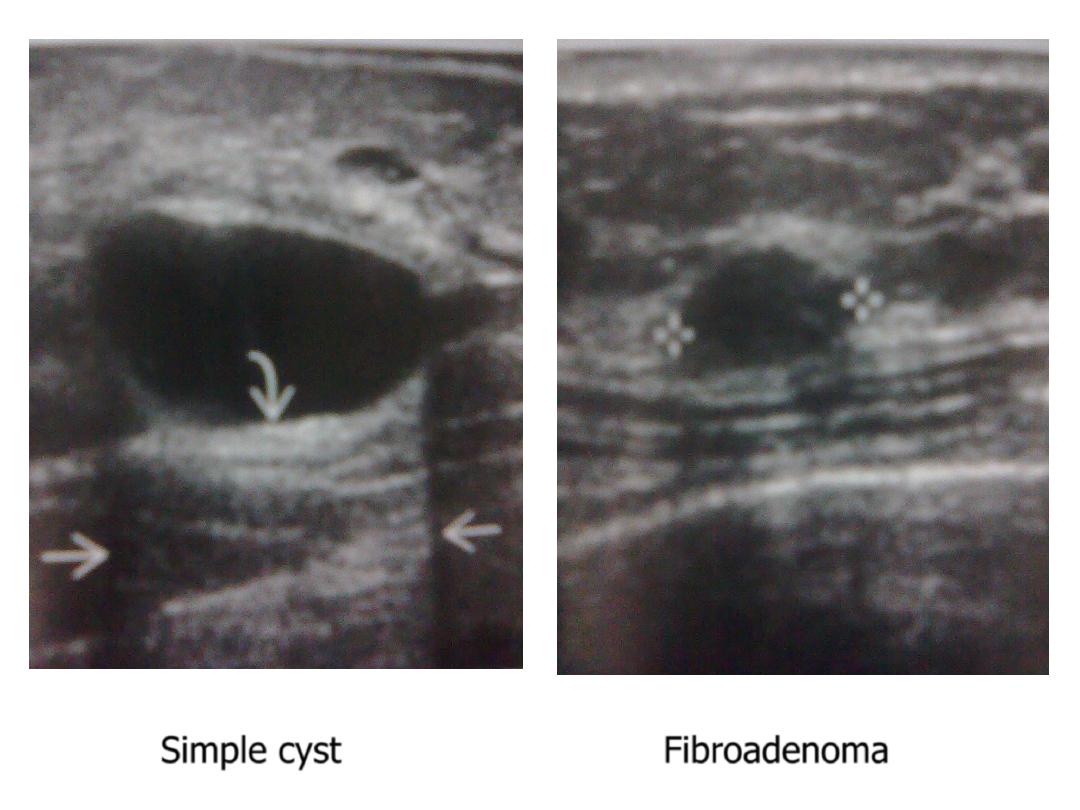
Simple cyst
Fibroadenoma
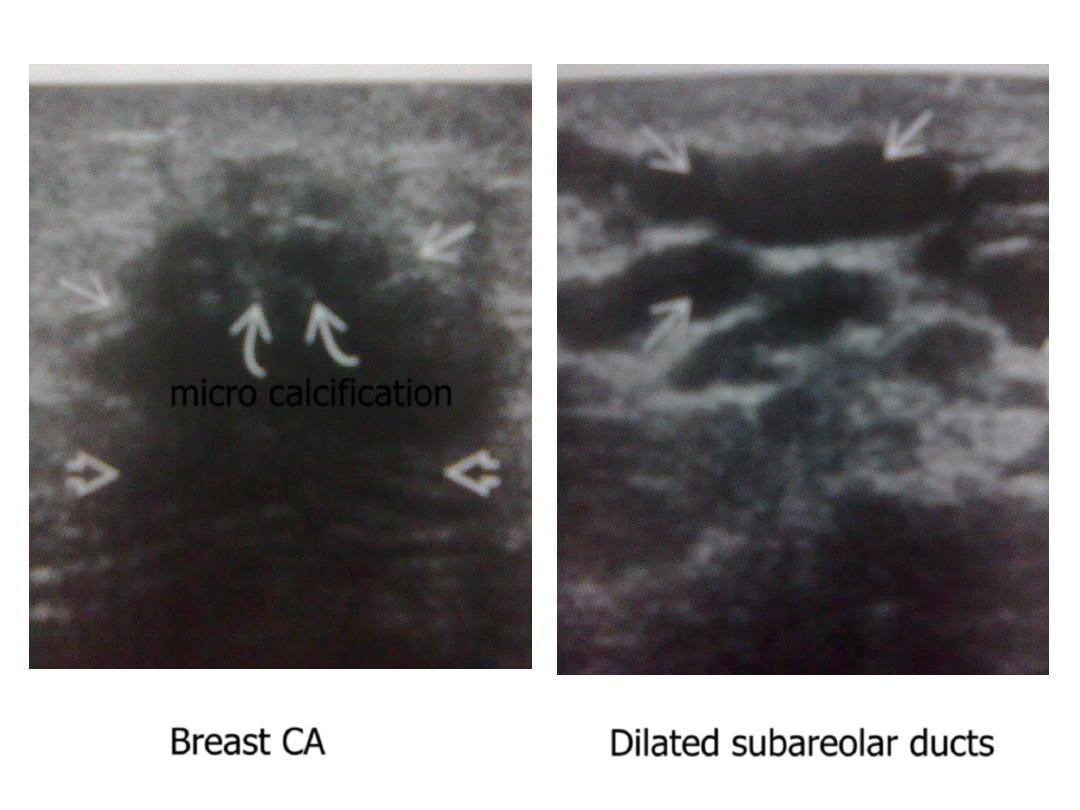
Breast CA
Dilated subareolar ducts
micro calcification

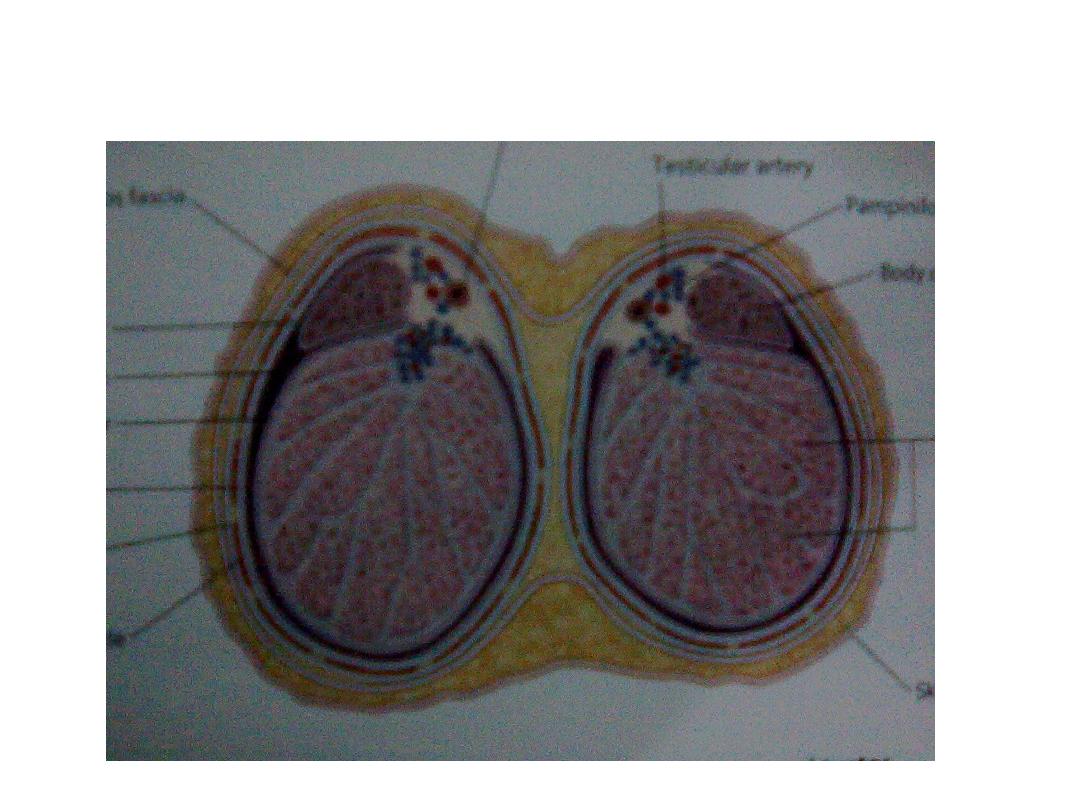
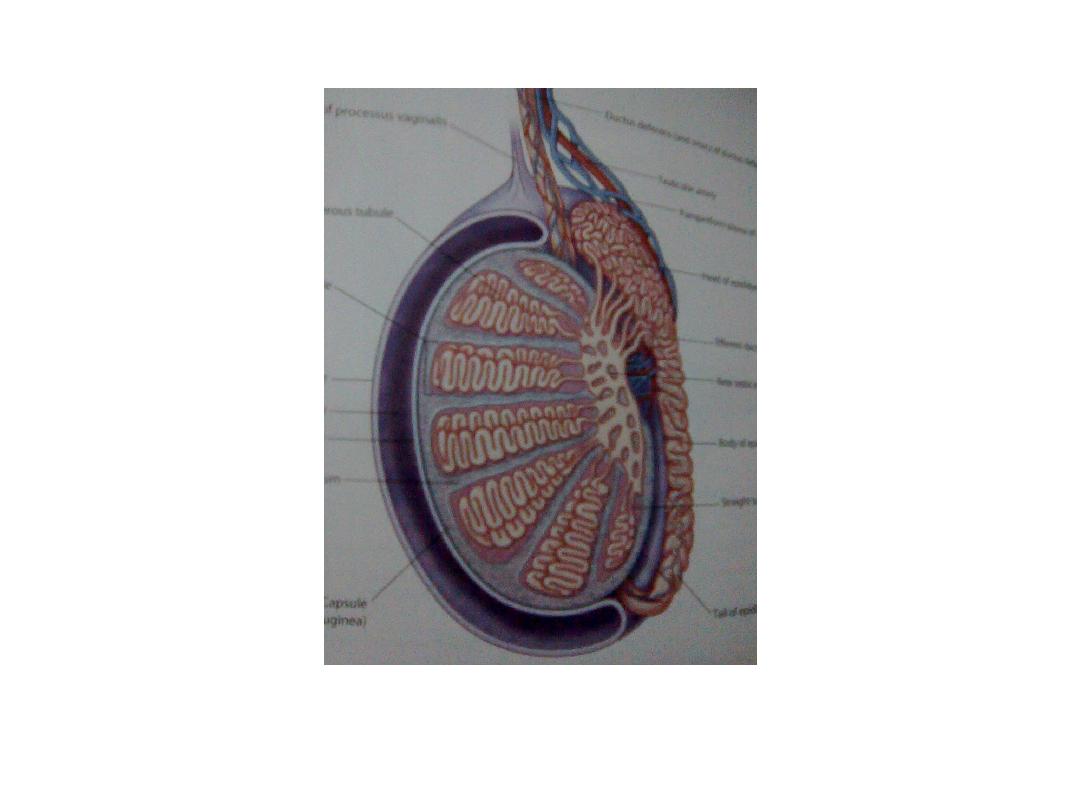
Normal scrotal anatomy
• Testes :
site within the scrotal
size 3.5X3 cm in longitudinal scan
shape & texture ovoid , smooth outline , homogenous intermediate
echogenicity,
the mediastinum may appear as longitudinal
echogenic line at
the posterior aspect of the testes parallel to
epididymis
• Epididymis :
shape snake like structure consist of head , body & tail
size head is (5 – 15 mm) , tail is (1 – 3 mm) in diameter
site head is posterio – lateral to the upper pole of the
testes ,
body & tail taper downward
• Veins : may be seen normally & should be no more than 1 – 3 mm
• Fluid : Small amount of may outline normal testes especially in infant
• Skin & subcutaneous tissue : seen as hyperechoic layer 5 – 7 m in
thickness

How to do the examination
1. The patient lies supine .
2. Transverse scan performed to detect any
asymmetry .
3. Longitudinal scan performed for each side .
4. Transverse & longitudinal scans performed for
the inguinal area to detect undescended testes ,
LAP, hernia ….

Normal scrotal U/S
• Testes & epididymis : normal site , size & texture, no
focal
lesion seen .
• No varicocele
• No hydrocele
• Normal overlying skin & subcutaneous tissue

Abnormal scrotal U/S
• Testes & epididymis
* site : undescended testes
* size & texture :
1. swollen , focally or diffusely hypoechoic , heterogeneous : due to:
infection , infarction , trauma , malignancy
2. small echo poor : as end stage of:
infection , infarction , trauma , undescended testes
* Focal lesion :
1. cyst : well defined , smooth outline , echofree
common finding in any age but especially in elderly
2. complex : ill defined, irregular outline, heterogeneous, cystic &
solid components:
infection ( abscess ) , infarction , trauma ( haematoma)
3. solid :
seminoma & lymphoma : well defined , homogenously
hypoechoic
non seminoma germ cell tumor : ill defined , heterogeneous
with calcifications & cystic degeneration

continued abnormal scrotal U/S
• Varicocele :
95 % is Lt sided
echofree worm like structures > 2 mm in diameter
enlarged further by sitting , standing & Valsalva
maneuver
• Hydrocele : infection , infarction , trauma , malignancy, no
cause
• Skin edema :infection , infarction , trauma , malignancy

summary
• Painful scrotal swelling is due to :
infection
infarction
trauma
malignancy
in all cases there is :
skin edema
hydrocele
swollen testes & epididymis, focally or diffusely hypoechoic,
heterogeneous
differentiation is depending on clinical features & lab
• Painless scrotal swelling is due to :
innocent hydrocele
varicocele
innocent cyst
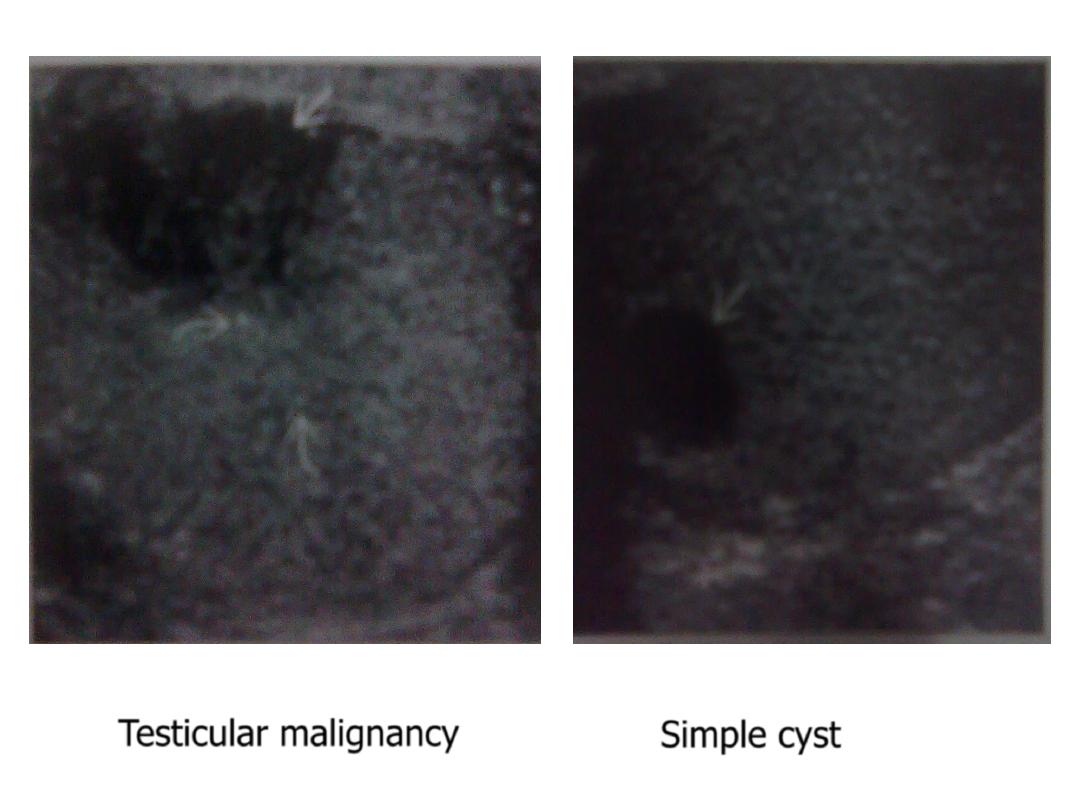
Testicular malignancy
Simple cyst
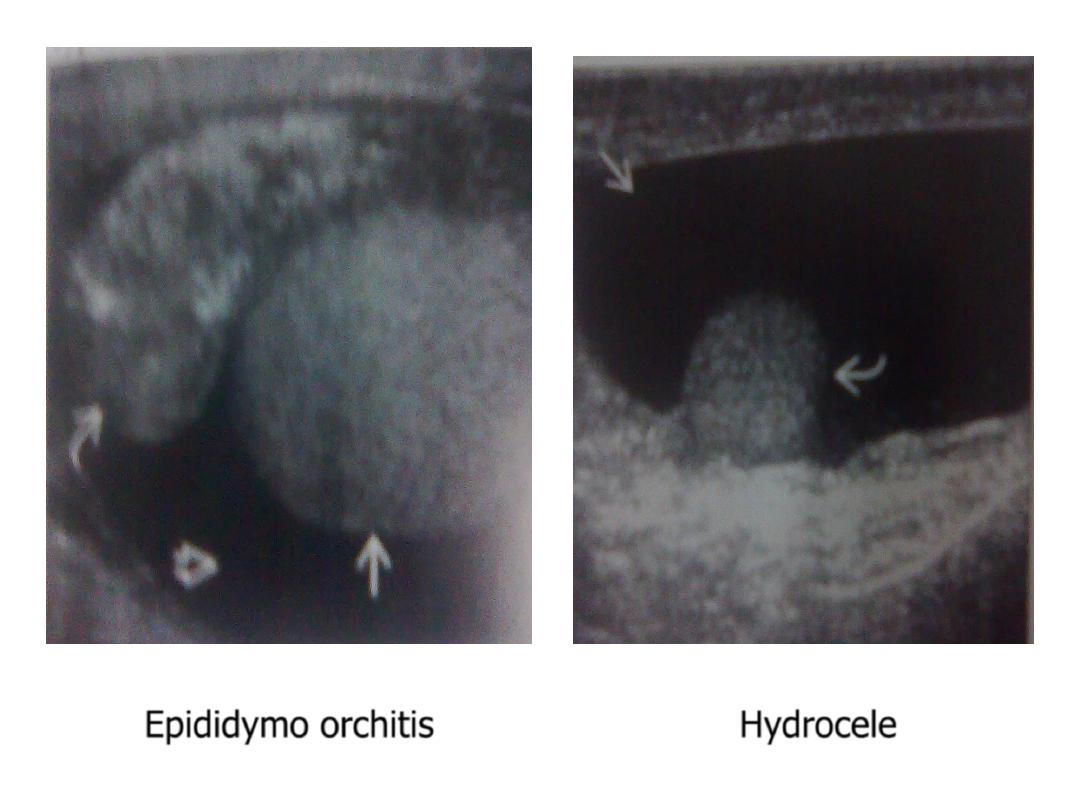
Epididymo orchitis
Hydrocele
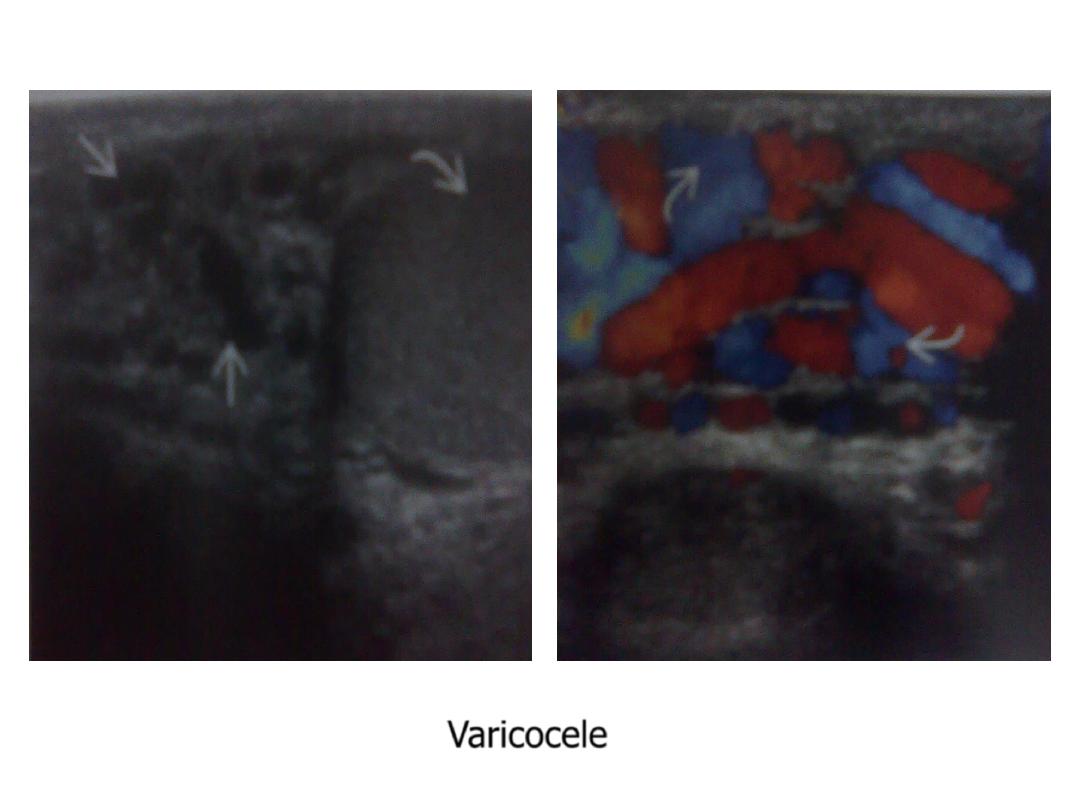
Varicocele
