
Spondyloarthropathies:
A group of related inflammatory joint disease, overlap
in their clinical features sharing immuno-genetic
association with HLA-B27.These include:
-Ankylosing spondylitis AS
axial spondyloarthritis
-Psoriatic arthritis
-Reactive arthritis
-Arthritis associated with inflammatory bowel
diseases.

Common criteria:
1- Asymmytrical inflammatory Oligoarthritis.
2- Sacroiliitis and inflammatory Spondylitis.
3- Inflammatory Enthesitis.
4-There is a striking association with HLA-B27 particularly
in AS >95% and Reiter disease 90% and when there is
sacroiliitis , uveitis or balanitis .
5-Tendency for familial aggregation.
6- Overlapping of extra- articular features.(as aortic root
fibrosis, (aortic incompetence, conduction defects),
uveitis ,conjunctivitis and psoriasis of skin or nail , sterile,
inflammatory bowel disease ,urethritis , prostatitis)
7-History of inflammatory back pain

• THE ETIOLOGY STILL NOT CLEAR .BUT COULD BE AN
ABNORMAL RESPONSE TO INFECTIOUS ORGANISM IN
GENETICALLY SUSPTABLE INDIVIDUAL. IN REACTIVE
ARTHRITIS THE TRIGGERING ORGANISM CAN BE
IDENTIFIED. IN OTHER DISEASE IN THE GROUP THE
ENVIRONMENTAL TRIGGERS REMAIN UNKNOWN.

• Axial spondyloarthritis
• Iflammatory low back pain and early morning
stiffness . The pain radiated to buttock or posterior
thigh. Symptoms are exacerbated by inactivity and
relieved by movement
• Enthesitis :episodic local or wide spread Fatigue
• Association of inlammatory bowel disease or
psoriatic skin or nail lesions(current, past or first
degree relatives).

Physical examination
• Reduced range of spinal movement in all directions
• Tenderness on stressing sacroiliac joints
• Pain and tenderness at enthesitis sites (Achilles’
insertion, plantar fascia origin, patellar ligament
entheses,
• gluteus medius insertion at the greater trochanter
and tendon attached to humeral condyles)

Disease activity assessment :
• Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index
(BASDAI)
• Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index
(BASFI) .
• Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score
(ASDAS-CRP).
•
• Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International
• Society Health Index (ASAS-H).

Investigations:
• MRI for detection of early sacroiliitis.
• MRI and ultrasound for detection of enthesitis’
• Acute phase reactant ESR , CRP elevated in active
inflammation but could be normal.
• Anemia and positive HLA B27.
• Calprotectin for screening of inflammatory bowel
disease.

Management :
• Education
• NSAIDs
• Physical therapy
• In severe or persistent peripheral involvement
sulfasalzine and methotrexate should be
considered(these medications have no influence on
spinal symptoms or disease progression).
• In severe cases or inadequate response or
intolerance to NSAIDs, biologic therapy Anti TNF or
IL-17 A inhibitor(seckinumab) should be consdered.
•
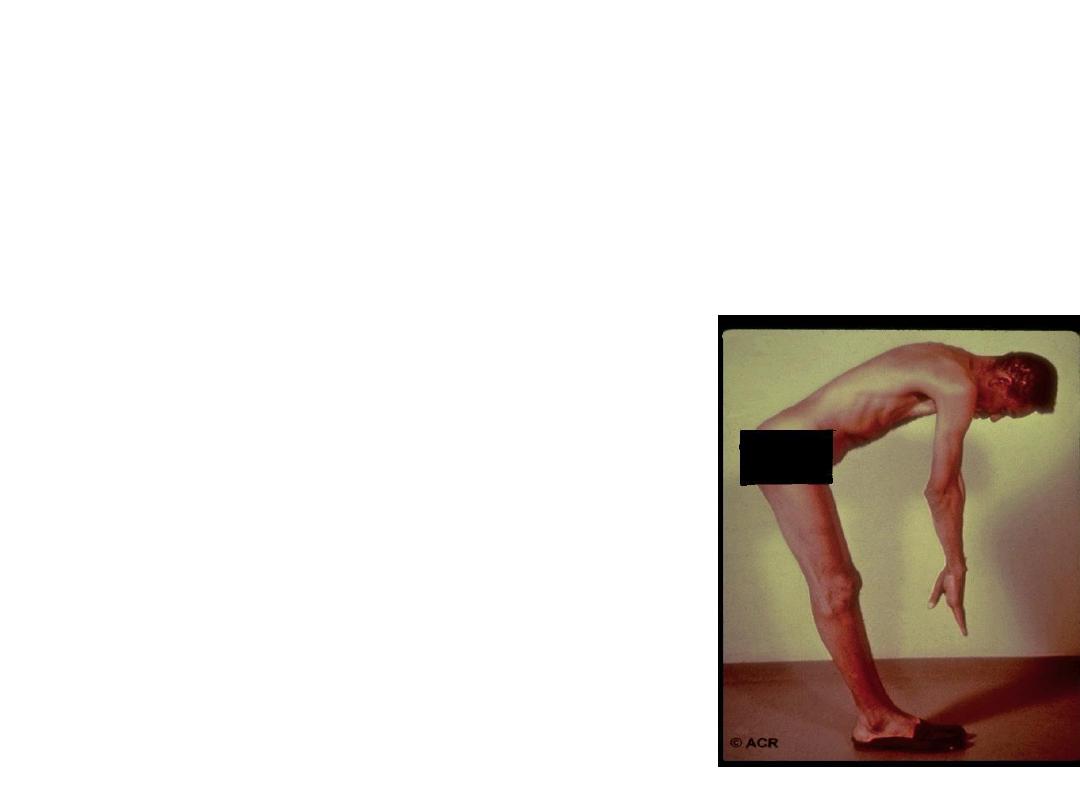

Ankylosing Spondylitis
Is characterized by chronic inflammatory arthritis
mainly affecting sacroiliac joints and the spine
leading to progressive bony fusion of the spine.

• Peak incidence in 2
nd
and 3
rd
decades, with male to
female ratio 3/1.
• More than 90% associated with HLA-B27.
• Etiology it is though due common environmental
pathogen in genetically susceptible individual,
although no specific trigger pathogen has been
isolated.
• Chronic prostatitis is common than usual in men
but it is no infective in nature. Increased fecal
carriage of Klebseilla aerogenese in AS and could
related to joint and eye exacerbation.

Clinical Features:Clinical features are the same as in
axSpA . AS evolve slowely from Axial SPA
-Spine become ankylosed rigid with secondary
osteoporosis, predispose to fracture. Spinal cord
compression is rare.
The extent of spinal fusion
Differ in severity in most cases not cause marked
flexion deformity, but in few cases marked kyphosis
of dorsal and cervical spine kyphosis which may
interfere with forward vision..
-Plueritic chest pain aggravated by breathing result
from costo-vertebral joint involvmet can
-

Pain due inflammation at the site ligament or
tendon insertion ( enthesitis )as plantar fasciitis,
achilis tendonitis.
-Fatigue is often a major complaint due to
interrupted sleep and due chronic inflammatory
processes .
-Peripheral arthritis and or enthesitis (40%) Like
hips, knees, ankles or shoulders. It could antedate
the spinal symptoms(10%)
Fatigue a common complaint in all SPA.
Anterior acute uveitis is a common extra skeletal
features and my precedes the joint disease.
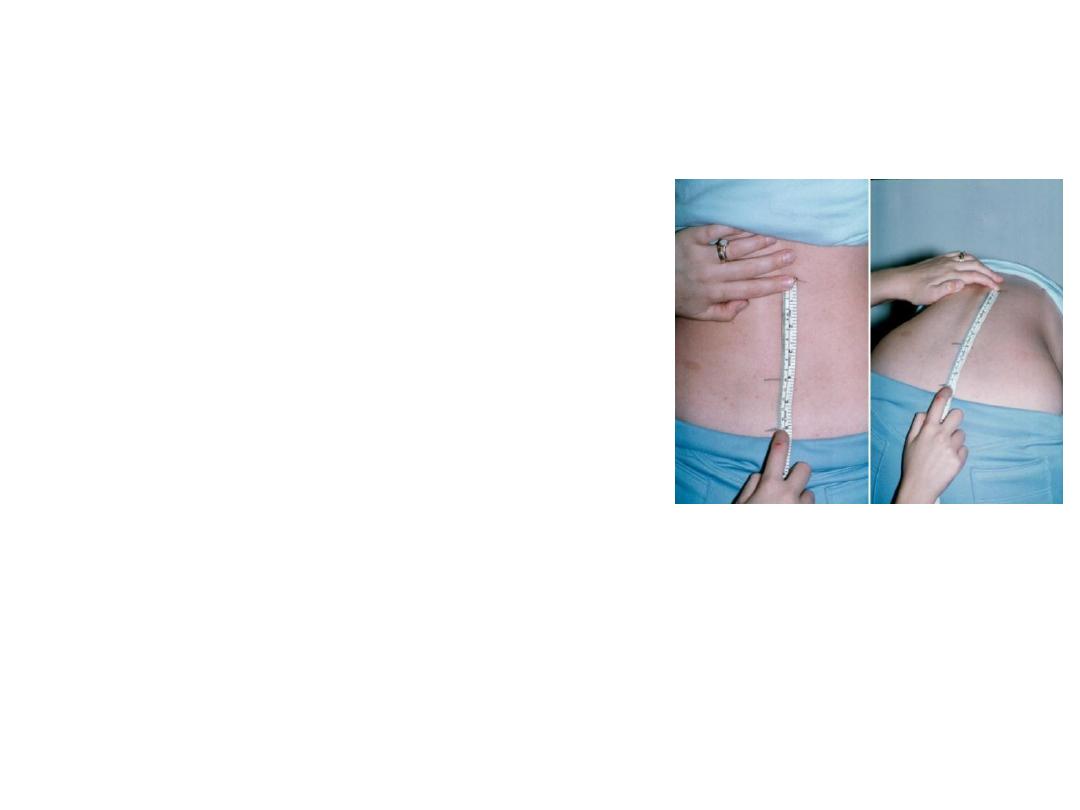
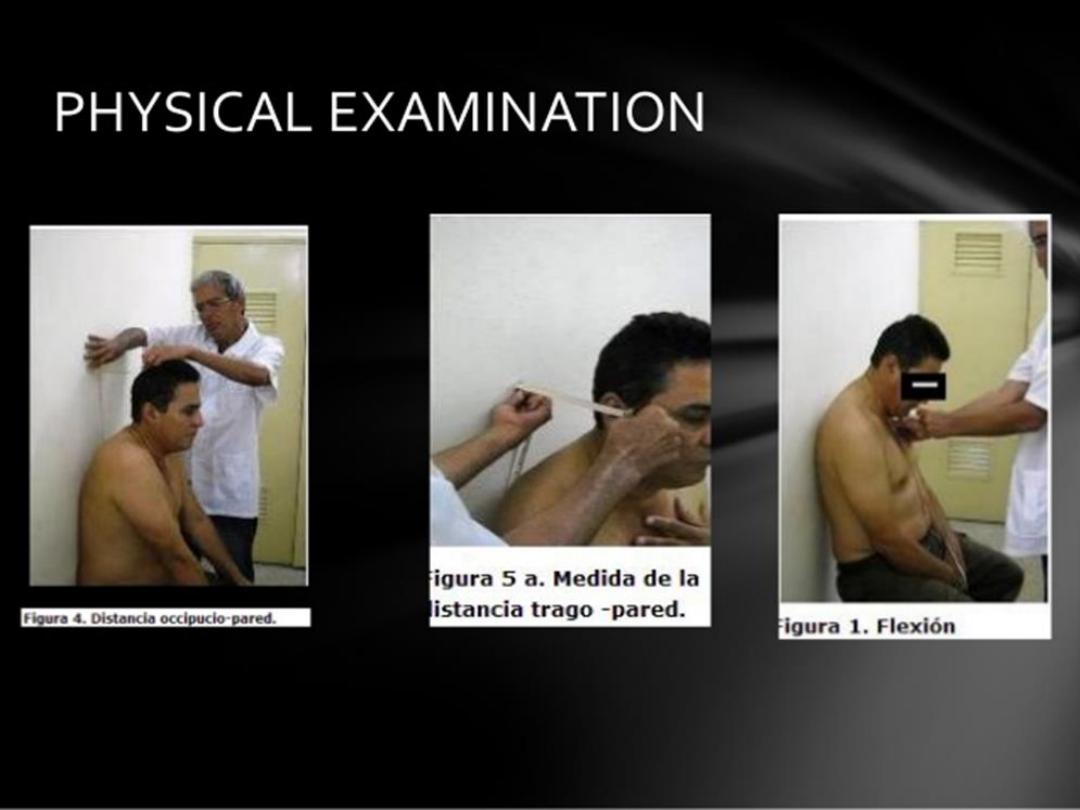
Physical examination:
• +ve schobber test.and restriction of spinal
movement in all directions.
• Pain on SIJ stressing
or compression
• Restriction of chest
expansion.
• Local tenderness at the site of active enthesitis.
• Sign of peripheral arthritis when exist.

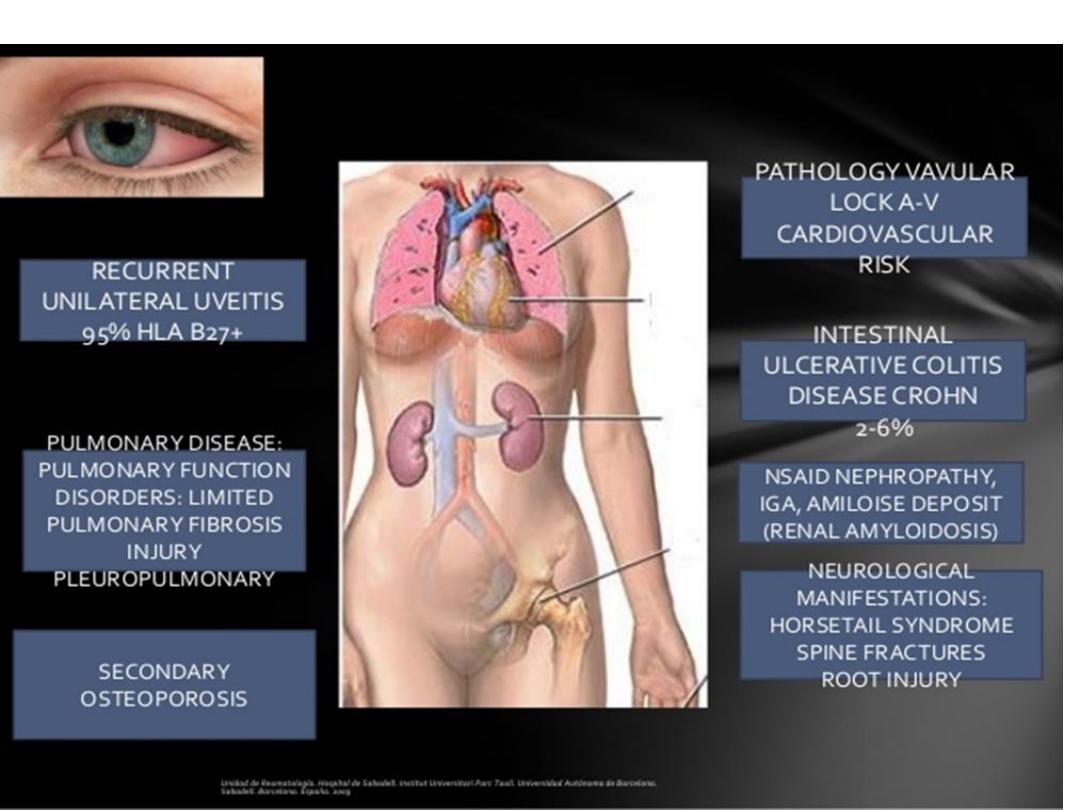
Extra-articular features of axial
spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis :
Fatigue, anaemia
Inflammatory bowel disease (up to 50% have IBD lesions
-anterior uevitis 25%, and conjunctivitis 20%.
-Prostatitis in about 80% in men usually asymptomatic.
-Cardiac(aortic and mitral incompetence, conduction
defect , pericarditis).
-Amyloidosis.
Osteoporosis
-Apical pulmonary fibrosis.

Investigations:
• ESR and CRP are usually raised in active disease. RF
,ACPA and ANA are negative. HLA typing may
helpful when the back pain suggestive of
inflammatory in nature and other investigations are
equivocal.

MRI is a sensitive tool to detect early changes before
radiological manifestations (NON –RADIOLOGICAL SPA)
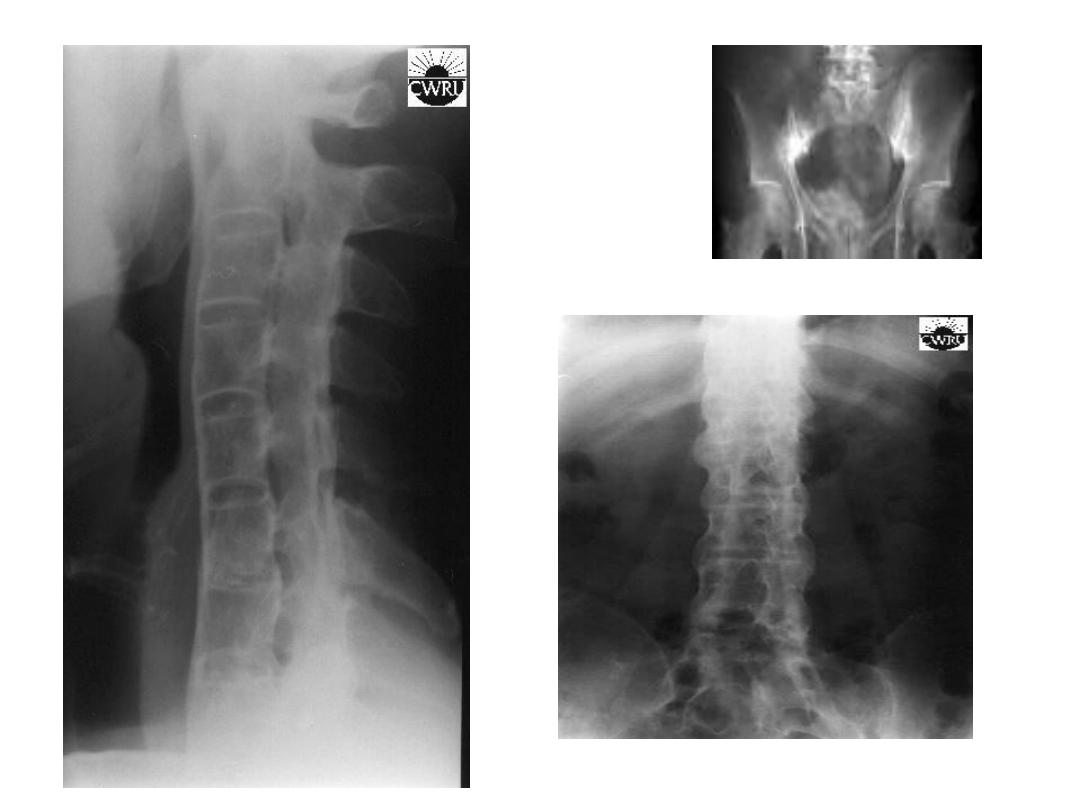
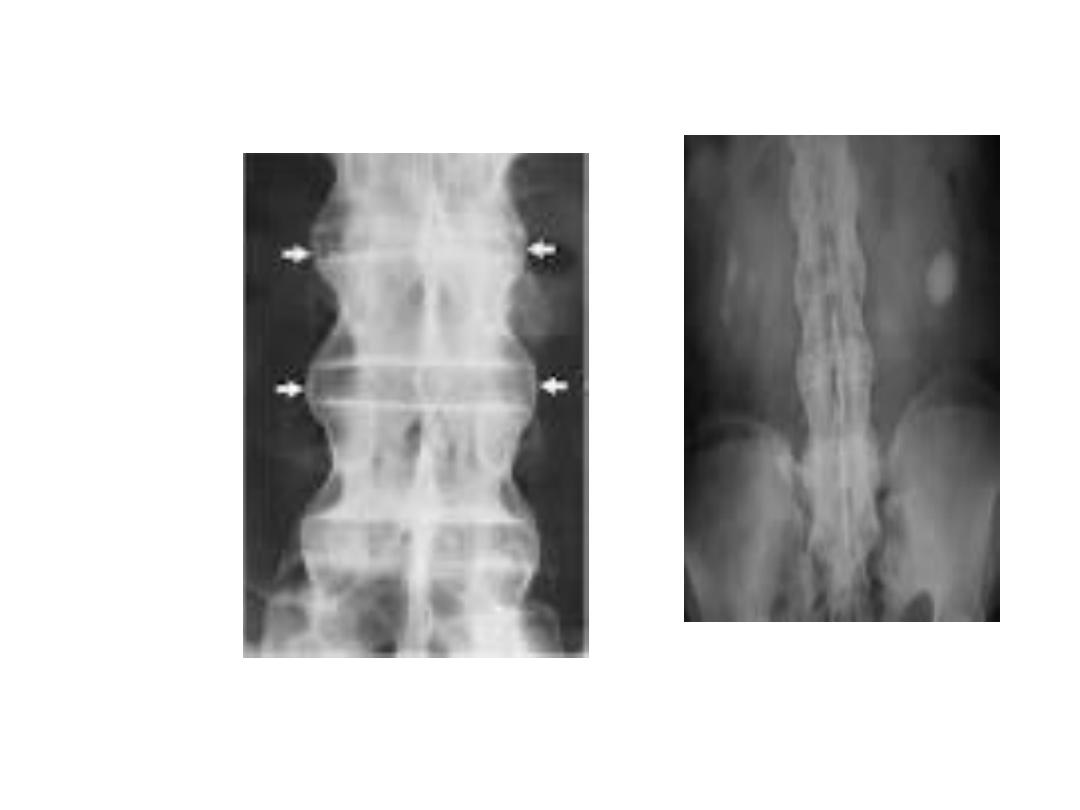
X-ray findings:
1-Sacroiliac joint irregular, widening, sclerosis, narrowing
then fusion.in early stages the plain x-ray apparently
normal so MRI of SIJ is needed to elicit early sacroiliitis.
2-Sequaring of vertebrea.
3- bridging Syndsmophyte.
4-Ossification of long. Ligament and facetal joint fusion.
5-Bamboo spine appearance.
6-Erosion at site of enthesitis and erosive changes of
peripheral joints.
7-Osteoporosis and atlanto-axial dislocation as late features

• DISEASE ACTIVITY IN AS CAN BE ASSESSED BY BATH
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS DISEASE ACTIVITY
INDEX (BASDAI), AND ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS
DISEASE ACTIVITY SCORE (ASDAS). THESE INDICES
ARE IMPORTANT IN ASSESSING INDICATION FOR
BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT

Management:
-Early Dx.
-Aim is to relieve pain and stiffness, maintain wide
range of movement and avoid deformity
development .
-Patient education and appropriate physical activity
are the cornerstones of management( daily back
extension exercises ) include morning warming up
exercises, swimming is ideal exercise, avoid bad
postures, and to punctuate prolong period of
inactivity with breaks.

• NSAIDs and analgesia for pain and stiffness ..
• -There is no evidence of the efficacy of DMARDs, including
sulfasalazine and methotrexate, for the treatment of axial
disease. Sulfasalazine may be considered in patients with
peripheral arthritis .
• Anti-TNF and IL-17 A therapy should be considered in
patients who are inadequately controlled on standard
therapy with a BASDAI
score of ≥ 4.0 and a spinal pain score of ≥ 4.0. or ASDAS ≥ 2.1
• -Local corticosteroid can be used in persistent plantar
fasciitis and other and in peripheral arthritis.
• - Oral corticosteroid may be require for uveitis.(should be
sent urgently to ophthalmologist).
• -Surgery. Hip, knees, shoulder restriction may need surgery.
Hip arthroplasty

• Over 75% of patients are
• able to remain in employment and enjoy a good
quality of life.
• Even if severe ankylosis develops, functional
limitation may not be marked, as long as the spine
is fused in an erect posture.
