
Infant Feeding
Breast feeding
Human milk is the most appropriate milk for human infant, it could be exclusive,
predominant, partial breast feeding.
Exclusive breast feeding mean giving breast milk only without any other substance .
Predominant breast feeding mean giving breast milk with non calorie containing substance
e.g. water or drug .
While partial breast feeding mean giving breast milk with calorie containing substance like
other milk and tea.
Anatomy of the breast
Breast is the largest exocrine gland, it consists of 18 segments which impeded in connective
tissues and fat, each segment consists of thousands of secretory units (alveoli). The alveoli
are surrounded by myoepithelial cells that have the ability of contraction, by which they
push milk to ductules then to larger ducts and to the lactiferous sinus that opens into the
nipple.
Physiology of breast feeding
The infant sucking reflex result in afferent impulse to the mother hypothalamus and then to
both anterior and posterior pituitary gland, from anterior pituitary the prolactin is secreted
which stimulate milk secretion in the acini of the alveoli of the breast, from the post pituitary
the secretion of oxytocin lead to contraction of myoepithelial cells which surrounded the
alveoli which squeeze milk into the larger duct, this called milk ejection reflex.
Advantage of breast feeding
First for the mother:
1- enhance the involution of uterus
2- decrease the incidence of breast cancer
3- emotional satisfaction
4- inhibit ovulation so as a method of contraception
Second for the baby:
1- mother milk is not allergic. Allergy to cow’s milk creates significant disturbances of
feeding, symptoms of cow’s milk allergy include: diarrhea, intestinal bleeding, occult
Melina, spitting up, colic and a topic eczema. Breast milk doesn't cause this because it
differs from cow's milk; in addition to contain secretory IgA.

2- decrease the liability for rickets because:
It contains double amount of vit. D, It contains the optimum calcium/ phosphate ratio (2:1)
this enable good absorption of calcium from gut.
N.B. as growth progresses, there will be an increased demand for vit. D, calcium and
phosphate, so we must supply the baby with extra vit. D starting for 3-4 months of age
onwards, along with exposure to sun light that adds the conversion of vit. D to active form.
3- Irons deficiency anemia is less frequent because;
Breast milk contains 1.5 times more iron than cow's milk. And better absorption
4- it has anti infectivity properties because :-
a. it contains bacterial and viral antibodies including secretary IgA which prevent
microorganism from adhering to the intestinal mucosa, also it contains IgG, IgM and IgD.
b. it contains lysosymes against bacteria and foreign bodies.
c. it contains lactoferrin (iron-binding protein), it has an inhibitory effect on the growth of
bacteria especially E.coli by it's link to iron i.e. deprive bacteria from its iron source leading
to bacterial stasis.
d. it contains lactoperoxide which is bactericidal.
e. it contains interferon which acts against viral infection.
f. it contains bifidus factor which enhances the growth of lactobacillus bifidus (normal flora
of the intestine that produce vit. K).
g. it contains bile salt which stimulate the lipase enzyme that kills Giardia lamblia and
Entameba histolytica.
h. it contains macrophage, lymphocyte (T and B cells) and epithelial cell, all of which act
against recurrent infection, G.E, and ARI.
i. low ph of the breast.
j. always breast milk is clean, not need heating, not need sterilization, and not need
preparation which may contaminate milk.
5- psychological satisfaction for the baby and mother.
6- Economical advantage.
-- CONDITIONS FOR WHICH HUMAN MILK HAS BEEN SUGGESTED TO HAVE A
PROTECTIVE EFFECT
Acute disorders
Diarrhea
Otitis media
Urinary tract infection
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Septicemia
Infant botulism
Chronic disorders
Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
Celiac disease
Crohn's disease
Childhood cancer
Lymphoma
Leukemia
Recurrent otitis media
Allergy
Obesity and overweight
Hospitalizations
Infant mortality
Technique of breast feeding
1- Proper position:
The mother should be relaxed and sit comfortably supporting her back, the infant should be
warm and dry, held by his mother in horizontal position facing her mother (not facing
the ceiling) that his abdomen in contact with mother's abdomen, his head is supported
by mother elbow and the buttock is supported by the hand of same side, so that the
hand of the other side is free, so can support the breast by C shaped way and avoid
scissoring way.
2- Proper attachment of baby to the breast (proper latch on);
Signs of proper attachment: all of upper areola and most of lower areola engaged in the
mouth of baby, the baby's upper lip and lower lip are averted, the baby's cheeks are
fuelled, baby's chin is in contact with the mother breast, there is no pain during
sucking and the sound of swallowing is heard by the mother.
To start feeding, the mother should stimulate rooting reflex of the baby by touching the
corner of the baby's mother by her nipple, so by this reflex the baby will turn his face
and open the mouth toward the stimuli, then the mother should engage her nipple and

areola in the baby's mouth. To finish feeding, the mother finger is introduce into the
baby's mouth between the gums or onto the internal aspect of the check to unlatch the
nipple and stop feeding, rather than pulling the nipple from the mouth.
After each feeding, the infant mouth corner should be cleaned, baby is held in erect position
for few minutes with several taps over back to eructate him, then put to sleep on the
cot on his right side.
Establishing and maintaining breast feeding
1-
initiate breast-feeding within 1 hr of birth
and four hrs. after s.c. and if there is no
contraindication for oral feeding we should start breast feeding, to go into rhythmic sucking.
2- Rooming in: that is to put the baby beside his mother
Place the newborn and mother skin-to-skin
to satisfied her and decrease the worry of the mother.
3- No need extra water unless the weather is hot.
Do not give sterile water, glucose, or formula
unless indicated
4- The baby must be exclusively breast fed in the first 4 and 6 months of life
5- 85% of the milk will be finish in the first 5 min. of feeding and in the 2
nd
five min. the
baby finish all milk, slow feeder infant take about 15-20 min.
6- Feeding at night will lead to prolactin secretion and milk supply.
7- Psychological factor: no factor important than happy and relax state of the mother, and the
mother should be fully alert when breast feed her baby.
8- The infant should be fed on demand, but infant who cannot be fed on demand he/she
should be fed every 3 hrs. on day and every 4 hrs. at night.
9- Bottle feeding will stop breast feeding because it lead to confusion of the baby between
the nipple and the teat of the bottle.
10- Mother's diet should be balanced.
Criteria of adequacy of breast feeding
1- The baby is calm, happy and sleep well after feeding.
2- Normal bowel motion, no constipation.
3- Normal urine output.
4- Normal weight gain: 20-25 gm/day.

Criteria of inadequate breast feeding
1- the baby is crying most of the time.
2- Long meal time (grasp the breast for a long period).
3- Very short sleep.
4- Loss of weight or failure to gain weight.
5- Constipation.
6- oliguria.
factors influencing milk Productions and secretions
1- Endocrine factor: prolactin, oxytocin, etc.
2- Anatomical factor: under developed breast, retracted nipple.
3- Mechanical factor: the Breast should be fully evacuated to enhance the process of milk
production and secretion so need good sucker.
4- Psychological factor, such as fear and stress of the mother.
5- Nutritional status of the mother.
6-drugs like chloropromozin (largectil), methachlopromid ( plasil) increase milk production,
diuretic and contraception ( hormonal) decrease milk production.
Mothers should be encouraged to nurse at each breast at each feeding starting with the breast
offered 2nd at the last feeding. The mature milk when secreted from the breast compose of
two parts, the first part called fore milk and second part called hind milk, if the baby take
both breast by one fed he will take only the fore milk which contain more lactose than water,
so the baby develop diarrhea (fore milk diarrhea). To treat this condition it is preferable to
empty the 1st breast before offering the 2nd in order to allow complete emptying.
Some conditions make difficult breast feeding:
A- on mother side:
1- Flat or inverted nipple.
Treatment:
a- antenatal treatment: probably not helpful, e.g. stretching the nipple, most nipples
improved around time of delivery.
b- soon after delivery:
1-build mother confidence explain that her breast will improve but need patience.
2- help her to position her baby.
3- help her to try different positions (other positions that easier for her), e.g. under arm
position.

4- use pump or syringe method to make nipple stand out.
5- for 1
st
w. express breast milk and feed baby with cup, or express the milk into the baby's
mouth.
2- Breast engorgement:
Painful, edematous, shinny overlying skin, milk not flow.
Causes: plenty of milk, delayed starting to breast feed, infrequent removal of the milk
(infrequent suckling).
D.D: full breast; heavy breast, milk flow easily, no fever and not shiny.
Prevention: start feeding soon after delivery, encourage unrestricted breast feeding.
Treatment: do not rest the breast.
*if baby able to suck: feed infrequently
*if baby not able to suck: express the milk by hand or with pump
Before feed warm compress or warm shower, massage to neck and back of the mother to
stimulate oxytocin reflex and light massage to the breast toward the chest of the mother.
After feed: cold compress on breast to reduce edema.
3- Mastitis
Mastitis may follow breast engorgement or a condition called a blocked duct. it occurs in 2-
3% of lactating women and is usually unilateral, manifesting with localized warmth,
tenderness, edema, and erythema after the 2nd postdelivery week. Sudden onset of breast
pain, myalgia, and fever with fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and headache can also occur.
Organisms implicated in mastitis include Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, group A
streptococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Bacteroides spp.
Diagnosis is confirmed by physical examination. Oral antibiotics and analgesics, while
promoting breast-feeding or emptying of the affected breast, usually resolve the infection. A
breast abscess is a less-common complication of mastitis, but it is a more serious infection
that requires intravenous antibiotics as well as incision and drainage, along with temporary
cessation of feeding from that breast.
Causes of blocked duct and mastitis:
1- infrequent or short breast feeding
2- poor draining of part or all the breast due to pressure from clothes, pressure from finger
during feeds
3- damaged breast tissue (due to trauma)
4- bacteria allowed entry (due to nipple fissure)

Treatment:
Improve draining of breast by treat the cause like remove the narrow clothes, advise
frequent feeding, start feeding on an affected side then on affected side, gentle massage
toward nipple, warm compress, if no improve use antibiotics like fluxacillin, erythromycin,
complete rest.
4-Nipple Pain
Nipple pain is one of the most common complaints of breast-feeding mothers in the
immediate postpartum period. Poor infant positioning and improper latch are the most
common reasons for nipple pain beyond the mild discomfort felt early in breast-feeding. If
the problem persists and the infant refuses to feed, consideration needs to be given to nipple
candidiasis, and both mother and baby should be treated if candidiasis is found. In some
cases, especially if accompanied by engorgement, it may be necessary to express milk
manually until healing has occurred
5-Nipple fissure and sore nipple:
Causes: improper position or attachment (latch on), or due to Candida infection.
Treatment: treat the cause like correct position and attachment, treat Candidiasis for baby
and mother, wash breast once and avoid use soap, avoid medicated lotion or ointment, rub
hind milk on areola after feed.
B- on baby side:
1- Catarrhal and blocked nose: due to upper ARI.
Rx: normal saline nasal drop or warm water nasal drop.
2- oral thrush; as mentioned.
3- tongue tie: short frenulum.
4- hare lip.
5- poor suck as in prematurity.
6-Milk Leakage
Milk leakage is a common event in which milk is involuntarily lost from the breast either in
response to breast-feeding on the opposite side or as a reflex in response to other stimuli,
such as an infant's cry. Milk leakage usually resolves spontaneously as lactation proceeds
Contraindication of breast feeding
A-on mother side:
1- mental and neurological disease of the mother.
2- infections like malaria, septicemia, typhoid fever, T.B., viral hepatitis and CMV infection.
3-secretion of toxic drug: like anticoagulant, antithyroid drugs, cytotoxic drugs.
4-chronic debilitatory disease, like H.F., renal failure, un controlled D.M.
B-on baby side:
1- inborn error of metabolism, like galactosemia, phanylketonurea.
2- cleft lip and palate.
Colostrum
It is the 1
st
milk produced after delivery continue for 3 days. At 3
rd
-10
th
day of infant life it
transform into the transitional milk and finally to mature milk, the amount of colostrum is
15-50 ml/day it is bright lemon in color, more alkaline than mature milk and has more
specific gravity, also have anti-infective and laxative effect which is benefit to get rid from
mecanium.
Content of colostrums: more protein, more mineral, less CHO and fat.
Protein 2.7 gm/100ml, fat: 2.9 gm/100ml, lactose 5.3gm/100ml, mineral 0.5 gm/100ml
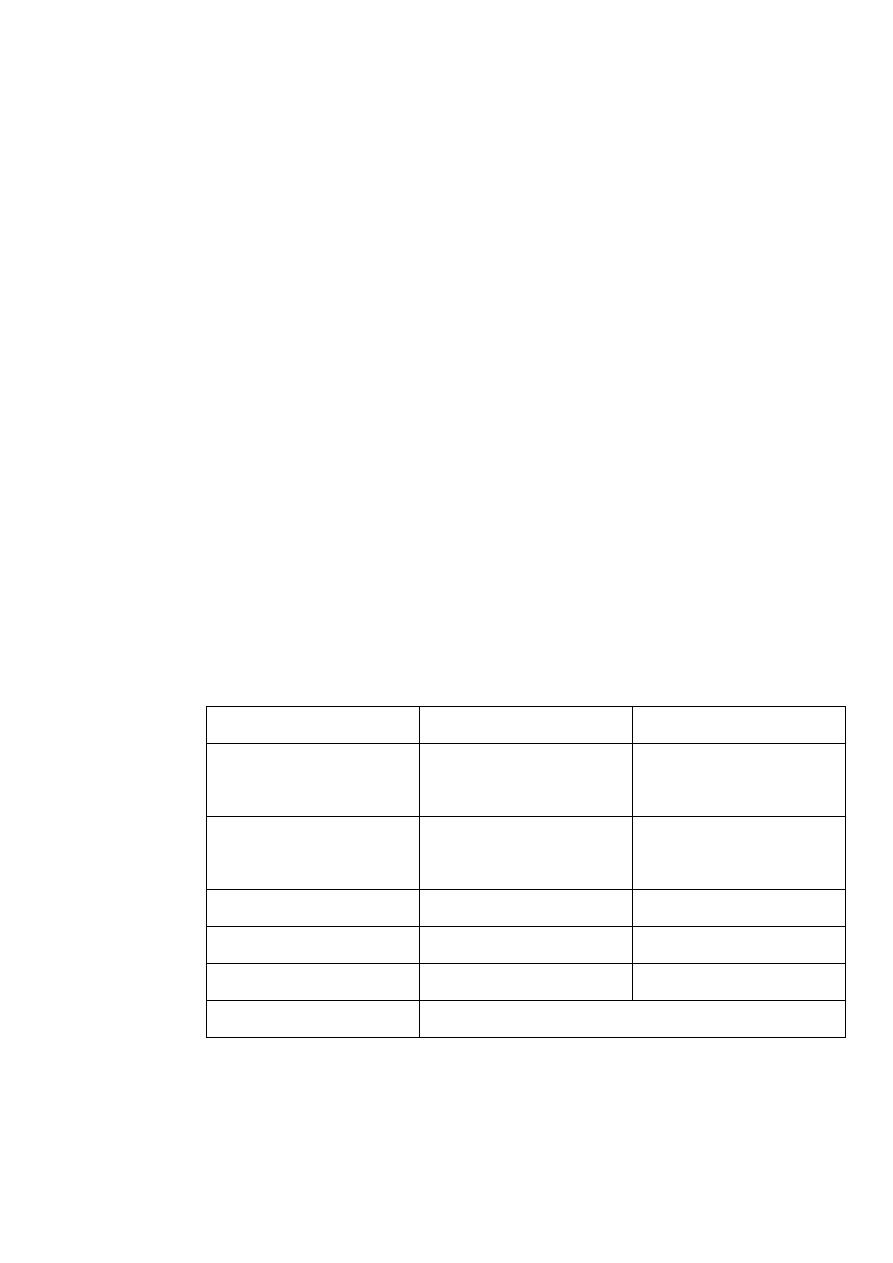
Comparison between human milk and cow's milk
Cow's milk
Human milk
Material
3.3 (80% casein, 20%
whey)
1 (30% casein, 70 %
whey)
Protein gm/100ml
4 (40% unsaturated,
60% saturated)
4 (6o % unsaturated,
40% saturated)
Fat
4.5
7
Carbohydrate (lactose)
67 Kcl/100ml
67 Kcl/100ml
Calorie
0.8%
0.2%
Mineral
The same
Water
Vitamins: cow's milk is low in vit. C and D, breast milk contain adequate vit. C and D
provided that the mother in good diet and exposed to some light, cow's milk contain more
vit. K than human milk, both types contain adequate vit. A and B complex.

Bacterial content: although human milk is essentially uncontaminated by bacteria,
pathogenic organisms in significant number may enter the milk from mastitis. Tubercle,
typhoid bacilli, herpes, hepatitis B, rubella, mumps, HIV and CMV may be found at times in
the milk of women infected by these organisms.
Cow's milk however is good culture for pathogenic bacteria, and many infections are milk
borne including streptococcal disease, diphtheria, typhoid fever, salmonellosis and
brucellosis, in addition to bacteria that cause G.E and diarrhea.
Digestibility:
The stomach empties more rapidly after human milk than after whole cow's milk. The curd
of cow's milk is reduced in size by boiling and makes less tough and much smaller by
evaporation or by add acid and alkali.
drugs and breast feeding
Contraindicated:
Antineoplastic, amphetamine, bromocriptine, cimetidine, chloramphenicol, ergots, heroin,
immunosuppressant, iodide, meprobamate, nicotin, Tetracycline, methimazol (antithyriod).
Avoid or give with great caution:
Aspirin (salicylats), atropine, birth contracaptive pill, cascare, calcifirol, metoclopramide,
metronidazole, Phenobarbital, primidine.
Probably save but give with caution:
Anesthetic, Acetaminophen, Aldomet, Chloropromazine, Cadine, Digoxin, Hydralazin,
Prednisollon, Theophyllin.
Formula feeding
Technique of artificial feeding
The mother and baby should be comfortable, unhurried and free from distraction, the infant
should be hungry, warm and fully a wake and should be held as if he is breast feeding. The
bottle should be held so that milk not air go through the nipple of the teat, the bottle is
warmed to body temperature, the temperature is tested by dropping milk on to the wrist. The
nipple hole should be of size so that milk drops slowly, the eructation of air swallowed
during feeding is important to avoid regurgitation and abdominal discomfort (this technique
is the same in breast feeding).

Indications of formula feeding
1- all contraindications of breast feeding insufficient breast milk (this is compose only 2% of
breast feeding mother), employment of the mother outside, twins and metabolic disease:
Types:
1- substitutive (no breast milk).
2- complementary breast and formula:in each feed, and supplementary one feed from breast
and the second feed from formula.
Types of milk formula
1- liquid milk
a- raw milk: this is not advised for infant feeding, it forms large curds in the stomach is
slowly digested and is easily contaminated.
b-pasteurized milk: pasteurization destroys pathogenic bacteria and modified casein, raw
milk is heated at 73cº for 15 min. then rapidly cooled, pasteurized milk should be boiled
when used for infant feeding, it is allowed to stand in the refrigerator for as long as 48h.
c- homogenized milk: in this milk the fat globules are broken into minute particles so
smaller and less tough curd produced in stomach
d- evaporated milk: the advantages are can keep for months without refrigerator, casein and
fat and softer so less curd in stomach , this milk can be feed in higher concentration (one
ounce → 44 KCL)
e- condensed milk: about 45% cane sugar has been added, more sweetened milk →↑ CHO
content to 60%. Although readily digested, it has no use in infant feeding for more than short
periods when a high calorie diet is desired.
2- dried milk: prepared by evaporating water from milk to dry for each 100cc of liquid milk
is transformed into 12.5gm powder (1:8).
a- dried whole milk: fat content is 3.5%.
b- dried skim milk: non fat skim milk, fat content o.5%, in half skim milk fat content is 1.5%
are available for infant with fat intolerance, should not be used in 1
st
2 y. of life, it's high
protein and mineral content may cause sever dehydration.
Advantages of dried milk:
1- sterile and highly saluted.
2- composition is constant.

3- can be stored for along period.
4- effect of heat on protein make it easily digested (casein is destroyed).
5- can be modified to different children.
6- less expensive.
Modified formula;
1- low lactose milk
2- lactose free milk e.g. isomil for galactosemia
3- hypo allergic milk (isomil) contain no milk protein, replaced by Soya protein completely
4- phenylalanine free milk (lofenalac) for phenylketonuria
6-Low Na milk for congested heart failure
3- acidified milk: these milk require less hydrochloric acid for gastric digestion done by
a- chemically : adding lactose, citrus or acetic acid to milk
b- biologically : adding lactobacillus
How much to feed?
80-120 kcal/kg/24 h. (110 kcal/kg/24h.), each 30 ml = 1oz = 20 kcal
Techniques and preparation:
Bottle is rounded not angled, teat is suitable in size, material and flow
Sterilization: boiling 5-10 min., or with Na hypochlorid tablet. How to reconstitue.? Ratio
1:8 ; one scoop 4gm reconstitute in 30 ml of water. American scoop is 8gm.
Weaning
Aims:
1- the child can not tolerate more than 1 liter/day, so with increasing needs for energy, more
solid food should be added.
2- with growth, babies requires more food items, such as mineral and vitamins that can not
be supplied by milk.
3- to train G.I.T. digest starch and other solid food.
4- to induce child dependence using spoon and cup by himself.
Basis and technique of weaning:

1- should start at the age of 4-6m.
2- weaning should be gradual to prevent G.I.T upset, also sudden weaning cause
psychological upset.
3- do not start at summer.
4- should not be start at convalescent period of any disease.
5- replacing on meal for milk feed: any new food should be initially offered once a day with
small amount (1-2 teaspoonful) new food are generally best accepted if fairly thin or dilute.
6- it is usually wise to offer the same food daily until the baby become accustomed to it, and
not introduce new food more after than every 1-2w. e.g. of food item:
a- fruit: washed banana is readily digested and enjoyed by most infants
b- vegetables: should be freshly cooked, vegetables are usually added to infant's food by 7m.
of age
c- eggs: the yolk of the eggs is used initially, egg white should be introduced with caution
from allergy. Potato start at the
2
nd
6m. of life, rice, bread added of 6-8m. of life, meat can
use by about 6m. of age. Citrus food after 1y., fish after 1y., tomato after 1y.
food additives: artificial flavors and colors have been associated with respiratory allergies,
urticaria and angioderma.
