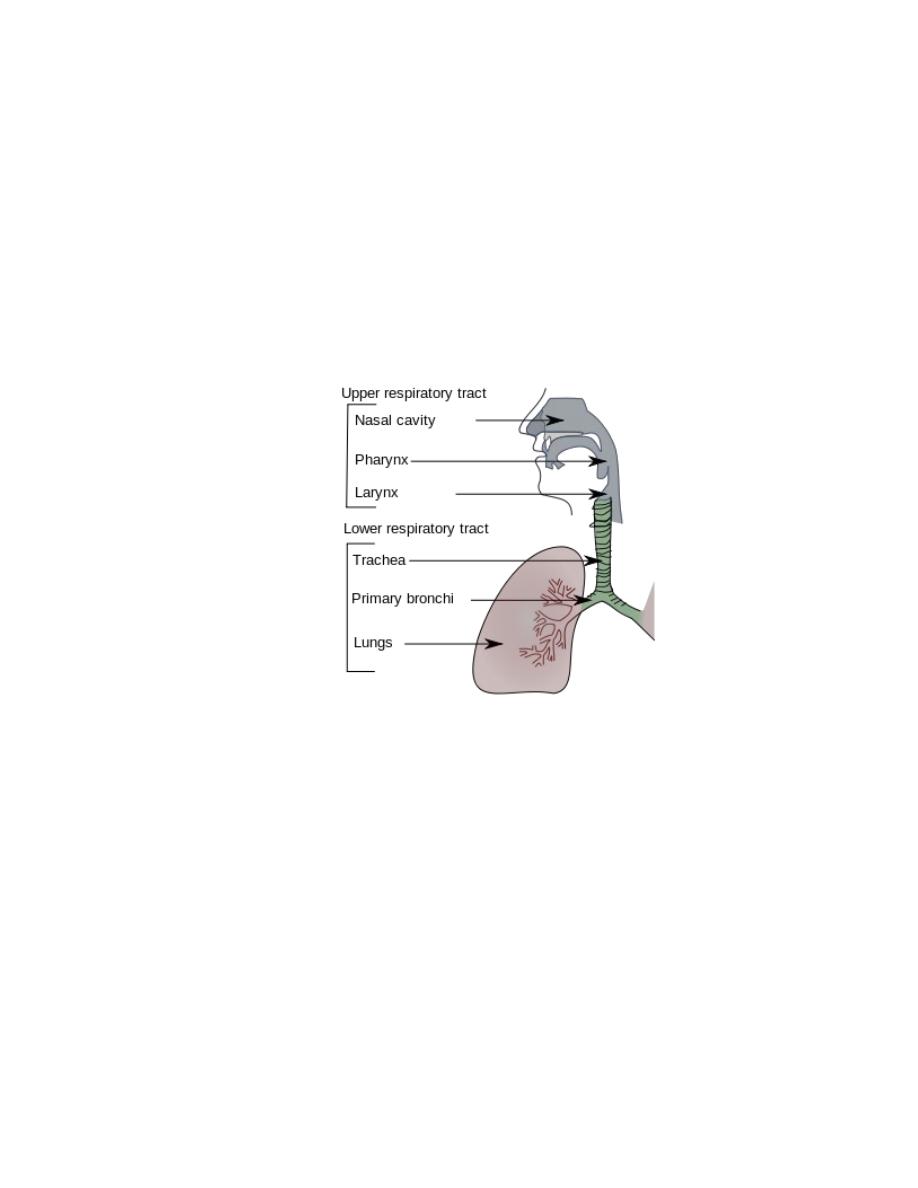
Air Way Obstruction )upper air way )
Is defined as blockage of the portion of the air ways located above thoracic inlet ,
manifested during inspiration because the pressure within upper air way is
negative relative to atmosphere ( negative pressure causing collapse of the air way)
Upper air way obstruction classified clinically into :-
1- congenital 2- acquired
Also classified into supra glottis or subglottis obstruction presented as
strider which is whistled sound
Upper air way obstruction classified according to to cause :-
A- new born ( until one month of age ) :---
1-foreign material( meconium and amniotic fluid )
2-bilateral cho-anal atresia
3-cong. Sub-glottic stenosis
4-micrognathia as in pierr Robin syndrome and Diagorgi syndrome .
5-macroglosia as in hypothyrodism &down syndrome
6-cong. Anomalies of the larynx , pharynx & trachea .
7-vocal cord paralysis
8-laryngospasm ( as in intubation and aspiration )

B- infancy ( 1—12 month of age )
1-laryngomalacia ( commonest ) 2-sub-glotic stenosis 3- rhinitis
4-vascular ring 5- tongue tumor & ectopic thyroid
C-Toddler ( 1—3 years ):---
1-viral croup ( commonest ) 2- spasmodic croup
3-F.B inhalation(forign body ) 4-bacteria trachitis
5-tonsil & adenoid hyperatrophy
6- retropharyngial abscess 7- diphteria ( rare )
D- above 3 years :--.
1- epiglotitis 2- F.B 3- trauma 4-angio-edema 5-IMN ( infec. Mono
nucleosis ) 6-anaphylaxasis 7- peritonsilar abscess in adolescent 8- diphtheria (
rare )
Cong. Anomalies :----
Laryngiomalacia :-
is defined by collapse or flabiness of supreglottis structures ( epiglotis or
arytenoid cartilage) during inspiration resulting in air way obstruction
which usually benign & self limited .
The symptom usually appear in the first two weeks of life and severity increased
for up to 6 months .
Clinical features :---
stridor is main presentation appear at birth or shortly after birth &
become symptomatic during first year of life ( but may delay to several
Years if infant has very large arytenoid stridor is loudest at :--- 1- feeding
of child 2- quit relaxing 3- supine position or neck flexion ,4- crying
and agitation
stridor is deminished at :-- at sleep
Stridor is exacerbated by viral infection

Symptom usually begin within first 2 weeks of birth and increased
symptoms within 4-8months, improved within 8-12 months and resolute
by 12-18 month of age or may extend to 24 months
Laryngoscope used in diagnosis of disease
Treatment :--
most infant are treated conservatively feeding modification like pacing ,
thickened liquid and food and upright posture , Many infant need antireflux
therapy infant has growth retarded or failure or hypoxia which needs
tracheostomy or epiglotoplasty
Subglottic stenosis :----
either cong. Or acquired ( which more common due to aggressive management in
preterm baby with intubation or mechanical ventilation resulting residual air way
damage to larynx .
stridor is main presentation ( recurrent or persistant croup ), occurred in
both inspiration and expiration and worsen with age
Treatment by tracheostomy or reconstructive surgery
Foreign Body :---
most victims are older than infant and toddler ( children of less than 3 years of
age account for 73% of cases , 33% of objects aspirate are nuts particularly
peanuts .
A positive history must never be ignored ( a negative history may be
misleading ) .Sudden chocking or coughing episode accompany by wheezing
are highly suggestive of an air way F.b .
F.B mostly lodged in a bronchus ( right bronchus in 58%)

Acquired causes of upper air way obstruction :-
involved either supra or sup glottic structures
How to diffrentiated between them :----
Example supra glotic supglotic
1- epiglot., peritonsilar abscess croup,
retro-pharangial abscess F.B,
trachitis,
angio-ed.
2-stridor 2- quit 2-Loud
3-voice 3-muffled 3-hoarse
4-dysphagia 4-yes 4-no
5-sitting up or arching posture 5-yes 5-no
6-barking cough 6- no 6- yes
7-fever 7-high 40 c 7-low 38-39
8-toxicity 8-yes very toxic 8-no unless trachitis.
9-trismus 9-yes 9-no
10-drooling 10-yes 10-no
11-facial edema 11- yes 11-no unless angio-edema

Epiglottitis :---
is pediatric emergency , dramatic & potentially lethal condition
because of inflamed air way may obstruct suddenly& totally leading to
death infection lead to acute onset of inflammatory edema in lingual
surface of epiglottis where submucosal surface is lossely attached
the edema is rapidly progress to involve aryepiglottis fold , arytenoid and
entire subglottis leading to frank air way obstruction .
Caused by H. influenza type B which recovered from surface of
epiglotitis or from blood culture.
Age of incidence is 2—7 years ( peak age 3.5 year )
ClF :---usually no prodromal symptoms ( fever is first symptome followed
by strider , labored breathing , dysphagia and sore throat )
1- no other family members are ill .
2- is fulminating course of high fever , sore throat , dysphagia, dyspnea,
stridor, drooling , more progress to total obstruction & prostration
unless adequate treatment are given( stridor is late finding& suggest near
complete air way obstruction ).
3- moderate to sever respiratory distress( S.T. fulminating pulmonary
edema may present )
4- cynosis occurs in sever cases.
5- cherry red enlarged epiglotis by laryngoscope
6-X-ray of lateral film of neck showing thumb sign as swollen epiglotis
7- in young patient ---- neck is hyper-extended, while in older patients
prefer sitting up position ,learning forward , mouth open &tongue
protruded .
Classical triad symptoms ( dysphagia , drooling and distress ).
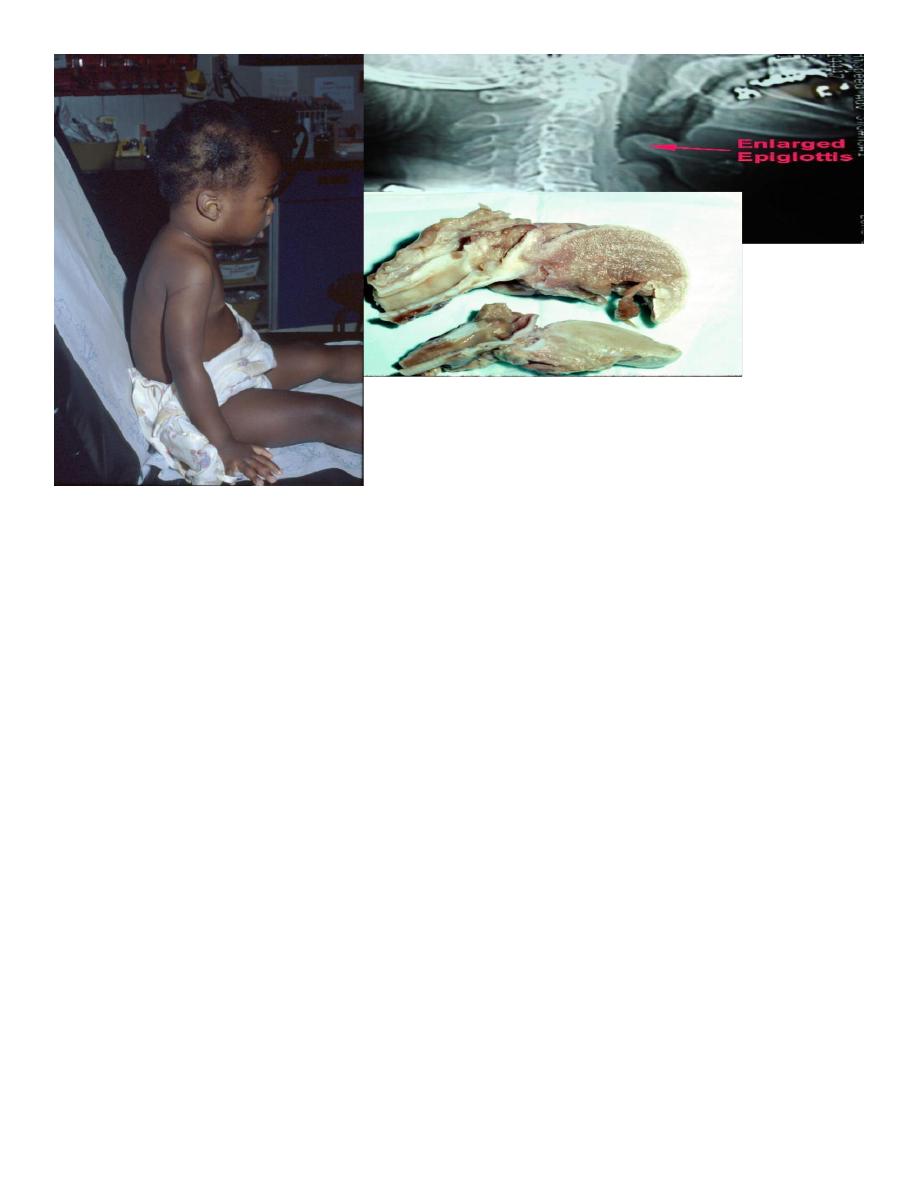
8-most pts have concomitant bacteremia ocasionally ( other infection are
present like pneumonia , O.M , cervical LAP , while meningitis , arthritis
are rare. blood culture is positive in 12-15% to 90%
culture from epiglottis surface is positive in 50-75% CXR with
consolidation in 15% ( because may associated with pneumonia) .
DD :--
1- croup 2- bacherial trachitis 3- F.B aspiration
4- ludwig angina 5- retropharyngial & peritonsilar abscess
Treatment :-- Aims of treatment :- 1- relieving of air way obstruction
2-eradication of infection agent
3-avoid any procedures that lead to
anxiety like blood aspiration unless secure airway .
Never place the child in supine position as it may lead to resp. arrest
1- admission for any suspicion of disease where close observation
should be done .

2-endotrachial intubation is currently preferred method of treatment (
6% of children die without artificial airway , compared to less than 1% of
those with artificial airway .)
3-Antibiotic – ceftrixone or cefotaxime or combination of ampiciline +
chlormphenico or ampiciline + sublactum duration of treatment is 7—10
days ( most patients safely extubated within 2—3 days ) .
Prevention :--- by H. infl. Vaccine .
Croup :---
is defined as term referred to a heterogeneous group of mainly acute &
infectious process that are characterized by bark like or brassy cough ,
may be associated with inspiratory strider .
Is caused by viral infection mostly Commonly occur in late fall &
early winter .
Has 2 types --- 1- infectious type . 2- spasmodic type( recurrent
type )
Etiology :--
75% by PIV , can be caused by adeno, measles, influeza, and RSV
, Can be caused in 3.6% by mycoplasma .
Pathology :-- 1- inflammatory edema
2-destructed ciliated epithilia
3-exudate

ClF :----
1- age is between 6 month to 3 years ( now age is 3 month to 5years )
with peak age in second year
2- most patients proceeded by URTI of several days of less than 5 days
3-at first mild brassy cough with intermittent stridor & if obstruction is
( resp. distress is increased , the stridor become continuous ass. with
resp.distress unusual except in young infant ) .
4-infection going down to reach bronchi & bronchiols leading to resp.
distress with elevation of temperature with reach to 40 .
5- if croup is suspected , examination is deferred & O2 is administered
until patient is transferred to place of hospital where Optimal
management possible
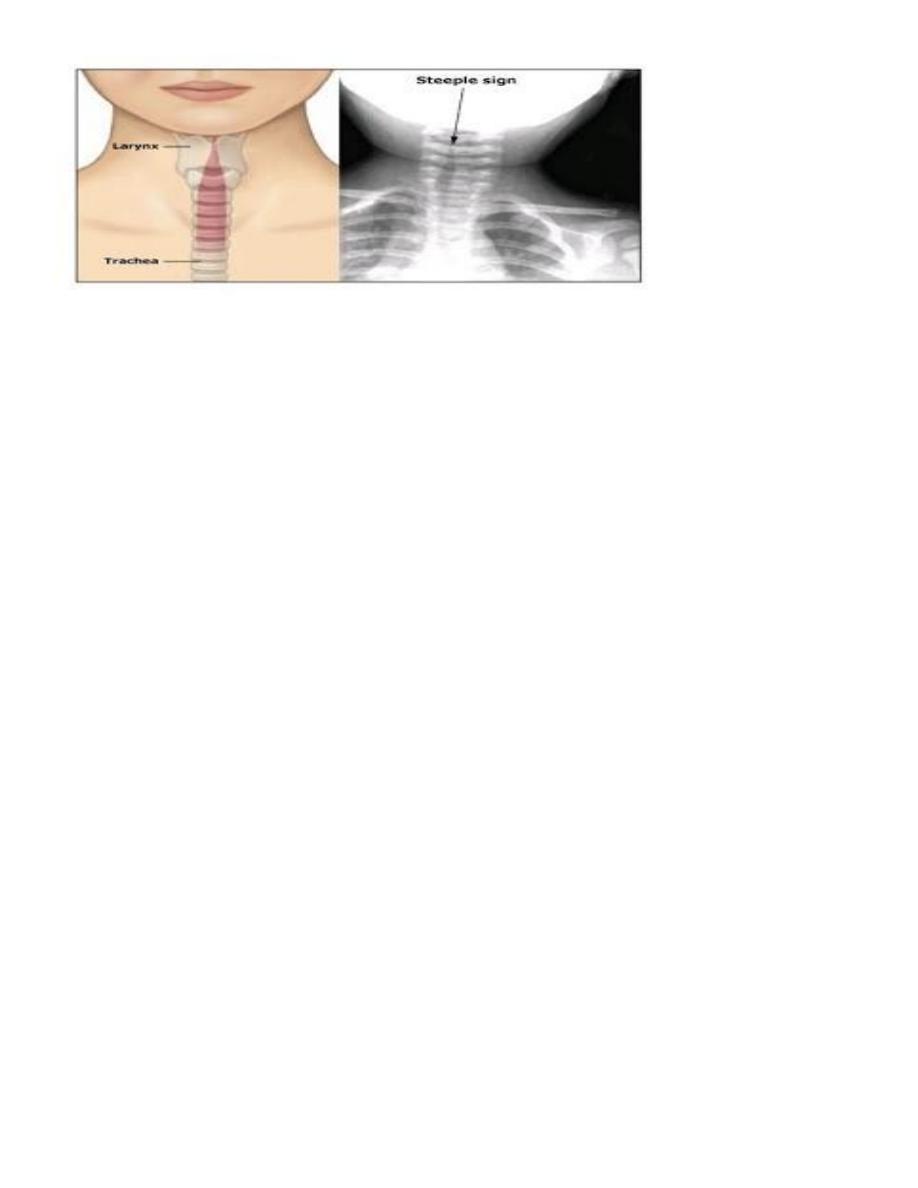
6- X-ray reveals steeple sign ( mean narrow subglotic space) & is not
assoc. with disease severity .
duration of illness ranged from several days to rarely several wKs
Spasmodic croup :----( recurrent croup ):---
clinically is similar to infectious croup except that finding of
infection in a patients & family are absent .
Age of presentation is 1—3 years
precipitating factors are :--
1- viral infection in some cases only . 2-allergic & psychological
factors 3- G.E.R which may role important
Pathology :-- normal epithilial & pale watery edema
ClF :---1- most frequently occurs at night or evening .
2-occurred in sudden onset that may proceed mild to moderate
coryza .
Note :- croup may be early sign of asthma .
The child may be awaken with barking cough , noisy inspiration &
respiratory distress and may be appeared anxious & frightened .
3- afebrial
4-distress may be exacerbated by excitation & usually diminished
within several hours & following days .
Such episode usually several times .
DD :---
1- epiglotitis 2- trachititis 3- diphtheria ( present gray white
appearances on pharyangial examination) .
4-measles croup 5-F.B aspiration 6- angio-edema
7-retropharangial & peritonsilar abscess 8- hypocalcaemia with
laryngial tetany 9-extrensic compression of air way like hematoma
or mass

CX :-- occurs in 15% with viral croup .
1- commonest cx. Is extension of infection to involve other region
of resp. tract like middle ear , bronchial & pul. Parenchyma
2- trachitis 3- interstial pneumonia
4-broncho pneum.( is unusual unless aspiration of gastric contents
occurred during period of resp. distress although 2nd bacterial infection
is rare )
5-pneumothorax & pneumomediastinum ( common CX. Of
tracheostomy ) .
Causes of death in croup :---
1- laryngial obstruction
2- tracheostomy Cx like pneumo thorax & mediastinal
emphysema .
How differentiate clinically between laryngomalacia and subglttic
stenosis :--
Clinical laryngomalacia subglottic stenosis
1-age of onset first month &increased up to at birth
6 month
2-stridor inspiratory both inspiratory
expiratory
3-fate improved with age worse with age
4- position of patient yes no
including arching or sitting up

How differentiate clinically between epiglotitis and croup
Factors epiglotitis croup
1-age 2-7years( 3.5years) 3months-5years
2-onset sudden gradual
3-other member no yes
of family
4-stridor quit loud
5- voice muffled hoarse
5-dysphagia yes no
6-fever & toxicity yes no
7-barking cough no yes
How differentiate between types of croup:--
Factors infectious spasmodic
1-age of onset 3months-5years 1-3years
2-onset gradual sudden
3-fever low grade fever a febrile
4-duration of stridor days hours –
5- recurrence sometime mostly recurr
