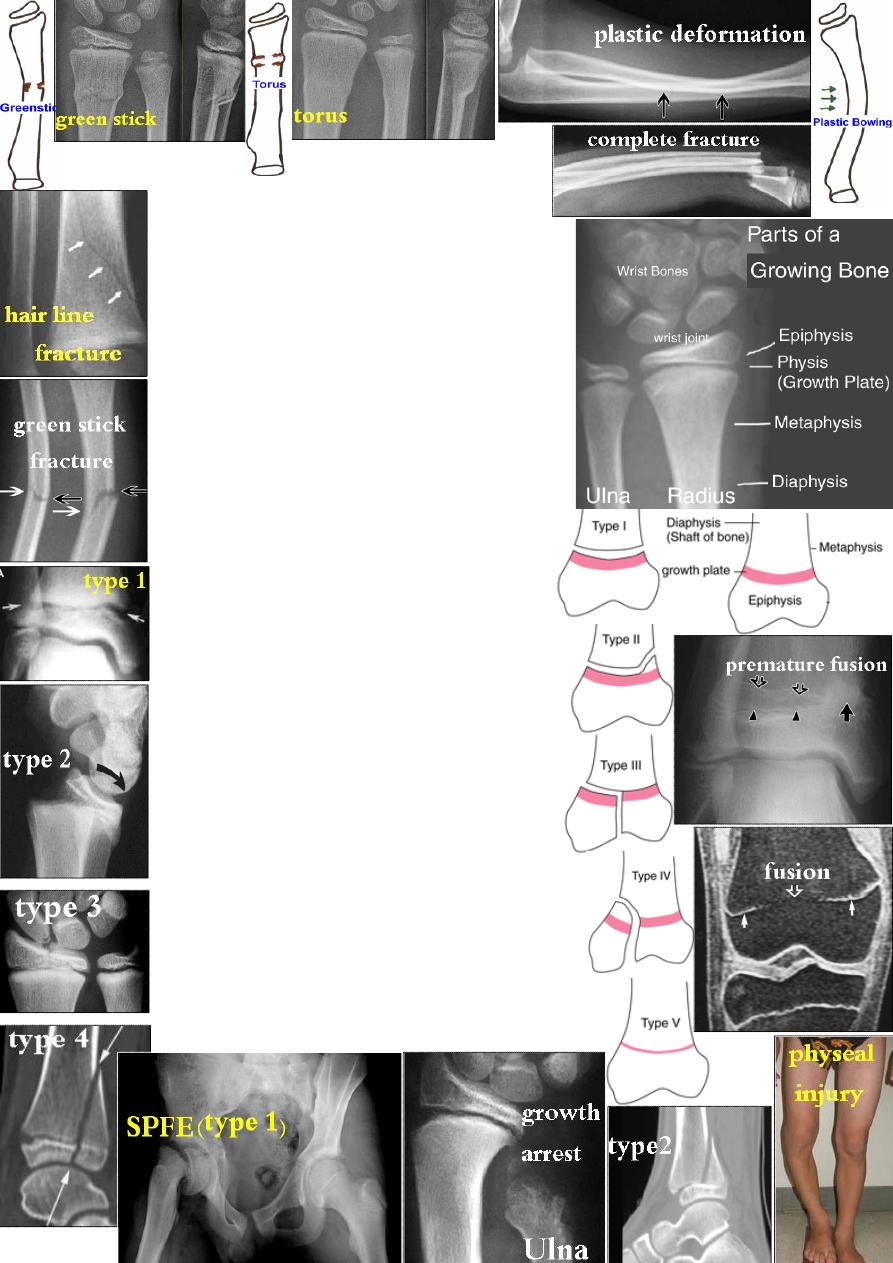
Paediatric fractures:
Fractures in children could be:
1- complete # like adult #,
2- green stick incomplete #, 3- torus (buckle) #,
4- plastic deformation or 5- physeal injury.
physeal injuries:
Physis or growth plate consists of 4 layers
(from superficial to deep):
1-resting layer. 2-hypertrophied layer.
3-proliferating layer. 4-calcified layer.
About 10% of # in children occur through
the physis. These usually run transversely
through the hypertrophied or calcified layer,
both have little effect on growth which takes
place in the proliferating layer. So, if a # pass
through proliferating layer, then premature
fusion &later growth disturbance may occur.
Classification of physeal injuries:
(Salter-Harris)
І- transverse # through the hypertrophied or
calcified layer. Usually occur in infants, but also
may occur at puberty like slipped upper femoral
epiphysis. Prognosis is good.
П- transverse # through the physis, but at the
edge it splits off a triangular fragment from
the metaphysis. Prognosis is also good.
Ш- vertical # through the epiphysis then
transversely through the physis splitting a
segment off the epiphysis. This require accurate
reduction to prevent growth disturbance.
ІV- fracture that split the epiphysis & metaphysis.
Prognosis is similar to type Ш.
V- longitudinal compression of the physis causing
crushing which may end with growth arrest due to
bony fusion. The
# is not
visible, so the diagnosis
is retrospective.
