1
د.عادل الهنداوي
Injuries of the ankle &foot:
the ankle is formed by lower tibia& fibula
forming the ankle
mortise + the talus lying in the mortise.
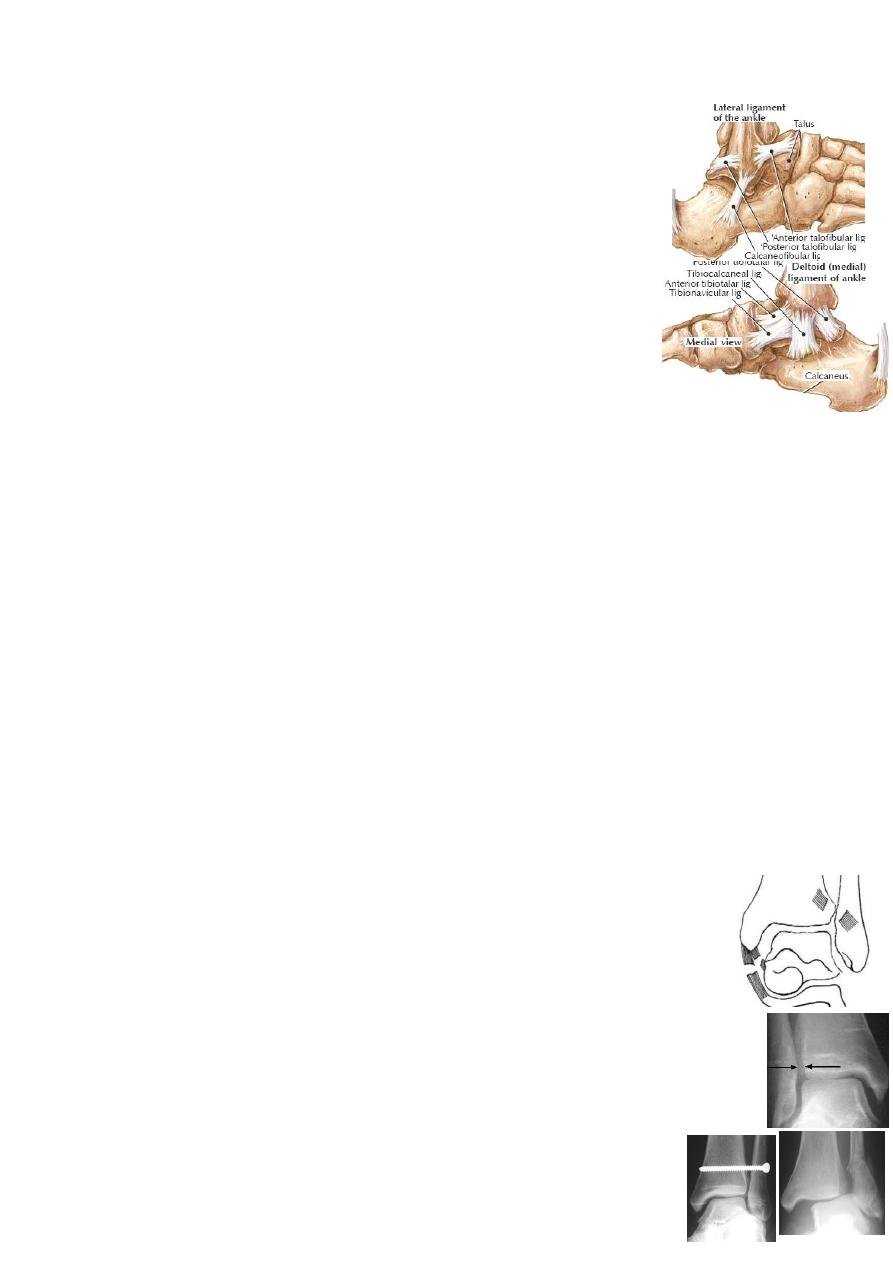
The ankle is stabilized by 3 groups of ligaments:
1-lateral collateral ligament→ anterior &posterior talofibular(TFL) &
calcaneofibular ligaments(CFL).
2-medial collateral(deltoid) ligament→ superficial &deep.
3-inferior tibiofibular ligaments→ anterior & posterior.(syndesmosis)
Ankle ligaments injuries:
>90% involve the lateral ligaments.
Injuries of the lateral ligaments:
MOI: twisted ankle with inversion &plantar flexion→ partial or complete tear of
ATFL→ CFL→ PTFL.
CF: swollen bruised ankle with tender lateral side &painful inversion.
X-ray: AP, Lateral &oblique views: may show avulsion of tip of lat. malleolus.
Stress view shows talar tilt(unstable ankle) if the tear is complete. *Exclude foot
injury &ankle # or tibiofibular(syndesmosis) diastasis.
Treatment:
Partial tear(sprain &strain): elastic bandage until swelling subsided, active
exercise, correct heel-toe gait &avoid dangling the foot.
Complete tear: 6weeks below-knee cast→ 4weeks ankle brace &physiotherapy.
Surgical repair is advisable in top class athletes.
Complication: Recurrent lateral instability: occurs in 20% after complete lat
lig tear. CF: attacks of giving way &instability; O/E: excessive inversion & +ve
anterior drawer test. X-ray: show talar tilt on inversion stress. Ŗ: conservative→
raise lateral side of heel &extend it laterally, peroneal muscles exercise &brace.
If all these fail→ operative: lig repair or peroneus brevis tenodesis.
Deltoid ligament tear: usually associated with fibula # or diastasis.
X-ray: widening of medial joint space.
Treatment: CR→ 8 weeks below-knee cast. If CR fails→ OR(soft tissue
interposition).*the AP view of the ankle should be in 30˚internal ankle
rotation(mortise view) to see the lateral joint space.
Inferior tibiofibular ligaments tear: usually associated with other
injuries(e.g.# fibula or deltoid lig tear). If both ant &post TFL are torn
→ complete tibiofibular joint separation(TF diastasis).
If only anterior TFL is torn→ partial diastasis.
MOI: ankle external rotation or abduction force.

2
CF: tender swelling over front of ankle. Squeeze test→ pain over
the syndesmosis.
X-ray: with complete tear→ wide ankle mortise.
Treatment: Partial tear→ 3weeks elastic bandage.
Complete tear→ urgent ORIF with transverse screw→ 8weeks cast.
Complication: if operation is delayed→ persistent pain &instability.
Fractures of the ankle(Pott's #):
is common.
MOI: the patient stumble &fall(foot is anchored while body go forward)→
talus rotate&/or tilt in the mortise→ # of one or both malleoli ± ligament tear.
The pattern of injury depends on foot position (supinated or pronated) &force
direction on talus(external rotation, adduction, abduction or combination).
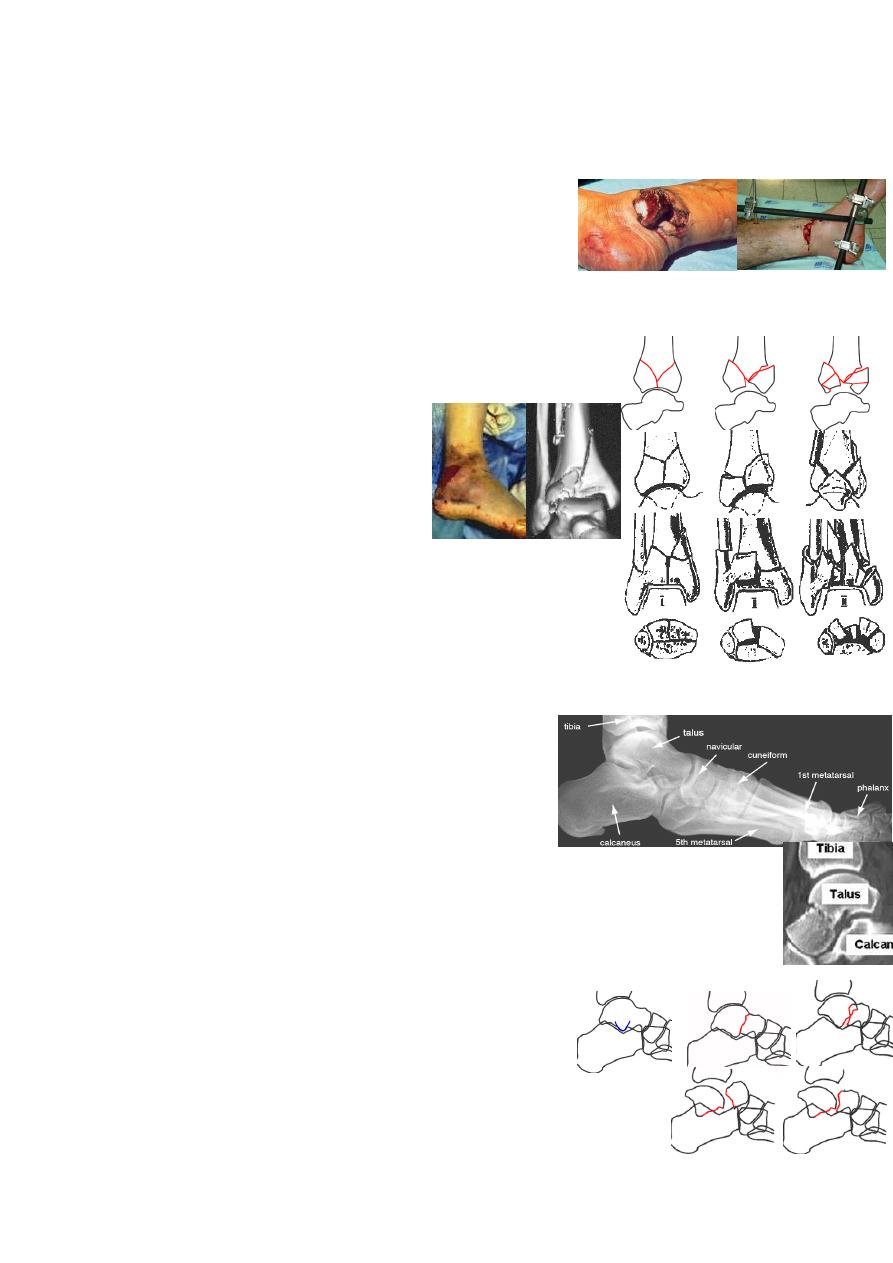
Danis -Weber classification: according to level of fibula #:
A→ transverse fibula # below syndesmosis ±
vertical # of
medial malleolus(adduction injury).
B→ oblique fibula # at syndesmosis
±
transverse medial
malleolus # or deltoid lig tear(external rotation injury).
C→ fibula # above syndesmosis(TFL &interosseous lig tear)
± diastasis, medial injury, posterior malleolus #(abduction &
external rotation injury).
CF: swollen deformed ankle.
X-ray: AP view→ joint space;
Lat view→ fibula #;
Mortise view→ diastasis.
Treatment: there are 4 principles: 1-don’t delay(rapid severe swelling)
2-treat the entire injury(# &lig tear). 3-accurate reduction(intraarticular).
4-check &maintain reduction.
Undisplaced type A&B #→ 2weeks split below-knee cast→ checking x-ray→
8weeks complete cast.
Undisplaced type C #→ can be the same Ŗ but better ORIF.
Displaced type A&B #→ CR &casting; if failed or displaced later→ ORIF.
Displaced type C #→ ORIF.
X-ray signs of ligament tear (# instability &need of ORIF) are:
1-wide medial joint space >4mm; 2-wide TF space >6mm;
3-talar tilt; 4-asymmetry of talotibial space.
Methods of fixation: fibula #→ plate &screw; medial malleolus→
3
malleolar screw or tension band wiring; TF diastasis→ transverse TF screw.
Complications: malunion, nonunion &ankle stiffness.
Open ankle #: most can be Ŗ by ORIF except severe cases→ external fixation.
Pilon fractures:
MOI: axial force like FFH will drive the talus up striking tibial plafond.
CF: severe swelling with # blisters &ankle deformity.
X-ray: comminuted distal tibia # extending into the ankle.
CT is better & 3D CT is the best.
Rüedi classification: І: undisplaced;
П: minimally displaced;
Ш: markedly displaced.
Treatment: first treat the soft tissue
swelling by 2-3weeks elevation then:
І→ 12weeks below-knee cast(NWB).
П→ ORIF using plate &screws(wound breakdown &infection).
Or skeletal traction through calcaneal pin for 12weeks.
Ш→ skeletal traction or external fixation(indirect reduction
through ligamentotaxis).
Complication: infection, nonunion & OA.
Foot injuries
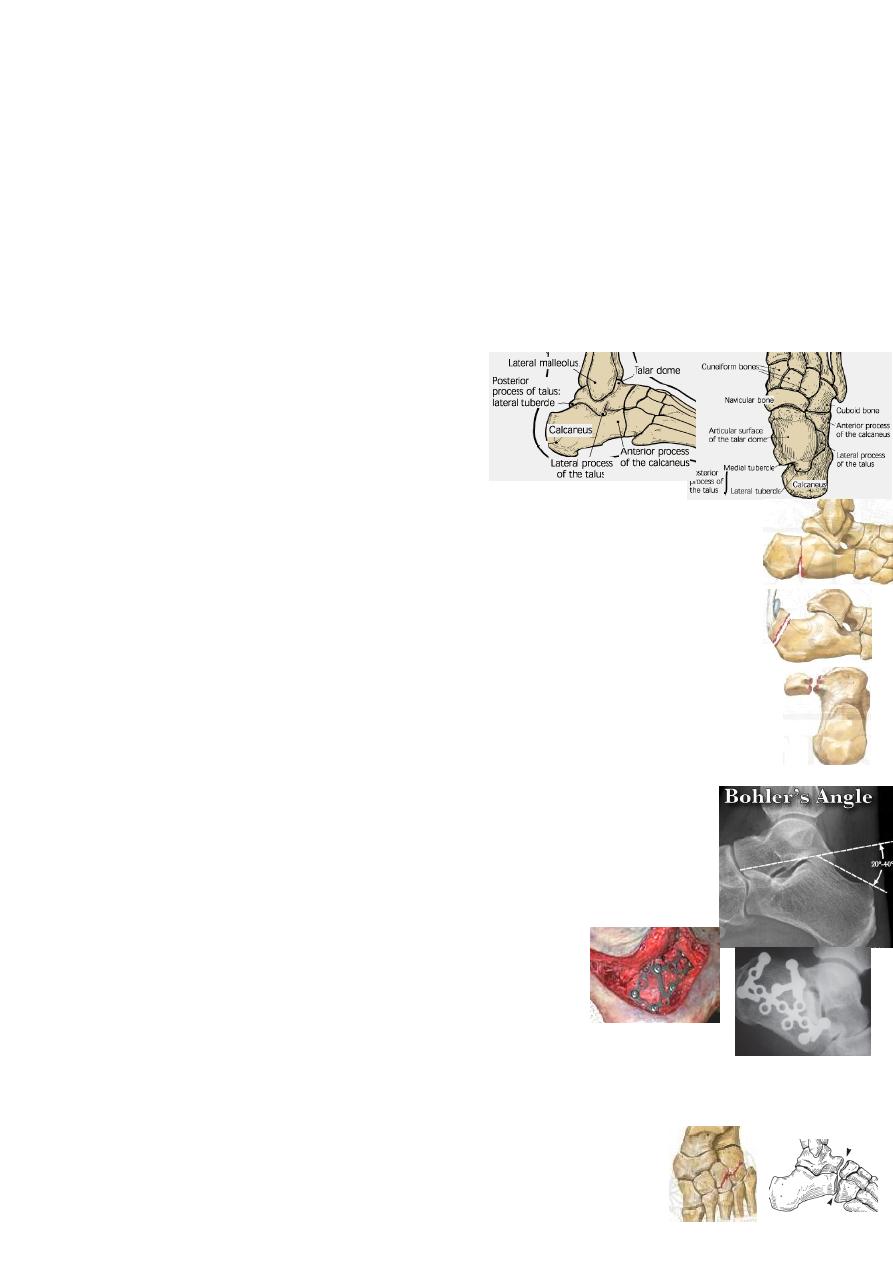
Injuries of the talus:
are uncommon.
MOI: severe violence like FFH, RTA or severe twisting injury.
*the blood supply of talar body comes mainly from neck vessels running from
anterior to posterior; if these are torn(by neck #)→ talar body avascular necrosis.
CF: swollen foot &ankle; deformity; skin split or tented→ slough later.
X-ray: AP, Lat &oblique views; CT for body #.
Look for # of talar head, neck, body, talar processes, or osteochondral #
&for ≠ of midtarsal, subtalar &ankle joint.
Fractures of talus head→ are rare.
Fractures of talus neck→ Hawkins:
І: undisplaced #; П: displaced # with subtalar joint ≠;
Ш: displaced with ankle joint ≠; ІV: with talonavicular ≠.
Fractures of talus body→ are rare.
Fractures of lat &post processes →occur with ankle lig injury.
4
Osteochondral #→ often missed; needs CT for diagnosis.
Treatment:
Type І→ 8weeks below-knee cast(4weeks NWB).
Type П→ MUA &12weeks NWB cast. If fail→ ORIF.
Type Ш&ІV→ ORIF by k-wires or lag screws.
Complications: early→ skin damage: debridement &delayed closure.
→ talar detachment: clean &reduce.
late→ malunion; avascular necrosis of talus body(50% in displaced neck #).
→ OA of subtalar or ankle joints due to malunion, avascular necrosis or
cartilage damage; Ŗ→ arthrodesis of the affected joint.
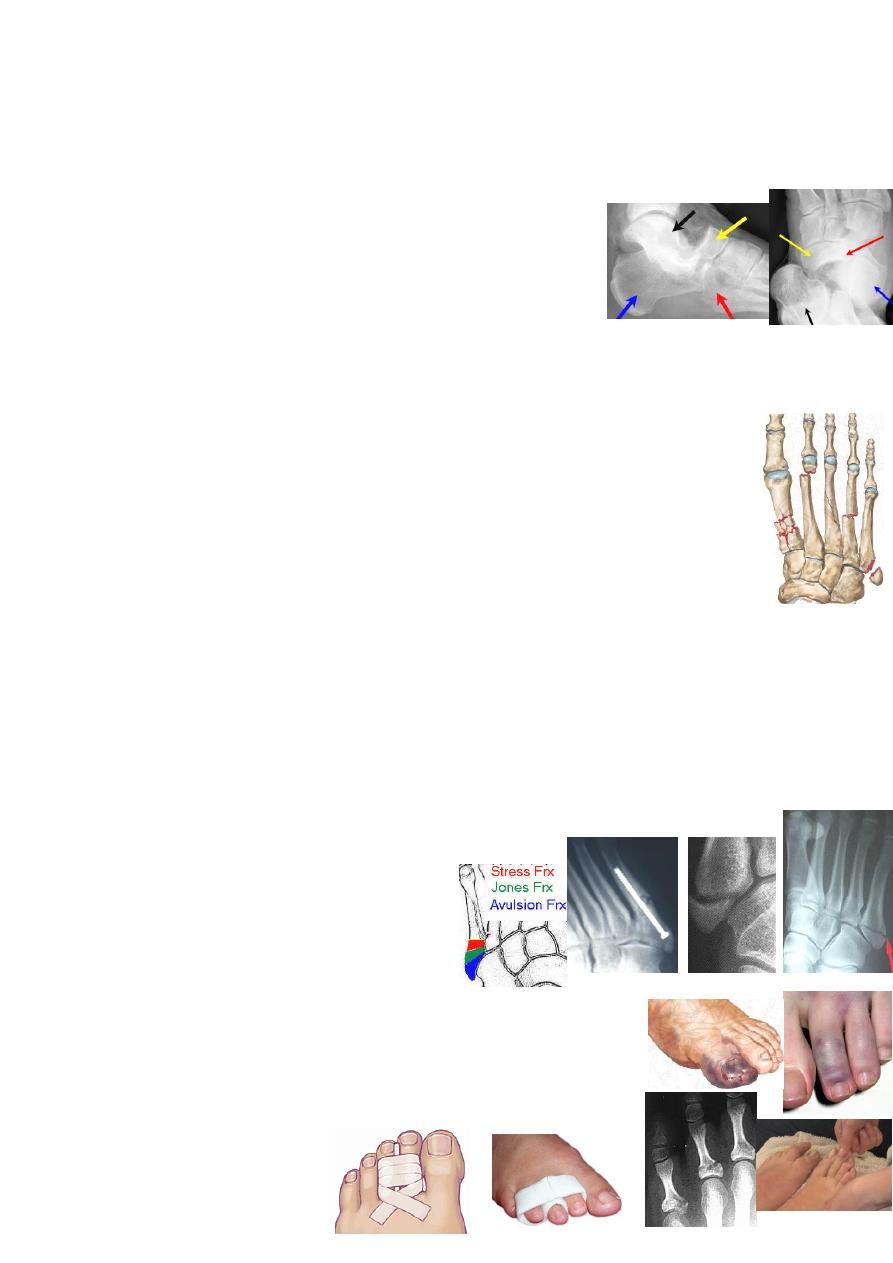
Fractures of the calcaneum:
are common.
MOI: usually FFH e.g. ladder(20% have also spine, pelvis, or hip injury);
Traction injury causes avulsion #; direct blow is rare.
Calcaneal # are either extra-articular or intra-articular(involve the subtalar joint).
Extra articular #(25%): are easy to Ŗ with good prognosis like:
Anterior process #, body(behind talocalcaneal joint), calcaneal tuberosity
(avulsion by Achilles tendon), Sustentaculum tali &inferomedial process.
Intra articular fractures(75%): either: 2parts # or 3parts #: joint depression
type or tongue type.
CF: swollen bruised foot with short broad heel;ankle movements are normal.
X-ray: AP, Lat, oblique &axial(Harris) views.Measure tuber-joint
(Böhler's)angle on lat view: 20˚-40˚ is normal.If # is displaced→ <20˚.
CT(especially coronal image) is the best for accurate diagnosis.
*calc # in 10% is bilateral &10% have spine #.
Treatment:
Extra articular #→ 2weeks elevation, exercise &
crepe bandage→ 4weeks NWB→ 4weeks PWB.
For displaced tuberosity #→ ORIF by cancellous screw.
Intra articular #:
Undisplaced→ the same conservative Ŗ.
Displaced→ ORIF: screws(±bone graft to fill defects)&lateral buttress plate.
Complications:
Early→ swelling &blistering &even compartment syndrome.
Late: 1- malunion→ short, wide &valgus heel.
2-Peroneal tendon impingement. 3-subtalar OA.
5
Mid-tarsal injuries→ sprain of midtarsal joint;
#(navicular, cuboid, cuneiforms); # - ≠ (talonavicular, calcaneocuboid joints).
MOI: twisting force, FFH, crushing injury.
CF: swollen bruised foot; compartment syndrome.
X-ray: all tarsal bones should be clearly seen.
Treatment: sprain→ crepe bandage. *often # &#-≠ are missed.
undisplaecd #→ 1week elevation→ 6weeks cast.
displaced #→ may needs ORIF: screw or k-wire.
fracture-dislocation→ CR or OR &k-wire fixation.
Tarso-metatarsal injuries: sprains or #-≠ of the 5 joints.
MOI: high velocity injury.
X-ray: is not easy to interpret, take multiple views &compare with normal.
Concentrate on 2
nd
&3
rd
metatarsal.
*
Treatment: sprain→ 4weeks cast.
# - ≠→ CR or ORKF &8wk cast.
Metatarsal fractures: are common. 4 types:
MOI: direct blow→ crush #.
Twisting injury→ spiral #.
Traction injury→ avulsion #.
Repetitive stress→ stress #.
Treatment:
Undisplaced #→ few days elevation &exercise→ 6weeks cast.
Displaced #→ the same Ŗ but significant displacement in the sagittal plane
especially of 1
st
metatarsal→ CR or open RKF.
Traction injury:
forced foot inversion may avulse(by peroneus brevis) the base of 5
th
metatarsal.
x-ray: transverse #. A peroneal ossicle may be mistaken for a #(it is bilateral).
Treatment: few days elevation &crepe bandage.
if pain is severe→ cast.
Severe displacement→ ORIF by screw.
Metatarsophalangeal joints injuries: sprain→ strapping.
dislocation→ closed reduction or ORKF & few weeks cast.
Fractured toe→ few weeks strapping to its neighbor.

6
