Enzymatic Defects
G6PD Defeciency
Is X-linked disease , is most important dis. Of hexose
mono phosphate pathway , is responsible for 2 clinical
syndromes :--
a-
an episodic H. A ( hemolytic anemia ) induced by
infection , drugs , fava bean .
b-
spontaneous chronic non spherocytic hemolytic
anemia .
A--- episodic H.A ;---
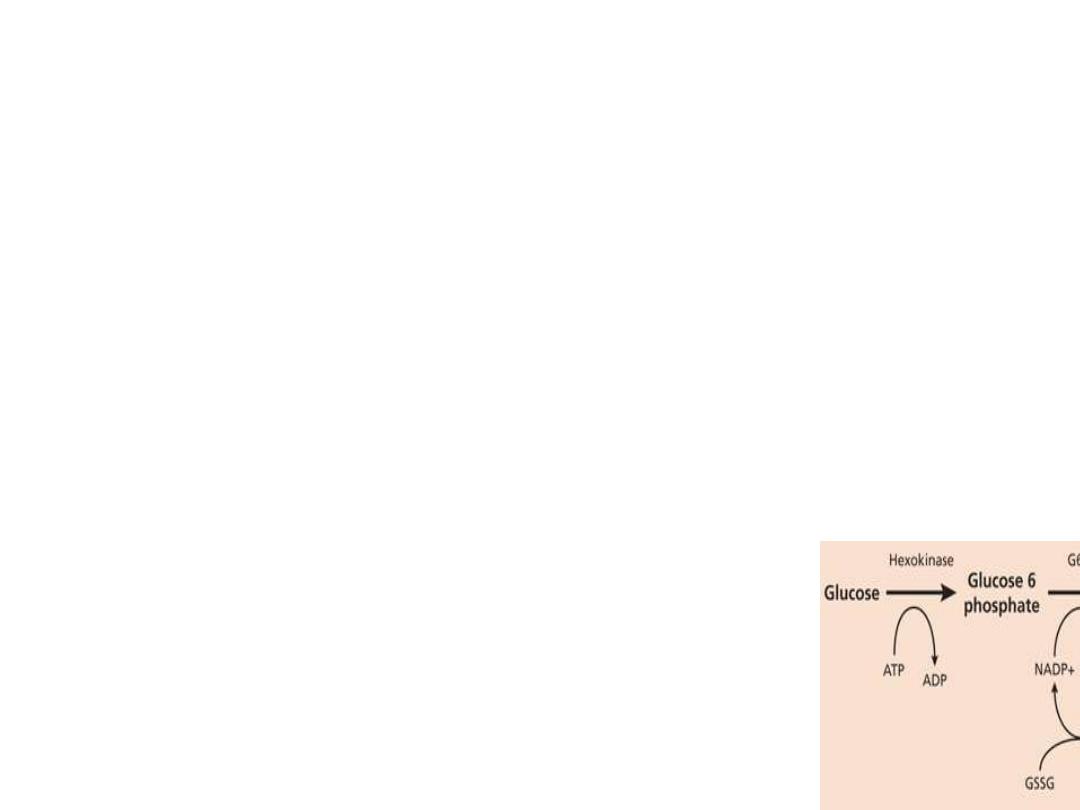
Oxidized glutathione
NADP -----by G6PD ---NADPH---Glutathione
reductase
reduced glutathione
( as anti oxidents )
Glutathione act to neutralized agent that potentially oxidized either Hb or
components of Red cell membrane .
If reduced glutathione can not sustained to remove O2 radicalls generated by
oxidants drugs leading to Hb precipitate forming heinz body and
Red cell membrane is critically damaged leading to premature destruction
or hemolysis .
•
.

Clinical feature
recurrent or episodic attack of H.A where clinically appear as pallor &
red urine , developed after 24-48hr after ingestion of oxidant properties
•
Agent precipitate hemolysis in patients with G6PD def.
:---
•
A-
medication :---
1
- antibiotic
like nalidexic acid , chloromphenicol, sulfa.,
nitrofuradantin
2
- anti malaria
3
- others like phenacetin , asperin,
vit. K analogue , phenazopyridine .
•
B-
chemical as benzene , naphthalene , phenylhydrazine .
•
C
- illness ;- D.K.A , hepatitis , sepsis .
•
the degree of hemolysis varies with
:---
•
1-
inciting agent .
2-
amount of ingestion
3-
the severity of enzyme def. in the patients .
•
If hemolysis is sever
– Hb uria , jaundice
& Hb is reduced to be life threatening .
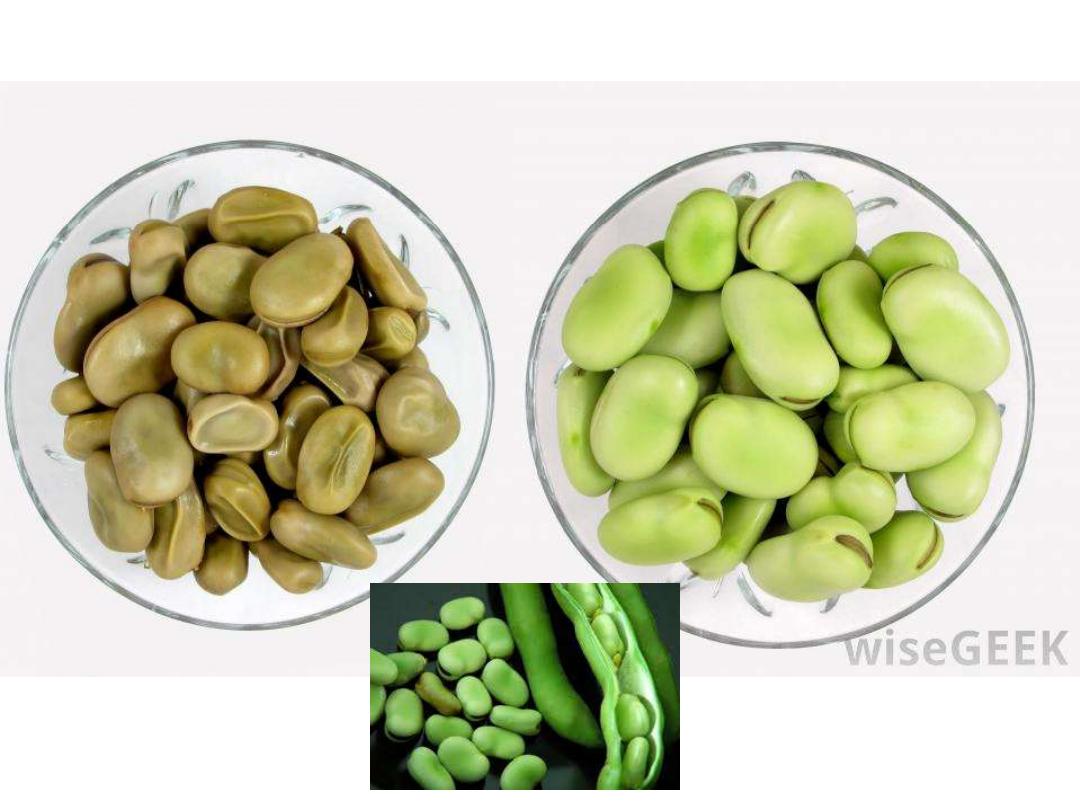
Favism mean
as acute H.A induced by fava bean & thought to more freguent
associated with G6PD B minus variant
.
•
Lab finding :----
•
1-
decreased PCV ,
•
2-
IF episode is sever resulting Hb emia & Hb-uria
•
note :
most individual with G6PD are asymptomatic & no clinical manifestation
unless triggered by infection , drugs and fava bean
•
If haemolysis is sever leading to Hb binding protein called haptoglopin are saturated
and free Hb may appeared in the plasma and subsequently in urine . .
---2--

3
-unstained or supra-vital preparation of RBC reveal Heinz body(
Hb ppt)
.
4-
blood film ;- reveals a few fragmented cell & polychromatophilic (
bluish large RBC ) & the retic count often 5-15%
•
Diagnosis :--
•
1-
direct measurements of G6PD level within RBC ( enzyme activity in
affected person is 10% of normal or less ) .
•
2-
satisfactory screening test are based on -- :--
•
a- decoloration of methylene blue .
•
- on reduction of met Hb (
measured the reduction of met Hb production
after NADP reduction .
.
•
- on fluoroscent of NADPH(
is direct test to measure the generation of
reduction NADPH from NADP and the test is positive if blood spot is failed to show fluoresent
under U/V light ..
.
•
N .T
immediately after hemolysis ---increase retic count & young RBC have
significantly higher enzyme activitly than older cell in A- variaty & testing
may deferred for a few wks before diagnostically low level of enzyme can be
shown .
•
G6PD variants also can be detected by electrophoretic & molecular analysis
.

•
Fava bean ( green and dry are induced hemolysis)
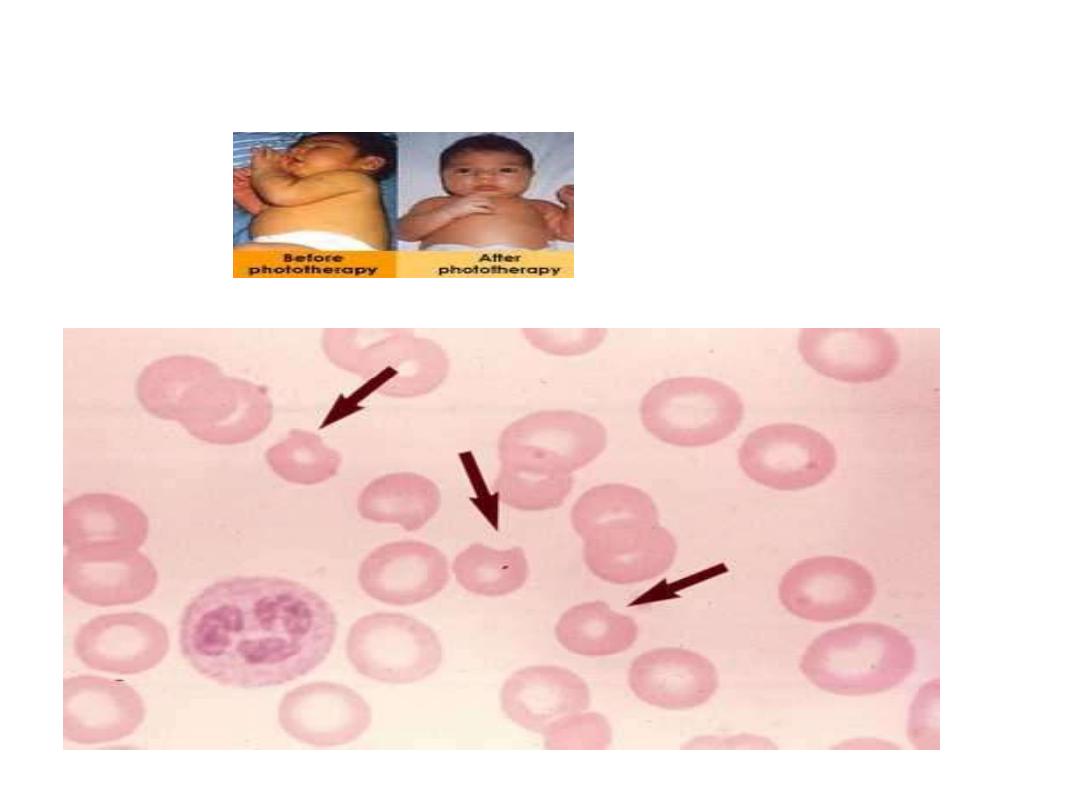
G6PDdef. Developed jaundice in neoborn baby
•
Heinz body

Prevention :--
1-
assay for G6PD for those pts are liable for G6PD
deficiency as in ethnic group , those with +ve family history of G6PD .
2-
avoid triggered factors that induced hemolysis
•
Treatment :---
•
1-
Admission to hospital .
•
2-
chart for observation ( PR , RR ) .
•
3-
frequent checking of PCV ,retic count .
•
4-
given I.V. fluid in form G/W or saline to induce more diuresis +
added NAHCO3 to prevent ppt of Hburia within renal tubules &
prevent its damage .
•
5-
if PCV continue to be decreased associated with increased
PR, RR , --- more anemia with cardiac compromised needs blood
transfusion .
•
--4--

Auto Immune Hemolytic Anemia
•
A number of extrinsic agents & disorders may lead to premature destruction
of RBC due to presence of antibodies .
•
The hallmark of this disease is a positive coombs tests
which detect
coated
of antibody ( IG ) or component of complements on the RBC surface .
•
erythroblastic fetalis is most important example in pediatric practice.
•
Auto Immune either :----a- warm type
•
b- cold type
•
Warm type :---2 type either :-
•
1-
transiant form ( account 70-80% of cases , occur between
2-12years & last 3-6 month
.
•
2-
prolong or chronic coarse which more frequent in infant &
children older 12year , hemolysis continue for months or years
.

Auto immune ( warm type ) due to :---
a-
idiopathic type ( primary ) .
B-
secondary
–
1-
lympho proliferative dis.
•
2-
CTD as in SLE
•
3-
Chronic infl. Dis as ulcerative
colitis
4-
non lymphoid tumor as in ovarian
tumor .
»
Auto immune ( cold type )
:-- with
cold reactive auto Abs( cryptogenic H.A )
•
a-
idiopathic type .
•
b-
secondary type ---:-
•
1-
lympho proliferative dis.
•
2-
infection as in mycoplasma , IMN
•
3-
paroxysmal cold Hburia .
•
c-
drug induced as in :--
by Hapten
mechanism as
pencillin , cephlosporine or
Ternary immune
complex as (quinidine
or quinine ,anti T.B, tetracyclin , insulin ) or
True antibody
as in
methyl dopa , Brufen ,voltarene ,interferone alfa ..

Diffrenitiation between warm from cold type
•
warm cold
•
1-c|f
pallor pallor
•
2- tempera.
35-40 c
less than 37
•
3-diag.
Direct coomb
test
indirect coomb
•
4- type of A.B
.
IgG
IgM
•
5- site of destruction
spleen
liver & spleen
•
6-complement
no need complement
need complement
•
7- treatment
prednisolone plasma pheresis
•
blood transfusion immune suppression
•
if no response IVIG OR NOT response to C.S or
•
chemotherapy like splenectomy
•
•
Rituxamab, mpnoclonal Ab
•
plasma pheresis in refractory cases which generally is not helpful
--7---
•

Guide lines for pediatric RBC transfusion
•
A--:-
children & adolescent :-
•
1-
acute blood loss of more than 25% circulatory blood loss .
•
2-Hb less than 8 gm/dl perioperative period .
•
3-
Hb of less than 8gm/dl & sympt. Chronic anemia.
•
4-
Hb of less than 8gm/dl & marrow failure.
•
5-
Hb of less than 13gm/dl & sever cardiopul. Dis.
•
B- Infant within 4 month .:--
•
1-
Hb of less than 13gm& sever cardiopul. Dis.
•
2-
Hb of less than 10gm & moderate pul. Dis.
•
3-
Hb
of less than 10
gm& major surgery .
•
4-
Hb of less than 8gm& sympto. Anemia .
•
- 8-

Guide line for pediatric platelets transfusion:--
A-
children & adolesent :---
•
1-
plat. Of less than 50 000 & bleeding .
•
2-
plat. Of less than 50 000 & invasive surgery .
•
3-
plat. Of less than 20 000& marrow failure with Hrr. risk factors .
•
4
-plat. Of less than 10 000 & marrow failure without Hrr. risk factors .
•
5-
plat. Dysfunction at any count with bleeding or invasive procedure.
•
B-infant of less than 4 months :--
•
1-plat
. Of less than 100 000 & bleeding or clinically unstable.
•
2-plat
. Of less than 50 000 & invasive procedure .
•
3-
plat. Of less than 20 000 & clinically stable .
•
4-
plat. At any count with plat. Dysfunction plus bleeding or invasive
procedure .
•
---9---

Guide lines for pediatric FFP Transfusion :--
In infant , children & adolescent
•
1-
sever cloting factor & bleeding or invasive procedure .
•
2-
emergency reversal of warfarine effects .
•
3-
DIC & bleeding .
•
4-
anticoagulant protein replacement ( anti thrombin 3 , protein
C & S )
•
5-
Plasma exchange replacement for thrombotic
–
thrombocytopenia purpura .
---10--
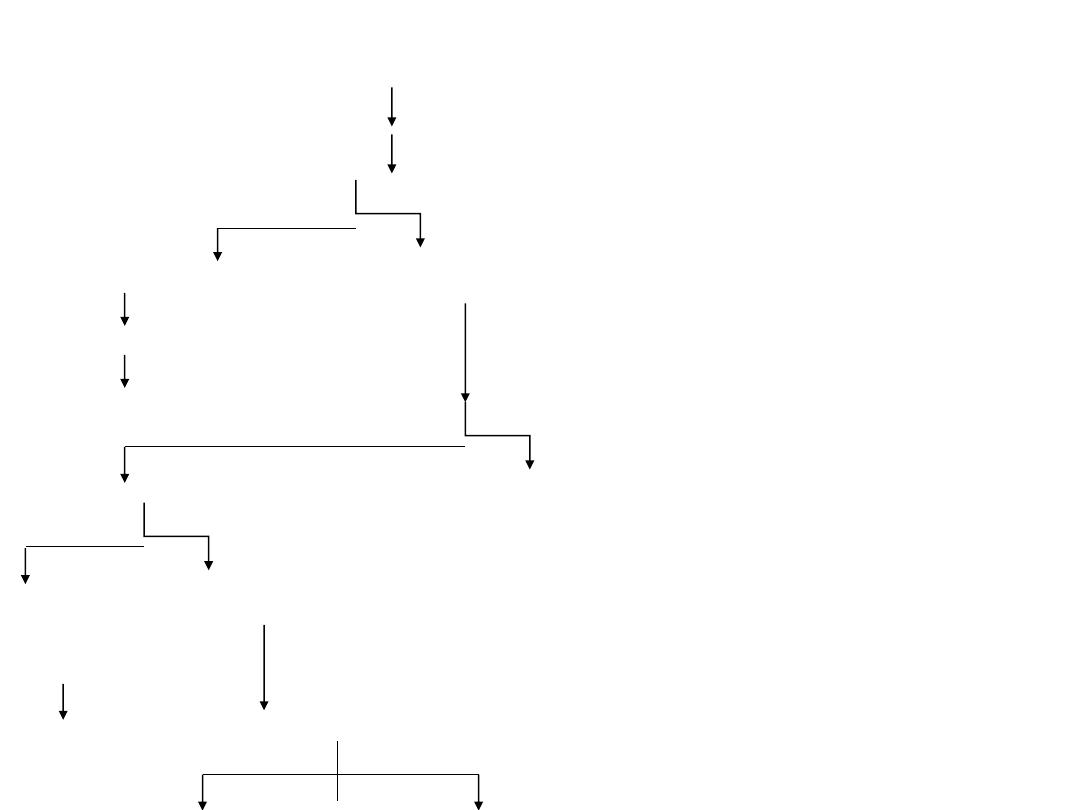
Approach patient with pallor
pallar
Send for Hb 1F decreased
Send
Retic count ( normal 1% ), more than 3% H.A
Low (< 1% ) for 2 occasion N or High(n= normal )
Send for
Hypoplastic anemia
Do
B.M. aspiration (Bone marrow) comb test
-ve +ve
MCV (n :75-90) 1) Immune H.A (investigate for the causes)
2) ABo or Rh incompatability (in neonate )
Low (< 75) normal or high
1) Blood loss,IDA do
2) Thalassemea
Send for peripheral blood smear
1) S.Iron , IBC,
2) HB- Electrophoresis
normal abnormal
1) blood loss 1) Hereditary spherocytosis –do osmotic fragility test
2) infection or Elliptrcytosis
3) rare cause )hexo kinase deficlency(
2) G6PD : biting cell in Blood film& assay after 6 wk
3) P.K. deficiency :-assay its level
4) D.I.C. send for PT,PTT,bleeding time+,platlat count&D-diamer
