CONGENITAL INFECTIONS(TORCH)
TOXOPLASMOSIS:
It results from vertical (transplacental) transmission of
Toxoplasma gondii from an acutely infected mother to
her fetus.
If infection occurs early in pregnancy :
low transmission, but severe disease.
Late in pregnancy : high transmission, but more
benign symptoms.

Clinical features:
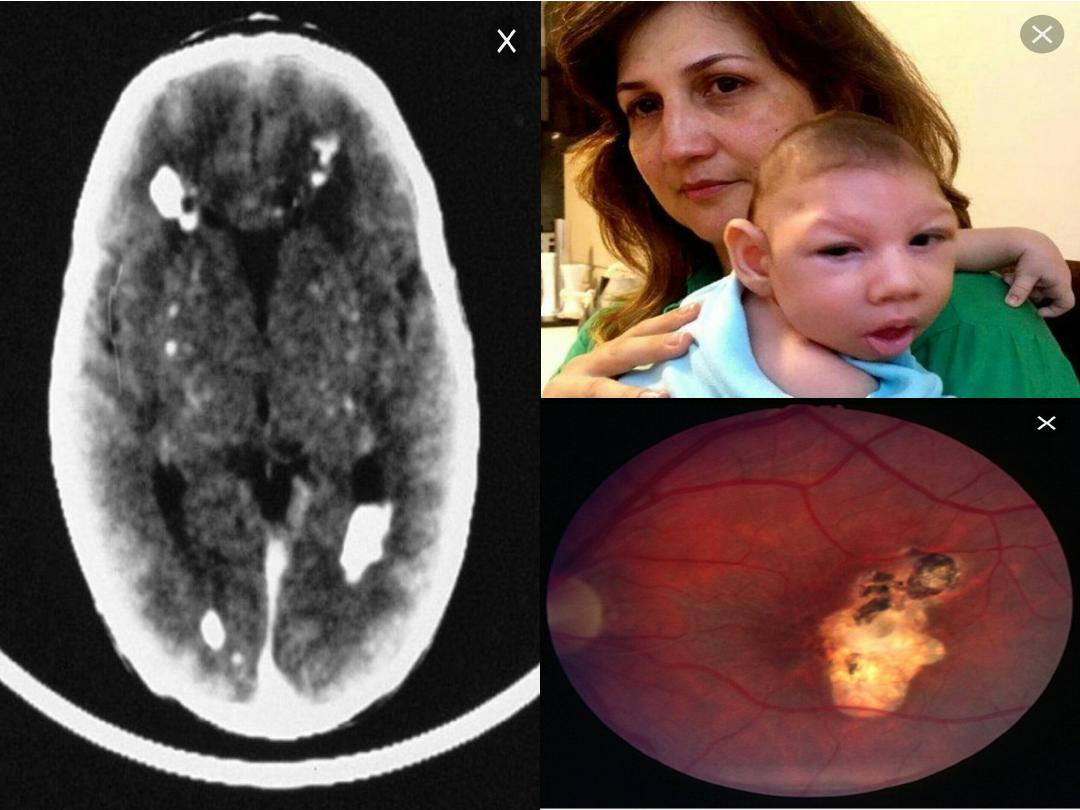
The classic findings of
S.G.A., hydrocephalus,
chorio-retinitis, and intra-cerebral calcifications.
Jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly(HSM).
Generalized maculopapular rash.
Seizures.
Long-term neurologic & developmental complications.
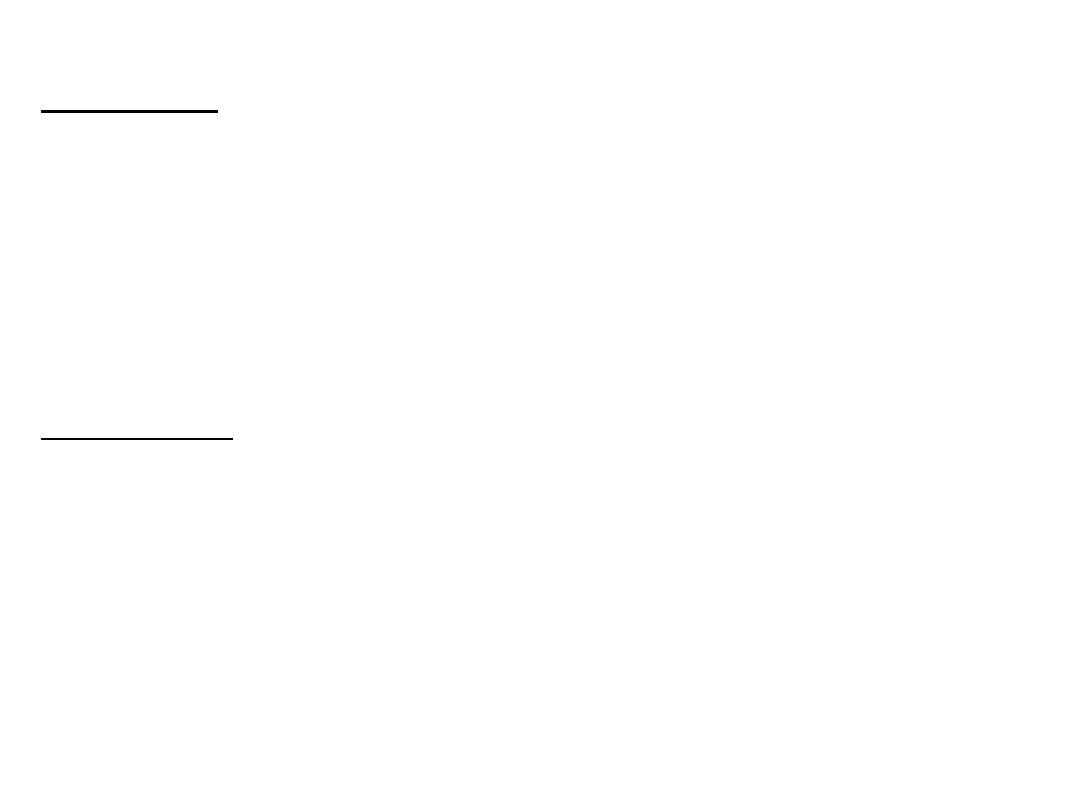
Diagnosis:
IgG-specific antibodies achieve a peak concentration 1-2
months after infection and remain positive indefinitely.
Specific IgM antibody determinations should be
performed to confirm disease.
Treatment:
Pyrimethamine (supplemented with folic acid) combined
with Sulfadiazine for symptomatic and asymptomatic
congenital infection for up to 1 year.

RUBELLA:
If infection is acquired during the first 4 weeks of
gestation; most newborns will have congenital defects.
Infection after 4 months' gestation does not seem to
cause disease.

Clinical features:
Classical triad of
cataract, cardiac defects(PDA), and
deafness
(sensorineural).
Meningoencephalitis, Mental retardation.
Jaundice, HSM, LAP(post auricular).
Thrombocytopenia.
Radiolucent bone disease.
Purpuric skin lesions "blueberry muffin" appearance
resulting from dermal erythropoiesis.

Diagnosis:
-
Detection of rubella-specific IgM antibody usually
indicates recent infection.
-Rubella virus can be isolated from blood, urine, CSF, and
throat swab specimens.
-Infants should be isolated while in hospital and kept away
from susceptible pregnant women when sent home.

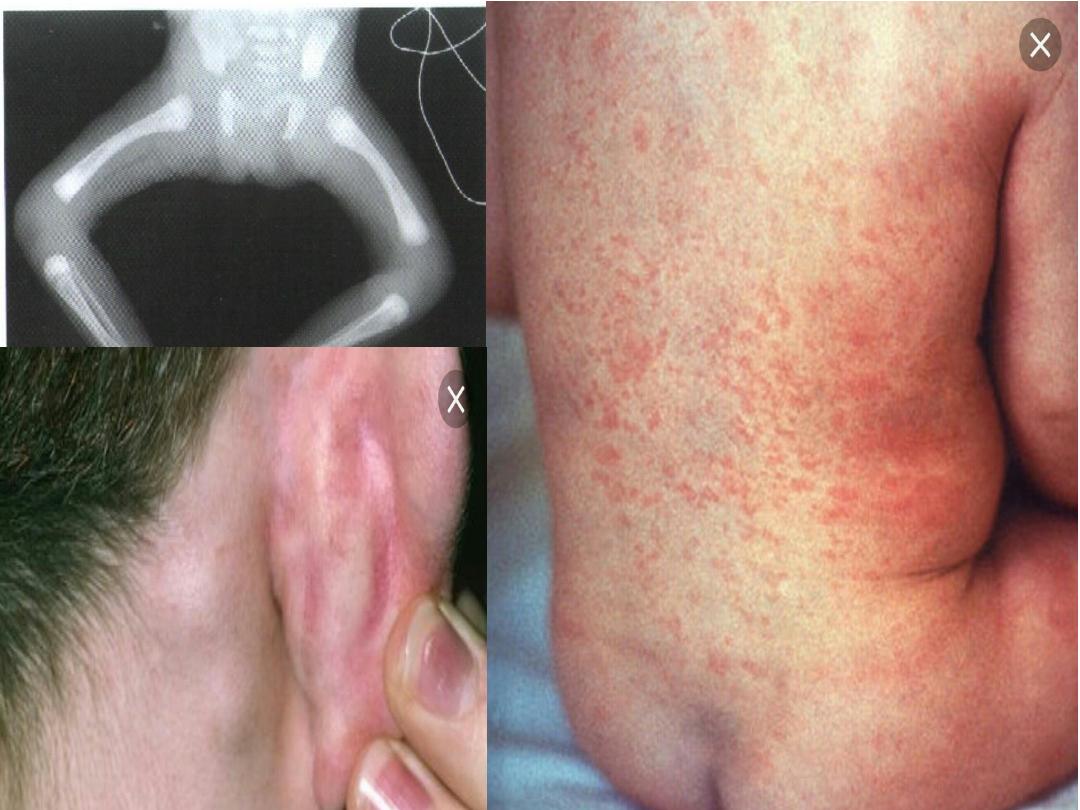
CYTOMEGALOVIRUS:
CMV is the most common congenital
infection, and is the leading cause of
sensorineural hearing loss, mental
retardation, retinal disease, and cerebral
palsy.

The earlier in gestation that the primary maternal
infection occurs, the more symptomatic the infant will be
at birth.
CMV infection acquired during birth or from mother's
milk is not associated with newborn illness or CNS
sequelae.

Clinical features:
Microcephaly.
Thrombocytopenia.
HSM.
Chorio-retinitis.
Hearing abnormalities.
A blueberry muffin appearance as the result of dermal erythropoiesis.
Skull films may reveal
periventricular calcifications
.
Diagnosis:
-Detection of the virus in urine or saliva.
-PCR can detect small amounts of CMV DNA in urine.
-Detection of CMV within the first 3 weeks after birth is
considered as a proof of congenital CMV infection.
Treatment:
No antiviral agents currently approved for the treatment
of congenital CMV infection.
Ganciclovir and Valganciclovir have shown a lack of
progression of hearing loss.

HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS:
HSV type 2 is responsible for most cases of primary
genital herpes & neonatal herpes simplex infection.
Neonatal infection is acquired from the mother
shortly
before or during passage
through the birth canal at
delivery.
Infants with HSV infections are more likely to be born
prematurely.

Clinical features
-
Most infants are normal at birth, and symptoms of
infection develop at 5-10 days of life.
-Disseminated disease involving multiple organ
systems, especially the liver and lungs.
-Localized infection to the CNS, skin, eyes, and
mouth.
HSV infection should be suspected in any neonate with
fever, irritability, abnormal CSF findings, and seizures.
HSV infections are often severe, and a delay in treatment
results in significant morbidity & mortality.
Diagnosis:
- Specimens for culture (blood, urine, saliva...).
- PCR is a sensitive method for detecting HSV DNA in
blood, urine, and
CSF.

Treatment:
Parenteral Acyclovir is the treatment of choice for neonatal
HSV infections.
CONGENITAL SYPHILIS:
It commonly results from
transplacental infection of the
fetus.
Syphilis during pregnancy has about 100%
transmission rate.

-Intrauterine infection can result in stillbirth, hydrops
fetalis, or prematurity.
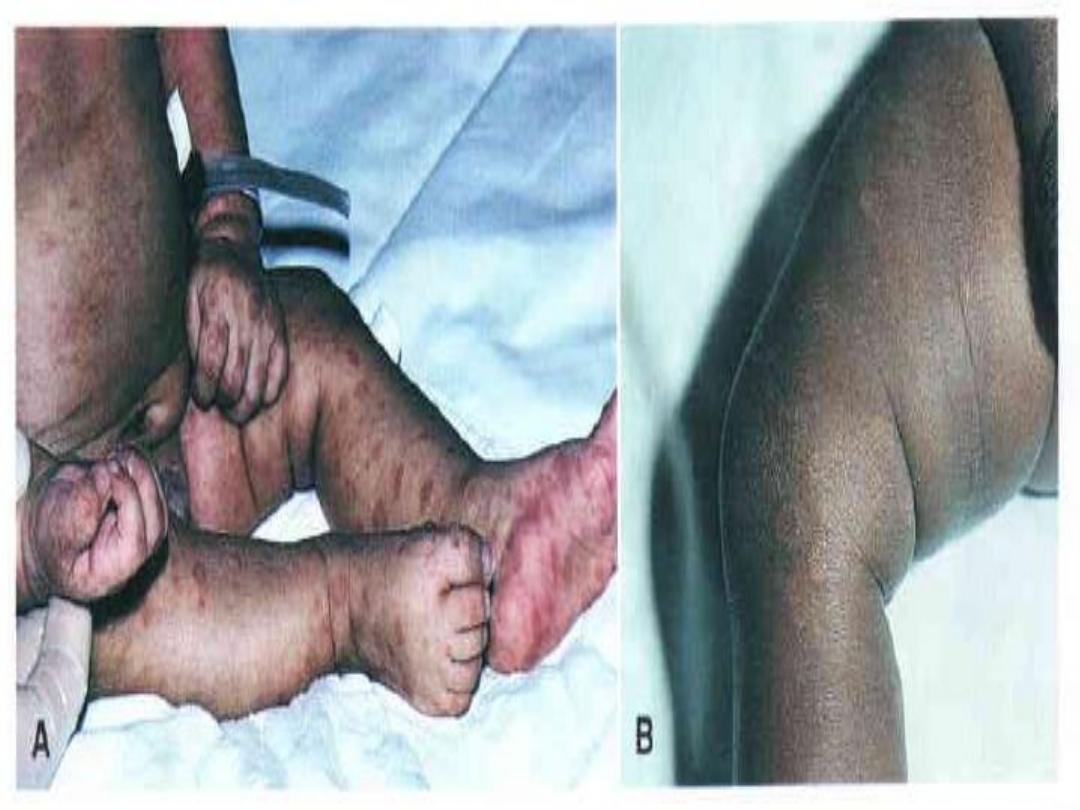
-Early manifestations:
Snuffles and poor feeding (syphilitic rhinitis).
HSM, LAP.
Severe pneumonia and osteochondritis.
A maculopapular desequamative rash develops over the
palms and soles and around the mouth and anus.
Hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia.
-Late manifestations:
Interstitial keratitis, deafness.
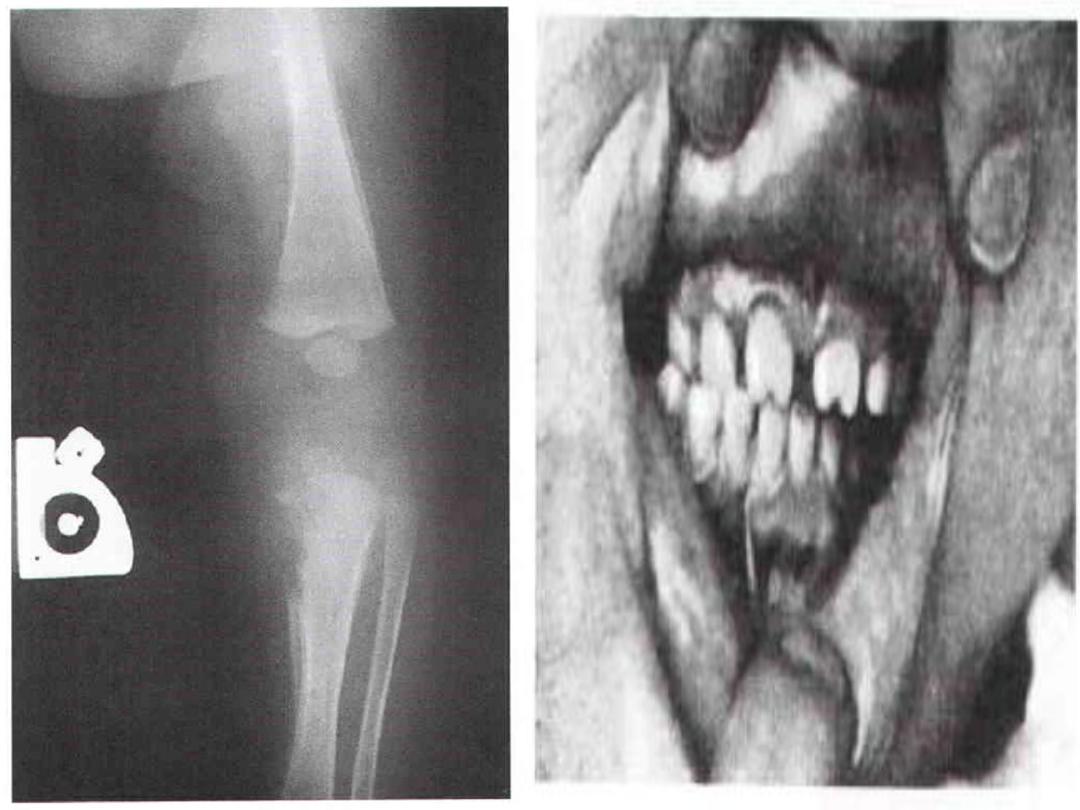
Hutchinson teeth, bowing of the shins.
Frontal bossing, mulberry molars.
Saddle nose.
Clutton joints.
TREATMENT:
Parenteral penicillin G (for 10 to 14 days) is the drug of choice for
treatment of syphilis.