Viral pneumonia

for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV)
nucleic acid

VIRAL C A PNEUMONIA
•
Clinical features of patients infected with 2019
novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China

By Jan 2, 2020, 41 admitted hospital patients had been
identified as having laboratory-confirmed 2019-nCoV
infection. Most of the infected patients were men (30 [73%]
of 41); less than half had underlying diseases (13 [32%]),
including diabetes (eight [20%]), hypertension (six [15%]), and
cardiovascular disease (six [15%]). Median age was
49·0 years (IQR 41·0–58·0). 27 (66%) of 41 patients had been
exposed to Huanan seafood market. One family cluster
was found. Common symptoms at onset of illness were fever
(40 [98%] of 41 patients), cough (31 [76%]), and myalgia or
fatigue (18 [44%]); less common symptoms were sputum
production (11 [28%] of 39), headache (three [8%] of 38),
haemoptysis (two [5%] of 39), and diarrhoea (one [3%] of 38).
Dyspnoea developed in 22 (55%) of 40 patients (median
time from illness onset to dyspnoea 8·0 days [IQR 5·0–13·0]).

26 (63%) of 41 patients had lymphopenia. All 41 patients
had pneumonia with abnormal findings on chest CT.
Complications included acute respiratory distress
syndrome
(12 [29%]), RNAaemia (six [15%]), acute cardiac injury
(five [12%]) and secondary infection (four [10%]). 13
(32%) patients
were admitted to an ICU and six (15%) died. Compared
with non-ICU patients, ICU patients had higher plasma
levels
of IL2, IL7, IL10, GSCF, IP10, MCP1, MIP1A, and TNFα

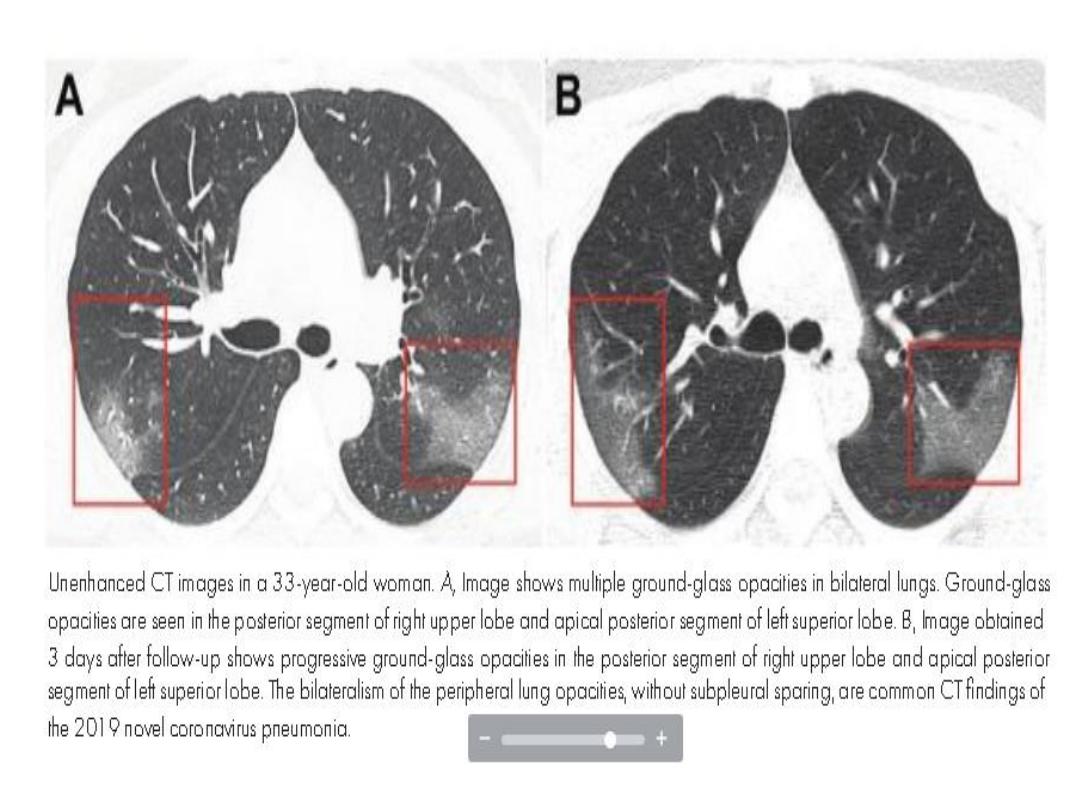
33-year-old woman presented to the hospital
with a 5-day history of fever and cough of
unknown cause. She indicated that she
worked in Wuhan, China (the center of novel
coronavirus outbreak) but had traveled to
Lanzhou, China, 6 days before presentation
to the hospital.

At admission, her body temperature was
elevated to 39.0°C (102.2°F) and coarse
breath sounds of both lungs were heard at
auscultation.

Laboratory studies showed leucopenia (white
blood cell count: 2.91 × 10 9 /L). e white blood cell di
erential count showed 70.0% neutrophils and 0.1%
eosinophils. ere were elevated blood levels for C-
reactive protein (16.16 mg/L; normal range, 0–10
mg/L), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (29 mm/h;
normal range, <20 mm/h), and D-dimer (580 ng/mL;
normal range, 500 ng/mL). Unenhanced chest CT
showed mul- tiple peripheral ground-glass opacities in
both lungs (Figure, A) that did not spare the subpleural
regions. Real-time uorescence polymerase chain
reaction of the patient’s sputum was positive

• On the basis of epidemiologic characteristics,
clinical manifestations, chest images, and
laboratory ndings, the diagnosis of 2019-
nCoV pneumonia was made. After receiving 3
days of treatment, combined with interferon
inhalation, the patient was clinically worse
with progressive pulmonary opacities found at
repeat chest CT